Report Overview
Cellulose Derivatives Market - Highlights
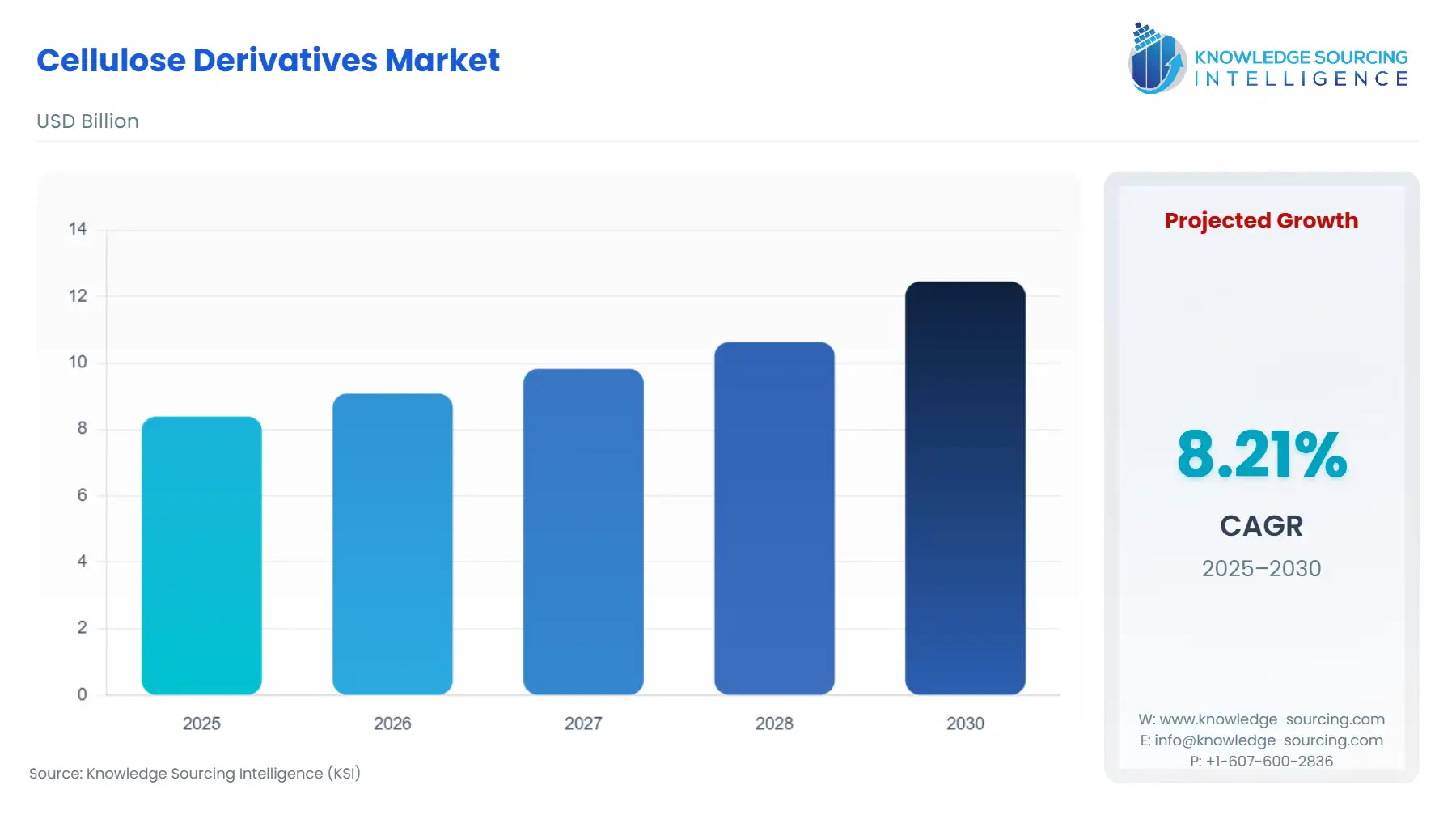
Cellulose Derivatives Market Size:
Cellulose Derivatives Market, at a 8.21% CAGR, is projected to increase from USD 8.391 billion in 2025 to USD 12.448 billion in 2030.
Cellulose derivatives, a critical class of versatile biopolymers, are produced by chemically modifying natural cellulose, primarily sourced from wood pulp or cotton linter, to yield functionally distinct products like cellulose esters (e.g., Cellulose Acetate) and cellulose ethers (e.g., Methyl Cellulose). These derivatives are not mere commodities; they function as essential performance additives, acting as thickeners, binders, film formers, and rheology modifiers across a spectrum of industrial and consumer applications. The market's foundational strength stems from the renewability of its core raw material, cellulose, granting it a key advantage over purely synthetic alternatives in an increasingly sustainability-focused global economy. This necessity is fundamentally derived from the growth and technological evolution within key downstream sectors, notably pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, personal care, and construction materials, where their unique functional properties are indispensable to end-product performance and regulatory compliance.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The global consumer shift toward plant-based and "clean label" ingredients dramatically increases the demand for cellulose derivatives (e.g., CMC, MC) as natural-origin thickeners and stabilizers in the Food & Beverage sector. This consumer preference acts as a powerful pull factor. Concurrently, rigorous mandates from regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA for precise drug delivery and consistent pill quality necessitate the non-negotiable use of high-purity cellulose ethers (e.g., HPMC) as specialized pharmaceutical excipients, creating inelastic demand. Furthermore, the global regulatory crackdown on single-use, non-biodegradable plastics compels packaging and textile industries to substitute petroleum-based polymers with bio-based alternatives like Cellulose Acetate, directly increasing its market volume.
Challenges and Opportunities
The primary constraint on market expansion is the persistent volatility and high cost of Dissolving Wood Pulp (DWP), the core raw material, which directly impacts the profitability and final pricing of cellulose derivatives, creating purchasing headwinds for price-sensitive bulk end-users. A major opportunity lies in leveraging sustainability mandates by innovating process chemistry to minimize the use of non-recyclable solvents and chemical reagents, thereby enhancing the overall green profile of the product. The development of new, high-value applications, such as advanced bio-based films for pharmaceutical controlled release systems and novel biodegradable plasticizers for Cellulose Acetate, offers a significant opportunity to shift the sales mix toward high-margin, specialized products.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The production of cellulose derivatives is critically dependent on two primary feedstocks: dissolving wood pulp (DWP) and cotton linter pulp. DWP, derived from hardwood or softwood, represents the bulk source and is subject to significant pricing volatility driven by global forestry policies, energy costs, and the competing demand from the viscose staple fiber (VSF) industry. Chemical reagents such as caustic soda and acetic anhydride, necessary for etherification and esterification, introduce further cost instability. Fluctuations in the price of DWP directly translate into non-linear production cost changes, forcing manufacturers to engage in long-term contract pricing and hedging to stabilize their cost structures and prevent severe margin erosion.
Supply Chain Analysis
The cellulose derivatives supply chain is characterized by a multi-stage, global process. It begins with the procurement of DWP, sourced predominantly from established forestry regions in North America and Scandinavia, and cotton linters, primarily from Asia. The complex chemical conversion process, requiring significant capital investment, is concentrated in major industrial hubs, including East Asia (China, Japan), North America (US), and Europe (Germany, Belgium). Logistical complexity arises from transporting the bulk raw materials to production sites and then distributing the refined, differentiated powder or granular products globally. This concentration of specialized manufacturing capacity creates critical regional dependencies and exposes the supply chain to geopolitical risks or localized operational disruptions.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Government Regulations
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
European Union | Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 (REACH) / EU Green Deal | REACH imposes stringent registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction requirements on chemical substances, including derivatives, increasing compliance costs but raising the barrier to entry for lower-quality non-EU producers. The Green Deal promotes bio-based materials, driving preferential demand for cellulose derivatives as a sustainable alternative. |
United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) / Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Status | FDA's affirmation of cellulose derivatives (e.g., MC, CMC) as GRAS for food applications legitimizes their use as essential food additives, directly boosting consumer and manufacturer confidence and sustaining demand in the Food & Beverage and Pharmaceutical sectors. |
India | Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) / Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) | CDSCO's strict standards for pharmaceutical excipients mandate the use of high-grade cellulose ethers in drug formulation. FSSAI approval ensures that food-grade cellulose derivatives meet national safety standards, facilitating high-volume demand from the rapidly growing generic drug and processed food industries. |
Cellulose Derivatives Market Segment Analysis
By Type: Cellulose Acetate (Cellulose Esters)
The Cellulose Acetate segment is experiencing a renewal of demand, primarily driven by the global imperative to replace non-biodegradable petroleum-based plastics. Its key growth driver is its inherent status as a renewable, bio-based polymer that is biodegradable under appropriate composting conditions, giving it a strong competitive advantage in environmentally regulated markets. Specifically, the regulatory push against single-use plastics, particularly in the European Union and parts of North America, directly increases the demand for Cellulose Acetate in applications like biodegradable films, specialized packaging (e.g., blister packs, coatings), and non-textile filters. Furthermore, the textile industry's shift toward sustainable fibers, led by major fashion brands' environmental commitments, sustains demand for cellulose acetate fiber in high-quality, eco-conscious apparel. Recent product innovations, such as the development of bio-based plasticizers and improved recycling processes, further enhance its long-term viability and adoption rate, stabilizing its price and performance profile against competing bioplastics like PLA.
By End-User: Pharmaceuticals
The Pharmaceuticals segment represents one of the most stable, high-margin consumption bases for cellulose derivatives, characterized by extremely stringent quality requirements and non-substitutable functionality. The essential growth driver is the critical role derivatives, notably Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) and Methyl Cellulose (MC), play as non-toxic, chemically inert excipients in drug formulation. HPMC is crucial for controlling the release kinetics of oral dosage forms, forming the structural matrix in sustained-release tablets and acting as a primary component in capsule shells. Given the rigorous testing and regulatory approval required for pharmaceutical excipients by bodies like the FDA, manufacturers are reluctant to switch approved materials, creating highly inelastic, brand-specific demand. The expanding global market for generic and complex dosage form drugs, especially in Asia, guarantees continuous, escalating volume demand for these high-purity, technically arduous cellulose ethers.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Geographical Analysis
US Market Analysis
The US market is defined by its maturity and high demand for specialized, high-purity grades, particularly within the Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care sectors. Growth drivers include the extensive R&D expenditures by major pharmaceutical companies, creating a constant need for novel excipients and film formers. The US market exhibits strong demand for performance-driven products in the Paints & Coatings and Construction sectors, where cellulose ethers are valued for their viscosity and rheological properties, rather than solely on price. Local factors, such as FDA approvals and state-level renewable material mandates, exert a decisive influence on consumption patterns for food-grade and sustainable derivatives.
Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil represents the largest market in South America, primarily fueled by the rapid expansion of the Food & Beverage and Construction industries, linked to urbanization and a growing middle class. The key demand factor is the high-volume requirement for low-cost cellulose derivatives, such as CMC and low-viscosity HEC, used as thickeners and stabilizers in mass-produced processed foods and as water retention agents in cement mortars and tile adhesives. Local demand is price-sensitive, placing a competitive advantage on manufacturers with efficient, low-cost production or localized supply chains capable of navigating complex import/export logistics.
German Market Analysis
Germany is a cornerstone of the European market, characterized by stringent quality standards and a strong alignment with sustainability goals. This growth is predominantly driven by the high-value Pharmaceutical, Coatings, and specialized Construction chemicals sectors, which demand ultra-high-purity and functionally tailored cellulose derivatives. Local factors include proactive government promotion of circular economy principles, which encourages the substitution of conventional plastics with biodegradable cellulose esters, and the influence of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and its REACH regulation, which elevates the competitive position of compliant, high-quality European suppliers.
UAE Market Analysis
The UAE market is heavily concentrated in the Building & Construction sector, propelled by large-scale infrastructure and commercial real estate projects in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. The core growth catalyst is the requirement for high-performance cellulose ethers in specialized construction chemicals, such as self-leveling mortars and plaster systems, which must withstand the region's extreme heat and humidity. Local demand is highly focused on product performance, with HPMC and HEC grades used to control water retention and improve workability in cementitious materials under arid conditions, making product quality a non-negotiable purchasing criterion.
China Market Analysis
China functions as both the world's largest consumer and a primary global manufacturing hub for cellulose derivatives. Demand is voluminous and diverse, driven by the massive scale of its domestic Construction, Food & Beverage, and Textile industries. Local demand is stimulated by state-led investment in affordable housing and infrastructure, which necessitates immense quantities of cellulose ethers. Concurrently, the domestic pharmaceutical market and the textile sector’s focus on sustainable fibers further bolster demand, though the market remains highly competitive and price-sensitive due to the large presence of localized, high-capacity domestic producers.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The global Cellulose Derivatives Market features a highly consolidated top tier of multinational chemical specialists competing primarily on product quality, functional consistency, and extensive regulatory support. The competitive matrix is defined by two key battlegrounds: high-purity, low-volume pharmaceutical excipients, where high barriers to entry reward technical consistency (e.g., Shin-Etsu, Ashland), and high-volume, price-sensitive industrial grades (e.g., construction), where cost efficiency and localized production capacity are decisive (e.g., Dow, Shandong Head). Vertical integration into DWP sourcing or downstream formulation expertise provides key competitive insulation against raw material volatility and technological substitution risks.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. is strategically positioned as a global leader in high-purity cellulose ethers, focusing specifically on the highly regulated Pharmaceuticals and premium Food & Beverage end-user segments. The company’s core product strength lies in its METOLOSE and TYLOSE brands of methylcellulose (MC) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), known for their ultra-high purity, batch-to-batch consistency, and advanced functional properties crucial for controlled-release drug delivery systems. Shin-Etsu leverages its deep technical expertise and strict quality control protocols to maintain its premium pricing and market dominance in specialized excipients, where consistency and regulatory file approval outweigh cost considerations for customers.
Ashland Inc
Ashland Inc. operates as a leading specialty additives company with a significant, globally diversified portfolio of cellulose ethers, prominently featuring Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) and Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (HPC). Ashland's strategy centers on serving multiple, less cyclic end-user markets, including Personal Care & Cosmetics (e.g., through products like Natrosol HEC) and Pharmaceuticals. The company continually invests in capacity expansion and product development to tailor derivatives for specific functions, such as rheology modification in coatings or film formation in topical applications, positioning itself as an innovation-driven supplier focused on application-specific performance rather than commodity volume.
Dow Chemical Company
Dow Chemical Company maintains a robust position in the cellulose ethers market, primarily supplying high-volume industrial grades to the Building & Construction and Paints & Coatings end-user markets. Dow's WALOCEL and CELLOSIZE product lines leverage the company’s massive global production footprint and backward integration capabilities to offer cost-effective, high-performing methylcellulose (MC) and Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC) derivatives. Their strategic focus is on providing reliable supply and technical support for large-scale, functional applications such as tile adhesives, mortars, and exterior coatings, where their products act as essential water retention and workability agents, driving demand through operational scale and reliability.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Developments
June 2024: Ashland announced the appointment of Omar Irani as Vice President of Strategy, M&A, and Portfolio Management. This move signals a focus on strategic portfolio optimization and capacity/capability growth through potential future acquisitions, impacting its cellulose ether market position.
February 2024:Karün Eyewear launched glasses frames made from Cellulose Acetate recovered from cigarette butts via a scalable IMEKO process. This innovative product launch demonstrates a new, circular economy application for Cellulose Acetate, boosting its sustainable material demand profile.
Cellulose Derivatives Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2025 | USD 8.391 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2030 | USD 12.448 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 8.21% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Segmentation | Type, Application, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Cellulose Derivatives Market Segmentation:
BY TYPE
Cellulose Esters
Cellulose Acetate
Cellulose Acetate Butyrate (CAB)
Others
Cellulose Ethers
Methyl Cellulose (MC)
Ethyl Cellulose (EC)
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (HEC)
Others
BY APPLICATION
Thickners & Binders
Viscosity Modifiers
Film Formers
Others
BY END-USER
Pharmaceuticals
Food & Beverage
Personal Care & Cosmetics
Building & Construction
Paints & Coatings
Others
BY GEOGRAPHY
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
Germany
France
United Kingdom
Spain
Italy
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Israel
Others
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Indonesia
Thailand
Others