Future of 5G – In the Development of Cloud Technology

With the deployment of standalone 5G networks accelerating in 2021, the cloud will need to reinvent itself. Mobile devices will be able to easily transfer large amounts of data due to 5G and to manage this data cloud and its various architectures will play a major role. This is particularly true at the enterprise level, forcing cloud providers to increase storage capacity and adjust prices accordingly. For instance, in February 2021, IBM announced a 1u all-flash storage system for on-premises IT environments that can scale to hold 1.7 petabytes (PB) of data as part of an effort to make data management easier across a hybrid cloud computing environment. Additionally, the surging adoption advanced technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), among others is expected to accelerate the need for 5G cloud services. These technologies are reshaping the market by assisting users in monitoring, analyzing, and visualizing unprocessed data. Adopting these emerging technologies in conjunction with cloud solutions would assist enterprises in improving their visualization capabilities as well as making complex data accessible and usable. Google Cloud launched Vertex Al, a machine learning platform that assists enterprises in maintaining and deploying artificial intelligence (AI) models, in May 2021. This factor would also aid in the efficient management and development of machine learning projects throughout the development lifecycle.
Furthermore, in the coming years, service providers and private companies will continue to assess the most cost-effective ways to expand capacity and capability in 5G deployment plans. In terms of the data center, 5G promises faster access to information, which will drive more edge data center construction. As more data becomes latency-sensitive and requires faster access, there is a shift away from large-core, small-edge data center architecture and toward the smaller-core, larger-edge architecture. A data center might be as simple as a single server or as complicated as a rack containing a high proportion of servers. Companies that provide public cloud computing services such as Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, Google, and more have data centers that they make available to other businesses. In the coming years, more and more end-user traffic will pass through a data center. According to the Cisco VNI Forecast, 86 percent of total end-user/device traffic touched a data center in 2015, and this traffic share increased to 94 percent by 2020.
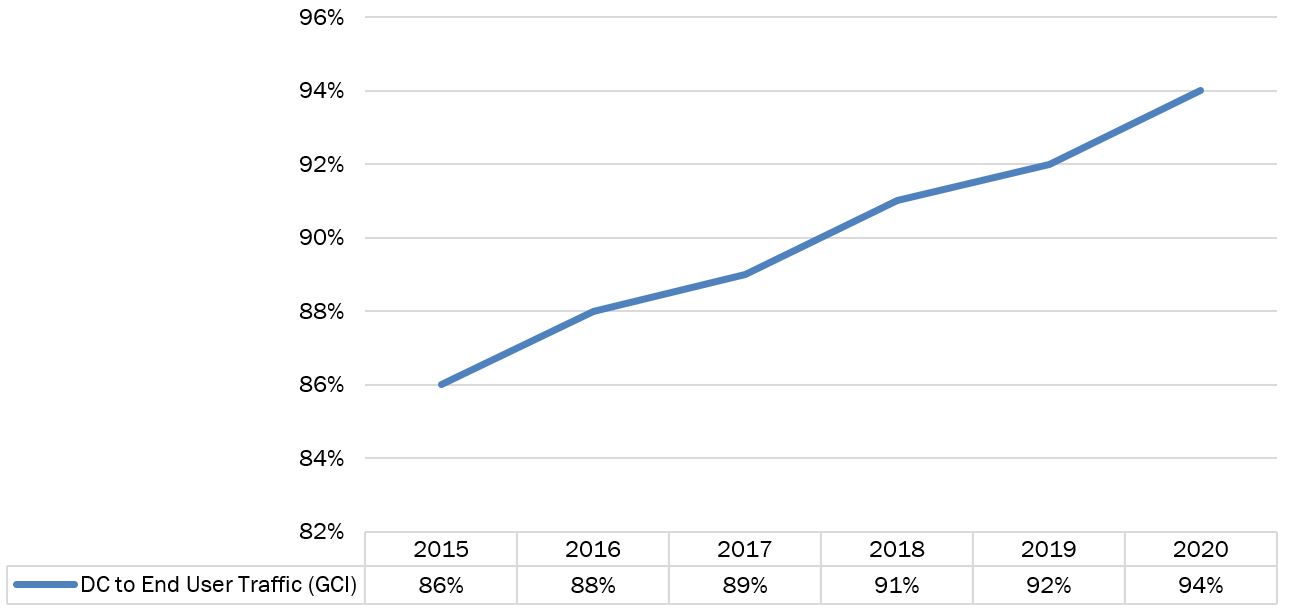 Source – Cisco
Source – Cisco
However, data security and privacy concerns about data loss, data breaches, unanticipated emergencies, application vulnerabilities, and online cyber-attacks allied with cloud-based solutions are expected to act as restraints for the growth of cloud-based solutions. Revenues in healthcare, government, IT and telecom, BFSI, and other sectors may suffer as a result of this. According to the arXiv.org e-Print database, in 2019, almost 60% of corporate-related data and information on storage drives was held insecurely.
Impact of 5G on Cloud and Data Centers
5G technology will be extremely beneficial to the cloud computing industry. This is due to the fact that cloud-based technology innovations are more efficient. The technology enxhances the integration by having low to nil latency, leading to better communications. Furthermore, the goal of service providers using Cloud Native ideas and technology is to reach web size and economies of scale. Large enterprises such as Intel and IBM, are investing in network cloudification. This involves extending cloud platforms, technologies, and virtualization capabilities across a network to make it more agile and scalable. Networks are leveraging 5G to quickly migrate toward this software-defined architecture to fulfill operational and application demands as consumer and enterprise bandwidth demands grow. Furthermore, the cloud is a beneficial area for non-device storage in everything from healthcare applications to autonomous vehicles, and even down to wearables and mobile apps. These technologies will perform better if they leverage the cloud and have 5G connections. The dependability, performance, and efficiency of cloud-based products and services should all increase. As a result of these advancements, cloud business spending will accelerate. For instance, in June 2021, FloLive, which developed a cloud-based solution for stitching together private, local cellular networks to create private global IoT 5G networks for its customers, raised $15.5 million in funding. The money will be used to expand the company's service, including investing in and building out its tech stack, upgrading its network to 5G where it's being used, and developing a global SIM2Cloud. According to the data by Flexera 2021 State of the Cloud Report, respondents anticipate a 39 percent growth in cloud spending in the following 12 months.
Organizational Spend On Public Cloud, Average % Across All Respondents
Next 12 Months Current Cloud Spend
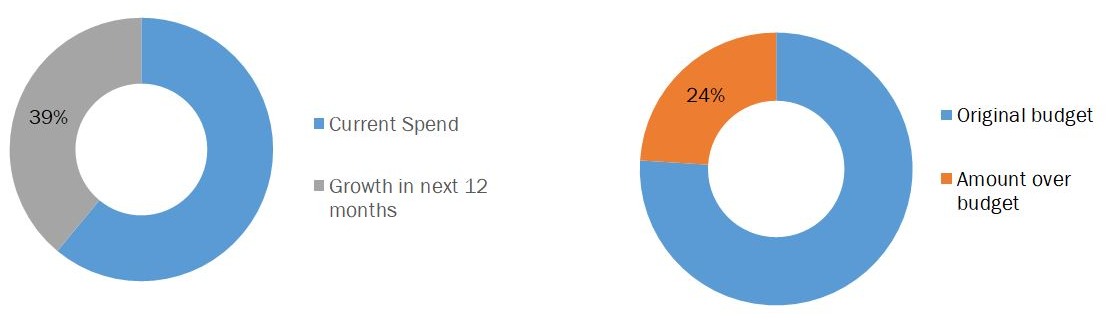
Source –Flexera 2021 State of the Cloud Report
The 5G New Radio (NR) air interface is one of the most important aspects of 5G. It improves performance by utilizing new mobile spectrums with high-speed latency capabilities. URLLC (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication) capabilities will be enabled by 5G, enabling use cases such as V2X and Telesurgery, as well as Cobots, where end-to-end latency is predicted to be in milliseconds. eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) capability will be accessible in 5G for use cases that require a high data rate, such as augmented reality and virtual reality.
In addition, the impact of 5G on cloud and data centers has led to a series of developments by major companies in the market, which is further expected to expand the demand for these services in the future. For instance –
- TIM and Google announced new cooperation involving cloud and edge computing services at the beginning of March 2020, based on an MoU agreed in November 2019. TIM stated at the time that it aimed to make €1 billion from cloud services by 2024, at pace with the fast-increasing cloud market.
- In December 2021, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Amazon's cloud computing platform, launched a managed service called AWS Private 5G. To establish a private 5G network and connect devices, AWS will provide small cell radio units, servers, 5G core and RAN software, and SIM cards. The service automates the setup procedure, allowing for the support of more devices.
- Etisalat and Microsoft teamed up in October 2021 to use Azure Multi-access Edge Compute to unleash new 5G scenarios as part of their strategic collaboration. The alliance involves establishing 5G edge compute plug-and-play infrastructures for organizations to run industry solutions, leveraging Etisalat Core Orchestration and Azure ARM capabilities.
- In September 2021, IBM and Telefónica unveiled a multi-year strategic partnership to employ IBM intelligent automation technologies and services to deploy UNICA Next, Telefónica's first cloud-native 5G core network platform.
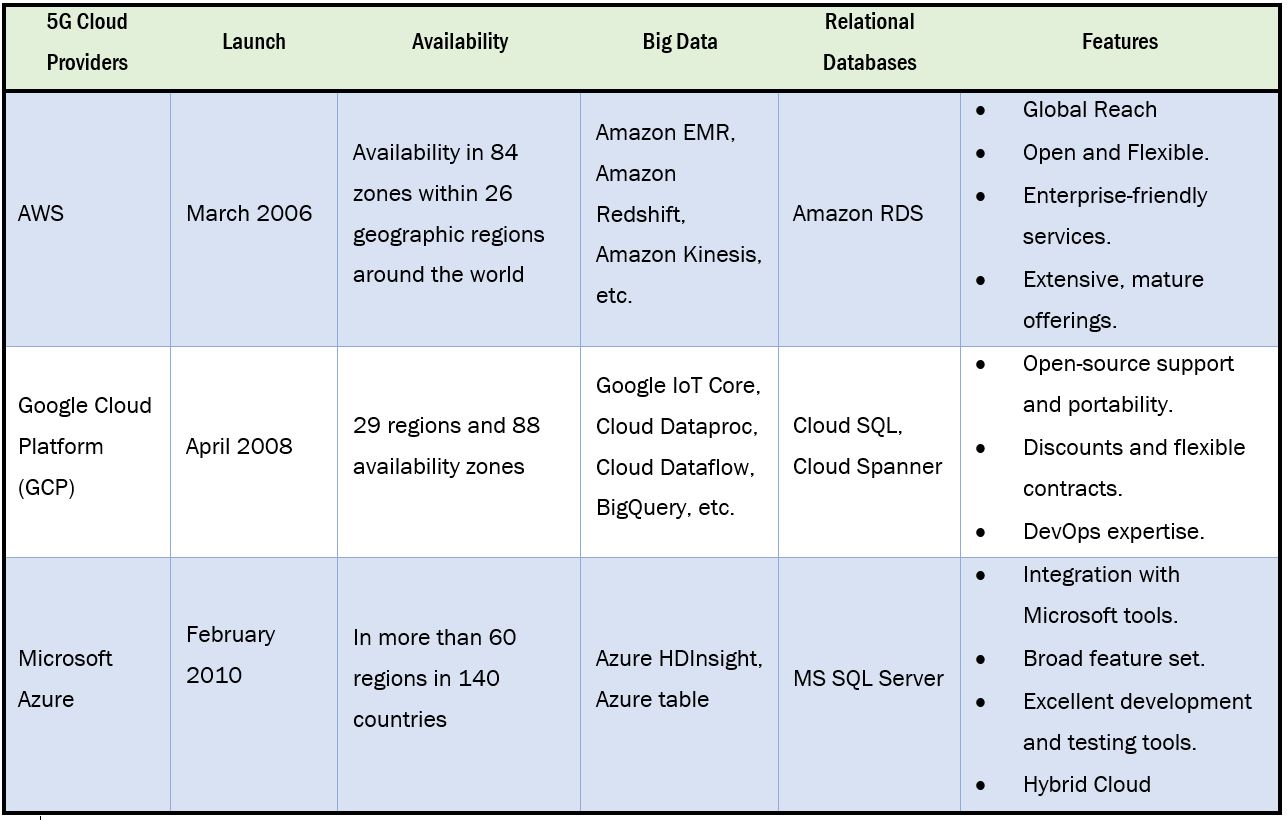
AWS, MICROSOFT, GOOGLE
In terms of 5G cloud service providers, the top three companies dominating the market are AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Services Provided by Cloud Providers
| Name of Company | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| AWS | Amazon EC2 | Amazon Web Services | Amazon Web Services |
| Microsoft | Microsoft Private Cloud | Microsoft Azure | Microsoft 365 |
| - | Google App Engine (Python, Java and, many) | Google Applications |
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
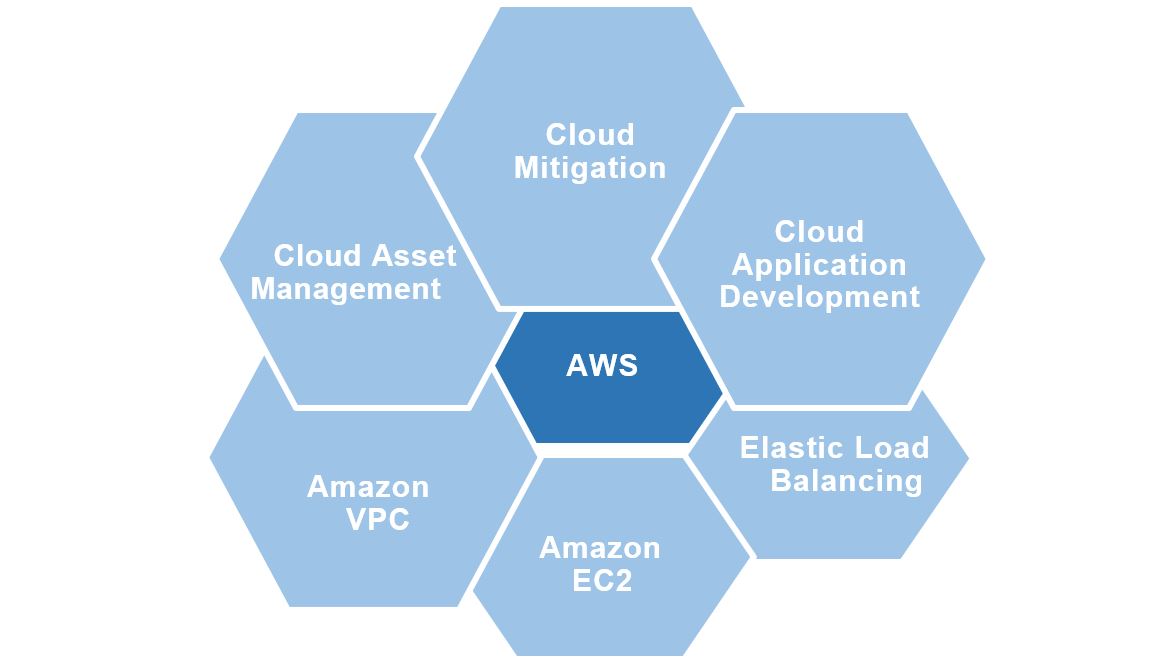
Amazon Web Services provides on-demand cloud services to enterprises all around the world on a pay-as-you-go basis. AWS is used by platforms like Slack and Netflix to provide continuous uptime 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Even when COVID-19 has a negative influence on enterprises and the workforce, AWS is assisting its clients in handling the surge in demand while working from home. AWS' services comprise networking, storage, remote computing, mobile development, email, analytics, and security, to name a few. It provides a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) that does not interact with other networks, enhancing virtual privacy. In addition, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an AWS introductory feature. This feature makes it easier to create groups of users.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud is a collection of cloud computing services that run on Google's infrastructure for its user-centric products. Computing, storage, analytics, and machine learning (ML) are among the cloud services it offers. Networking, Big Data, the internet of things (IoT), management tools, security, and Cloud AI are among the platform's other features. Google cloud services are built on the same infrastructure as Google's other end-user products, such as YouTube, Gmail, and Google Search. Furthermore, it permits cloud resource pooling - this is a service that allows the provider to give interim services to a large number of clients. It also has a multi-layered security mechanism in place to keep critical information safe.
- Microsoft Azure
Microsoft has the largest enterprise customer base of the three main companies, owing to widespread adoption of Microsoft Windows, Microsoft 365 (previously Office 365), and Microsoft Dynamics. It's proven simple for many customers to layer new Microsoft Azure cloud services on top of current technologies. Microsoft Azure's integration with business intelligence tools (especially Power BI), industry-specific solutions (for example, Microsoft Cloud for Retail or Microsoft Cloud for Manufacturing), and a significant focus on enterprise support are all key differentiators. On its website, Microsoft advertises nine separate IoT cloud services. Its key solution for data intake into the cloud via IoT devices is Azure IoT Hub. The service offers secure connectivity with IoT devices as well as device management features including device provisioning.
 Impact Of Covid-19 On 5g Cloud And Data Centers
The global health crisis served as a driver for demonstrating the benefits and flexibility of cloud computing, resulting in increased adoption. The pandemic has brought into sharp focus factors such as flexible computing power, high availability, disaster recovery, lower back up and disaster recovery costs, resilient core for business process and business continuity, legacy skill risk, remote workforce management, safe return to work, and business agility, allowing for resilient business functions. According to a recent Flexera survey, Covid-19 has resulted in a considerable rise in cloud spending for 29% of leaders.
Impact Of Covid-19 On 5g Cloud And Data Centers
The global health crisis served as a driver for demonstrating the benefits and flexibility of cloud computing, resulting in increased adoption. The pandemic has brought into sharp focus factors such as flexible computing power, high availability, disaster recovery, lower back up and disaster recovery costs, resilient core for business process and business continuity, legacy skill risk, remote workforce management, safe return to work, and business agility, allowing for resilient business functions. According to a recent Flexera survey, Covid-19 has resulted in a considerable rise in cloud spending for 29% of leaders.
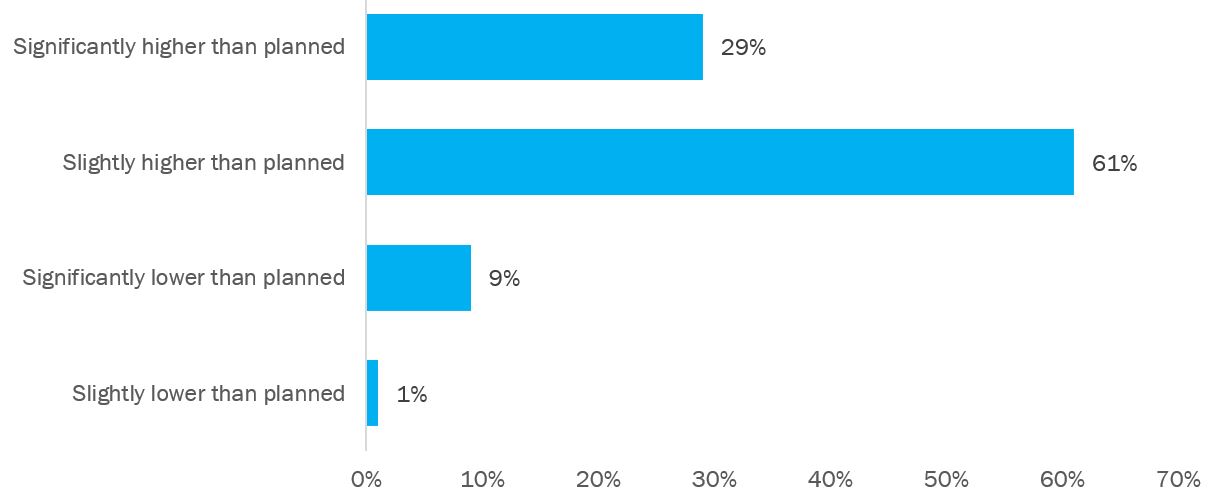 Source: Flexera 2021 State of the Cloud Report
Source: Flexera 2021 State of the Cloud Report
The importance of the cloud for organizational continuity with remote workforces and smooth online collaboration has been highlighted by pandemic and remote working scenarios. In all companies, the use of public clouds is rapidly increasing. For instance, in May 2021, PayPal increased its multi-year Google Cloud cooperation as Covid-19 promoted a surge in online payments. This expansion has resulted in a huge increase in public cloud spending, which may have been boosted even further by the COVID-19 outbreak. As per the Flexera survey report, 36 percent of businesses spent more than $12 million per year on IT, and 83 percent reported that they spend more than $1.2 million per year on cloud computing. These percentages are up from last year when 20% of businesses reported annual spending of more than $12 million and 74% reported annual spending of more than $1.2 million.
Furthermore, because of greater access to internet-related services, as well as nationwide lockdowns imposed by governments around the world, demand for data centers surged.
Annual Public Cloud Spend By Enterprises
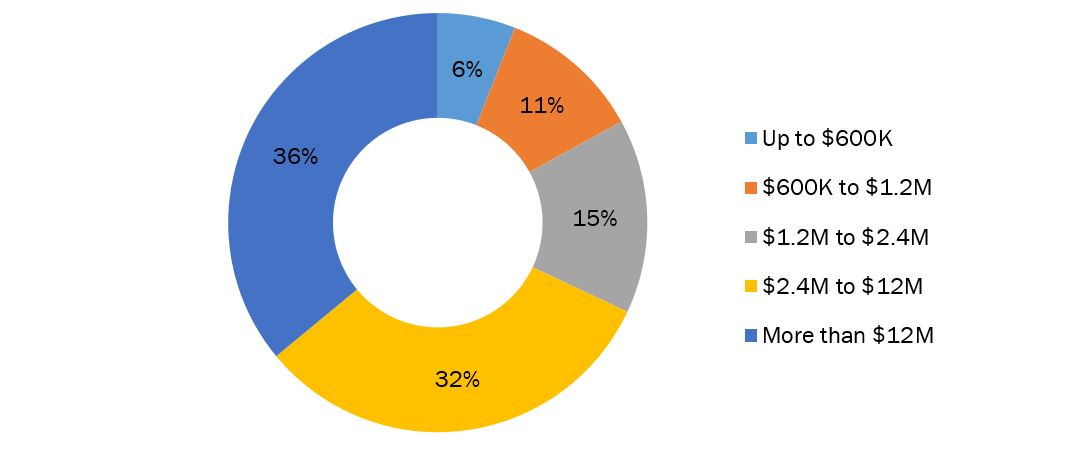
Source: Flexera 2021 State of the Cloud Report
About the author
Anamika Khanduri is a Market Research Analyst at Knowledge Sourcing Intelligence LLP. She is well-skilled in qualitative research. Her field of expertise is obtaining and analyzing data on worldwide market consumers and competitors. To read more articles by her and for more information regarding multiple global markets, visit www.knowledge-sourcing.com.
Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest White Papers
Next-Gen Elderly Care: How AI is Driving Industry Transformation
Recently
The Terrifying Potential of the 5G Devices
Recently
Testing and Quality Assurance to Validate 5G Performance
Recently
Digital Transformation & Improvements With 5G and SD-Wan Edge Computing
Recently