Report Overview
Global Influenza Vaccine Market Highlights
Influenza Vaccine Market Size:
The Global Influenza Vaccine Marketis expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.3%, reaching a market size of USD 11.7 billion in 2031 from USD 8.3 billion in 2026.
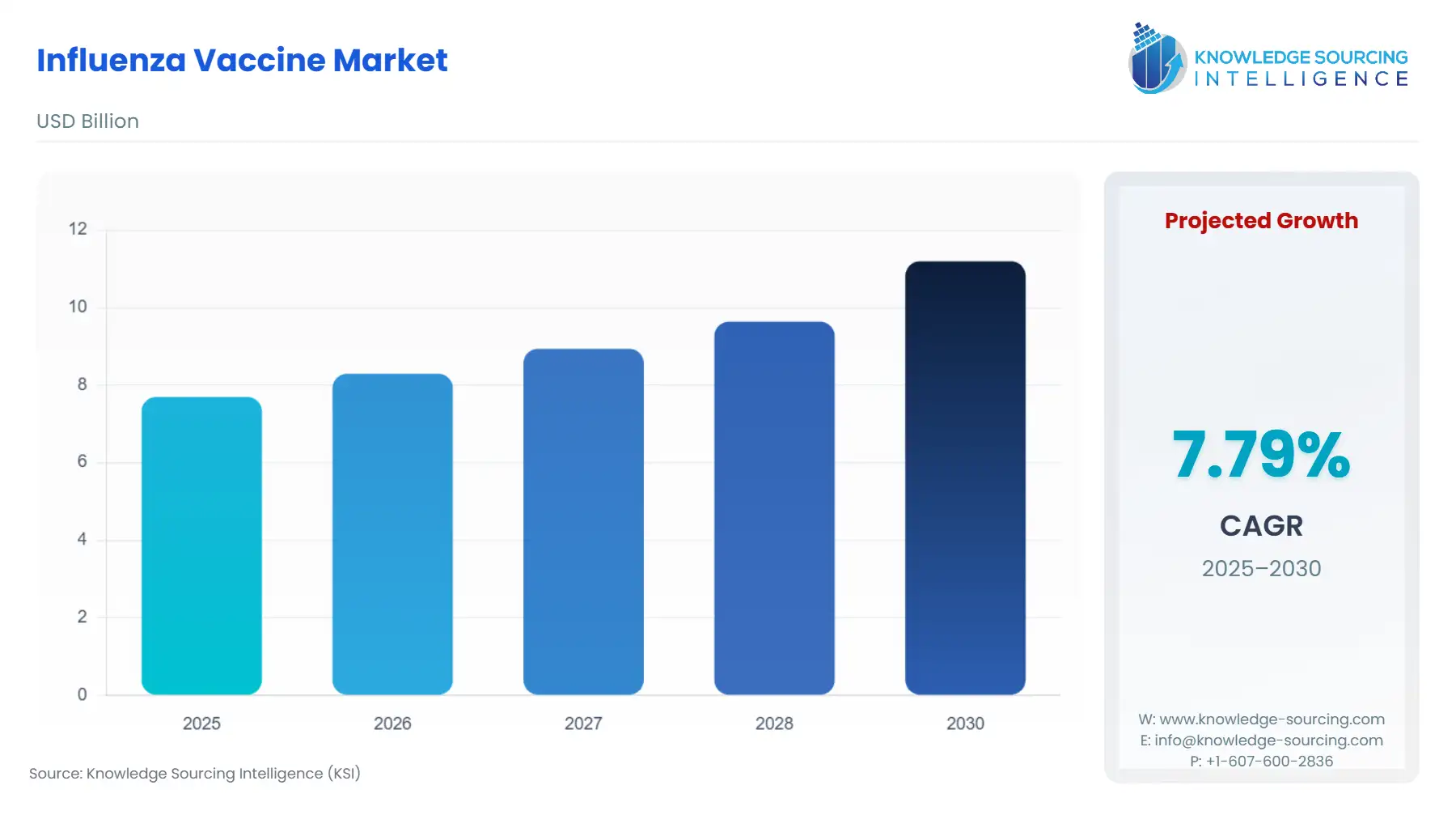
Influenza Vaccine Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
Three verified forces drive demand. First, annual WHO strain recommendations and national implementations (FDA/EMA) create recurring, time-bound procurement cycles that guarantee baseline seasonal volume for manufacturers. Second, public immunization programs (CDC, national health ministries) fund large, centralized purchases and prioritize high-risk groups, expanding predictable institutional demand. Third, technology diversification — notably mRNA and combination influenza/COVID candidates that achieved positive Phase 3 readouts or regulatory interactions — raises demand for new fill/finish capacity, adjuvants and clinical supplies as developers pursue label expansion and public-sector contracts. Each driver directly increases ordered doses, accelerates contract timelines, or shifts procurement toward vendors with relevant platform capabilities.
Challenges and Opportunities
The tariff environment in the United States exerts a favorable influence on the global influenza vaccine market, as human vaccines imported under HTS classifications such as 3002.20 or 3002.41 are subject to a zero-duty regime. This duty-free status significantly reduces import-related cost burdens for overseas manufacturers and enables multinational vaccine producers to supply the U.S. market without facing direct tariff-driven price escalation. As a result, competitive positioning in the U.S. is primarily determined by manufacturing efficiency, regulatory clearance, and distribution capability rather than customs-related cost disadvantages. While ancillary trade measures, classification requirements, and regulatory documentation remain critical, the absence of import duties continues to support cross-border supply, facilitate diversified sourcing, and enhance the strategic attractiveness of the United States as a high-value destination for seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccine exports.
Key headwinds: strain-match uncertainty and seasonality compress revenue windows and raise inventory risk for manufacturers and purchasers; supply concentration among a few producers creates geopolitical and logistic vulnerabilities in procurement. Opportunities: regulators’ streamlined strain-change pathways and Fast Track designations enable faster market entry for combination and mRNA vaccines, creating new demand segments (e.g., adult boosters, combination formulations). Public-sector tenders and pandemic preparedness funding provide large, low-margin volume opportunities for manufacturers that can demonstrate rapid strain updates and robust supply commitments. These forces change demand profiles by privileging flexible, high-capacity suppliers and by widening programmatic indications that expand eligible populations.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
(Section included because vaccines are a physical product.) Vaccine input demand concentrates on antigen production capacity (egg-based, cell-culture, recombinant or mRNA lipid nanoparticles), adjuvants (e.g., MF59/Matrix-M), sterile vials/syringes and cold-chain logistics. Official product filings and press releases show higher procurement of adjuvants and fill/finish slots when new high-dose or adjuvanted formulations are introduced, putting upward pressure on sterile consumables and adjuvant supply during the pre-season window. Pricing negotiations in public tenders remain opaque but national procurement documents and tender circulars (South Africa, Brazil) indicate cost sensitivity; governments favor suppliers offering dose security and domestic production partnerships over premium pricing, constraining manufacturers’ ability to pass raw-material cost inflation directly to public buyers.
Supply Chain Analysis
Production is geographically clustered: large-scale antigen manufacturing and fill/finish hubs are in North America, Europe, Australia (Seqirus/CSL) and selected Asian sites. Strain change and lot release deadlines create fixed windows for antigen manufacture, which concentrate global transport and cold-chain demand in late summer/early autumn for northern hemisphere supply. Logistical bottlenecks arise at fill/finish capacity and cold-chain distribution; official lot-release and seasonal composition notices (FDA, EMA) create synchronized production peaks that amplify these constraints. Dependence on specialized inputs (adjuvants, single-use bioreactors, vials) creates single-point supply-risk during public tender cycles, increasing the value of local manufacturing partnerships in procurement decisions.
Government Regulations
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
United States | FDA — seasonal influenza vaccine composition and lot-release guidance | FDA annual composition and lot-release timing sets production deadlines and creates predictable demand cycles; CDC procurement and ACIP recommendations determine public-sector volumes. |
European Union | EMA / CHMP — vaccine strain recommendations and marketing authorization procedures | EMA strain endorsements and centralised MA routes speed or restrict market entry across EU; ECDC national recommendation variance influences country-level tender sizes. |
World (global guidance) | WHO Global Influenza Programme — biannual vaccine composition recommendations | WHO recommendations synchronize hemisphere timing and are adopted by many national programs, anchoring global demand windows and strain selection. |
Influenza Vaccine Market Segment Analysis:
Quadrivalent (By Vaccine Technology) — Demand dynamics
Historically, quadrivalent formulations expanded marketable dose applications by covering both B-lineages; however, policy shifts toward trivalent use in certain jurisdictions (e.g., U.S. move to trivalent for 2024–2025 per FDA/CDC notices) changed demand composition and procurement specifications. Where quadrivalent remains recommended (many EU countries and high-coverage pediatric programs), public buyers require broader strain coverage, maintaining stable demand for quadrivalent antigen production and associated manufacturing capacity (cell-based/recombinant platforms). Manufacturers offering both trivalent and quadrivalent portfolios gain flexibility in tendering across jurisdictions; nonetheless, strain-selection timing and lot-release deadlines impose manufacturing sequencing that can limit rapid switch between formats within a season. Quadrivalent demand particularly strengthens pediatric and school-based immunization procurement, which are typically nationally funded and scheduled, thereby creating predictable annual volume. Suppliers that can guarantee multi-format production and rapid regulatory strain-updates command preference in tenders, because buyers prioritize dose availability and logistic simplicity over marginal unit price differences.
Elderly (By End-User) — Demand dynamics
Elderly populations drive high-value demand because of higher hospitalization risk and government prioritization. National immunization recommendations and focused reimbursement for ?65 (CDC, MHLW, many EU member states) create stable, often fully funded procurement streams for high-dose or adjuvanted vaccines targeted at older adults. Health agencies increasingly prefer formulations with evidence of superior protection in older cohorts; company press releases and regulatory filings for adjuvanted or high-dose products (e.g., company product labels and EMA assessment reports) influence tenders toward premium formulations despite cost sensitivity. This creates a bifurcated demand profile: a baseline demand for standard dose vaccines and incremental premium demand for targeted elderly formulations. Procurement authorities evaluate cost-effectiveness and hospital-bed avoidance metrics, so vaccine suppliers that publish robust effectiveness and hospitalization-reduction evidence position themselves to win higher-value contracts. For manufacturers, meeting demand in this segment requires capacity for adjuvant supply, targeted clinical data and reliable supply assurances timed to national campaign dates.
Influenza Vaccine Market Geographical Analysis:
US Market Analysis
US demand is anchored by CDC ACIP recommendations and FDA lot-release cycles; CDC’s 2025 guidance and FDA composition notices determine annual public tender volumes and private market timing, concentrating procurement in Q2–Q3. Public payment programs and employer-sponsored clinics create both institutional and retail channels.
Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil’s PNI conducts national vaccination campaigns and procures domestically produced vaccines (Butantan) and imports; government campaign schedules establish substantial annual public demand and favor local manufacturers with stable supply commitments.
Germany Market Analysis
Germany’s STIKO and RKI guidance drive federal and state procurement; strong pediatric and elderly recommendations sustain demand for both standard and high dose/adjuvanted vaccines, with centralized reimbursement affecting manufacturer selection.
South Africa Market Analysis
South Africa’s NDOH/NICD guidance shows constrained public procurement (limited adult coverage) but early seasonal activity prompts targeted purchases for high-risk groups; tenders and bid circulars shape supplier selection and favor cost-competitive offers.
Japan Market Analysis
MHLW policy targets older adults and high-risk groups with routine seasonal vaccination; centralized recommendations and municipal implementation create predictable demand, with domestic manufacturers and importers active in tenders.
Influenza Vaccine Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
Major global players (from provided list) include Seqirus (CSL), GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Sanofi Pasteur, Moderna, Pfizer, Novavax and others. Official company releases and regulatory filings indicate strategic positioning:
Sanofi Pasteur — focuses on high-dose/adjuvanted vaccines and combination candidates; FDA Fast Track designations for its combination candidates underscore strategic pursuit of adult booster markets (Sanofi press release Dec 11, 2024).
Moderna, Inc. — advancing mRNA seasonal and combination influenza/COVID candidates with positive Phase 3 data and BLA interactions in 2024–2025, targeting rapid strain matching and differentiated clinical profiles (Moderna press releases Jun 2024; May 2025).
GSK — maintains large seasonal supply and adjuvant portfolios; official shipping notices for 2024–25/2025–26 seasons show capacity to meet large public tenders and on-time lot release requirements (GSK press releases July 2024/2025).
These companies compete on demonstrated clinical effectiveness for target populations, production flexibility for strain changes, adjuvant technology, and the ability to secure public procurement contracts.
Influenza Vaccine Market Developments:
June 2025 — Moderna announced positive Phase 3 results for a seasonal influenza and COVID-19 combination candidate (June 2025 press release).
December 2024 — Sanofi received FDA Fast Track designation for two combination influenza/COVID candidates for adults ?50 (Dec 2024 press release).
July 2024 — GSK began shipping trivalent influenza vaccine doses for the 2024–25 US season following FDA lot-release approval (July 2024 press release).
Influenza Vaccine Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 8.3 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 11.7 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 7.3% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vaccine Technology, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Influenza Vaccine Market Segmentation:
By Vaccine Technology
Trivalent
Quadrivalent
By End-User
Children
Adolescents
Adults
Elderly
By Geography
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
UK
Germany
Italy
Spain
Others
Middle East and Africa
Israel
Saudi Arabia
Others
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
India
Australia
South Korea
Taiwan
Thailand
Indonesia
Others