Report Overview
Canada AI for Predicting Highlights
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Size:
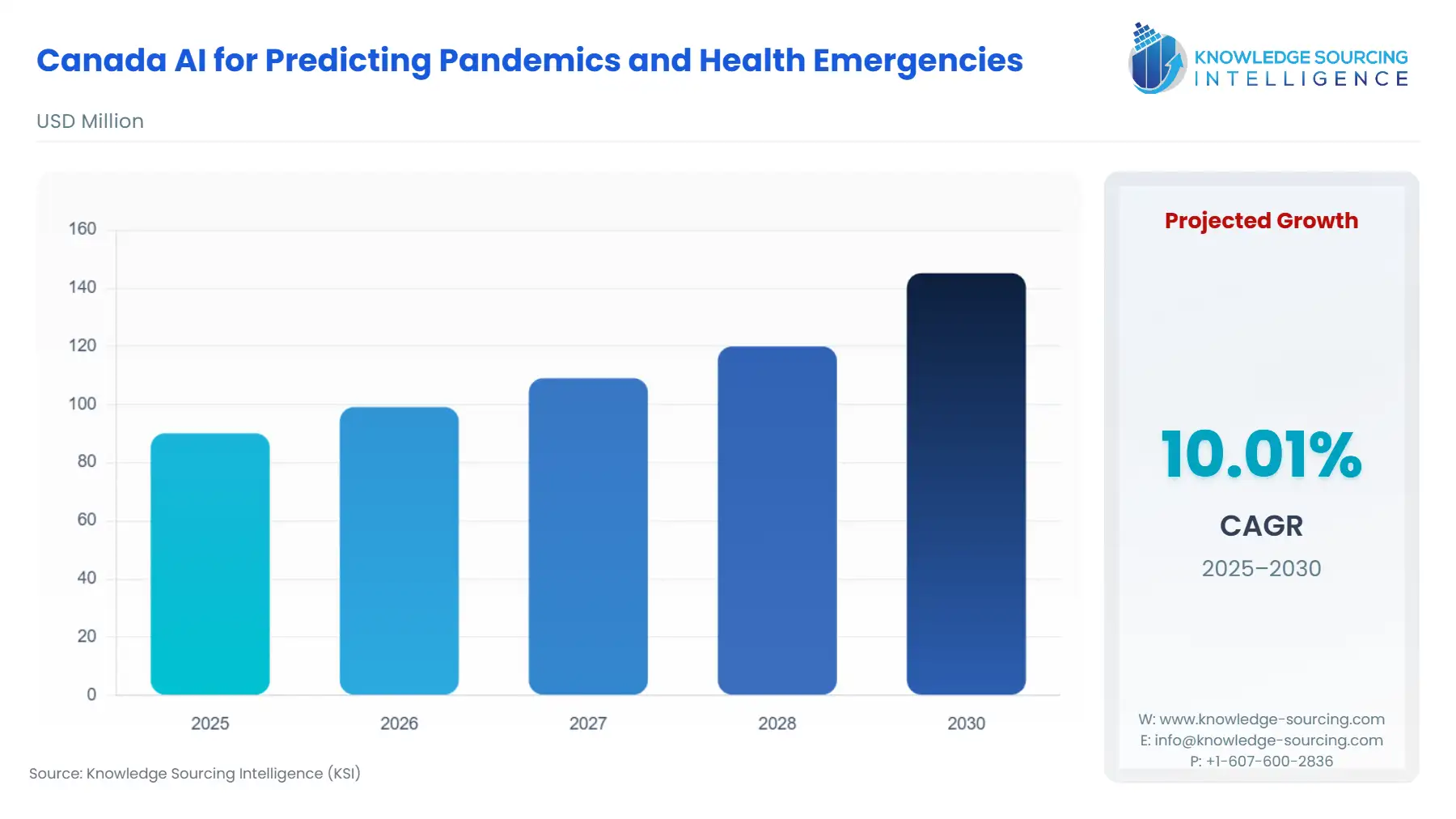
The Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 10.01%, reaching USD 145.223 million in 2030 from USD 90.112 million in 2025.
The Canadian AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies market represents a specialized, high-growth subset of the broader health technology sector, rapidly transitioning from a purely research-driven field to one with verifiable public sector commercial adoption. The market's current dynamics are fundamentally shaped by the confluence of direct public funding mechanisms and post-pandemic political will to establish a robust, sovereign national data infrastructure capable of preemptive threat detection. This imperative is driving a clear and measurable increase in procurement and resource allocation towards software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms specializing in machine learning, complex data integration, and predictive epidemiological modeling. The core challenge for market players remains the navigation of a complex, provincially-administered healthcare system, necessitating collaborative models with academic institutions and deep integration with existing Public Health Agency data platforms to unlock large-scale demand.
________________________________________
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Government investment acts as the singular, most significant growth catalyst. The $2 billion commitment to the Canadian Sovereign AI Compute Strategy, launched in 2024-2025, allocates funds to build both commercial and public supercomputing infrastructure. This development dramatically lowers the capital expenditure barrier for start-ups and researchers developing high-performance computing (HPC)-intensive AI models, directly increasing the addressable market for sophisticated predictive software by enabling its operational feasibility. Furthermore, the AI Compute Access Fund explicitly targets the high cost of compute resources for Canadian innovators, directly accelerating the commercialization of complex algorithms into deployable software solutions, thereby increasing product supply and market competition.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A primary constraint is the fragmented nature of Canadian health data, which is governed provincially, imposing significant integration and standardization challenges that directly limit the scalability and generalizability of national-level AI prediction models. This data silo issue diminishes demand for off-the-shelf solutions and elevates the necessity for highly customizable Services components. The main opportunity arises from the validated use of novel data sources—including real-time digital health data, social media, and wastewater surveillance—for early warning systems. This technical shift compels Government & Public Health Agencies to acquire AI platforms that leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) and advanced time-series forecasting algorithms to fuse heterogeneous inputs, creating a new, verifiable demand segment.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The AI for Pandemic Prediction supply chain is fundamentally intangible, focusing on a knowledge and data pipeline rather than physical components. The critical dependencies exist in the upstream supply of high-quality, ethically sourced, and de-identified health and surveillance data, which is primarily controlled by provincial health authorities and government agencies. Key production "hubs" are concentrated around the National AI Institutes (Amii, Mila, Vector Institute), which translate research capacity into commercial-ready algorithms. Logistical complexities revolve entirely around regulatory clearance, secure cloud environments, and establishing robust, real-time data ingestion pipelines from disparate provincial and municipal sources. The core dependency is a specialized talent pool of data scientists and machine learning engineers trained in public health informatics, creating a severe supply-side constraint on service delivery and model maintenance.
- Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Federal, Provincial, Territorial (FPT) Governments | Pan-Canadian AI for Health (AI4H) Guiding Principles | Establishes a common framework for Equity, Privacy, and Safety. This formal guidance reduces regulatory risk for procurement by Public Health Agencies, accelerating demand by institutionalizing a baseline for acceptable AI technologies and fostering public trust. |
| Federal | Health Canada (as related to Medical Devices Regulations) | AI software used for diagnosis or treatment is regulated as a medical device. This mandates a stringent, costly, and lengthy approval pathway, which can constrain the time-to-market for predictive tools that have a direct clinical application, thereby limiting Software demand until clearance is secured. |
| Federal | Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy / Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada (ISED) | Provides $60 million in funding (2021-2026) to the National AI Institutes to translate research into commercial applications. This initiative directly fuels the Services segment by subsidizing collaborative projects between academia and industry, creating initial demand for proof-of-concept deployments. |
________________________________________
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Outbreak Prediction & Detection
The Outbreak Prediction & Detection segment is driven by the governmental and public health imperative to shift from reactive containment strategies to proactive preemption, a policy goal enshrined in post-pandemic preparedness planning. The core growth driver is the proven ability of machine learning models to analyze non-traditional, heterogeneous data—such as social media chatter, aggregate mobility data, and real-time laboratory test volumes—to generate signals earlier than traditional, laboratory-confirmed surveillance systems. This capability creates direct need for Software platforms capable of continuous, real-time data fusion and predictive modeling (e.g., nowcasting and short-term forecasting). Public Health Agencies are now prioritizing solutions that offer not merely prediction, but also the visualization and interpretation of uncertainty ranges, requiring a sophisticated user interface layer that propels demand for user-friendly, cloud-deployed analytical tools. The need for transparency and explainability in high-stakes prediction further accelerates demand for proprietary AI services that validate and refine these models.
- By End-User: Government & Public Health Agencies
Government and Public Health Agencies represent the largest, most critical end-user segment, fundamentally shaped by public policy and sovereign data control requirements. The primary growth driver is the legislated and budgetary mandate for national data sovereignty and computational security, as articulated in the Canadian Sovereign AI Compute Strategy. This mandate compels agencies to procure On-Premises or secure Cloud-based solutions that guarantee data is processed and stored within Canada, bypassing reliance on foreign infrastructure. The market is also critically influenced by the need to integrate AI tools with existing legacy public health informatics systems (e.g., provincial disease registries). This necessitates procuring high-cost, specialized Services contracts for system integration and workflow re-engineering, often overshadowing the cost of the base software license. The sustained, long-term procurement of Software is therefore contingent on an AI solution's demonstrated interoperability and adherence to pan-Canadian data-sharing standards.
________________________________________
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The Canadian AI for public health market is a highly specialized landscape dominated by small, research-intensive start-ups and Canadian branches of established multinational firms. Competition is focused on verifiable accuracy of predictive models, interoperability with existing provincial electronic health records (EHRs), and establishing trust with government agencies through academic partnerships. Market share is not acquired through price competition, but through successful proof-of-concept deployments and aligning product roadmaps with federally funded initiatives like the Pan-Canadian AI Strategy.
- BlueDot
BlueDot, a Toronto-based company, is strategically positioned as a pioneer in the market, focusing specifically on infectious disease surveillance and outbreak risk assessment. The company's core product is a proprietary, cloud-based platform that uses natural language processing and machine learning to scour hundreds of thousands of data sources—including official government reports, airline ticketing data, and news reports—in 65 languages. This intelligence platform predicted the outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, ahead of the WHO, a verifiable event that significantly bolstered its credibility and strategic positioning with public health customers globally. Its strategic imperative centers on securing long-term service contracts with government and intergovernmental agencies by leveraging its demonstrated first-mover advantage and historical accuracy in preemptive threat intelligence.
- Aifred Health
Aifred Health, based in Montreal, offers an AI-driven clinical decision support device, though its primary focus is on mental health. Aifred's strategic positioning in the broader AI for health ecosystem is significant due to its successful navigation of Canadian regulatory approval. The company announced the Health Canada Approval for the sale and commercialization of its AI-driven clinical decision support device to optimize treatment choice in major depression in 2024. This regulatory milestone demonstrates a core competency in achieving federal approval for a complex, AI-driven medical device, a crucial capability that is directly transferable to the high-stakes AI for Pandemics market, particularly for systems that would fall under the Medical Devices Regulations (e.g., diagnostic-assist tools for novel pathogens).
- Deep Genomics
Deep Genomics, another Toronto-based firm, applies its AI expertise to genetic medicine. While not a direct pandemic prediction player, its core technology platform is highly relevant to post-detection response. The company's focus is on using its proprietary AI to find and develop treatments for genetic diseases by deciphering the functional impact of genetic variations. This positions Deep Genomics as a critical competitive factor for the Pharmaceuticals and Biotech Companies end-user segment, particularly for those engaged in rapid vaccine or therapeutic development following the detection of a novel pathogen. Their strategic positioning leverages the high-throughput, high-accuracy processing of genomic data, a capability essential for rapid pathogen identification and countermeasure design.
________________________________________
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Recent Developments:
- September 2025: BlueRock Therapeutics announced the first patient treatment in the pivotal Phase III clinical trial for its investigational cell therapy, bemdaneprocel, for Parkinson's disease. While BlueRock's focus is on cell therapy, this development, sourced from the company's press release, confirms their continued, high-capital-intensive clinical trial capacity and commitment to advanced biotherapeutics, demonstrating robust R&D investment within a key Canadian-headquartered biotech entity.
- July 2025: BlueRock Therapeutics announced that the first patient received investigational therapy in the Phase 1/2a clinical trial of OpCT-001 for the treatment of primary photoreceptor diseases. This event, sourced from the company's press releases, indicates an expansion of BlueRock's clinical development pipeline beyond Parkinson's disease, utilizing their advanced cell therapy platform. This continued investment in cutting-edge R&D capacity underscores the robust nature of the life sciences end-user segment in Canada.
- January 2024: Aifred Health concluded its North American Clinical Trial and initiated the preparation of regulatory filings to seek US and Canadian approval for its AI-driven clinical decision support platform for major depression. This milestone, sourced directly from the company's official press release, marks a significant de-risking event for the company's technology. The successful completion of this regulatory-focused trial provides a crucial blueprint for other Canadian AI companies seeking to commercialize their technologies within the high-barrier-to-entry healthcare sector.
________________________________________
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 90.112 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 145.223 million |
| Growth Rate | 10.01% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment Mode, Application, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Canada AI for Predicting Pandemics and Global Health Emergencies Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Software
- Services
- Hardware
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODE
- Cloud-based
- On-Premises
- BY APPLICATION
- Outbreak Prediction & Detection
- Disease Surveillance
- Contract Tracing
- Risk Assessment
- Health Trend Forecasting
- Public Health Resource Allocation
- Others
- BY END-USER
- Government & Public Health Agencies
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Research Institutions
- Pharmaceuticals and Biotech Companies
- Academic Institutions
- Others