Report Overview
Global Airway Stent Market Highlights
Airway Stent Market Size:
The global airway stent market is expected to grow from US$141.017 million in 2025 to US$181.331 million in 2030, at a CAGR of 5.16%.
Global Airway Stent Market Introduction
Airway stents support management of tracheal and bronchial obstruction in malignancy and select benign conditions. Demand does not follow broad demographic trends; instead, it reflects procedure volumes, material-specific clinical preferences, and the ability of manufacturers to satisfy region-specific regulatory and purchasing requirements. This report examines how those drivers shift real purchasing behaviour across geographies and clinical environments.
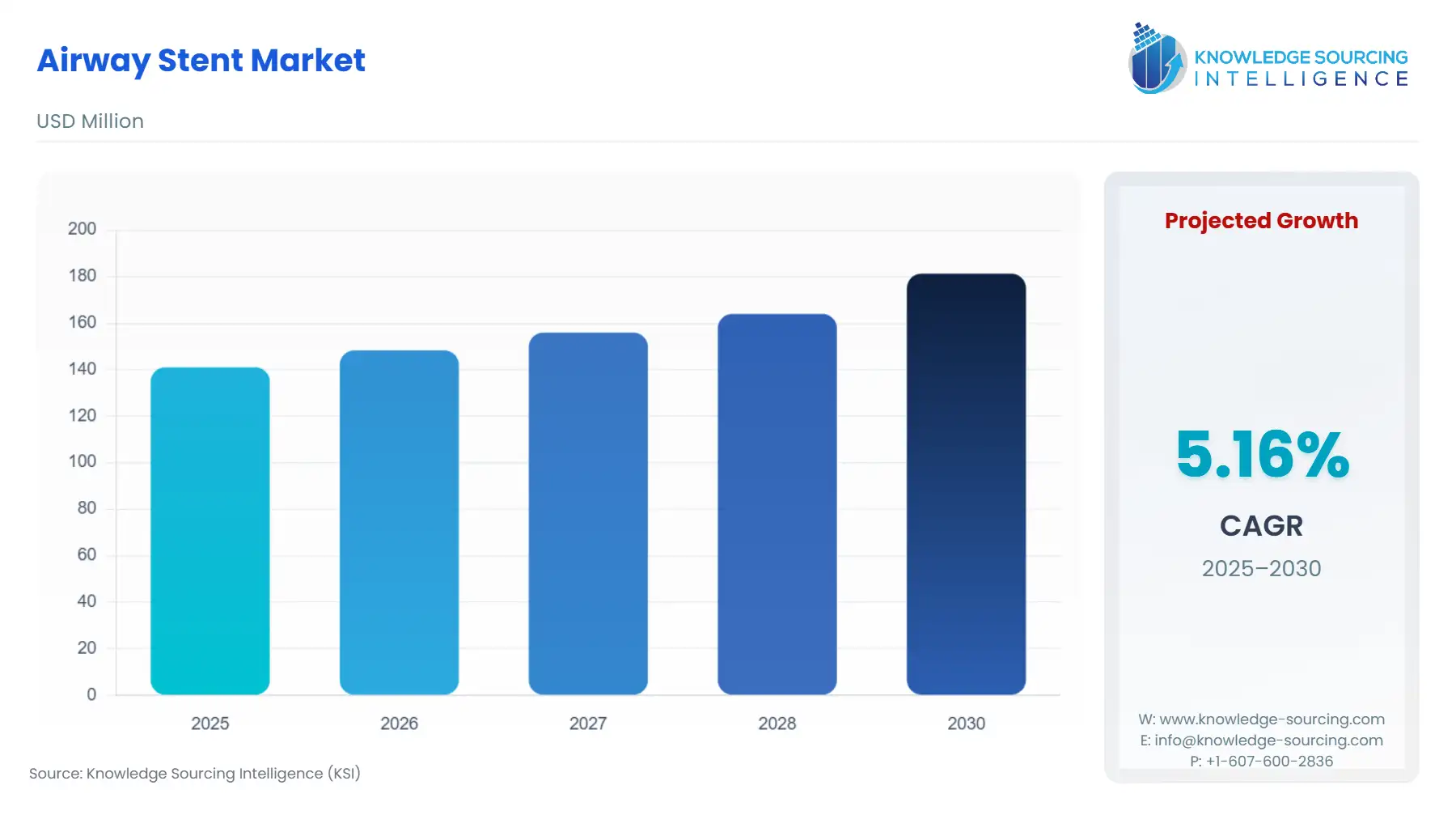
Global Airway Stent Market Growth Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Three verifiable catalysts generate direct demand. First, the persistent burden of lung cancer and central-airway obstruction expands the clinical pool requiring palliative airway intervention. Second, hospitals increasingly adopt minimally invasive bronchoscopy-based approaches, raising demand for stents compatible with through-the-scope and over-the-wire systems documented in clinical literature. Third, product enhancements—smaller nitinol designs, improved silicone formulations, and radiopaque markings—enable treatment of anatomically challenging stenoses and broaden clinical eligibility. Collectively, these demand drivers translate directly into higher procedure throughput and more frequent device procurement in high-volume oncology and interventional pulmonology centres.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The impact of U.S. tariffs on the Global Airway Stent Market is becoming increasingly pronounced as trade policies continue to influence medical device supply chains, component sourcing, and manufacturing economics. Although airway stents are classified as high-value Class II medical devices—generally benefiting from favorable import treatment—tariffs applied to upstream components such as medical-grade metals, silicone polymers, nitinol alloys, and precision machining equipment have raised the cost structure for both domestic and international manufacturers supplying the U.S. market. Additionally, tariffs on Chinese and Southeast Asian manufactured medical devices have incentivized companies to diversify production away from low-cost manufacturing hubs, leading to higher short-term transition and compliance expenses.
Regulatory tightening in the U.S. and EU elevates evidence and surveillance obligations, raising compliance costs and marginalizing smaller manufacturers. This constraint reduces supplier diversity and raises device pricing pressures for hospitals. However, opportunities arise where device characteristics—anti-migration features, easier deployment, reduced operative time, or better secretion-management performance—provide workflow or safety advantages. Hospitals actively prioritize such features in tender requirements. Another opportunity stems from regional inventory hubs and reliable logistics networks: suppliers offering fast replenishment and full traceability gain preferential access to large tenders, shifting buying behaviour toward firms with robust distribution and regulatory infrastructure.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Airway stents rely on medical-grade silicone, nitinol tubing, radiopaque fillers, and specialized polymer coatings. Silicone availability is stable but cost-sensitive to medical-grade compounding capacity in Europe and North America. Metal stents depend on nitinol, whose pricing reflects alloy processing and precision micro-manufacturing constraints. Suppliers with vertically integrated metal-processing capabilities maintain more stable pricing and faster lead times, strengthening their competitive position. Global supply disruptions in elastomers, metallic tubing, or sterilization capacity directly influence procurement cycles; hospitals often shift to suppliers with reliable inventory and predictable costing, reinforcing demand for firms with diversified raw-material supply chains.
- Supply Chain Analysis
Production is geographically segmented. Silicone-stent manufacturing is concentrated in Europe, where specialized molding and finishing capabilities exist. Metal and hybrid stents are heavily produced in Asia, particularly within advanced nitinol-processing clusters. U.S. and Ireland manufacturing sites from diversified medtech firms handle precision assembly, sterilization, and quality control. Distribution depends on regional warehouses and regulatory compliance requirements such as UDI, labeling, and post-market reporting. Hospitals emphasize procurement from suppliers with dependable regional inventories to avoid cancellation or delay of scheduled bronchoscopic procedures. These supply-chain realities materially shape vendor selection and long-term purchasing patterns.
Global Airway Stent Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
FDA — Premarket Notification Requirements for Esophageal and Tracheal Prostheses |
Increased premarket testing and surveillance obligations raise entry barriers and shift hospital demand toward suppliers with established compliance systems. |
|
European Union |
EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) |
Rigorous clinical evaluation, technical documentation, and post-market surveillance requirements elevate compliance costs and push buyers toward MDR-compliant incumbents. |
|
China |
National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) |
Local registration, UDI obligations, and in-country testing requirements encourage partnerships with domestic manufacturers and influence hospital preference for registered, locally supported products. |
Global Airway Stent Market Segment Analysis
- By Material Type — Silicone
Silicone airway stents remain central to clinical practice in benign stenosis and selected malignant obstruction because removability, lower tissue ingrowth, and predictable secretion management are consistent advantages recognized in clinical studies. The market impact of silicone was reinforced when Novatech’s TRACHEOBRONXANE™ DUMON® family received a 510(k) substantial-equivalence decision in October 2024, restoring formal U.S. access and validating manufacturer quality systems. Demand for silicone stents is concentrated in tertiary care centres that manage post-surgical complications, airway reconstruction, and long-term benign pathologies, where removability is a strict requirement. Procurement teams in such facilities evaluate vendors based on molding consistency, available sizing matrices, radiopacity, and the presence of robust post-market surveillance systems. Because silicone stent fabrication requires specialized expertise and tightly controlled manufacturing environments, buyers disproportionately favour suppliers with proven quality histories and stable production geographies. These dynamic channels global demand toward long-established silicone producers with regulatory maturity and dependable supply logistics.
- By End-User — Hospitals and Clinics
Hospitals dominate global demand because airway stenting requires advanced imaging, surgical backup, trained interventional pulmonologists, and emergency airway management capabilities. Demand rises in centres with large oncology caseloads, particularly those performing high volumes of bronchoscopic palliation. Hospital purchasing committees prioritize stents that reduce procedure time, minimize readmission risk from mucus plugging or migration, and simplify deployment. Devices offering consistent expansion profiles, reliable radiopacity, and through-the-scope delivery are particularly attractive because they streamline workflows in bronchoscopy suites. Hospitals also integrate supply-chain performance into vendor evaluation—suppliers with local inventory, comprehensive training programs, and responsive adverse-event reporting systems gain preferential access to high-value tenders. These institutional criteria significantly shape demand, narrowing approved vendor lists and concentrating procurement around manufacturers capable of providing both clinical value and operational reliability.
Global Airway Stent Market Geographical Analysis
- United States
High lung-cancer incidence and advanced tertiary-care capacity underpin consistent demand. Hospitals require FDA-cleared devices supported by robust post-market systems, and procurement favours suppliers demonstrating regulatory reliability and consistent supply.
- Brazil
Demand is concentrated in large urban oncology centres addressing late-stage presentations. Limited national screening coverage increases reliance on palliative bronchoscopic procedures, creating steady need for both silicone and metal stents.
- France
Local manufacturing from established silicone producers strengthens clinician familiarity and supports reliable procurement in public hospitals. Domestic availability shortens lead times and reinforces preference for silicone-based solutions.
- South Africa
Demand concentrates in provincial tertiary centres managing resource-intensive oncology cases. Procurement emphasizes cost, availability, and supplier reliability given logistical and budgetary constraints.
- China
NMPA registration requirements and expanding tertiary-care capacity shift demand toward manufacturers with local regulatory presence. Domestic production and joint ventures improve access, accelerating adoption in large urban hospitals.
Global Airway Stent Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
Key verified companies include Boston Scientific, Novatech SA, Cook Medical, MICRO-TECH (Nanjing), MICRO-TECH Europe, Medtronic, and Merit Medical Systems.
- Novatech SA
Novatech specializes in silicone airway stents, with manufacturing and warehousing in France. Its TRACHEOBRONXANE™ DUMON® line received an FDA substantial-equivalence decision in October 2024, strengthening its competitive position in the U.S. market. The company’s specialization in silicone molding and removability-focused stent design secures its role as a preferred supplier in high-complexity airway-management centres.
- Merit Medical (Endotek Division)
Merit Medical markets the AERO and AEROmini nitinol stent lines, emphasizing delivery-system flexibility, distal-airway reach, and compatibility with through-the-scope procedures. Its product strategy targets hospitals seeking workflow efficiency and a broad size portfolio. Expansion of its nitinol product range in 2024 reinforced its presence in bronchoscopy-driven markets.
Global Airway Stent Market Developments
- October 2024 — Novatech SA obtained an FDA 510(k) substantial-equivalence decision for the TRACHEOBRONXANE™ DUMON® silicone airway-stent family.
- 2024 — Merit Medical expanded its AEROmini nitinol airway-stent portfolio with additional sizes, enhancing coverage for distal and anatomically complex airway segments.
Global Airway Stent Market Segmentation:
- By Material Type
- Metal
- Silicone
- Hybrid
- By End-User
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America