Report Overview
Germany Responsible AI Market Highlights
Germany Responsible AI Market Size:
The Germany Responsible AI Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 26.20%, reaching USD 81.826 million in 2030 from USD 25.562 million in 2025.
The German market for Responsible AI is an emerging sector driven by a confluence of strong governmental policy, a deeply ingrained cultural emphasis on data privacy and ethical standards, and the impending regulatory requirements of the European Union. Responsible AI, an intangible asset, encompasses the tools, services, and governance frameworks that ensure AI systems are developed and used in a lawful, ethical, and trustworthy manner. This includes addressing issues of fairness, transparency, accountability, and security. Germany, with its history of strong data protection laws and a robust industrial base, is at the forefront of this market's development. The shift is not merely technological but systemic, as businesses seek to integrate responsible practices into their AI lifecycles to mitigate risk and build public trust.
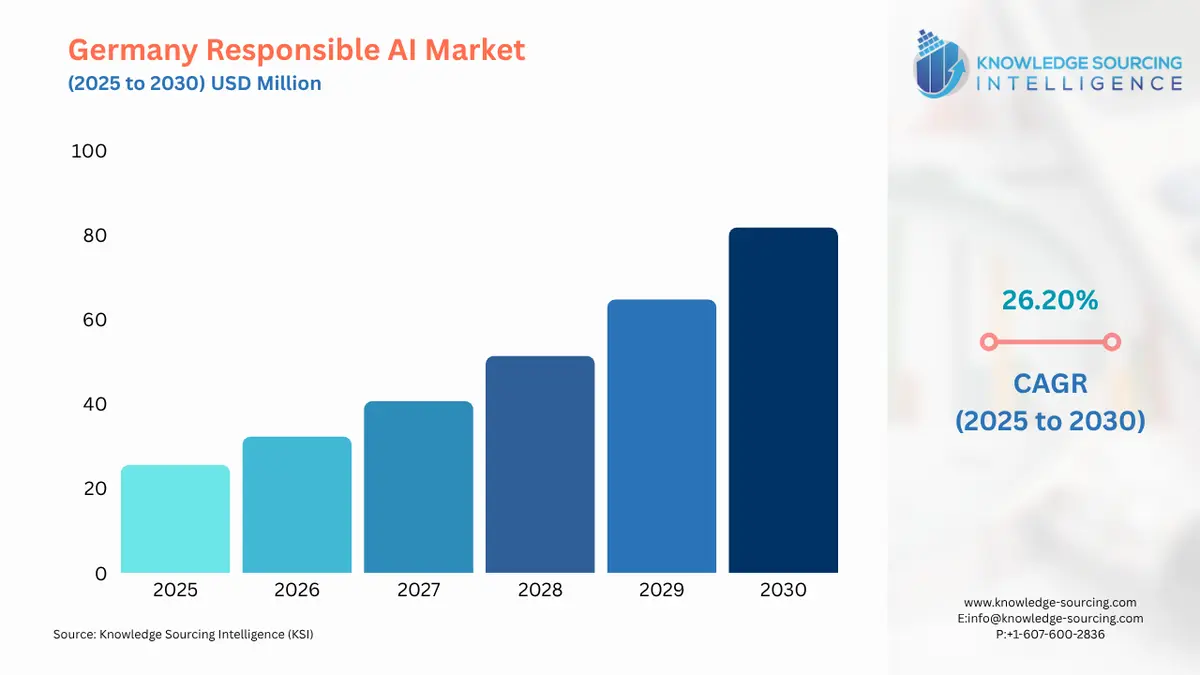
Germany Responsible AI Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The Responsible AI market in Germany is propelled by the immediate regulatory imperative of the EU AI Act. This landmark legislation, with its risk-based framework, directly creates a market for software and services that enable compliance. Companies developing or deploying "high-risk" AI systems—such as those used in critical infrastructure or credit scoring—are now required to implement robust risk management systems, maintain quality management systems, and ensure their models are transparent and auditable. This legal mandate forces demand for Responsible AI solutions as a non-negotiable business expense, moving it beyond a purely ethical consideration. The EU AI Act is a catalyst, transforming what was once a voluntary best practice into a legal obligation.
In parallel, the German federal government's "AI Made in Germany" strategy, launched in 2018, actively fosters a demand for responsible AI. The strategy allocates billions of euros to AI research and development with the explicit goal of creating AI that is not only technologically advanced but also secure, ethical, and aligned with European values. This public funding, alongside initiatives from research institutions like the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, directly stimulates the development of responsible AI tools and talent. It creates an ecosystem where academic innovation in areas like algorithmic transparency and bias detection is directly supported and encouraged, leading to the commercialization of responsible AI products. The government's strategic focus on responsible development acts as a foundational demand signal for the market.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the German Responsible AI market is the complexity and fragmentation of the regulatory landscape. While the EU AI Act provides an overarching framework, its implementation at a national level, as seen in Germany's draft of the AI Market Surveillance and Innovation Promotion Act, requires navigation of multiple existing authorities and a new, coordinating body like the Federal Network Agency (BNetzA). This multi-layered regulatory environment creates uncertainty for businesses, which can slow adoption. The need to comply with multiple, sometimes overlapping, regulations—from the GDPR to the AI Act—serves as a headwind.
This complexity, however, presents a significant opportunity. The challenge of compliance directly fuels demand for specialized software tools and services. Companies require solutions that can automate compliance checks, provide audit trails for AI decisions, and offer governance platforms to manage the entire AI lifecycle. This creates a market for "AI Governance" platforms that simplify the regulatory burden. Furthermore, the imperative for trust and transparency presents an opportunity for companies to differentiate themselves. In a market where responsible AI is a legal and ethical necessity, companies that can verifiably demonstrate their commitment to fairness and accountability can gain a competitive advantage and build deeper trust with customers and partners.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for the German Responsible AI market is not a traditional physical network but a knowledge-based ecosystem. Its "raw materials" are highly specialized human capital, including AI ethicists, data scientists, and compliance experts, as well as high-quality, auditable datasets. The key "production hubs" are Germany's leading research institutions, such as the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, and technology centers in cities like Berlin and Munich. These hubs are the primary source of talent and intellectual property. The supply chain's dependencies are on the availability of a skilled workforce and the continuous generation of research on fairness, transparency, and accountability. Logistical complexities revolve around the seamless transfer of knowledge from research to commercial application and the ability of companies to access and manage large, sensitive datasets in a compliant manner.
Germany Responsible AI Market Government Regulations:
The German Responsible AI market is defined by a robust regulatory framework that mandates responsible practices. The following table highlights the key regulations and their impact on demand.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | EU AI Act | The EU AI Act, with its risk-based framework, is the most powerful driver of demand for Responsible AI. Classifying AI systems as "high-risk" and imposing strict requirements on them forces companies to invest in software and services for compliance, risk management, and documentation. This regulation transforms responsible AI from a voluntary measure into a legal obligation, thereby creating a market for compliance-as-a-service solutions. |
| Federal Government | The German AI Strategy | The German AI Strategy is a strategic framework that has allocated billions of euros to fund AI research and development with an explicit focus on ethical, secure, and human-centric AI. This government policy directly stimulates the creation of a supply of responsible AI technologies by funding research and fostering a collaborative ecosystem. This, in turn, fuels demand from industries that receive public funding or seek to align with national strategic priorities. |
| Federal Government | Data Ethics Commission | The Data Ethics Commission, established by the German government, provides guidance on ethical data and AI practices. While non-binding, its recommendations serve as a blueprint for companies and public sector bodies, creating demand for solutions that help them adhere to these ethical principles. This drives the market for services such as ethical auditing, bias detection, and fairness assessments, which are not just about legal compliance but also about building public trust. |
Germany Responsible AI Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component: Services
The services segment is a core driver of the German Responsible AI market's expansion. This growth is fueled by the need for specialized expertise that companies cannot maintain in-house. These services include ethical AI audits, bias assessments, and the development of custom AI governance frameworks. Organizations in sectors like BFSI and healthcare, where AI decisions have a significant social impact, are compelled to seek external validation and expertise. A company using an AI model for credit scoring, for example, must demonstrate that the model is fair and non-discriminatory. This requires a third-party audit to verify that the model's decisions are not biased against protected groups. This need for assurance drives the market for professional services. Furthermore, the continuous evolution of regulations and ethical best practices means that companies need ongoing support to remain compliant and to manage the long-term lifecycle of their AI systems responsibly, creating a sustainable demand for consulting and managed services.
- By End-User: Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a key end-user for Responsible AI in Germany, driven by the development of autonomous driving systems. These systems are classified as "high-risk" under the EU AI Act, creating a clear and direct need for responsible AI software and services. The core driver is safety and accountability. Companies must ensure that their AI systems can make transparent and auditable decisions in complex, real-world scenarios. This necessitates a robust framework for testing, validating, and monitoring AI models for safety, reliability, and ethical decision-making. For instance, an autonomous vehicle's AI must demonstrate how it makes a split-second decision in a collision avoidance scenario. This requirement extends to the entire supply chain, as manufacturers require their component suppliers to provide verifiable evidence of responsible AI development. The high-stakes nature of the applications makes responsible AI an essential part of the product development lifecycle, not an afterthought.
Germany Responsible AI Market Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape in the German Responsible AI market is characterized by a blend of specialized German startups, established international software firms, and a strong presence of research-to-market players like the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Competition is driven by the ability to offer comprehensive solutions that address the dual demands of regulatory compliance and ethical assurance.
- Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft: The Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft is a central, non-competitive force in the market. As Europe's largest application-oriented research organization, it conducts extensive research into the technical and social dimensions of responsible AI. Its strategic position is to serve as a bridge between foundational academic research and industrial application. By developing tools for explainable AI (XAI), bias detection, and robustness testing, Fraunhofer provides the foundational technology that can be licensed or spun off into commercial ventures. For example, its institutes have developed and launched the "Responsible AI Research Lab" and showcased a multilingual AI model that can be integrated into business processes in compliance with data protection regulations. Fraunhofer's role is to de-risk the initial R&D for the private sector and provide the technical and ethical expertise that underpins the market.
- Volkswagen AG: Volkswagen AG is a major demand-side player in the Responsible AI market, but also a developer of internal solutions. The company's strategic positioning is to integrate AI into every part of its value chain, from vehicle development to production. Recognizing the high-risk nature of automotive AI, Volkswagen is investing up to one billion euros in AI by 2030, with an explicit focus on responsible development. Its "WE & AI" initiative, a major internal training program, is a strategic move to embed responsible AI principles directly into its corporate culture. This internal focus demonstrates the imperative for large companies to take ownership of responsible AI development, creating a strong internal demand for related services and platforms, while also influencing the standards for their external suppliers.
Germany Responsible AI Market Developments
- June 2025: Mila launched its new AI for Climate Studio, a dedicated initiative to leverage AI for a sustainable future. This development represents a significant institutional focus on commercializing AI for environmental purposes, providing a dedicated platform for collaboration between researchers and industry to accelerate the development of climate tech solutions.
Germany Responsible AI Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 25.562 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 81.826 million |
| Growth Rate | 26.20% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Germany Responsible AI Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Software Tools & Platforms
- Services
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- On-Premises
- Cloud
- BY END-USER
- Healthcare
- BFSI
- Government and Public Sector
- Automotive Industry
- IT and Telecommunication
- Others