Report Overview
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Highlights
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Size:
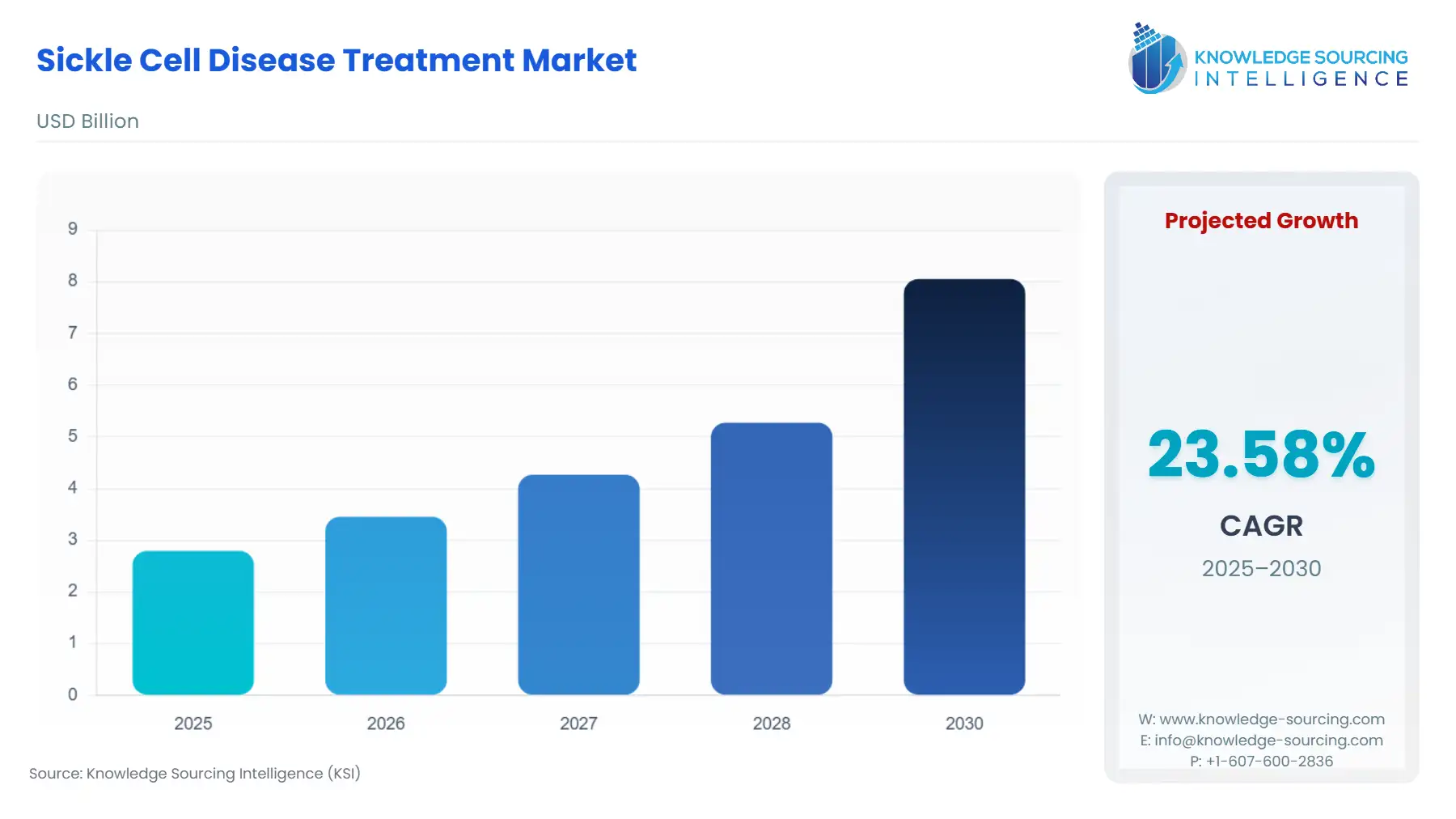
The sickle cell disease treatment market is projected to expand at a 23.58% CAGR, achieving USD 8.053 billion by 2030 from USD 2.794 billion in 2025.
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is permanent and disabling genetic blood predominantly characterized by acute chest syndrome, sickle pain crisis, jaundice, hemolytic anemia, splenic sequestration, and gradual affected organ damage. Sickle cell disease complications develop during childhood and are linked to reduced life expectancy. Early diagnosis, management, and therapy of sickle cell disease have the ability to alter the course of the condition, lessen signs and symptoms, stop long-term organ damage, and increase life expectancy. Therapies and medications that address the underlying etiology of sickle cell disease and its acute and chronic consequences have historically been in shortage. Sickle cell disease is more prevalent in people with sub-Saharan African ancestry, while it can also affect those with Hispanic, South Asian, Southern European, and Middle Eastern ancestry.
The use of hydroxyurea and consistent follow-up treatments post-diagnosis assist in the treatment of sickle cell disease. Hydroxyurea, a potent myelosuppressive drug, can significantly lower the frequency of painful episodes experienced by SCD patients. Through the consistent adoption of such fundamental measures, the mortality rate for infants born with SCD can be lowered from 80% to lower than 5% and the productive life span can be extended to more than four decades. In addition, the World Bank suggests that genetic counseling along with widespread diagnosis can eventually lead to the disease's eradication.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Drivers:
- Favorable initiatives by governments and NPOs
The prevalence of SCD and the painful consequences of the onset of SCD among children are stimulating the formulation of beneficial welfare policies by different governments and international organizations. For instance, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare of India announced that the union budget relevant to FY 2023-24 contains special monetary provisions for the elimination of sickle cell anemia disease in India by the end of 2047. Consequently, a pilot project has been launched in India due to which approximately 993,114 people have been screened and the National Health Mission is providing treatment support by issuing free hydroxyurea tablets and blood transfusions in necessary cases. In addition, the World Bank announced that from 2019 it would significantly increase its SCD treatment intervention in selected African countries by integrating public and private healthcare sectors of these countries. Apart from this, the US National Institutes of Health announced that it will be funding a five-year research project to reduce the healthcare restraints for SCD patients across the USA by granting US$5.5 million. Therefore, the beneficial policies and support offered by governments and NPOs across the world to aid patients suffering from SCD are anticipated to propel the growth of the SCD treatment market.
- The unavailability of medication for treating the root cause of SCD limits the growth of the sickle cell disease treatment market.
Pharmacotherapy, bone marrow transplantation, and blood transfusions are some of the most commonly used treatments for sickle cell disease. The present medication targeting sickle cell disease only has the ability to relieve the symptoms of sickle cell disease and lower the probability of future complications as a result of the disease among patients. Due to the prominent risks involved in bone marrow or stem cell transplantation procedures, such treatments are opted for only in a lower percentage of patients. Therefore, the lack of substantial treatment for sickle cell disease to eradicate the root cause of the disease slows down the rapid growth of the sickle cell disease treatment market. However, the active research and investments by leading pharmaceutical companies into gene-altering therapies could develop efficient treatments for SCD patients over the course of the forecast period.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Key Developments:
- In October 2022, Pfizer Inc., a leading international pharmaceutical company acquired Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc., a company primarily involved in the research, development, and production of effective treatments for patients suffering from sickle cell disease.
- In July 2022, Editas Medicine declared the first successful patient trial of its newly developed cell therapy as a medicine for sickle cell disease and in addition, the FDA released the clinical trial hold on the said therapy named EDIT-301.
- In February 2022, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc.'s PYRUKYND product containing mitapivat for the treatment of adults with an uncommon, disabling, permanent hemolytic anemia called pyruvate kinase deficiency.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Geographical Outlook:
- North America's sickle cell disease treatment market is expected to grow in the forecast period.
The sickle cell disease treatment market in North America is likely to expand due to the prevalence of sickle cell disease in the region and the advancements in sickle cell disease treatments by pharmaceutical companies and research establishments. The Centers for Disease Prevention and Control reported that approximately 100,000 people suffered from sickle cell disease in the US, and in addition, it was estimated that about 1 among 13 American citizens of African ethnicity carried the sickle cell disease trait in their bodies. The rising disposable income levels and the constant research into sickle cell disease treatments by key pharmaceutical companies such as Novartis AG and Bristol-Myers Squibb Company are expected to rise the consumption of sick cell disease treatment across North America.
In addition, the high prevalence rates of sickle cell disease in African countries are anticipated to grow the Middle East and Africa region’s sickle cell disease treatment market. The Standford Medicine Board concluded that most of the children with sickle cell disease have African or Hispanic family backgrounds. The World Bank revealed that the prevalence of sickle cell disease in most African countries like the Republic of Congo and Nigeria ranges from 20% to 30% whereas, in some countries like Uganda, the prevalence rates reach as high as 45%. In addition, the social welfare initiatives taken by international health organizations and pharmaceutical companies to help provide medical aid to sickle cell anemia patients shall stimulate the consumption of sickle cell disease treatment across different countries in Africa. For instance, the health ministers in Africa collaborated to initiate an awareness and prevention campaign to lower the deaths resulting from sickle cell disease in their respective regions. Hence, the sickle cell disease treatment market in the Middle East and Africa region is expected to significantly rise over the forecast period.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.794 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 8.053 billion |
| Growth Rate | 23.58% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Treatment, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Market Segmentation:
- SICKLE CELL DISEASE TREATMENT MARKET BY TREATMENT
- Blood Transfusion
- Pharmacotherapy
- Bone Marrow Transplant
- SICKLE CELL DISEASE TREATMENT MARKET BY END-USER
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Others
- SICKLE CELL DISEASE TREATMENT MARKET BY GEOGRAPHY
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America