Report Overview
Neurosurgical Robotics Market - Highlights
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Size:
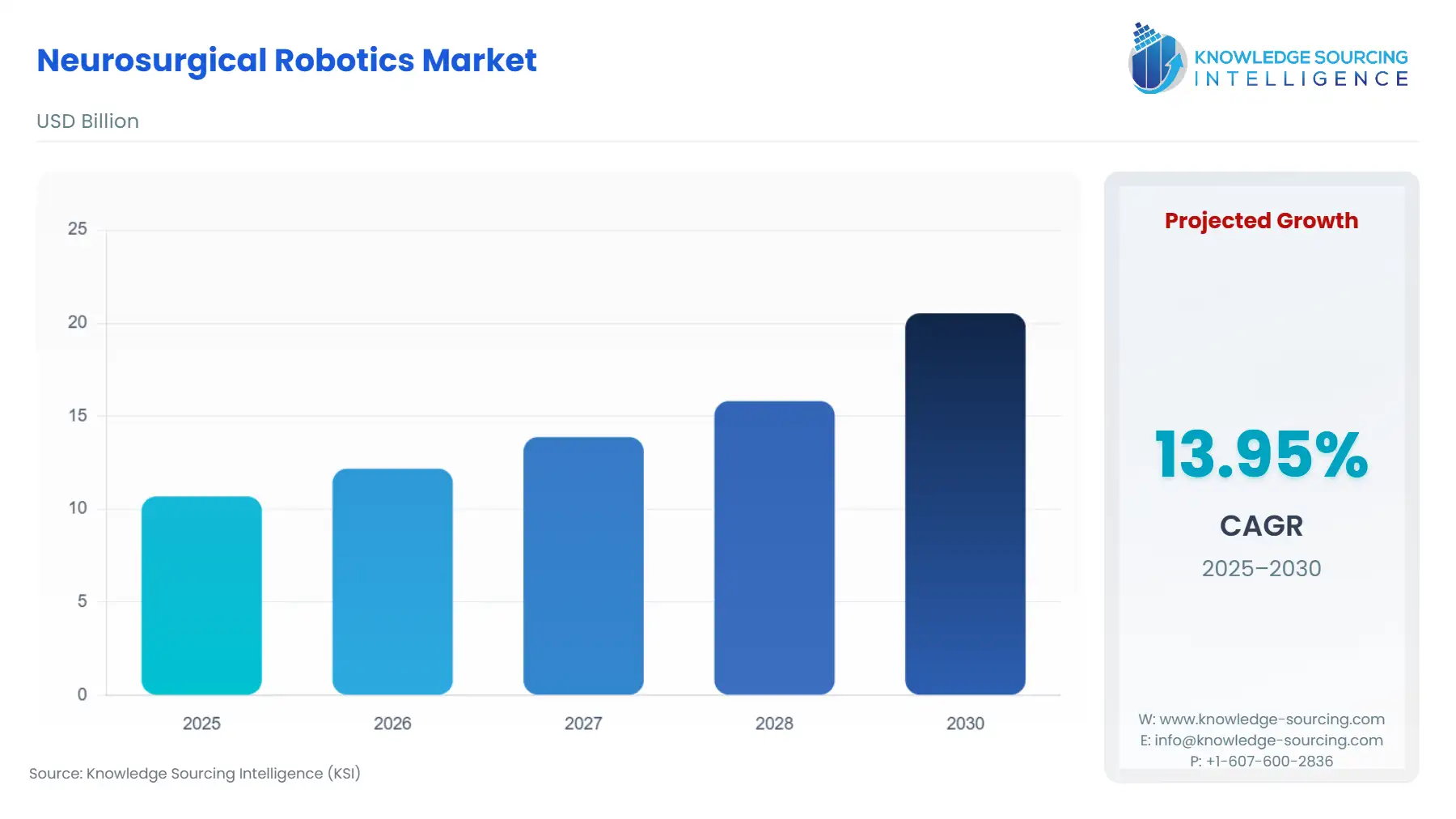
The Neurosurgical Robotics Market will expand from USD 10.687 billion in 2025 to USD 20.531 billion by 2030, driven by a 13.95% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
The neurosurgical robotics market has transitioned from a niche surgical augmentation tool to a critical capital investment for tertiary care centers globally. This evolution is fundamentally driven by the demonstrable clinical benefits of robotic assistance, primarily in precision and procedural efficiency. Robotic systems provide unparalleled navigational and mechanical stability during delicate operations on the central and peripheral nervous systems, directly impacting surgical outcomes. As healthcare systems globally face increasing pressure to optimize resources and enhance patient safety, the technological value proposition of robotics, namely, reduction in human-induced variability and improved targeting accuracy, becomes an economic and clinical imperative for hospitals seeking to maintain their competitive position in complex procedural care.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The market expansion is propelled by several macro and micro factors that directly amplify the demand for robotic systems. First, the escalating global burden of neurological disorders, including movement disorders like Parkinson's disease, epilepsy, and various brain and spinal tumors, creates a fundamental increase in the volume of complex neurosurgical interventions required. The application of robotic systems, such as for the highly accurate electrode and lead placement required in DBS and SEEG, transforms previously complex freehand or frame-based procedures into repeatable, image-guided processes. This capability encourages surgeons to attempt more complex cases and drives hospitals to invest in capturing this patient cohort.
Second, the convergence of robotics with advanced intraoperative imaging and Artificial Intelligence (AI) elevates the utility of these platforms. Modern neurosurgical robotic systems integrate seamlessly with intraoperative CT (iCT) and MRI, providing real-time feedback that enhances instrument placement precision. This technological shift directly increases demand by making the robotic system a comprehensive intraoperative solution rather than a mere mechanical arm, thereby justifying the substantial capital expenditure for institutional purchasers. The enhanced precision offered by these integrated systems is a direct demand catalyst, as it reduces the probability of revision surgeries, an attractive financial and clinical outcome for end-users.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant challenge facing the market is the substantial initial capital investment and the associated long-term maintenance and disposal costs. The high cost of adoption acts as a considerable barrier to entry, particularly for specialty neurosurgical centers and hospitals in developing economies, restricting market penetration primarily to well-funded academic and private institutions. This cost constraint directly suppresses demand volume, forcing potential buyers to prioritize only the most critical or high-volume surgical specialties for initial robot investment.
The primary opportunity, however, lies in the expansion of system utility into the cranial segment beyond current applications. Robotics is well-established in spine procedures, but the Cranial Neurosurgery segment presents a high-value opportunity. Developers are focused on advancing flexible robots and microsurgical systems that can assist in tumor resection and vascular procedures, moving beyond stereotactic trajectory guidance. Success in these complex applications, where haptic feedback and dexterity are paramount, will unlock massive untapped demand by allowing robotic platforms to participate in the most challenging and highest-reimbursement procedures. Furthermore, the development of smaller, more mobile, and lower-cost systems designed specifically for Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) offers a distinct opportunity to broaden the customer base beyond traditional hospitals.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market In-Depth Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Spinal Neurosurgery
The spinal neurosurgery segment commands significant market attention, primarily because robotic systems demonstrably solve a critical, high-volume problem: the accurate and reproducible placement of spinal instrumentation, such as pedicle screws. Misplacement can lead to severe neurological or vascular complications. The precision afforded by robotic guidance and navigation systems, such as the Mazor X platform or similar systems, significantly mitigates this risk. The demand for these systems is directly driven by the increasing global prevalence of degenerative disc disease, spinal deformities (e.g., scoliosis), and spinal trauma requiring fusion procedures. Hospitals utilize the robotic technology as a patient safety and marketing tool, directly increasing the demand for the technology by enabling them to perform procedures with improved accuracy metrics and reduced fluoroscopy exposure, a key benefit for both patient and surgical staff.
- By End-User: Hospitals
Hospitals represent the foundational end-user for neurosurgical robotics due to their extensive capital budgets, high procedure volumes, and comprehensive infrastructure. The core demand driver in this segment is the strategic imperative to achieve a competitive edge in complex surgical service lines. The high cost of these systems is amortized by the high volume of procedures (cranial and spinal) that a tertiary hospital can perform. Furthermore, the installation of robotic suites is strongly correlated with the ability to attract top-tier surgical talent and participate in advanced clinical research. The infrastructure of a large hospital, including dedicated operating rooms, advanced imaging capabilities (iCT/iMRI), and specialized maintenance staff, is essential for maximizing the utilization and efficacy of these complex systems. The demand is therefore anchored in clinical necessity combined with the institutional pursuit of advanced technological capability.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis (North America)
The United States market is characterized by a high adoption rate of neurosurgical robotics, driven by a mature reimbursement landscape and a strong institutional emphasis on leading-edge technology. Demand is catalyzed by favorable insurance and Medicare reimbursement policies for complex robotic-assisted spinal and cranial procedures, which underwrite the high capital cost of the systems. Moreover, a high density of neurological disease specialists and a consumer-driven preference for minimally invasive surgery compel major health systems to invest heavily.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Brazil's neurosurgical robotics market presents a mixed-demand profile. Adoption is largely concentrated in the elite private hospital sector within major metropolitan areas (e.g., São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro). The key local factor affecting demand is the stark divide in healthcare funding: while the public system faces funding constraints that limit capital expenditure on expensive robots, the affluent private sector views robotics as a premium service differentiator.
- German Market Analysis (Europe)
Germany's demand for neurosurgical robotics is driven by a strong commitment to quality-of-care standards and a robust academic medical system. The local factor influencing demand is the country’s high-precision engineering heritage and a healthcare system that values evidence-based technology adoption. German hospitals prioritize systems that demonstrate superior clinical data and long-term reliability.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The Saudi Arabian market exhibits a nascent but accelerating demand for neurosurgical robotics, almost entirely supported by significant government-backed investment in high-end healthcare infrastructure. Demand is a component of Vision 2030, a strategy that aims to transform the domestic healthcare sector into a regional hub for specialized medical tourism. Local factors include the government’s explicit funding for large-scale hospital construction and technology procurement, which insulates the market from local private financing constraints.
- Japanese Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
Japan represents a highly sophisticated market where demand is driven by the imperative to manage an aging population with a high prevalence of age-related neurological disorders. The key local demand factor is the stringent, lengthy, and highly protective regulatory approval process from the government. This regulatory environment historically favors domestic manufacturers and established global players willing to invest in long-term, localized clinical data generation.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The competitive landscape in the neurosurgical robotics market is highly concentrated, marked by intense innovation and strategic mergers and acquisitions (M&A) among a few dominant, highly capitalized medical technology conglomerates. The barrier to entry remains prohibitively high due to the immense R&D costs, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the specialized clinical training required. Competition centers on technological differentiation, including the degree of integration with intraoperative imaging, navigational accuracy, and the versatility across spinal and cranial applications.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Company Profiles
- Medtronic plc: Medtronic plc is a foundational player in the neurosurgical robotics domain, establishing market leadership through its strategic integration of advanced systems. Its primary offering in this space includes the Mazor X Stealth Edition system.
- Stryker Corporation: Stryker Corporation solidifies its position by leveraging a broad portfolio and strategic M&A to expand its neurological presence. The firm’s offerings focus on both the hardware and integrated surgical solutions.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Recent Developments:
- In September 2024, Stryker announced the completion of its acquisition of NICO Corporation, a move designed to strengthen its presence in the neurosurgical space. This M&A activity integrated NICO’s minimally invasive technology, primarily focused on tumor and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) procedures, into Stryker's existing neurosurgical portfolio.
- In September 2024, ZEISS launched its new KINEVO 900 S robotic visualisation system for neurosurgery, an advanced successor to the KINEVO 900, unveiled at the 2024 Congress of Neurological Surgeons.
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 10.687 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 20.531 billion |
| Growth Rate | 13.95% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, Application, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Neurosurgical Robotics Market Segmentation:
By Product Type
- Stereotactic Neurosurgical Robots
- Spinal Surgery Robots
- Robotic Radiosurgery Systems
- Navigation and Guidance Systems
- Others
By Application
- Spinal Neurosurgery
- Cranial Neurosurgery
By End-User
- Hospitals
- Specialty Neurosurgical Centers
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Taiwan
- Thailand
- Indonesia
- Others