Report Overview
Canada AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Highlights
Canada AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market is predicted to surge from USD 249.988 million in 2025 to USD 587.4343 million by 2030, posting a CAGR of 18.63%.
Canada AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market Key Highlights
The Canadian AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market is characterized by a high concentration of specialized, domestically-born enterprises with deep ties to the nation's world-class research institutes in Toronto, Montreal, and Edmonton. The market is defined by software and service providers that leverage machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and sophisticated graph databases to accelerate the most complex and time-consuming stage of scientific and commercial research: forming and validating new hypotheses. This advanced computational infrastructure allows organizations to analyze exponentially larger and more diverse datasets—from proprietary clinical trial data to global academic literature—transforming the search for novel drug targets, materials, or financial strategies. The market’s trajectory is inextricably linked to the continued government prioritization of a "Sovereign AI" ecosystem, focusing heavily on enabling computational access and commercialization to translate academic excellence into industry productivity gains.
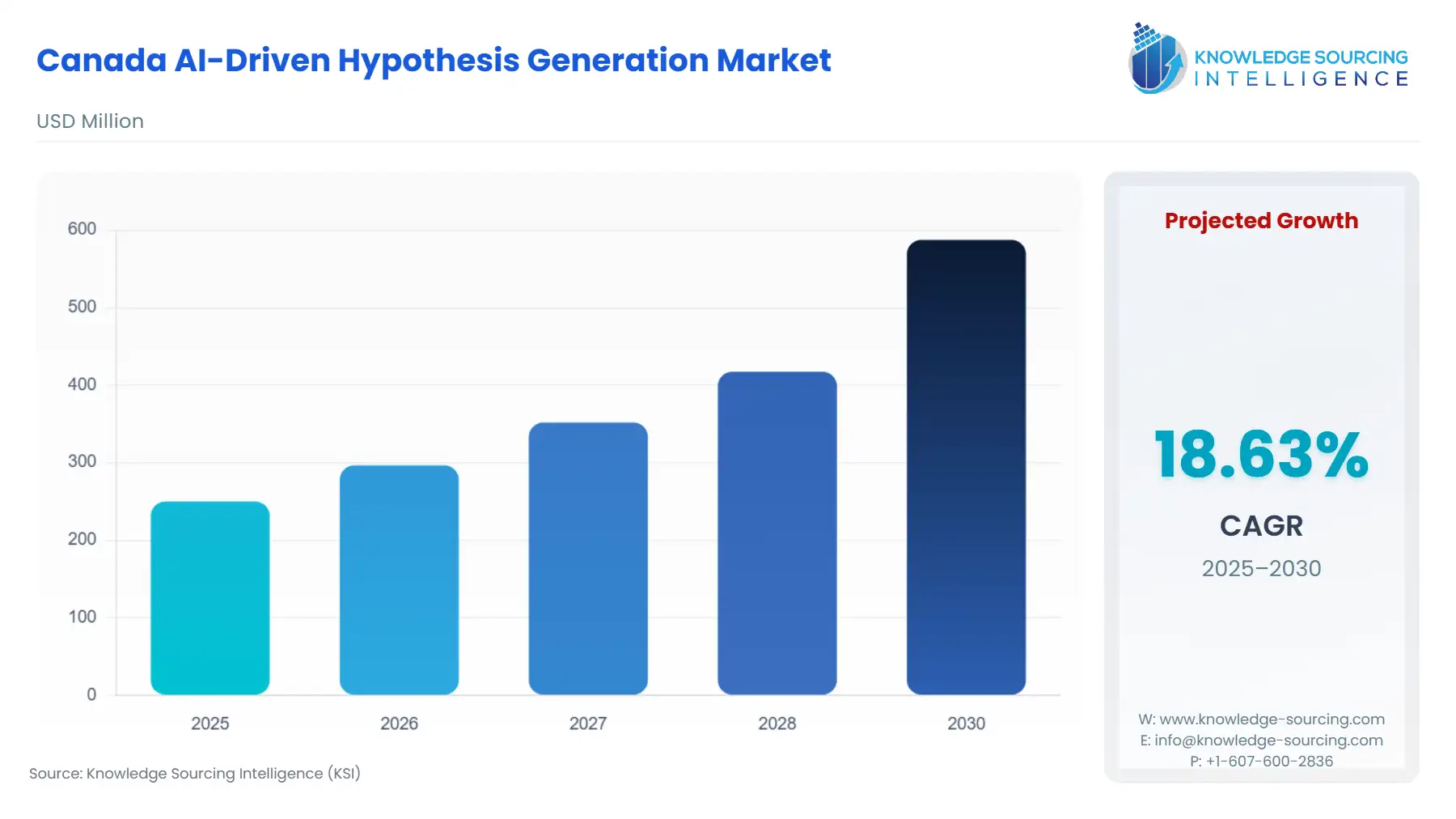
Canada AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
- Federal and provincial government investment in AI infrastructure is the foremost catalyst, creating direct demand for specialized AI services. Initiatives like the AI Compute Access Fund—offering up to $300 million to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) for accessing high-performance compute power—directly lower the operational cost barrier for adopting sophisticated hypothesis generation software. This investment enables biotech and life sciences startups, which form the core customer base, to acquire and run complex machine learning models that predict drug-protein interactions and novel compound efficacy. Furthermore, the explicit goal to accelerate drug development timelines drives pharma companies to acquire platforms that can analyze vast chemical space and scientific literature quickly, increasing demand for AI-Powered Literature Mining Tools that generate testable hypotheses from disparate data sources.
Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge is the "adoption problem," where Canadian industries, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), lag in integrating advanced AI tools. This constrains market expansion as potential end-users lack the necessary in-house data infrastructure and specialized talent to fully utilize complex AI platforms. Conversely, a substantial opportunity lies in the burgeoning market for graph-based hypothesis generation platforms. These platforms explicitly map the relationships between biological entities, chemical compounds, and diseases, providing a highly explainable and auditable path from data to hypothesis. This transparency directly addresses industry-wide concerns regarding the "black-box" nature of some deep learning models, making the technology more palatable to risk-averse pharmaceutical and healthcare end-users and thereby increasing demand for solutions with clear interpretability.
Supply Chain Analysis
The Canadian AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market's supply chain is predominantly intangible, revolving around three critical non-material assets: high-performance computing (HPC) power, specialized human capital, and proprietary training data. Key "production hubs" are the three national AI institutes—Mila (Montreal), Vector Institute (Toronto), and Amii (Edmonton)—which serve as primary sources for research, talent, and technology transfer. Logistical complexities stem from the "digital sovereignty" imperative, requiring domestic companies to balance the need for scalable, often US-owned, cloud computing services (e.g., Microsoft, Amazon, Google) with governmental mandates for domestic data storage and processing, as highlighted by ongoing debates around the US CLOUD Act. The industry's dependency is centered on global competition for AI talent and the uninterrupted provision of GPU-based compute resources, both of which face high global demand and cost volatility.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Federal (Proposed) | Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) / Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED) | AIDA, as part of Bill C-27, aims to establish a framework for high-impact AI systems. This introduces a potential regulatory compliance cost for developers of AI-driven hypothesis tools used in critical sectors like healthcare, potentially slowing new product adoption until compliance standards are clear. |
| Federal | Health Canada / Medical Devices Regulations (1998) | Health Canada's existing pre-market licensing scheme for Medical Devices (including Software as a Medical Device, SaMD) largely excludes AI software from rigorous review if it's "intended only to support" provider decision making (human-in-the-loop). This ambiguity accelerates the adoption of AI-driven diagnostic hypothesis tools by reducing the regulatory friction for lower-risk, decision-support applications. |
| Federal (Non-Binding) | Pan-Canadian AI for Health (AI4H) Guiding Principles | These principles promote transparency, equity, and person-centricity in AI adoption. While non-binding, they create de facto market standards, increasing demand for AI platforms that offer robust explainability features and clear audit trails to demonstrate adherence to ethical guidelines. |
In-Depth Segment Analysis
By Application Area: Drug Discovery & Life Sciences
The Drug Discovery & Life Sciences segment is the market's commercial epicenter, driven by the critical imperative to enhance the efficiency and success rate of the preclinical pipeline. Traditional drug development suffers from high failure rates, with preclinical stages representing a massive sink of time and capital. AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation platforms directly address this by performing in silico screening, target identification, and lead optimization with unprecedented speed. The key growth driver is the quantifiable reduction in the time required to move from an initial target to a validated lead compound. Companies leverage graph-based and multimodal AI platforms to ingest complex, high-dimensional data—including omics data (genomics, proteomics), chemical libraries, and electronic lab notebook information—to generate novel, statistically-supported hypotheses about disease mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. This capability is not merely an improvement but a fundamental change in the scale of experimentation, creating persistent demand for advanced AI solutions that de-risk the earliest, most speculative phases of R&D.
By Software Type: AI-Powered Literature Mining Tools
AI-Powered Literature Mining Tools constitute a foundational software segment propelled by the exponential growth of published scientific literature. With millions of biomedical articles published annually, a single human researcher cannot fully integrate the global body of knowledge. The core growth driver for these tools is the need to efficiently convert unstructured text and image data from patents, academic journals, and conference abstracts into structured, machine-readable knowledge graphs. These tools use sophisticated Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract entities (e.g., genes, proteins, diseases) and their relationships, allowing researchers to rapidly uncover "hidden" hypotheses—connections between concepts that no single researcher could identify manually. The tool's ability to consolidate, curate, and surface contextual evidence is critical for validating new hypotheses and preventing the pursuit of already-disproven ones, thereby acting as a critical productivity accelerator for academic and commercial R&D teams.
Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Canadian AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation market features a high-growth competitive landscape dominated by specialized, domestic life sciences AI firms that have successfully leveraged Canada's academic ecosystem. Competition focuses less on commodity pricing and more on the validated efficacy of a platform's proprietary knowledge graph, the strength of its partnerships with pharmaceutical giants, and its ability to handle complex, multimodal data. Major Canadian players are positioning themselves as critical partners in the global drug discovery value chain.
BenchSci
BenchSci is strategically positioned as a leader in AI-Powered Literature Mining, primarily through its proprietary ASCEND platform. The company focuses on accelerating preclinical R&D by using machine learning to parse scientific publications, images, and patents, translating this unstructured data into a structured, comprehensive biomedical knowledge graph. Its strategic positioning is centered on being the AI-assistant for the scientist, significantly improving the selection of antibodies, reagents, and animal models. Recent activity, such as the September 2025 announcement of a strategic partnership with Thermo Fisher Scientific, demonstrates a move to integrate its AI-powered research tools directly into the global laboratory and supply chain ecosystem.
Cyclica
Cyclica focuses on the upstream drug discovery pipeline, leveraging its proprietary Polypharmacy Prediction Platform (P3) and Ligand Design (Ligand Design). Its strategic positioning is to provide a comprehensive, end-to-end AI platform for polypharmacology, which models how a drug candidate interacts with multiple biological targets simultaneously. Cyclica’s technology is rooted in structure-based and ligand-based machine learning methods, focusing on generating novel and optimized drug candidates with reduced off-target effects. This approach directly targets the demand for safer and more effective lead identification.
Deep Genomics
Deep Genomics concentrates its efforts on developing transformative therapies for genetic diseases using its proprietary AI Workbench platform. The company's strategic focus is on interpreting the impact of genetic variations on biological mechanisms, moving beyond traditional drug target identification to explore novel therapeutic approaches, especially within RNA biology. This specialization allows them to command a niche but high-value segment, offering a distinct advantage in target discovery for diseases with a clear genetic etiology.
Recent Market Developments
- October 2025: BenchSci announced a three-year license agreement with the global pharmaceutical company Sanofi to access and use its ASCEND Platform. This high-profile agreement represents a significant commercial milestone, demonstrating the validated efficacy and enterprise-level demand for AI-driven literature mining and hypothesis generation platforms within the top tier of the global pharmaceutical industry.
- September 2025: BenchSci, a leader in AI solutions for preclinical R&D, announced a strategic partnership with Thermo Fisher Scientific. The collaboration is focused on co-developing AI-powered research tools and digital capabilities, including enterprise software solutions and optimized reagent selection, leveraging BenchSci’s ASCEND™ AI technology. The development expands BenchSci’s reach by integrating its AI expertise with Thermo Fisher’s global footprint of laboratory equipment and consumables, aiming to accelerate experimental design and R&D productivity for scientists.
- September 2024: BenchSci announced a new partnership with The Company of Biologists, integrating access to a large library of high-quality scientific publications, including five specialist peer-reviewed journals, into its ASCEND platform. This capacity addition directly enhances the value proposition of the platform by providing its AI models with a larger, higher-quality knowledge base, allowing for the generation of more robust and evidence-based hypotheses for preclinical researchers.
Canada AI-Driven Hypothesis Generation Market Segmentation
- BY SOFTWARE TYPE
- AI-Powered Literature Mining Tools
- Graph-Based Hypothesis Generation Platforms
- Domain-Specific Predictive Modeling Tools
- Multimodal AI Platforms
- Others
- BY APPLICATION AREA
- Drug Discovery & Life Sciences
- Healthcare & Diagnostics
- Materials & Chemical Research
- Financial & Business Analytics
- Academic
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODE
- Cloud-Based
- On-Premise