Report Overview
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Highlights
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Size:
The Indonesia indoor farming market is estimated to attain a market size of US$82.561 million by 2030, growing at a 5.66% CAGR from a valuation of US$62.682 million in 2025, during the forecast period of 2025 to 2030.
The Indonesian indoor farming market has witnessed positive growth due to a considerable surge in investments in recent years, mostly because of shrinking arable land, rising consumer demand for regional, sustainable products, and migration to megacities. One way to address the challenges presented by Indonesian indoor farming is the use of hydroponic and greenhouse technologies.
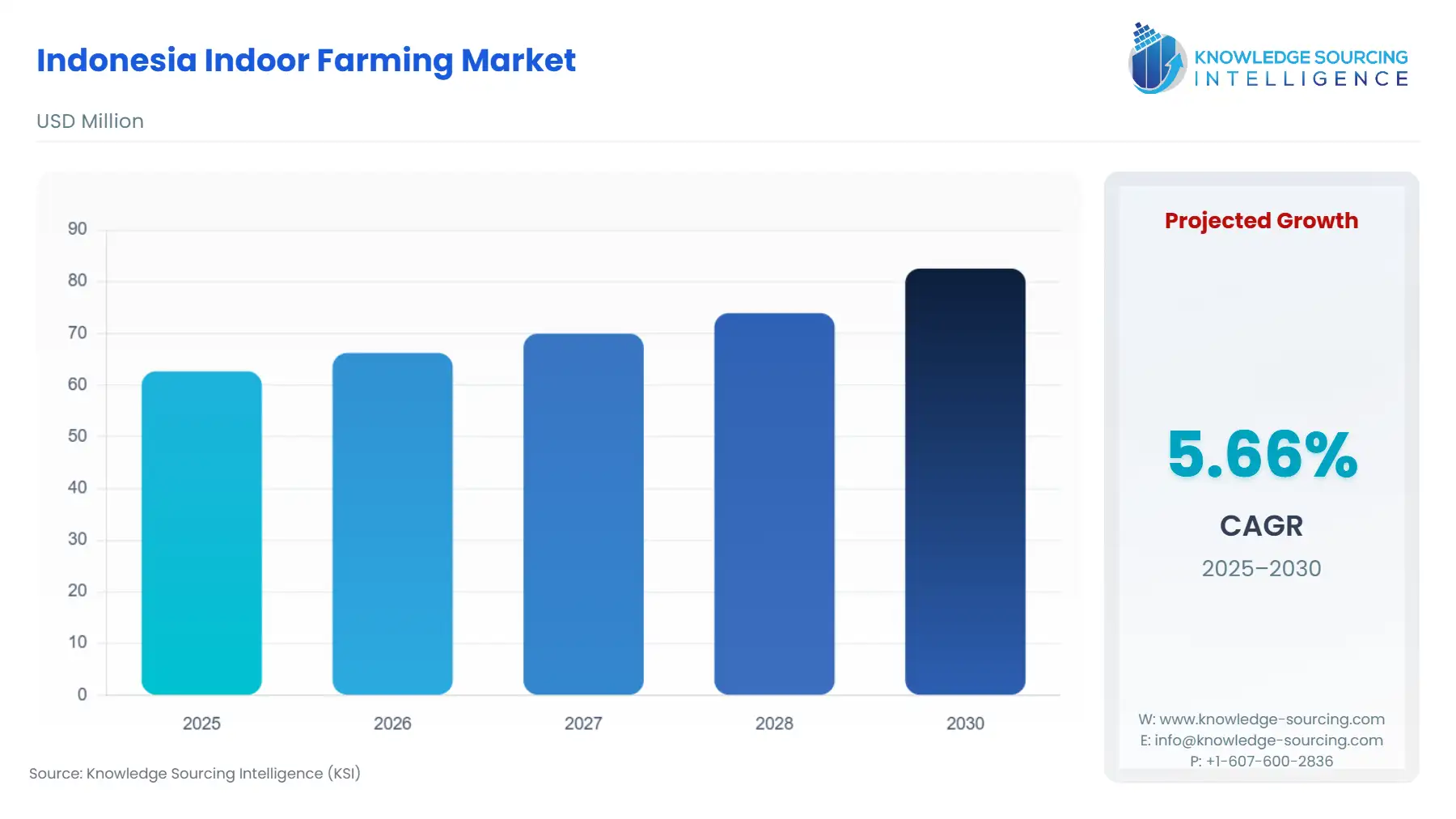
The Indonesian indoor farming market is estimated to grow at a moderate rate, fueled by the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural products amid shrinking arable land, which is anticipated to have a favorable market impact till the forecast period. In addition, the rising government initiative towards the promotion of indoor farming will encourage more companies to focus on meeting the evolving end users' requirements, which has further paved the way for future market expansion.
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Overview
Report Metric
Details
Study Period
2021 to 2031
Historical Data
2021 to 2024
Base Year
2025
Forecast Period
2026 – 2031
& Scope:
The Indonesian indoor farming market is segmented by:
- Growing System: Indonesia's indoor farming market is segmented by growing systems into hydroponics, aeroponics, aquaponics, soil-based, and hybrid. Hydroponics involves plants growing in a nutrient-rich water solution without soil. Aeroponics delivers nutrients directly to plants through the mist. Aquaponics utilizes fish waste to provide nutrients for plants, while plants help filter water for the fish. Soil-based methods rely on soil for crop cultivation. Hybrid systems combine elements from two or more growing systems.
- Facility Type: By facility type, Indonesia’s indoor farming has been segmented into glass or poly greenhouses, indoor vertical farms, container farms, and indoor DWC systems. Within the glass or poly greenhouse, with appropriate temperature and humidity, the productivity and quality of the crops can be increased manifold with the least use of chemicals. Indoor DWC (Deep Water Culture) is done involving the roots suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution, This system is space-sufficient and compact.
- Crop Type: By crop type, Indonesia’s indoor farming has been segmented into fruits and vegetables, herbs and microgreens, flowers and ornamentals, and others. The fruits and vegetables segment will have a significant share owing to the growing demand for natural and healthy diets. With the increased demand for naturopathy, herbs, and microgreens will also show significant growth during the forecast period.
Moreover, due to constant population growth, the demand for vegetables, especially potatoes, which are mainly consumed in Indonesia, has witnessed considerable growth, which is impacting its overall production scale. As per Statistics Indonesia, in 2023, the country’s potato production reached 1.503 million tons, which represented a 10.43% increase over the preceding year’s production scale. Likewise, the same source also specified that the consumption of other vegetables, such as tomatoes, experienced a 1.34% growth in the same year.
Top Trends Shaping the Indonesia indoor farming Market
1. Adoption of Smart Farming Technologies
- Indonesia's indoor agriculture industry is rapidly adopting smart technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and automated climate control systems. These technologies enable farmers to track the health of plants, manage irrigation, light, and nutrient supply precisely. Indoor farms can maximize crop yields, cut waste, and minimize operation expenses by utilizing data analysis, thus making the business sustainable and scalable.
2. Growth of Vertical Farming in Urban Areas
- With Indonesia's increasing urbanization, particularly in urban centers such as Jakarta and Surabaya, the absence of available arable land is forcing farmers to farm vertically. Vertical farming, or growing crops in stacked layers or vertically sloping surfaces, allows for the highest output with the least space. Controlled environment and artificial light (e.g., LED grow lights) can produce year-round, making it perfect for high-density locations where demand for fresh produce is increasing.
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Growth Drivers vs. Challenges
Drivers:
- Decreasing Size of Arable Land: The decreasing arable land has been a significant challenge for Indonesia, leading to many innovations in line with agricultural developments. The percentage of land area was 14% in 2020 and came to 13.9% in 2021. Moreover, the value added to the GDP by agriculture, forestry, and fishing in Indonesia increasingly depends on this land, as it was 12.5% in 2023, which was 13.3% in 2021.
Additionally, various initiatives have been made to increase the productivity and supply in agriculture. For example, in March 2023, a high-tech indoor farm designed in the manner of eco-architecture is being built in the Innovative City of Nuanu in Bali, Indonesia, because of a partnership between the Nuanu community and the provider of indoor farming technology, iFarm.
Additionally, a fully integrated seed-to-meal dine-in platform with indoor growth chambers and farming as a service for anybody who wishes to grow food in their community was built by GREENS, a hyperlocal meta-framing firm with headquarters in Jakarta, Indonesia, in August 2022. It will benefit 240 non-farmers with its farming solutions.
- Rising Demand for Fresh, Pesticide-Free Produce: Indonesian consumers are becoming health-conscious, particularly in the middle- and upper-income segments. There is a rising demand for produce that is organic, free of pesticides, and traceable. Indoor farming, being free from uncontrolled environmental conditions, can fulfill these requirements more consistently than outdoor farming. This change in consumer demand is driving the development of high-end indoor farm products that are sold in urban supermarkets, farmers' markets, and internet platforms at premium prices.
- Government Support and Food Security Focus: The Indonesian government started to set its national agenda at the forefront of food security and sustainable agriculture. Supportive efforts for urban agriculture, tax allowances for agritech companies, and research and development subsidies are contributing to an increasingly friendly landscape for indoor farming startups. As an integral part of larger measures in lessening reliance on imports as well as boosting national food resilience, indoor farming is rapidly acknowledged as a foundation pillar for country food systems moving forward.
Challenges:
- High Initial Cost: Even with its long-term promise, the upfront cost of setting up an indoor farm can be staggering. Constructing controlled-environment systems complete with irrigation, lighting, ventilation, and monitoring technology costs a lot of money. This makes indoor farming out of reach for most smallholder farmers, who remain the backbone of Indonesia's agriculture. Unless financing becomes more accessible, the growth of the sector will likely be restricted to urban startups and well-capitalized ventures.
- High Energy Consumption: Running indoor farms requires high energy consumption, especially for artificial lighting (such as LEDs) and cooling systems, especially in Indonesia's hot and humid climate. Such high electricity consumption not only raises operational costs but also sustainability issues unless renewable energy sources are utilized. Without energy-efficient measures or green subsidies, long-term profitability and environmental sustainability may be threatened.
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
| Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Size in 2025 | US$62.682 million |
| Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Size in 2030 | US$82.561 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 5.66% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| List of Major Companies in the Indonesia Indoor Farming Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Indonesia Indoor Farming Market Segmentation:
By Growing System
- Hydroponics
- Aeroponics
- Aquaponics
- Soil-based
- Hybrid
By Facility Type
- Glass or Poly Greenhouse
- Indoor Vertical Farm
- Container Farm
- Indoor DWC System
By Crop Type
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Herbs and Microgreens
- Flowers and Ornamentals
- Others