Report Overview
Agricultural Chelates Market - Highlights
Agricultural Chelates Market Size:
Agricultural Chelates Market is projected to expand at a 5.15% CAGR, attaining USD 1.448 billion in 2031 from USD 1.071 billion in 2025.
The Agricultural Chelates market is a crucial sector within the larger specialty fertilizers and micronutrient industry, addressing the persistent global challenge of soil micronutrient deficiency. Chelating agents function by binding to essential metal ions (like Iron, Zinc, and Manganese), protecting them from precipitation and immobilization in the soil—a common occurrence in alkaline conditions, thereby maximizing their bioavailability to crops. This technological solution is foundational to enhancing nutrient use efficiency (NUE) and optimizing yields in high-intensity farming systems worldwide. The market's structural dynamics are fundamentally dictated by agronomic necessity, regulatory constraints, and the escalating demand for nutrient-dense, high-value crops, all of which directly influence the procurement patterns of agricultural producers globally.
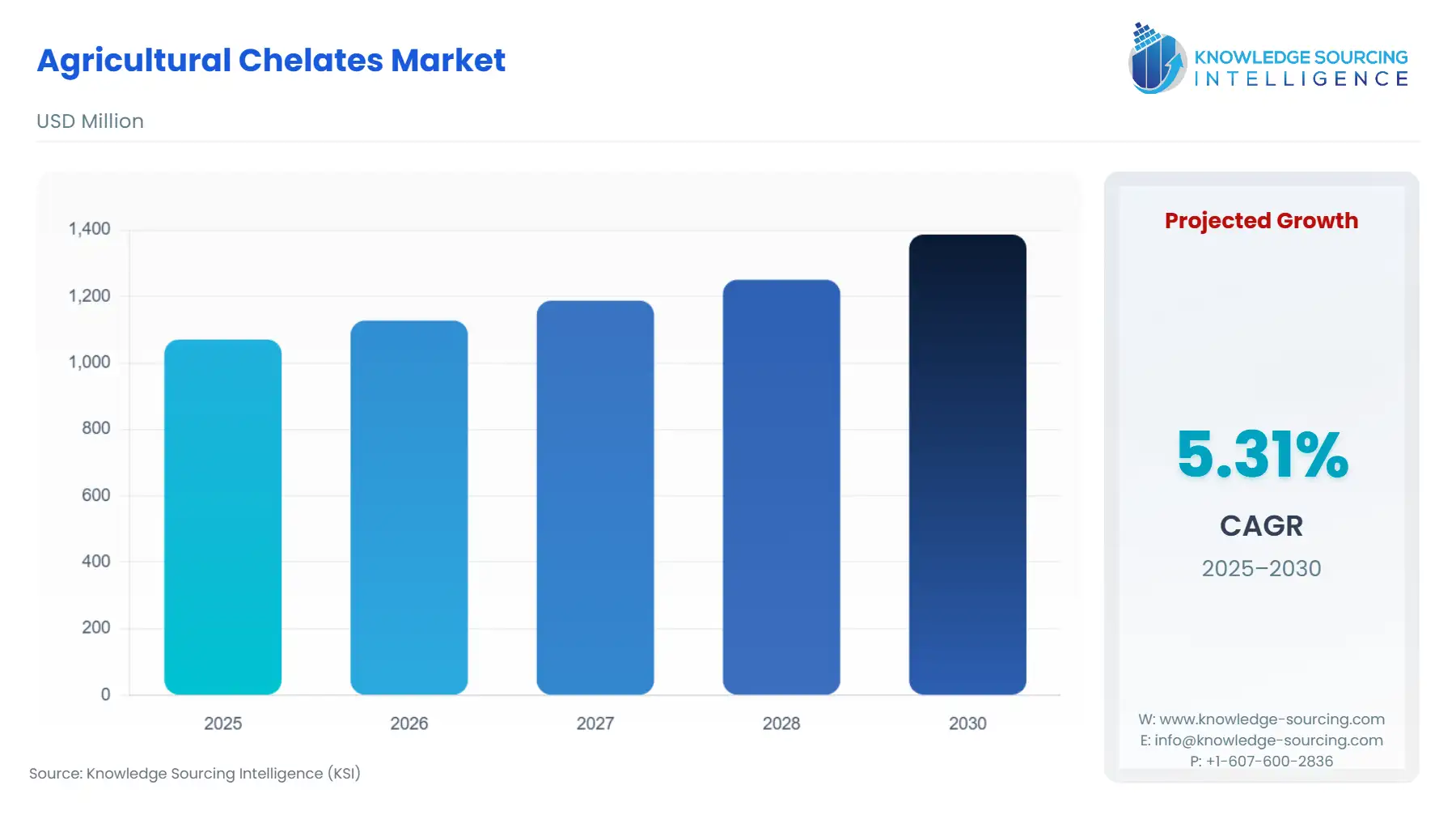
Agricultural Chelates Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The pervasive global issue of micronutrient deficiency in arable soil serves as the strongest demand driver, as intense and continuous cropping practices deplete essential minerals like Zinc and Iron. Chelates directly address this deficiency by ensuring these nutrients remain soluble and available for plant uptake, creating an immediate and continuous demand for corrective action to maintain yield. Furthermore, the rising adoption of precision agriculture and advanced irrigation techniques like fertigation acts as a market catalyst. These sophisticated systems necessitate high-efficiency, highly soluble nutrient delivery mechanisms to operate effectively, directly increasing the demand for water-soluble, stable chelate formulations over conventional salt fertilizers. This emphasis on efficiency and targeted nutrition compels growers toward high-performance chelated products.
Challenges and Opportunities
A significant market challenge is the environmental persistence of non-biodegradable synthetic chelates, such as EDTA, which can leach into water bodies and cause environmental harm. This concern creates a public and regulatory constraint, negatively impacting the demand for legacy products. Conversely, this constraint concurrently generates a major opportunity in organic and biodegradable chelates. The push for sustainable and organic farming practices, coupled with stricter European regulations (like REACH), accelerates the demand for bio-based and readily degradable alternatives like LingoSulphates and IDHA. Producers who can certify and scale production of these eco-friendly formulations gain a competitive advantage and access to premium, environmentally conscious market segments.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The Agricultural Chelates market is a physical product market, with pricing fundamentally tied to key chemical intermediates. Synthetic chelates like EDTA are reliant on commodities such as Ethylenediamine (EDA) and Monochloroacetic acid (MCA), while DTPA requires Diethylenetriamine (DETA). Volatility in the pricing and supply of these petrochemical-derived precursors directly impacts the final chelate product cost and, consequently, demand elasticity among price-sensitive farmers. The pricing dynamics of the final chelated product are also linked to the chelated metal (e.g., Iron, Zinc, Manganese), whose commodity prices fluctuate. Organic chelates, such as Aminoacids and LingoSulphates, are less exposed to petrochemical price risk but their pricing is influenced by the agricultural commodity feedstock and fermentation costs, often making them a higher-priced alternative to their synthetic counterparts.
Supply Chain Analysis
The global agricultural chelates supply chain is structured around the conversion of bulk petrochemical derivatives and commodity metals into highly specialized formulations. Key production hubs are concentrated in regions with robust chemical manufacturing capabilities, notably China, Western Europe (e.g., the Netherlands, Germany), and the US, due to proximity to precursor chemical feedstock. Logistical complexities stem primarily from the handling and transport of corrosive or specialized chemical intermediates and the subsequent distribution of the final product, often in powdered or liquid form, to diverse, geographically dispersed farming communities. Market dependencies are critical at the upstream level, relying on stable global supply chains for the petrochemical precursors like EDA and DETA. Downstream distribution relies on established networks of agricultural co-operatives and fertilizer blenders to reach the end-user farmer.
Agricultural Chelates Market Government Regulations
Regulatory frameworks significantly influence product development and market acceptance, specifically driving demand toward more environmentally responsible solutions.
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
European Union | REACH Regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) | REACH mandates rigorous data submission and registration for all chemical substances, including chelates, imported or manufactured over one ton annually. This directly increases the compliance cost for synthetic chelates like EDTA, accelerating the demand shift towards certified, biodegradable alternatives like IDHA to minimize registration burden and environmental risk profile. |
European Union | Fertilizing Products Regulation (FPR) (EU) 2019/1009 | The FPR harmonizes the rules for fertilizers bearing the CE marking, incorporating stringent safety and quality requirements, including lower limits for cadmium and other contaminants. This creates a regulatory imperative for manufacturers to use purer raw materials and drives demand for high-quality, traceable chelate products compliant with the new pan-European standards. |
United States | USDA National Organic Program (NOP) | The NOP dictates which substances are permitted for use in certified organic farming. By explicitly listing or restricting certain inputs, NOP directly influences the demand for organic chelates (e.g., LingoSulphates, Aminoacids) and severely constrains the use of most synthetic chelates, creating a high-value niche market for approved natural formulations. |
Agricultural Chelates Market Segment Analysis
Synthetic EDTA (By Type)
The demand for Synthetic EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) remains robust due to its cost-effectiveness, high stability, and established utility as a general-purpose chelating agent for various micronutrients (Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu). EDTA maintains a significant revenue share because of its high affinity for metals across a relatively wide pH range, offering a reliable, economic solution for prophylactic nutrient management, particularly in slightly acidic to neutral soils. In large-scale commodity cropping (Grains and Cereals), where input cost is a critical factor, EDTA’s favorable price point and proven performance make it the dominant choice, driving consistent, high-volume demand. While facing competition from biodegradable alternatives in environmentally sensitive markets, the established supply chain, manufacturing scale, and application versatility of EDTA solidify its position as the market's enduring workhorse, essential for foundational nutrient delivery globally.
Foliar Application (By Application)
The Foliar Application segment commands high demand due to its capacity for immediate, high-efficiency nutrient delivery, bypassing the challenges of soil chemistry. When crops exhibit acute micronutrient deficiencies, or when soil conditions (such as high pH) render soil-applied nutrients unavailable, foliar spraying of chelates offers the fastest corrective measure. This method dramatically improves Nutrient Use Efficiency (NUE) because the chelates are absorbed directly by the plant leaves, minimizing nutrient loss through immobilization or leaching. This capability is highly valued in high-value crop cultivation (Fruits and Vegetables), where quality and time-sensitive nutrient management directly impact market price and yield, thus driving concentrated demand for highly soluble and stable chelate formulations specifically designed for foliar application.
Agricultural Chelates Market Geographical Analysis
United States Market Analysis (North America)
The US market is characterized by sophisticated farming practices and significant cultivation of high-value crops, driving demand for premium chelate formulations. The widespread adoption of precision agriculture and variable rate technology compels growers to prioritize highly efficient applications, favoring chelated products to maximize ROI per acre. Demand for chelates, particularly for Iron and Zinc, is robust in the Western and Midwestern US to combat alkaline soils which reduce nutrient availability. Furthermore, the presence of major domestic chemical producers and a developed distribution network ensures high product availability. The market is increasingly sensitive to sustainable practices, pushing manufacturers to introduce biodegradable or organically compliant options to capture the growing specialty crop sector.
Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Brazil represents a rapidly expanding market, where demand is largely driven by the colossal scale of its Grains and Cereals (soybeans, corn) cultivation. The expansive use of intensive agriculture has led to documented micronutrient deficiencies across vast areas of Brazilian soil, particularly Zinc and Copper. The country’s high commodity crop production mandates the use of chelates to ensure maximum yield potential, directly translating into high-volume demand for cost-effective synthetic products like EDTA. Infrastructure investment in new agricultural frontier regions and the increasing adoption of efficient farming techniques further accelerate demand for chelated solutions compatible with large-scale, mechanized farming and fertigation systems.
Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
The German market is a highly regulated and mature environment, where demand for chelates is strictly managed by EU environmental and chemical safety regulations (REACH). This regulatory stringency creates a high premium for compliance. As a result, demand is heavily skewed toward bio-based and highly biodegradable chelates (e.g., IDHA) to minimize environmental liability and ensure product marketability. While the total volume may be lower than in other regions, the high-value Turf and Ornamentals sector and specialized greenhouse cultivation drive consistent, technically demanding requirements for high-purity, low-impact chelate formulations.
Saudi Arabia Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The Saudi Arabian market’s demand for agricultural chelates is unique, driven primarily by the severe challenges of arid climate, calcareous (high pH) soils, and water scarcity. These factors exacerbate iron deficiency (chlorosis), necessitating the use of the most persistent and effective iron-specific chelates, such as EDDHA, which remains stable and effective in extremely alkaline conditions. Government-backed initiatives to bolster domestic food security through controlled environment agriculture (greenhouses) and irrigation projects directly increase the targeted demand for water-soluble chelates suitable for fertigation systems. The imperative here is not just yield, but the very possibility of growing high-value crops under harsh environmental constraints.
China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
China is a dominant force, representing a massive market for agricultural inputs due to its high population density and the imperative for domestic food self-sufficiency. Demand is propelled by the need to remediate widespread micronutrient depletion in intensely farmed soils. The market favors a balance of high-volume, affordable synthetic chelates for commodity crops and specialized, higher-purity chelates for its rapidly expanding Fruits and Vegetables sector. Furthermore, the US-China trade tensions and US tariffs on certain chemical imports historically created volatility and a push for domestic substitution within China's chemical industry, increasing its self-reliance in chelate production and influencing regional supply dynamics, but primarily impacting trade flows rather than fundamental agronomic demand.
Agricultural Chelates Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Agricultural Chelates market competition is defined by a global rivalry between established multinational chemical conglomerates with diversified portfolios and specialized regional producers focused on niche biodegradable products. Success hinges on controlling raw material supply, achieving efficient production scale, and possessing the technical expertise to formulate crop- and soil-specific solutions.
BASF SE
Strategic Positioning: BASF SE, a global chemical leader, strategically positions its agricultural chelates portfolio as a component of its broader crop protection and nutrition solutions. Its strength lies in its vast global manufacturing footprint, integrated supply chain for chemical precursors, and a strong focus on sustainability-driven innovation. This integration allows BASF to offer a stable supply and develop next-generation, low-impact products to capture European and North American demand for eco-friendly inputs.
Key Products/Services (Verifiable Details): BASF's product line includes Dissolvine chelating agents, which encompass a range of synthetic types like EDTA, DTPA, and the biodegradable agent IDHA. The company has strengthened its value chain for chelating agents by setting up or expanding production facilities, such as the investment to strengthen its production plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany, to increase market share in the European region, focusing on these chelating agents.
Nouryon
Strategic Positioning: Nouryon (formerly AkzoNobel Specialty Chemicals) is a major player with a focus on high-performance chelates, particularly the biodegradable segment. Its strategy centers on leveraging its specialty chemicals expertise and capacity for sustainable production to meet the increasing global and regulatory demand for environmentally benign products, securing a strong position in markets driven by compliance and premium pricing.
Key Products/Services (Verifiable Details): Nouryon's key product is the Dissolvine range of chelating agents, including the highly effective EDTA and DTPA variants. The company has demonstrated its commitment to sustainability by achieving International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC PLUS) at its Herkenbosch facility in the Netherlands (announced January 2025), enabling the production of biodegradable chelates with up to a 100% renewable carbon index (RCI) using biobased and bio-circular feedstocks.
Agricultural Chelates Market Developments
These verifiable developments highlight the industry's focus on sustainable chemistry and strategic capacity expansion to meet evolving market demands.
January 2025: Nouryon Chemicals Holding B.V. Receives ISCC PLUS Certification
Nouryon Chemicals Holding B.V. announced receiving the International Sustainability and Carbon Certification (ISCC PLUS) certification at its Herkenbosch facility in the Netherlands. This certification enables the company to produce biodegradable chelates with up to 100% renewable carbon index (RCI) using biobased and bio-circular feedstocks, directly addressing the environmental persistence challenge and increasing the supply of certified sustainable products.
August 2024: CHS Inc. Launches Trivar EZ Granular Chelated Micronutrient
CHS Inc. launched a new granular chelated micronutrient fertilizer blend called Trivar EZ. This product represents the first of six new products from the company, incorporating its patented Levesol chelating agent. The launch aims to improve crop yields by enhancing the accessibility of micronutrients to crops, signaling an expansion in the US market's offering of proprietary, specialized chelate formulations.
Agricultural Chelates Market Segmentation:
BY TYPE
Synthetic
Ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA)
Ethylenediaminedihydroxy-Phenylacetic Acid (EDDHA)
Diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (DTPA)
Others
Organic
Amino Acid
Fulvic Acid
Humic Acid
Others
BY CROP TYPE
Grains and Cereals
Pulses and Oilseeds
Commercial Crops
Fruits and Vegetables
Turf and Ornamentals
BY APPLICATION
Soil
Foliar
Fertigation
Others
By Geography
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
Germany
France
United Kingdom
Spain
Italy
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Israel
Others
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Indonesia
Thailand
Others