Report Overview
Emergency Lights Market - Highlights
Emergency Lights Market Size:
Emergency Lights Market, sustaining a 7.14% CAGR, is anticipated to reach USD 13.222 billion by 2030 from USD 9.366 billion in 2025.
The global emergency lights market represents a non-discretionary procurement segment within the commercial and industrial building sectors, fundamentally underpinned by life-safety regulations rather than economic cycles alone.
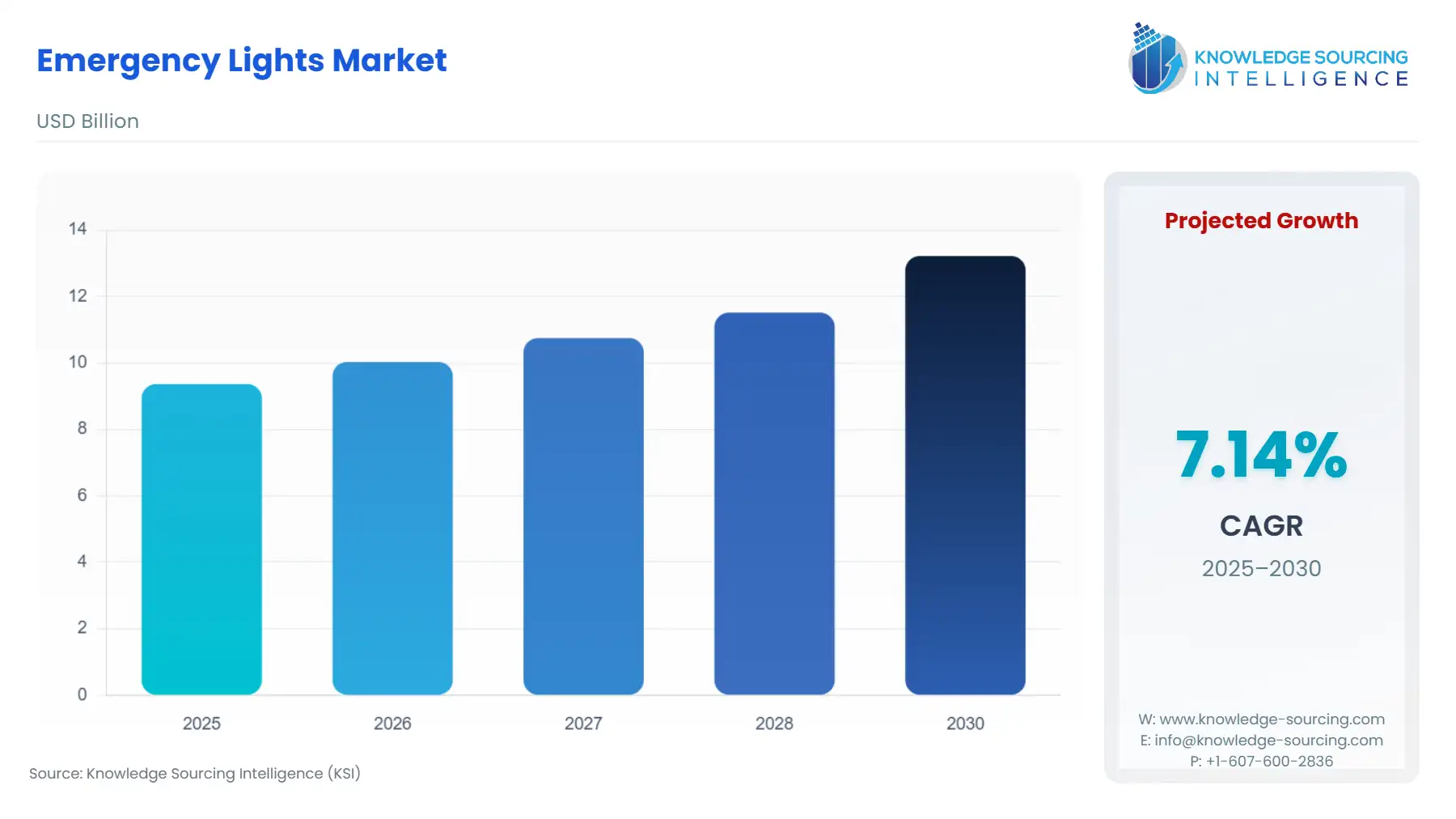
This market's primary function is to provide reliable, continuous illumination of egress paths, stairwells, and critical areas upon the failure of normal power supply, a necessity governed by rigorous international and local building codes. The ongoing replacement of legacy fluorescent and incandescent systems with energy-efficient Light Emitting Diode (LED) technology is currently the most significant trend, concurrently driving demand for smaller, more powerful battery backup solutions and creating a pathway for smart, networked emergency lighting systems. The imperative for compliance, coupled with the long-term operational cost savings offered by LED systems, solidifies this market's resilience and forward trajectory.
Emergency Lights Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Mandatory building safety codes, such as the US-based NFPA 101 Life Safety Code and the International Building Code (IBC), establish the foundation for demand. These codes enforce non-negotiable standards for minimum illumination levels along exit routes and for the duration of battery backup (typically 90 minutes), effectively guaranteeing a replacement and retrofit demand for every commercial, public, and high-rise residential structure globally. This regulatory environment directly increases demand for highly reliable emergency lights that comply with specific illumination requirements (e.g., 1 foot-candle average, $0.1$ foot-candle minimum on egress paths). Furthermore, urbanization and the continuous global expansion of commercial and public infrastructure, including airports, rail networks, and data centers, necessitate the immediate installation of compliant, modern emergency lighting systems in every newly completed structure.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the market is the volatility and regulatory scrutiny surrounding key raw materials, specifically the price fluctuations and environmental disposal complexities of battery components like Nickel and Cadmium. This factor elevates the initial purchase price of emergency lighting units, creating resistance in price-sensitive procurement scenarios. Concurrently, the significant opportunity lies in the rapid adoption of Central Battery Powered systems in large commercial and industrial buildings. Centralized systems consolidate all battery maintenance into a single, protected location, which directly addresses the demand for reduced, centralized maintenance labor and easier compliance audits, creating a higher-value proposition over multiple self-contained units. This shift is particularly pronounced in large-scale infrastructure projects like transit tunnels and hyperscale data centers.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The emergency lighting market is a physical product segment highly reliant on the supply of semiconductors for LED components and critical metals for battery chemistries. The maturation of Lithium-ion (Li-ion) systems is introducing price volatility tied to Lithium, Cobalt, and Nickel commodity markets, even as it enables a superior product. Manufacturers utilize supply chains concentrated in Asia-Pacific for LED chips and battery cell assembly. Legacy Lead-Acid and Nickel Cadmium (NiCd) solutions remain in use for cost-sensitive projects, but their higher environmental disposal costs and bulkier form factor increasingly penalize their competitiveness. The long lifecycle and superior energy density of Li-ion systems provide a higher total value proposition, moving the market to accept a higher initial component price to secure lower long-term operational and replacement costs.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for emergency lights is fundamentally segmented into raw component sourcing and final product assembly. Key production hubs for LED components, microprocessors, and battery cells are concentrated across the Asia-Pacific region, primarily in China, Vietnam, and South Korea. This geographical concentration creates dependencies vulnerable to logistical friction and political developments. For instance, the imposition of US tariffs on Chinese-manufactured electrical components increases the total landed cost for brands supplying the North American market, requiring strategic shifts toward regional assembly nodes or alternative sourcing. This complexity necessitates multi-sourcing and sophisticated inventory management to meet the non-negotiable demand dictated by construction and safety deadlines globally.
Emergency Lights Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
NFPA 101: Life Safety Code (National Fire Protection Association) |
Directly mandates the installation, performance (e.g., 90-minute minimum runtime), and placement of emergency lighting in all commercial and public buildings, guaranteeing a base level of continuous demand for compliant products. |
|
United States |
UL 924 Standard (Underwriters Laboratories) |
A product safety standard that requires emergency lighting and exit signs to automatically illuminate upon power failure. This creates a non-negotiable technical barrier to entry, channeling demand toward certified, high-quality, and tested systems. |
|
European Union |
EN 1838: Emergency Lighting (European Committee for Standardization) |
Defines specific photometric, colorimetric, and performance requirements for emergency lighting, ensuring product uniformity across the EU. This standardization facilitates cross-border trade but compels manufacturers to meet a precise technical specification, impacting demand for non-compliant, low-cost imports. |
|
Global |
International Building Code (IBC) (International Code Council) |
Adopted globally by many nations and jurisdictions, the IBC sets design and construction requirements, including those for egress. Its enforcement directly drives the initial demand for emergency light installation in all new construction and major renovation projects. |
Emergency Lights Market Segment Analysis
- By Power Type: Self-Contained
The Self-Contained segment, where the battery is integral to the lighting fixture, drives demand in smaller commercial spaces, retrofits, and decentralized installations due to its simplified wiring requirements and ease of installation. Demand in this segment is strongly tied to the refurbishment cycle of existing buildings and the construction of smaller commercial or multi-family residential units, which often lack the space or need for a complex central battery room. The recent shift to Li-ion chemistry in self-contained units acts as a potent demand driver: the lighter weight and extended life of Li-ion batteries significantly reduce replacement frequency and maintenance labor, making these units economically superior over the long term compared to legacy NiCd or Lead-Acid models. This value proposition compels facility managers to specify Li-ion self-contained units for dispersed power applications, even at a higher initial cost.
- By End-User: Industrial
The Industrial End-User segment, encompassing manufacturing plants, chemical facilities, refineries, and warehouses, has unique and stringent demand characteristics primarily driven by specialized safety regulations for hazardous environments. Unlike commercial buildings, industrial demand focuses heavily on robust, explosion-proof, and high-output emergency luminaires (e.g., those certified for Class I, Division 1 environments) to provide high-risk task area lighting. Demand is also fueled by the constant need to retrofit existing facilities during capacity expansions or modernization programs to meet current OSHA and country-specific industrial safety standards. The necessity for reliable illumination in high-risk zones, where power failure can lead to catastrophic process incidents, translates into a constant, non-negotiable demand for the highest durability and most technically certified emergency lighting products available.
Emergency Lights Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis (North America)
Demand in the US market is rigorously dictated by the mandatory enforcement of NFPA 101 and the IBC across state and municipal jurisdictions. This legal framework drives consistent replacement cycles, particularly in high-rise and densely populated metropolitan areas, which have adopted the most recent and restrictive code editions. A major local demand factor is the shift toward networked, intelligent emergency lighting systems that facilitate automatic compliance testing required by the codes, reducing the manual labor burden on facility managers. Furthermore, the market must navigate the total landed cost increase for products containing components or assembled units subject to US tariffs on Chinese goods, which influences sourcing and final retail price, particularly in the contractor-grade segment.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Brazil’s demand is largely concentrated in major urban centers where new infrastructure development, particularly commercial towers and large public transportation projects, dictates the installation of modern safety systems. A significant factor influencing local demand is the reliance on imported components, often subject to high national import duties, which inflates the final cost of higher-end, certified emergency lighting products. This condition often results in a bifurcated market: premium, internationally compliant systems for high-value corporate or government projects, and locally assembled, lower-cost, and sometimes less sophisticated solutions for the general residential and smaller commercial sector.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
The German market emphasizes energy efficiency and robust technical specifications, driven by stringent EU directives and local building codes that prioritize long-term sustainability and performance. Demand is heavily influenced by the European standard EN 50172, which mandates daily checks and monthly/annual tests for emergency lighting systems. This requirement acts as a powerful catalyst for the adoption of self-testing, networked, and wireless emergency lighting systems that automate compliance reporting, thereby reducing operational overhead. German demand favors established European brands with verifiable quality and local support, translating to a low-volume, high-value procurement environment.
- UAE Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The UAE market experiences demand surges correlated directly with its rapid, large-scale commercial, hospitality, and residential mega-project construction, driven by strategic government investment in tourism and real estate. The primary local factor is the required adherence to international standards (often NFPA-based) and the necessity for systems rated to operate reliably within the region's extremely high ambient temperatures. This climate imperative limits demand to systems utilizing robust components and advanced battery thermal management, favoring Central Battery Powered systems that keep critical components in environmentally controlled rooms, driving premium product specifications.
- India Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
Demand in India is characterized by rapid, large-scale urbanization and increasing awareness of fire and life safety, driven by the enforcement of the National Building Code (NBC). The sheer volume of new construction, particularly in the commercial office, retail, and public transit sectors, creates massive baseline demand. The market is highly price-sensitive, balancing the need for compliance with cost constraints. The demand for LED-based systems is strong, fueled by government initiatives promoting energy efficiency, but is tempered by local competition from unorganized sectors, which often undercuts the price of internationally certified, high-compliance products.
Emergency Lights Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Emergency Lights Market is characterized by the dominance of large, diversified multinational electrical infrastructure and safety companies that leverage existing distribution channels and brand trust established across power, lighting, and building automation sectors. Competition centers on product innovation in smart technology, battery chemistry, and compliance certification.
- Eaton Corporation plc: Eaton holds a strategic position leveraging its comprehensive Power Quality and Industrial Control portfolio. The company’s emergency lighting products, sold under various brands, focus on seamlessly integrating lighting control and life safety systems with uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and centralized battery power solutions. This integrated strategy specifically addresses the high-demand segment of data centers and large industrial facilities, where Eaton's established presence in power management drives emergency lighting procurement as a system-level sale, not merely a component sale. Verifiable product lines include self-contained LED exit signs and central monitoring panels designed for mandatory compliance testing.
- Schneider Electric SE: Schneider Electric competes aggressively by emphasizing its EcoStruxure platform, positioning emergency lighting as a key component of a digitally connected building ecosystem. The company focuses on intelligent, networked emergency lighting that enables real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and remote reporting capabilities required for complex commercial building compliance. Schneider Electric's strength lies in its ability to package emergency lights with broader building automation and power distribution solutions, particularly appealing to large institutional and commercial developers seeking centralized management for high operational efficiency. Their product innovation highlights self-testing features that reduce the time and cost associated with manual regulatory checks.
Emergency Lights Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 9.366 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 13.222 billion |
| Growth Rate | 7.14% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Power Type, Mode of Operation, Battery Type, End-User |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Emergency Lights Market Segmentation:
- EMERGENCY LIGHTS MARKET BY POWER TYPE
- Self-Contained
- Central Battery Powered
- EMERGENCY LIGHTS MARKET BY MODE OF OPERATION
- Maintained
- Non-Maintained
- EMERGENCY LIGHTS MARKET BY BATTERY TYPE
- Lithium Ion Phosphate
- Nickel Cadmium
- Nickel-Metal Hydride
- Lead Acid
- EMERGENCY LIGHTS MARKET BY END-USER
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- EMERGENCY LIGHTS MARKET BY GEOGRAPHY
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America