The Future of Gear Oils: Trends and Innovations

Gear oils are required for the smooth functioning and maintenance of this equipment. They are designed to satisfy certain performance criteria, such as temperature resistance, load-bearing capability, and wear protection. The gear oil industry is extremely competitive, with several global and regional firms participating.
Gear oil, often known as gear lubricant, is a lubricating oil that is particularly designed for use in gearboxes, differentials, and other gear systems. They are intended to decrease friction, wear, and heat generation inside gear assemblies, resulting in smooth operation and increasing the life of gears and bearings.
Companies in this industry prioritize product innovation, distribution channel growth, and strategic collaborations to increase market share and remain competitive. The gear oils market is likely to expand in the next years, driven by rising demand for high-quality lubricants in a variety of sectors, technical improvements, and a shift towards energy-efficient and ecologically friendly lubricants.
Gear oils come in a variety of viscosity grades, which manufacturers normally specify based on the gear system's working circumstances and needs. The oil's viscosity impacts its flow resistance as well as its capacity to maintain a lubricating coating between moving surfaces under varying loads and temperatures.
According to the International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers, global sales of all types of automobiles rose from 78.79 million in 2020 to 1.63 million in 2022. Thus, the substantial increase in car sales contributes to the increasing demand for gear oils.
Figure 1: Global Vehicle Sales in Million, 2020-2022
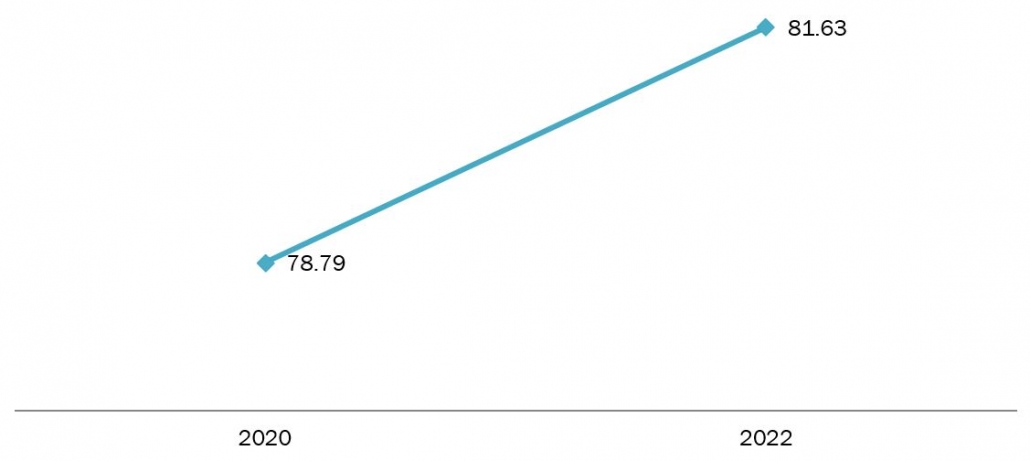 Source: International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers
Wind turbines use gear oils to lubricate their primary gearboxes and other gear motor components. This is due to the high temperatures, heavy loads, oxidation and corrosion, and bearing wear that occur throughout the power production process.
The usage of performance additives in synthetic oil formulation to satisfy particular criteria has resulted in a rise in demand for synthetic gear oils in wind turbines due to their better properties over mineral-based alternatives.
Globally, the quantity of electricity generated by wind energy is rapidly increasing, and the installed capacity of wind turbines grows year after year. The drop in offshore industry pricing has helped to boost the wind power production market by stimulating investments in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. This is expected to drive up demand for gear oils during the projected period.
According to the Global Wind Energy Council, 78 GW of wind generation capacity is to be added to electricity networks in 2022, which will further increase to 115 GW in 2023. It is expected to reach 125 GW in 2024, 135 GW in 2025, 150 GW in 2026, and 157 GW in 2027.
GWEC estimates 680 GW of additional worldwide wind capacity between 2023 and 2027, with 130 GW offshore. China leads with 300 GW, followed by Europe with almost 100 GW. Offshore wind will play an important role, with over 60 GW installed between 2023 and 2025 and 68 GW in 2026-2027.
Figure 2: Global New Wind Power Capacity Installation in GW, 2022- 2027
Source: International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers
Wind turbines use gear oils to lubricate their primary gearboxes and other gear motor components. This is due to the high temperatures, heavy loads, oxidation and corrosion, and bearing wear that occur throughout the power production process.
The usage of performance additives in synthetic oil formulation to satisfy particular criteria has resulted in a rise in demand for synthetic gear oils in wind turbines due to their better properties over mineral-based alternatives.
Globally, the quantity of electricity generated by wind energy is rapidly increasing, and the installed capacity of wind turbines grows year after year. The drop in offshore industry pricing has helped to boost the wind power production market by stimulating investments in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. This is expected to drive up demand for gear oils during the projected period.
According to the Global Wind Energy Council, 78 GW of wind generation capacity is to be added to electricity networks in 2022, which will further increase to 115 GW in 2023. It is expected to reach 125 GW in 2024, 135 GW in 2025, 150 GW in 2026, and 157 GW in 2027.
GWEC estimates 680 GW of additional worldwide wind capacity between 2023 and 2027, with 130 GW offshore. China leads with 300 GW, followed by Europe with almost 100 GW. Offshore wind will play an important role, with over 60 GW installed between 2023 and 2025 and 68 GW in 2026-2027.
Figure 2: Global New Wind Power Capacity Installation in GW, 2022- 2027
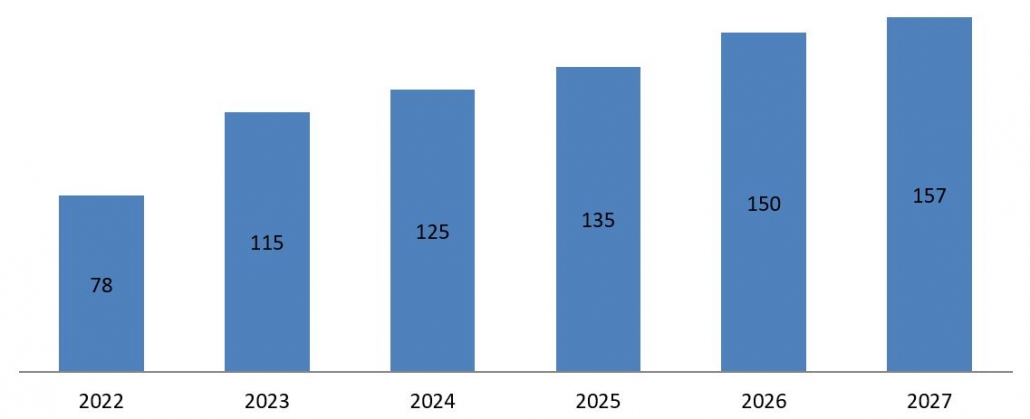 Source: Global Wind Energy Council
Gear systems are becoming more difficult since they have very accurate cut teeth and nicely polished surfaces. Furthermore, because they are smaller, the teeth and bearings are subjected to more stress. These stresses, along with vibration and shock, can cause frequent gear pitting (particularly micro pitting) in surface-hardened gears.
Furthermore, the systems work at high temperatures. For all of these reasons, utilizing a quality lubricant is critical. While current mineral oil lubricants perform well, synthetic gear oils have various advantages. These include increased viscosity-temperature for greater performance and wear prevention at severe temperatures, as well as improved thermal and oxidation resistance, allowing for considerably longer oil life and deployment at high temperatures. It also improves low-temperature performance, resulting in lower churning losses and better wear protection.
As industrial gear oil provides better lubricity and prevents rust and corrosion in gears, it is widely used in construction machinery and equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers.
Industrial gear oil is essential for smooth gear changes in manual transmissions and differentials because it provides load resistance, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, and anti-foam qualities. It is also utilized in hydraulic excavators' travel and swing reduction gears to improve machine performance, making it a critical component of industrial and construction equipment in a fast-developing industry.
The rising trend of energy efficiency in numerous sectors is predicted to generate demand for gear oils that may minimize friction and energy consumption. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that transportation fuel use accounts for approximately 29% of total US greenhouse gas emissions. As a response, the EPA has put in place restrictions like the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) requirements to increase fuel efficiency and minimize vehicle emissions. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The base oil in gear oils might be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of the two. Mineral-based gear lubricants are generated from crude oil and provide enough lubrication at a reduced cost. Synthetic gear oils, on the other hand, are chemically developed to give greater performance, such as a higher viscosity index, increased thermal stability, and enhanced wear prevention, particularly in harsh environments.
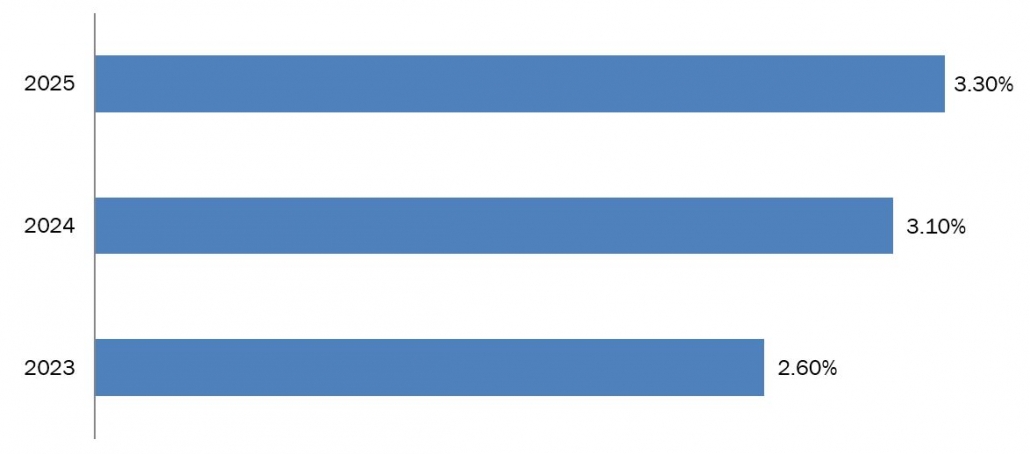
According to the International Energy Agency, the year-on-year change in worldwide electricity demand has directly or indirectly influenced the market for gear oils. In 2023, the electricity demand was 2.60%, which increased to 3.10 in 2024. It is further forecasted that the electricity demand will increase to 3.30% in 2025, according to the research.
Figure 3: Global Year-On-Year Electricity Demand in Percentage, 2023-2025
Source: Global Wind Energy Council
Gear systems are becoming more difficult since they have very accurate cut teeth and nicely polished surfaces. Furthermore, because they are smaller, the teeth and bearings are subjected to more stress. These stresses, along with vibration and shock, can cause frequent gear pitting (particularly micro pitting) in surface-hardened gears.
Furthermore, the systems work at high temperatures. For all of these reasons, utilizing a quality lubricant is critical. While current mineral oil lubricants perform well, synthetic gear oils have various advantages. These include increased viscosity-temperature for greater performance and wear prevention at severe temperatures, as well as improved thermal and oxidation resistance, allowing for considerably longer oil life and deployment at high temperatures. It also improves low-temperature performance, resulting in lower churning losses and better wear protection.
As industrial gear oil provides better lubricity and prevents rust and corrosion in gears, it is widely used in construction machinery and equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers.
Industrial gear oil is essential for smooth gear changes in manual transmissions and differentials because it provides load resistance, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, and anti-foam qualities. It is also utilized in hydraulic excavators' travel and swing reduction gears to improve machine performance, making it a critical component of industrial and construction equipment in a fast-developing industry.
The rising trend of energy efficiency in numerous sectors is predicted to generate demand for gear oils that may minimize friction and energy consumption. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that transportation fuel use accounts for approximately 29% of total US greenhouse gas emissions. As a response, the EPA has put in place restrictions like the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) requirements to increase fuel efficiency and minimize vehicle emissions. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The base oil in gear oils might be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of the two. Mineral-based gear lubricants are generated from crude oil and provide enough lubrication at a reduced cost. Synthetic gear oils, on the other hand, are chemically developed to give greater performance, such as a higher viscosity index, increased thermal stability, and enhanced wear prevention, particularly in harsh environments.
According to the International Energy Agency, the year-on-year change in worldwide electricity demand has directly or indirectly influenced the market for gear oils. In 2023, the electricity demand was 2.60%, which increased to 3.10 in 2024. It is further forecasted that the electricity demand will increase to 3.30% in 2025, according to the research.
Figure 3: Global Year-On-Year Electricity Demand in Percentage, 2023-2025
 Source: International Energy Agency
Environmental regulations should govern the selection and disposal of gear oils to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human health. Some gear oils may contain additives or base oils that are biodegradable or environmentally friendly, making them suitable for applications where environmental stewardship is a priority.
It is a critical component in vehicle gearboxes, differentials, and transfer cases. It lubricates the gears and bearings, providing smooth shifting and protecting them from wear and damage. Differentials transfer power from the engine to the wheels, guaranteeing smooth functioning. In transfer cases, power is transferred between the front and rear axles, depending on the terrain.
These oils contain additives that form protective films on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact between mating parts and reducing wear. Anti-wear additives, such as zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP), are commonly used to provide additional protection under high-pressure conditions, especially in gears subjected to heavy loads and sliding contact.
Gear oils are designed to resist the high pressures and stresses encountered by gear teeth during operation. Extreme pressure (EP) additives, such as sulfur-phosphorus compounds, are used in gear oil formulations to generate chemical coatings that prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce wear, especially in gears working under strong or shock loads.
Viscosity is an important feature of gear oils because it affects their capacity to maintain a lubricating coating between moving surfaces under varying operating circumstances. Gear oils are available in a variety of viscosity grades, which are normally determined by equipment manufacturers depending on load, speed, temperature, and gear type. Choosing the right viscosity grade enables optimal lubrication and prevents excessive friction and wear.
Asia Pacific is experiencing exponential expansion. The region's key emerging nations, notably China, India, and ASEAN, are driving demand for gear oils. Because of continuing development projects and population expansion, power consumption has increased over time.
The gear oil market is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors competing based on product quality, performance, price, and brand reputation. Key players in the market often invest in research and development activities to innovate and differentiate their product offerings.
The need for gear oils is intimately related to industrial operations such as manufacturing, building, mining, and electricity generation. As companies develop and modernize, there is an increased demand for efficient and dependable gear lubrication solutions to maintain smooth operation and reduce equipment downtime.
In conclusion, the gear oil market is predicted to rise gradually, propelled by industrial expansion, automobile production, infrastructural development, technical improvements, and regulatory compliance. However, market dynamics, economic conditions, and geopolitical considerations might all have an impact on the gear oil industry's growth trajectory in the next years.
Table 1: Key Developments
Source: International Energy Agency
Environmental regulations should govern the selection and disposal of gear oils to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human health. Some gear oils may contain additives or base oils that are biodegradable or environmentally friendly, making them suitable for applications where environmental stewardship is a priority.
It is a critical component in vehicle gearboxes, differentials, and transfer cases. It lubricates the gears and bearings, providing smooth shifting and protecting them from wear and damage. Differentials transfer power from the engine to the wheels, guaranteeing smooth functioning. In transfer cases, power is transferred between the front and rear axles, depending on the terrain.
These oils contain additives that form protective films on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact between mating parts and reducing wear. Anti-wear additives, such as zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP), are commonly used to provide additional protection under high-pressure conditions, especially in gears subjected to heavy loads and sliding contact.
Gear oils are designed to resist the high pressures and stresses encountered by gear teeth during operation. Extreme pressure (EP) additives, such as sulfur-phosphorus compounds, are used in gear oil formulations to generate chemical coatings that prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce wear, especially in gears working under strong or shock loads.
Viscosity is an important feature of gear oils because it affects their capacity to maintain a lubricating coating between moving surfaces under varying operating circumstances. Gear oils are available in a variety of viscosity grades, which are normally determined by equipment manufacturers depending on load, speed, temperature, and gear type. Choosing the right viscosity grade enables optimal lubrication and prevents excessive friction and wear.
Asia Pacific is experiencing exponential expansion. The region's key emerging nations, notably China, India, and ASEAN, are driving demand for gear oils. Because of continuing development projects and population expansion, power consumption has increased over time.
The gear oil market is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors competing based on product quality, performance, price, and brand reputation. Key players in the market often invest in research and development activities to innovate and differentiate their product offerings.
The need for gear oils is intimately related to industrial operations such as manufacturing, building, mining, and electricity generation. As companies develop and modernize, there is an increased demand for efficient and dependable gear lubrication solutions to maintain smooth operation and reduce equipment downtime.
In conclusion, the gear oil market is predicted to rise gradually, propelled by industrial expansion, automobile production, infrastructural development, technical improvements, and regulatory compliance. However, market dynamics, economic conditions, and geopolitical considerations might all have an impact on the gear oil industry's growth trajectory in the next years.
Table 1: Key Developments
Source: Knowledge Sourcing Intelligence Analysis
 Source: International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers
Wind turbines use gear oils to lubricate their primary gearboxes and other gear motor components. This is due to the high temperatures, heavy loads, oxidation and corrosion, and bearing wear that occur throughout the power production process.
The usage of performance additives in synthetic oil formulation to satisfy particular criteria has resulted in a rise in demand for synthetic gear oils in wind turbines due to their better properties over mineral-based alternatives.
Globally, the quantity of electricity generated by wind energy is rapidly increasing, and the installed capacity of wind turbines grows year after year. The drop in offshore industry pricing has helped to boost the wind power production market by stimulating investments in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. This is expected to drive up demand for gear oils during the projected period.
According to the Global Wind Energy Council, 78 GW of wind generation capacity is to be added to electricity networks in 2022, which will further increase to 115 GW in 2023. It is expected to reach 125 GW in 2024, 135 GW in 2025, 150 GW in 2026, and 157 GW in 2027.
GWEC estimates 680 GW of additional worldwide wind capacity between 2023 and 2027, with 130 GW offshore. China leads with 300 GW, followed by Europe with almost 100 GW. Offshore wind will play an important role, with over 60 GW installed between 2023 and 2025 and 68 GW in 2026-2027.
Figure 2: Global New Wind Power Capacity Installation in GW, 2022- 2027
Source: International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers
Wind turbines use gear oils to lubricate their primary gearboxes and other gear motor components. This is due to the high temperatures, heavy loads, oxidation and corrosion, and bearing wear that occur throughout the power production process.
The usage of performance additives in synthetic oil formulation to satisfy particular criteria has resulted in a rise in demand for synthetic gear oils in wind turbines due to their better properties over mineral-based alternatives.
Globally, the quantity of electricity generated by wind energy is rapidly increasing, and the installed capacity of wind turbines grows year after year. The drop in offshore industry pricing has helped to boost the wind power production market by stimulating investments in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. This is expected to drive up demand for gear oils during the projected period.
According to the Global Wind Energy Council, 78 GW of wind generation capacity is to be added to electricity networks in 2022, which will further increase to 115 GW in 2023. It is expected to reach 125 GW in 2024, 135 GW in 2025, 150 GW in 2026, and 157 GW in 2027.
GWEC estimates 680 GW of additional worldwide wind capacity between 2023 and 2027, with 130 GW offshore. China leads with 300 GW, followed by Europe with almost 100 GW. Offshore wind will play an important role, with over 60 GW installed between 2023 and 2025 and 68 GW in 2026-2027.
Figure 2: Global New Wind Power Capacity Installation in GW, 2022- 2027
 Source: Global Wind Energy Council
Gear systems are becoming more difficult since they have very accurate cut teeth and nicely polished surfaces. Furthermore, because they are smaller, the teeth and bearings are subjected to more stress. These stresses, along with vibration and shock, can cause frequent gear pitting (particularly micro pitting) in surface-hardened gears.
Furthermore, the systems work at high temperatures. For all of these reasons, utilizing a quality lubricant is critical. While current mineral oil lubricants perform well, synthetic gear oils have various advantages. These include increased viscosity-temperature for greater performance and wear prevention at severe temperatures, as well as improved thermal and oxidation resistance, allowing for considerably longer oil life and deployment at high temperatures. It also improves low-temperature performance, resulting in lower churning losses and better wear protection.
As industrial gear oil provides better lubricity and prevents rust and corrosion in gears, it is widely used in construction machinery and equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers.
Industrial gear oil is essential for smooth gear changes in manual transmissions and differentials because it provides load resistance, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, and anti-foam qualities. It is also utilized in hydraulic excavators' travel and swing reduction gears to improve machine performance, making it a critical component of industrial and construction equipment in a fast-developing industry.
The rising trend of energy efficiency in numerous sectors is predicted to generate demand for gear oils that may minimize friction and energy consumption. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that transportation fuel use accounts for approximately 29% of total US greenhouse gas emissions. As a response, the EPA has put in place restrictions like the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) requirements to increase fuel efficiency and minimize vehicle emissions. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The base oil in gear oils might be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of the two. Mineral-based gear lubricants are generated from crude oil and provide enough lubrication at a reduced cost. Synthetic gear oils, on the other hand, are chemically developed to give greater performance, such as a higher viscosity index, increased thermal stability, and enhanced wear prevention, particularly in harsh environments.
According to the International Energy Agency, the year-on-year change in worldwide electricity demand has directly or indirectly influenced the market for gear oils. In 2023, the electricity demand was 2.60%, which increased to 3.10 in 2024. It is further forecasted that the electricity demand will increase to 3.30% in 2025, according to the research.
Figure 3: Global Year-On-Year Electricity Demand in Percentage, 2023-2025
Source: Global Wind Energy Council
Gear systems are becoming more difficult since they have very accurate cut teeth and nicely polished surfaces. Furthermore, because they are smaller, the teeth and bearings are subjected to more stress. These stresses, along with vibration and shock, can cause frequent gear pitting (particularly micro pitting) in surface-hardened gears.
Furthermore, the systems work at high temperatures. For all of these reasons, utilizing a quality lubricant is critical. While current mineral oil lubricants perform well, synthetic gear oils have various advantages. These include increased viscosity-temperature for greater performance and wear prevention at severe temperatures, as well as improved thermal and oxidation resistance, allowing for considerably longer oil life and deployment at high temperatures. It also improves low-temperature performance, resulting in lower churning losses and better wear protection.
As industrial gear oil provides better lubricity and prevents rust and corrosion in gears, it is widely used in construction machinery and equipment such as bulldozers, cranes, excavators, and concrete mixers.
Industrial gear oil is essential for smooth gear changes in manual transmissions and differentials because it provides load resistance, anti-oxidation, anti-corrosion, and anti-foam qualities. It is also utilized in hydraulic excavators' travel and swing reduction gears to improve machine performance, making it a critical component of industrial and construction equipment in a fast-developing industry.
The rising trend of energy efficiency in numerous sectors is predicted to generate demand for gear oils that may minimize friction and energy consumption. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that transportation fuel use accounts for approximately 29% of total US greenhouse gas emissions. As a response, the EPA has put in place restrictions like the Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE) requirements to increase fuel efficiency and minimize vehicle emissions. This has resulted in the creation of gear oils that can improve fuel efficiency and lower carbon emissions.
The base oil in gear oils might be mineral oil, synthetic oil, or a combination of the two. Mineral-based gear lubricants are generated from crude oil and provide enough lubrication at a reduced cost. Synthetic gear oils, on the other hand, are chemically developed to give greater performance, such as a higher viscosity index, increased thermal stability, and enhanced wear prevention, particularly in harsh environments.
According to the International Energy Agency, the year-on-year change in worldwide electricity demand has directly or indirectly influenced the market for gear oils. In 2023, the electricity demand was 2.60%, which increased to 3.10 in 2024. It is further forecasted that the electricity demand will increase to 3.30% in 2025, according to the research.
Figure 3: Global Year-On-Year Electricity Demand in Percentage, 2023-2025
 Source: International Energy Agency
Environmental regulations should govern the selection and disposal of gear oils to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human health. Some gear oils may contain additives or base oils that are biodegradable or environmentally friendly, making them suitable for applications where environmental stewardship is a priority.
It is a critical component in vehicle gearboxes, differentials, and transfer cases. It lubricates the gears and bearings, providing smooth shifting and protecting them from wear and damage. Differentials transfer power from the engine to the wheels, guaranteeing smooth functioning. In transfer cases, power is transferred between the front and rear axles, depending on the terrain.
These oils contain additives that form protective films on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact between mating parts and reducing wear. Anti-wear additives, such as zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP), are commonly used to provide additional protection under high-pressure conditions, especially in gears subjected to heavy loads and sliding contact.
Gear oils are designed to resist the high pressures and stresses encountered by gear teeth during operation. Extreme pressure (EP) additives, such as sulfur-phosphorus compounds, are used in gear oil formulations to generate chemical coatings that prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce wear, especially in gears working under strong or shock loads.
Viscosity is an important feature of gear oils because it affects their capacity to maintain a lubricating coating between moving surfaces under varying operating circumstances. Gear oils are available in a variety of viscosity grades, which are normally determined by equipment manufacturers depending on load, speed, temperature, and gear type. Choosing the right viscosity grade enables optimal lubrication and prevents excessive friction and wear.
Asia Pacific is experiencing exponential expansion. The region's key emerging nations, notably China, India, and ASEAN, are driving demand for gear oils. Because of continuing development projects and population expansion, power consumption has increased over time.
The gear oil market is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors competing based on product quality, performance, price, and brand reputation. Key players in the market often invest in research and development activities to innovate and differentiate their product offerings.
The need for gear oils is intimately related to industrial operations such as manufacturing, building, mining, and electricity generation. As companies develop and modernize, there is an increased demand for efficient and dependable gear lubrication solutions to maintain smooth operation and reduce equipment downtime.
In conclusion, the gear oil market is predicted to rise gradually, propelled by industrial expansion, automobile production, infrastructural development, technical improvements, and regulatory compliance. However, market dynamics, economic conditions, and geopolitical considerations might all have an impact on the gear oil industry's growth trajectory in the next years.
Table 1: Key Developments
Source: International Energy Agency
Environmental regulations should govern the selection and disposal of gear oils to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human health. Some gear oils may contain additives or base oils that are biodegradable or environmentally friendly, making them suitable for applications where environmental stewardship is a priority.
It is a critical component in vehicle gearboxes, differentials, and transfer cases. It lubricates the gears and bearings, providing smooth shifting and protecting them from wear and damage. Differentials transfer power from the engine to the wheels, guaranteeing smooth functioning. In transfer cases, power is transferred between the front and rear axles, depending on the terrain.
These oils contain additives that form protective films on metal surfaces, preventing direct contact between mating parts and reducing wear. Anti-wear additives, such as zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP), are commonly used to provide additional protection under high-pressure conditions, especially in gears subjected to heavy loads and sliding contact.
Gear oils are designed to resist the high pressures and stresses encountered by gear teeth during operation. Extreme pressure (EP) additives, such as sulfur-phosphorus compounds, are used in gear oil formulations to generate chemical coatings that prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce wear, especially in gears working under strong or shock loads.
Viscosity is an important feature of gear oils because it affects their capacity to maintain a lubricating coating between moving surfaces under varying operating circumstances. Gear oils are available in a variety of viscosity grades, which are normally determined by equipment manufacturers depending on load, speed, temperature, and gear type. Choosing the right viscosity grade enables optimal lubrication and prevents excessive friction and wear.
Asia Pacific is experiencing exponential expansion. The region's key emerging nations, notably China, India, and ASEAN, are driving demand for gear oils. Because of continuing development projects and population expansion, power consumption has increased over time.
The gear oil market is highly competitive, with numerous manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors competing based on product quality, performance, price, and brand reputation. Key players in the market often invest in research and development activities to innovate and differentiate their product offerings.
The need for gear oils is intimately related to industrial operations such as manufacturing, building, mining, and electricity generation. As companies develop and modernize, there is an increased demand for efficient and dependable gear lubrication solutions to maintain smooth operation and reduce equipment downtime.
In conclusion, the gear oil market is predicted to rise gradually, propelled by industrial expansion, automobile production, infrastructural development, technical improvements, and regulatory compliance. However, market dynamics, economic conditions, and geopolitical considerations might all have an impact on the gear oil industry's growth trajectory in the next years.
Table 1: Key Developments
| Year | Development |
| November 2023 | ExxonMobil had begun production at Payara, Guyana's third offshore oil development, bringing its total production capacity to 620,000 barrels per day. The Prosperity vessel projected to achieve 220,000 barrels per day in the first part of next year, marked the third key step towards achieving a total production capacity of over 1.2 million barrels per day on the Stabroek Blocked by the end of 2027. |
| August 2023 | Chevron finalized its acquisition of PDC Energy, Inc. with shareholder approval. The acquisition comprises 275,000 net acres in the Denver-Julesburg Basin, which added over 1 billion barrels of oil equivalent proven reserves, as well as 25,000 net acres in the Permian Basin that was then in production. |
Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently