Report Overview
China Additive Manufacturing Market Highlights
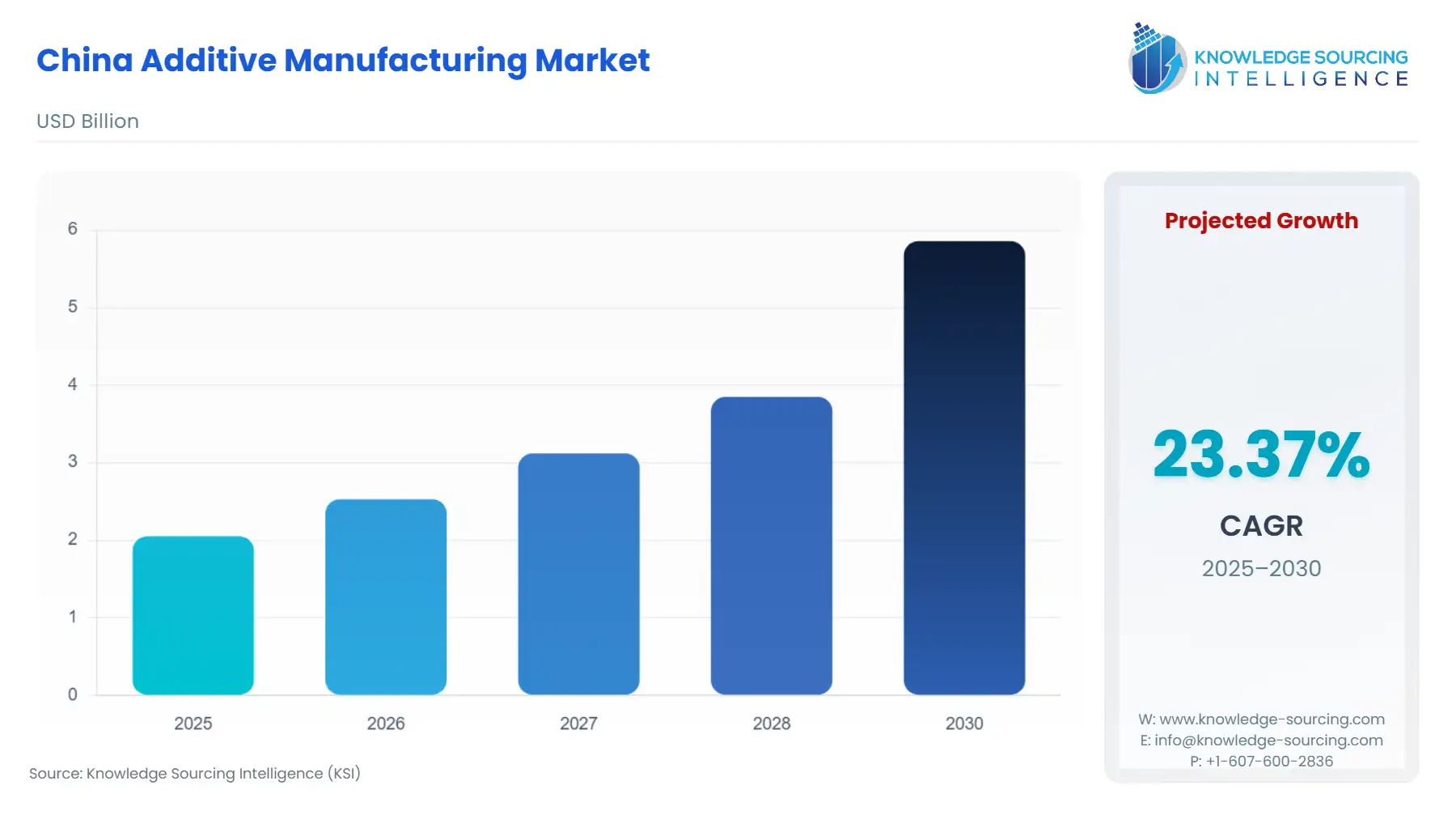
China Additive Manufacturing Market Size:
The China Additive Manufacturing Market is anticipated to surge at a CAGR of 23.37%, reaching USD 5.859 billion in 2030 from USD 2.05 billion in 2025.
The Chinese Additive Manufacturing market is transitioning rapidly from a foundational R&D focus to an application-centric industrialization phase, fundamentally reshaping the domestic manufacturing landscape. This strategic shift is backed by a concentrated national effort to secure a leading position in advanced manufacturing, viewing AM not as an optional technology but as an essential upgrade path for established industrial sectors. The market dynamics are characterized by vigorous domestic hardware competition, increased utilization of metal and ceramic materials, and a potent demand for customized solutions across high-value sectors such as aerospace and healthcare. This trajectory establishes AM as a key enabling technology for China's broader economic and technological self-sufficiency goals.
China Additive Manufacturing Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The paramount factor propelling market growth is the national mandate for industrial modernization. The explicit goal of the "Made in China 2025" policy to substitute a significant portion of traditional manufacturing with 3D printing directly translates into sustained, state-backed capital expenditure for AM systems. This regulatory push creates guaranteed demand for industrial-grade AM hardware and software licenses across state-owned enterprises and their supply chains. Furthermore, the burgeoning electric vehicle market is a potent growth driver for specialized metal AM components. OEMs are increasingly adopting AM for functional parts—like heat exchangers and complex structural nodes—to achieve aggressive lightweighting objectives, directly increasing the procurement of high-performance metal powder bed fusion (PBF) systems and high-value titanium and aluminum alloy powders.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge constraining growth is the elevated barrier to entry marked by the high initial capital investment for industrial AM systems. This financial hurdle limits adoption primarily to large corporations and research institutions, inhibiting market diffusion among smaller, agile manufacturers who could otherwise drive service requirements. An equally significant constraint is the limited availability of engineers and technicians proficient in AM design for manufacturing (DfAM) and post-processing. This skills gap bottlenecks the transition of R&D concepts into commercial production, suppressing the demand for advanced services. Conversely, the opportunity lies in the rising domestic demand for customized medical implants, a factor driving market penetration in the healthcare sector. The requirement for patient-specific devices compels manufacturers to adopt AM, creating a sustained, high-margin demand for both medical-grade AM services and certified polymer/metal materials.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Additive Manufacturing is inherently a physical product market. Key raw materials include polymer, metal, and ceramic powders/filaments. Pricing dynamics are heavily influenced by the raw material supply chain's complexity, particularly for high-performance metal powders like titanium and nickel superalloys, which require specialized spheroidization processes. The majority of the global production capacity for certain metal feedstocks is centrally controlled, but Chinese companies have been actively investing in domestic production and global mining assets to secure the upstream supply. This strategic investment aims to decouple domestic AM material costs from global supply volatility, a factor that will eventually increase the price competitiveness of Chinese-made metal AM services and drive up the internal demand for domestically sourced materials.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global AM supply chain is transitioning from a decentralized model to one with clear regional dominance, with China emerging as a critical global production hub, especially for polymer-based industrial and desktop machines. Logistical complexities stem from dependencies on foreign suppliers for highly specialized components, such as high-power lasers and advanced galvanometer systems used in PBF technology. While China possesses a robust base for general manufacturing, a dependency on specific foreign-sourced core components introduces a minor bottleneck. However, the domestic industry is actively localizing the production of these key elements, which reinforces the long-term trend of a self-contained, vertically integrated Chinese AM supply chain.
China Additive Manufacturing Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
People's Republic of China |
Made in China 2025 (State Council) |
Strategic policy that identifies AM as a core technology for industrial modernization, guaranteeing state investment and creating mandated demand for domestic AM hardware and services in targeted industries like aerospace and new energy vehicles. |
|
People's Republic of China |
14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Advanced Manufacturing (MIIT) |
Emphasizes the importance of AM technologies, translating into increased R&D funding and subsidies for domestic companies. This drives demand for new, higher-speed, larger-format industrial AM systems. |
China Additive Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis:
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Technology Analysis
The SLS technology segment is specifically propelled by its unparalleled suitability for batch production of complex polymer parts with minimal need for support structures. Sectors like consumer electronics and automotive prototyping demand robust, functional parts in small to medium volumes, a requirement that traditional injection molding cannot meet cost-effectively or rapidly. The versatility of SLS—capable of processing a wide range of materials, including nylon and polyamides—directly translates into increased system procurement by independent service bureaus. These bureaus leverage the high packing density and material diversity of SLS to aggregate demand from multiple clients, establishing it as a workhorse technology for rapid manufacturing rather than just prototyping, thereby driving sales of larger-build-volume machines.
- Aerospace & Defense End-User Industry Analysis
The need for AM in the Aerospace & Defense sector is uniquely driven by the imperative for part consolidation, lightweighting, and reduction of supply chain lead times for mission-critical components. Unlike other sectors, this industry operates under stringent certification requirements, meaning demand is heavily focused on certified metal PBF technologies (like Laser Sintering and EBM) and high-performance materials (e.g., titanium alloys). AM allows engineers to redesign components, consolidating dozens of parts into a single, complex geometry, which drastically cuts assembly time and weight—a critical metric for fuel efficiency and performance. This necessity is high-value, resulting in procurement of the largest, most technologically advanced metal AM systems and long-term service contracts for certified part production.
China Additive Manufacturing Market Competitive Analysis:
The Chinese AM market features intense competition between established global players and rapidly innovating domestic firms. This landscape is defined by the strategic dominance of local companies in the industrial and consumer segments, often challenging international market leaders on price and customization.
- Bright Laser Technologies (BLT): As a leading Chinese metal AM systems manufacturer, BLT specializes in Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) equipment, offering a holistic approach that includes equipment, metal powders, and engineering services. Their strategic positioning emphasizes large-scale industrial systems, such as the BLT-S series, for high-volume, precision manufacturing, primarily targeting the high-value Aerospace and Defense sectors with verified, end-use parts.
- Farsoon Technologies: Farsoon has successfully established itself as a major supplier of open-platform Polymer and Metal PBF systems. The company’s focus on an open material policy attracts a broad user base, from research institutes to manufacturing services. Its product portfolio, including the FS series of metal PBF machines, is strategically positioned to offer industrial-grade performance with greater user control over materials, capturing significant market share by reducing proprietary vendor lock-in.
China Additive Manufacturing Market Developments:
- May 2024: Chevron Oronite announced the final investment decision for a significant expansion of its lubricant additive facility in Ningbo, China. This capacity addition reinforces the local supply of chemical additive products, addressing the growing industrial and automotive sectors in the Asia-Pacific region.
- April 2024: Kings 3D Group launched five new heavyweight products, including the LASERADD-600 (a five-axis additive and subtractive CNC machine) and the high-efficiency four-laser metal 3D printing device, DiMetal-500M. The launches expanded their four major product lines to cover a comprehensive range of processes, demonstrating a focus on high-speed, multi-technology integration.
China Additive Manufacturing Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.05 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 5.859 billion |
| Growth Rate | 23.37% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, End-User |
| Companies |
|
China Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
- Material
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Laser Sintering (LS)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Fused Disposition Modelling
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Construction
- Consumer
- Others