Report Overview
Global Gene Synthesis Market Highlights
Gene Synthesis Market Size:
The Gene Synthesis Market will surge from USD 2.304 billion in 2025 to USD 5.234 billion by 2030, fueled by a 17.83% CAGR.
The Global Gene Synthesis Market provides the foundational technology for engineering biological systems, transitioning from a niche academic tool to a high-throughput industrial service critical for the rapid advancement of biotechnology.
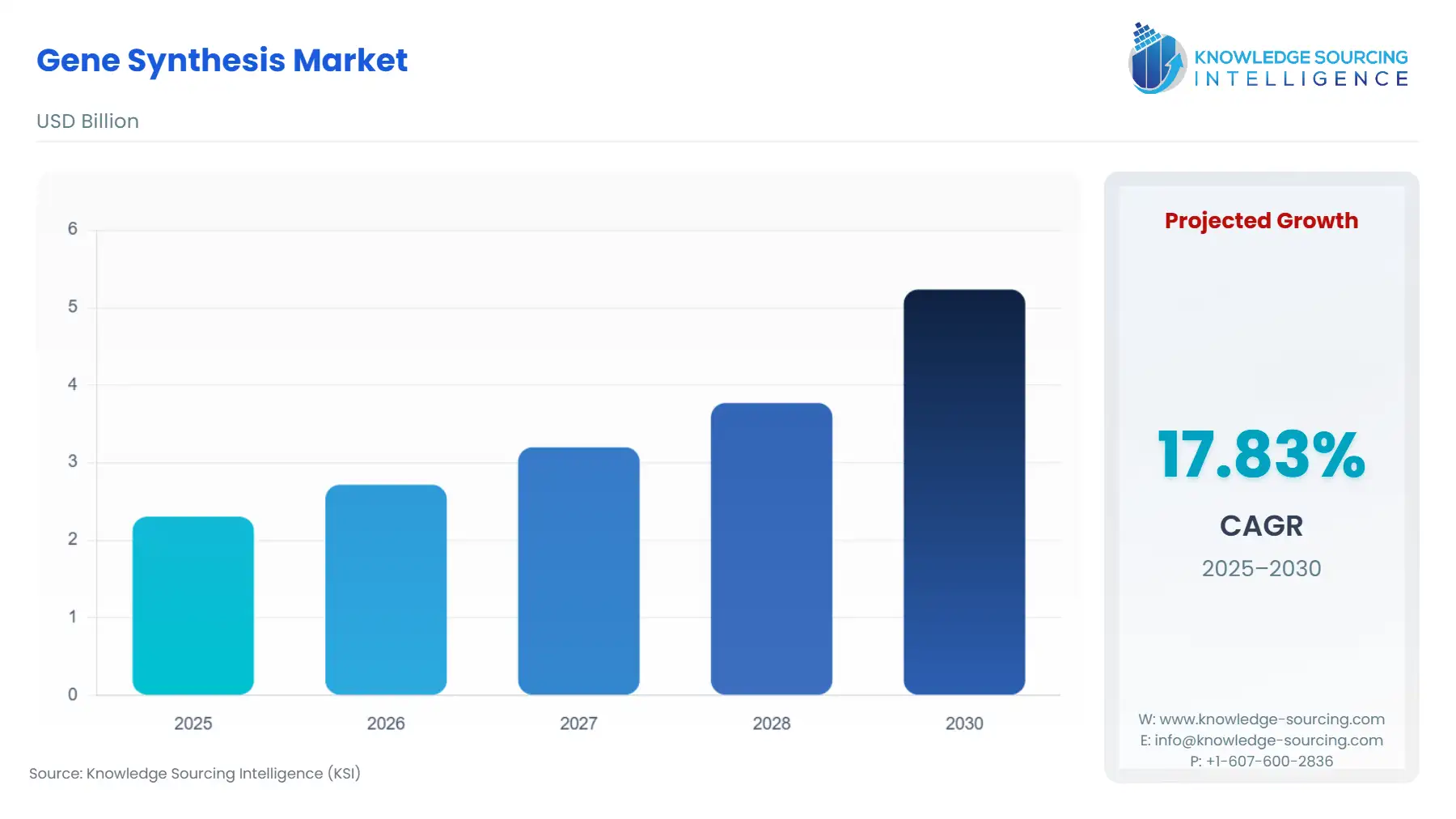
The market’s current trajectory is defined by the industrialization of DNA manufacturing, characterized by a persistent drive toward automation, cost reduction, and scale. This evolution is enabling research and commercial ventures across pharmaceutical, agricultural, and industrial sectors to rapidly prototype and deploy complex genetic designs, establishing synthetic DNA as an essential input commodity in the modern bioeconomy. This analysis details the core dynamics and structural forces driving demand and shaping the competitive landscape for industry stakeholders.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The burgeoning focus on cell and gene therapy development constitutes a primary catalyst for gene synthesis demand. These novel modalities require significant quantities of customized genetic material, such as specific gene sequences for vector construction or modified plasmids. The continuous cycle of iterative optimization in drug discovery, where researchers must synthesize multiple genetic variants to test efficacy and safety profiles, directly increases the demand volume for sophisticated synthetic genes. Furthermore, the expansion of synthetic biology into industrial biomanufacturing, which necessitates the engineering of microbial strains for sustainable chemical production, converts a scientific opportunity into a verifiable industrial demand for long, complex, and codon-optimized DNA sequences at a commercial scale.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant market challenge is the complexity and cost associated with synthesizing highly repetitive sequences or genes with extremely high or low Guanine-Cytosine (GC) content. These "difficult genes" experience lower success rates and longer turnaround times, placing a natural constraint on certain research pipelines and thus limiting potential demand in those specific areas. Conversely, the opportunity lies in the advancement of solid-phase and chip-based synthesis technologies. Technological improvements that lower the per-base cost and increase the accuracy for these complex genes will expand the addressable market by making previously cost-prohibitive or technically impossible research projects viable. This technological advancement acts as a direct catalyst for generating new research and commercial demand.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The Global Gene Synthesis Market fundamentally produces a physical product (synthetic DNA and oligonucleotides), making the supply chain for key raw materials a critical determinant of cost and capacity. The synthesis process relies heavily on specialized chemical reagents, primarily phosphoramidites and purification resins. Phosphoramidites, the molecular building blocks of DNA, are high-purity, often proprietary chemicals subject to stringent quality control. Price volatility or supply chain disruptions for these complex reagents can directly impact the cost structure of synthesis providers. The trend of continuous pricing decline in per-base synthesis costs is not solely due to technological improvements but also to economies of scale achieved in the procurement and synthesis of these chemical precursors, thereby making the end product more accessible and sustaining high-volume demand.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The gene synthesis supply chain is centralized, with production hubs primarily located in the United States, Europe, and increasingly, China. Production is characterized by a high degree of automation, utilizing proprietary high-throughput synthesis platforms (e.g., silicon-based chips). Logistical complexities arise from the need for cold-chain shipping for certain final products (plasmid DNA) and the requirement for robust material traceability, especially for critical raw materials like phosphoramidites, which are often single-sourced. The supply chain dependency is shifting towards a model where regional production and distribution hubs are becoming essential to meet time-sensitive rapid synthesis offerings, which is a key competitive differentiator and direct demand driver.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Government Regulations
Key government regulations and guidelines create a mandatory framework that directly shapes market operations and, critically, influences buyer behavior by mandating a minimum standard for transaction security.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
HHS Guidelines for Gene Synthesis Screening (Advisory) |
Creates a non-mandatory, but widely adopted, biosecurity screening standard. Providers' adherence to this framework reinforces trust, which is essential for institutional and government-funded academic demand. |
|
China |
Export Control Law (December 2023) / Ministry of Commerce |
Restrictions on the export of certain synthetic biology and gene editing technologies for human use. This directly encourages and secures domestic demand and manufacturing capacity within China for strategic technologies. |
|
Global |
International Gene Synthesis Consortium (IGSC) Harmonized Screening Protocol (Voluntary) |
Establishes a common, self-regulatory framework among leading providers for screening both sequences and customers against biosecurity concerns, effectively setting a minimum industry standard that customers in the pharmaceutical sector demand. |
Global Gene Synthesis Market Segment Analysis
- By Application: Diagnostics & Therapeutics Development
The Diagnostics & Therapeutics Development segment is a primary, demand-intensive consumer of synthetic genes. Therapeutic advancements, particularly in cell and gene therapy (CGT) and mRNA vaccines, create a non-discretionary, high-quality demand for custom DNA sequences. In CGT manufacturing, high-quality synthetic genes serve as templates for manufacturing the viral vectors (e.g., AAV, lentivirus) used to deliver therapeutic genes into patient cells. The process of optimizing viral vector yield and tropism requires the synthesis of numerous variants, driving up the need for highly accurate, clonally perfect, and often large-scale gene synthesis. As pharmaceutical pipelines for these advanced therapies continue to mature, the demand shifts from research-grade to cGMP-compliant, clinical-grade gene synthesis services, presenting a premium opportunity for market participants.
- By End-User: Academic & Research Institutes
Academic and Research Institutes form the volume-driving foundation of the gene synthesis market, generating consistent demand through publicly funded research programs. These institutes are the primary users of the technology for fundamental research in genomics, structural biology, and the initial stages of synthetic biology design. Demand in this segment is highly price-sensitive and volume-dependent. Institutional adoption of gene synthesis services is directly proportional to the relative cost reduction achieved by providers, as lower per-base costs enable researchers to undertake larger, more ambitious projects involving high-throughput screening of gene libraries. Furthermore, government funding initiatives in specific research areas, such as personalized medicine or infectious disease response, create targeted demand spikes for the rapid synthesis of custom genetic tools.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis (North America)
The US market remains the global epicenter for gene synthesis demand, driven by substantial venture capital and government funding flowing into the biotech and pharmaceutical sectors. Demand is amplified by the presence of a robust ecosystem of large biopharmaceutical companies and a vast network of academic research centers. Key factors propelling demand include the high adoption rate of CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies, which require custom guide RNAs and repair templates, and the rapidly accelerating clinical trial pipeline for cell and gene therapies, which translates directly into demand for cGMP-grade synthetic DNA materials.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
Germany's market demand is underpinned by strong federal investment in life sciences and a powerful industrial biotechnology sector, particularly in the chemical and manufacturing industries. Regulatory clarity and a culture of high-quality standards drive demand for reliable, verified gene synthesis services. The primary demand factor is the German government's sustained funding for advanced biological research and synthetic biology roadmaps, which positions the country as a significant end-user for tools that enable the bio-based production of chemicals and materials, moving the market past purely therapeutic applications.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Brazil represents the largest market in South America, with demand for gene synthesis services predominantly concentrated in agricultural biotechnology. The country’s status as the world's second-largest producer of biotech crops necessitates extensive research in genetic engineering to develop new traits for herbicide tolerance and insect resistance in major commodities like corn and soybeans. The National Technical Biosafety Commission (CTNBio)'s rigorous approval process for genetically engineered organisms fosters demand for high-quality, verifiable synthetic genetic constructs used in R&D pipelines to facilitate these approvals.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
Demand in Saudi Arabia is uniquely driven by large-scale, strategic government initiatives focused on personalized medicine and genomics, such as the Saudi Genome Program (SGP). The SGP's objective to establish a comprehensive genetic database for the local population and reduce the incidence of genetic diseases creates direct, substantial demand for next-generation sequencing tools and, subsequently, synthetic genes for use as controls, probes, and diagnostic development templates. This government-led focus on national health transformation acts as a concentrated, high-value demand vector.
- China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
China's market is characterized by rapidly increasing domestic manufacturing and a strategic government imperative to achieve global leadership in synthetic biology. Significant state and private capital is invested in building an extensive biomanufacturing infrastructure. This commercialization focus creates intense demand for high-throughput, low-cost gene synthesis services to enable the rapid development and scaling of engineered microbial strains for applications like novel food ingredients, sustainable chemicals, and pharmaceutical intermediates. The domestic market’s immense biomanufacturing capacity is converting research results into commercial-scale gene synthesis orders at an unparalleled rate.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Global Gene Synthesis Market exhibits a classic oligopolistic structure dominated by a few large-scale providers who leverage proprietary, automated platforms to achieve significant economies of scale. Competition is centered on speed, cost, sequence accuracy, and the ability to synthesize difficult, complex sequences. The key strategic imperative for market leaders is a shift from pure gene synthesis service providers to integrated synthetic biology solution providers that offer end-to-end services, including bioinformatics, plasmid preparation, and viral vector production.
- Twist Bioscience Corporation: Twist Bioscience’s strategic positioning is predicated on its disruptive, high-density silicon-based DNA synthesis platform. This technology enables the mass production of synthetic DNA libraries, gene fragments, and clonal genes at a scale and speed that rivals traditional methods. Its key offering, a platform for high-throughput synthesis, fundamentally targets the accelerating demand for gene variants in drug discovery and antibody development. The launch of services like Express Genes, with rapid turnaround times, directly addresses the market's need for speed, cementing its position as a key enabler for high-volume synthetic biology research.
- GenScript (GENEWIZ from Azenta Life Sciences): GenScript, through its GENEWIZ brand, is positioned as a full-service Contract Research Organization (CRO) specializing in gene synthesis and related molecular biology services. Its competitive edge is based on a global footprint, technical expertise in handling complex sequences, and robust quality control, including a commitment to biosecurity through the IGSC protocol. GenScript's strategy is to capture demand across the entire R&D spectrum, from early-stage academic research to late-stage biopharmaceutical development, providing not just the synthetic gene but also follow-on services like protein expression and antibody development.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Developments
- October 2025: Twist Bioscience and Element Biosciences Advance Collaboration with Launch of New Trinity Freestyle™ Sequencing Workflow
Twist Bioscience Corporation announced an advanced collaboration with Element Biosciences, Inc., leading to the launch of Twist's new Trinity Freestyle Fast Hybridization workflow for Element's AVITI sequencing system. This product launch integrates Twist's library preparation kits with Element's sequencer, significantly streamlining the sample-to-sequencer process. The core impact of this development is to reduce hands-on time and accelerate sequencing results for researchers, which, by extension, drives demand for the front-end product, Twist's synthetic DNA, by enabling faster and more efficient quality control and application deployment cycles.
Global Gene Synthesis Market Segmentation
- By Product Type & Service Type
- Gene Synthesis Products
- Gene Synthesis Services
- Software & Bioinformatics Tools
- By Technology
- Solid-Phase Synthesis
- Chip-Based Synthesis
- PCR-Based Enzyme Synthesis
- Others
- By Gene Type
- Standard Gene Synthesis
- Complex Gene Synthesis
- Codon-Optimized Genes
- Others
- By Application
- Synthetic Biology
- Genetic Engineering
- Diagnostics & Therapeutics Development
- Protein Engineering
- Industrial Biotechnology
- Others
- By End-User
- Pharmaceuticals and Biopharmaceutical Companies
- Contract Research Organisations (CROs)
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Diagnostics Laboratories
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Others
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- South Korea
- Taiwan
- Others
- North America