The Terrifying Potential of the 5G Devices

Introduction
In 5G networks, a cell is a service area denoted small geography. Every 5G device in a cell is connected to the Internet or phone network via an antenna built into the cell. In January 2022, the count of announced 5G devices increased by 1.5% to 1,276 devices. Of these, 873 are believed to be available commercially, accounting for 68.4% of all 5G devices announced. The commercial 5G devices have increased by 15.6% over the previous quarter according to the GSA report in February 2022. More than 400 5G smartphone models were released by 2021. At the start of 2021, 5G device shipments were on par with, if not exceeding, projections according to the Ericsson Mobility Report, in November 2021. 5G handsets accounted for 23% of global volumes in the tenth quarter of the cycle, compared to 8.7% for 4G at the same point in its cycle. Devices that support carrier aggregation using New Radio are becoming more common. The demand for real-time communication services, such as network slicing, is likely to rise as a result of massive expenditure on extended reality headsets and wearables devices. (Fixed Wireless Access) FWA will offer broadband to over 800 million people by 2027, through around 230 million connections boosting the demand for routers and modules. During the third quarter, 5G subscribers increased by 98 million, reaching over 570 million. More than 660 million 5G subscribers are expected by the end of 2021 owing to higher-than-expected demand in China and North America, aided in part by rolling out of 5G devices at lower prices.
 The rationale for the rise in 5G devices
The rationale for the rise in 5G devices
The demand for 5G devices is predicted to rise exponentially because of the growing connectivity, digital applications, and wearable technologies. Furthermore, updating current supporting infrastructures, such as modems, towers, and other equipment, is opening the doors for new participants. Emerging applications and business models, as well as lower device costs, have aided in IoT adoption, growing number of connected devices and endpoints around the world. Several manufacturers, such as Qualcomm and MediaTek, are introducing 5G chipsets, which are being used by several smartphone manufacturers. Previously, 5G support was limited to just flagship devices; however, mid-range handsets are now supporting 5G to provide more affordable chipsets in the market. One of the key benefits of 5G technology is that it offers more bandwidth, allowing for faster internet and download speeds. Download speed of up to 10 gigabits per second is also being made possible on 5G networks.
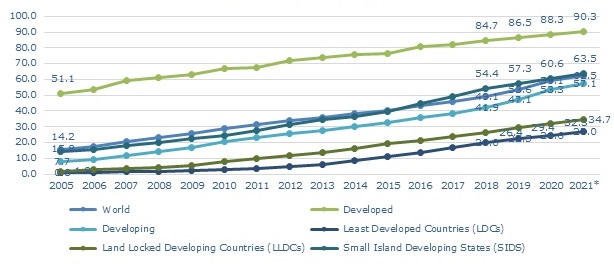 Source: ITU
Source: ITU
5G Subscriptions are expected to touch or exceed 4.4 billion by 2027 according to Erricson
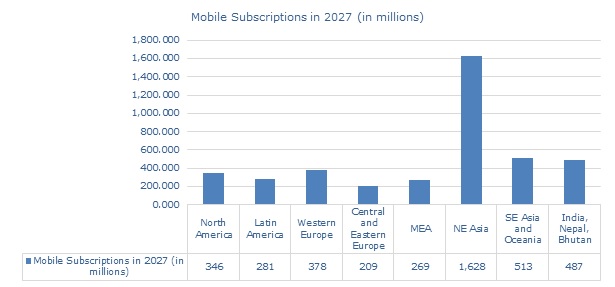 Source: Ericsson
Source: Ericsson
Breakthroughs in the 5G devices sector
- To increase device penetration, major chipmakers are also concentrating on 5G device components. Qualcomm, for example, made its 5G baseband commercially available, after the release of its X55 completely multimode 5G/4G/3G modem. In February 2020, Qualcomm unveiled its third generation of 5G modem with X60, as well as integrated 5G system-on-chip with Snapdragon 765G and 765. This X60 will enable the aggregation of sub-six-gigahertz and millimeter-wave frequency bands.
- According to Lenovo, the Yoga 5G is the world's first 5G PC, with ultra-fast connectivity, decreased latency, and broader bandwidth, since it supports both millimetre-wave full-band and sub-6GHz 5G networks.
- On February 9th, 2022, Samsung released the Galaxy Tab S8 Ultra tablet. A 14.60-inch touchscreen display with a resolution of 2960x1848 pixels and a pixel density of 240 pixels per inch is included with the tablet. An octa-core Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 processor powers the Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 Ultra. The Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 Ultra is powered by a 11,200 mAh battery, has 8 GB RAM, and runs on Android 12.
- Qualcomm announced the release of its next generation of Qualcomm RF Front End solutions for high-performance 5G mobile devices in February 2021. The products are designed to support the Qualcomm Snapdragon X62 and X65 5G Modem-RF Systems' power-efficiency and advanced performance capabilities, bringing together RF front-end components, modem, RF transceiver with artificial intelligence assistance, and mmWave antenna modules to allow OEMs to design flagship 5G devices.
- In Japan, the Lenovo Tab 6 5G was released in October 2021. The tablet features a 10.3-inch display, Snapdragon 690 processor, and a 5G connection. The tablet is Lenovo's first 5G-enabled Android tablet in Japan, according to the company. For dust/water protection, the tablet has received IPX3 and IP5X certifications. The battery, which has a capacity of 7,500 mAh, is expected to last a long period. The Lenovo Tab 6 5G has three modes: Kids, PC, and Learning.
- In June 2021, Siemens released the first industrial 5G router. The gadget connects regional industrial applications to community mobile wireless networks such as 5G, 4G (LTE), and 3G (UMTS). The router can be used flexibly to remotely monitor equipment, control components, and other industrial devices through a public 5G network. Simultaneously, Cisco unveiled a new line of catalyst industrial routers including 5G capabilities, designed to expand the enterprise network's power to the edge while providing the security, flexibility, and scalability required for IoT success.
- Franklin Wireless Corp., a market leader in broadband data communications, announced in December 2021 that Jextream 5G, a new sub-6 5G mobile hotspot, is now available for purchase through valued business partner C Spire. The product uses C Spire's cutting-edge 5G network for connectivity.
- Verizon debuted 5G Home Internet in Minneapolis and St. Paul in October 2020, delivering fast 5G Home Internet service and newly built hardware to users in eight cities. The 5G Internet Gateway, a company's first-to-market MMwave 5G CPE/Router, is the newest 5G Home gear. Customers may now enjoy rates of up to 1 Gbps using the 5G Internet Gateway, which allows many devices to run at the same time.
The Roll-Out of Smartphones has Skyrocketed
Increased technical breakthroughs and the need for ultra-high latency, ultra-low bandwidth, and enormous connectivity are projected to propel the industry forward. The increased demand for high-speed data connectivity for integrated IoT applications such as energy management and smart home products is expected to accelerate the adoption of 5G smartphones. Customers want the best-in-class 5G smartphone experience, thus industry players are concentrating on that.
- Samsung anticipated a significant shift towards standalone 5G networks in 2021, as well as further development of the 5G ecosystem, which will include applications that fully use 5G's transformative potential. On February 20, 2022, Samsung Electronics revealed the Galaxy S22 Ultra, which combines the best of its two smartphone series, the Note series with the professional-grade camera and performance of the S series, to set a new benchmark for premium smartphones. The Galaxy S22 has a built-in S Pen, improved Nightography, better video capabilities, and a battery life of over 24 hours. Samsung unveiled the Galaxy A71 5G and Galaxy A51 5G smartphones in April 2020, bringing 5G connectivity and new features to the popular Galaxy A series. The newly created items come with cutting-edge features such as a quad camera, infinity-O display, and 5G connectivity.
- The release of the iPhone 12 series in Q4 2020 boosted sales of 5G-ready handsets. Apple announced a 74% year-over-year increase in premium category sales, owing to the strong pace of the iPhone 12 series as iPhone owners are choosing to upgrade to 5G. Apple's supply chain too was remarkably durable in the face of component shortages, and it benefited from Huawei's collapse in China and Europe. Across all regions, Apple was the largest OEM in the premium class.
- The Xiaomi Mi 11 Lite 5G, that released in March 2021, was the first smartphone to use Snapdragon 780G 5G technology.
- OPPO India revealed in January 2021 that it plans to introduce more than six 5G-enabled devices in India that year, as the 5G-ready and IoT product categories become increasingly crucial for smartphone manufacturers in India.
- In March 2020, HMD Global unveiled freshly built Nokia 5G handsets as well as a brand-new hassle-free data roaming service. The Nokia 8.3 5G, which was released, is the company's first 5G smartphone. The Nokia 5.3 and Nokia 1.3, as well as the newest member of the Nokia 5310 family, have joined it. The Qualcomm Snapdragon 765G CPU, which supports 5G modem and is built on 7nm process technology, powers the 5G smartphone.
- According to Samsung Electronics' Research and Development of IT and Mobile Communications Division, 2020 was the year of Galaxy 5G.
- Huawei and Samsung have been building their baseband for their smartphones to lessen their reliance on other chip manufacturers and boost their differentiating possibilities through software and hardware integration. Vivo revealed in November 2019 that the X30 smartphone was powered by Samsung's Exynos 980 5G processor.
- Samsung anticipated a significant shift toward Standalone 5G networks in 2021, as well as further development of the 5G ecosystem, which will include applications that fully use 5G's transformative potential. On February 20, 2022, Samsung Electronics revealed the Galaxy S22 Ultra, which combines the best of its two smartphone series, the Note series with the professional-grade camera and performance of the S series, to set a new benchmark for premium smartphones. The Galaxy S22 has a built-in S Pen, improved Nightography, better video capabilities, and a battery life of over 24 hours. Samsung unveiled the Galaxy A71 5G and Galaxy A51 5G smartphones in April 2020, bringing 5G connectivity and new features to the popular Galaxy A series. The newly created items come with cutting-edge features such as a quad camera, infinity-O display, and 5G connectivity.
How Collaborations have Shaped the Industry
Device manufacturers, operators, and software companies have formed multiple levels of relationships, as well as a significant amount of investment. According to Gibson, collaborations that are driving the 5G market are already emerging.
- Vuzix Corporation, a leading provider of Smart Glasses and Augmented Reality (AR) technology and solutions, announced a partnership with Verizon to create a unique augmented reality experience for gaming and sports in December 2021.
- In collaboration with Lumen Technologies, HTC enabled wireless VR experiences on par with PCVR, powered by private 5G and edge computing, allowing enterprises to install and expand VR experiences on the go in 2021.
- Ooredoo announced a collaboration with Nokia in June 2021 for the deployment of Nokia's 5G fixed wireless access (FWA) on-premise gateway, which provides consumers across Oman with an exceptional and speedy in-home Wi-Fi experience. The new cutting-edge units will deliver a wonderful internet experience to both families and businesses.
- Verizon and Inseego announced the debut of the Inseego MiFi M2100 5G UW mobile hotspot in September 2020, which is designed to deliver lightning-fast speeds over Verizon's 5G Ultra-wideband and 4G LTE networks.
- In 2019, Signify and Ericsson announced their partnership to launch a 5G-based lighting solution for smart buildings. Signify, previously Philips Lighting, announced that its interior luminaire will be incorporated with Ericsson 5G radio dot in a collaborative effort that will let service providers add an indoor connection to buildings while lighting systems are being modified or installed.
- In 2019, Keysight Technologies announced a partnership with Motorola Mobility LLC to help the latter construct the world's first 5G new radio (NR) smartphone operating in the mmWave band. Motorola's devices were also brought into line with 3GPP standards and carrier criteria as a result of the strategic partnership.
Impact of Covid-19 on the adoption of 5G gadgets
With the support of IoT, 5G technology will provide ultra-high-speed network coverage and enable a slew of new applications. Because of the COVID-19 epidemic, 5G deployment has been pushed back. According to Ericsson's mobility report from November 2020, the net addition of mobile subscriptions in Q3 2020 was 11 million. This is due to the global epidemic and the resulting lockdown limitations. By the end of 2026, it expects 8.8 billion mobile subscriptions. COVID-19's spread has caused a severe supply chain disruption, which has slowed the rollout of 5G in the near and medium-term. As a result, the main 5G hardware delays, as well as the broader consequences of the economic downturn, apply. To deal with the current problem, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has mandated service providers to give more bandwidth to homes for 60 days. However, a 5G connection is projected to alleviate network connectivity problems in the long run.
What does the future hold for 5G devices?
Apple is working on its own in-house modem chips, similar to the Apple silicon and A-series processors, which will allow the corporation to lessen its dependency on modem chip manufacturers. Apple's analyst Ming-Chi Kuo recently predicted that the company might switch to its own 5G modems as soon as 2023. According to Nikkei Asia, Apple plans to build its own 5G modems for all future iPhones in collaboration with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). If successful, the Cupertino-based company's reliance on Qualcomm would be reduced.
Apple, Microsoft, Meta, Qualcomm, and Google are among the businesses working on AR and VR headsets. Meta announced its Project Cambria in October 2021 but the VR headgear will be released in 2022, likewise, Apple's first headset is expected to be released in 2022. T-Mobile announced in November 2021 that it will be the official North American launch partner for Qualcomm’s upcoming Snapdragon Spaces XR Developer Platform. In addition, starting in spring 2022, T-Mobile will engage directly with companies and developers to deliver immersive 5G experiences for AR glasses spanning entertainment, gaming, and other industries through the T-Mobile Accelerator. Further, in February 2022, Motorola and Verizon teamed up to design and engineer a neckband that would work with lightweight XR headsets such as Lenovo's ThinkReality A3 smart glasses. It has a small remote control-like pendant with the Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 processor, a 5,000mAh battery, a touchpad, a SIM card slot, speakers, and a range of sensors such as the gyroscope and barometer, and it looks like a necklace. The FCC has cleared the product.
The Orbic Speed 5G UW is a portable hotspot that can connect up to 30 Wi-Fi enabled devices for up to 12 hours at 5G speed. It is expected to release in 2022 with a long-lasting, rechargeable 4,400 mAh battery. Further, 5G's high speeds and minimal latency could make energy transmission more cost-effective. Faster broadband speeds could contribute to more efficient energy grid management, which might lead to less downtime. In the case of a power outage, for instance, 5G-enabled smart power grids might instantly deliver data and sensor-based insights into the problem. In Hawaii, a system designed in conjunction with Verizon analyses outages and monitors meters, which is an example of this sort of smart grid.
Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest White Papers
Next-Gen Elderly Care: How AI is Driving Industry Transformation
Recently
Testing and Quality Assurance to Validate 5G Performance
Recently
Digital Transformation & Improvements With 5G and SD-Wan Edge Computing
Recently
Market Ecosystem of 5G Network Slicing
Recently