Report Overview
China Responsible AI Market Highlights
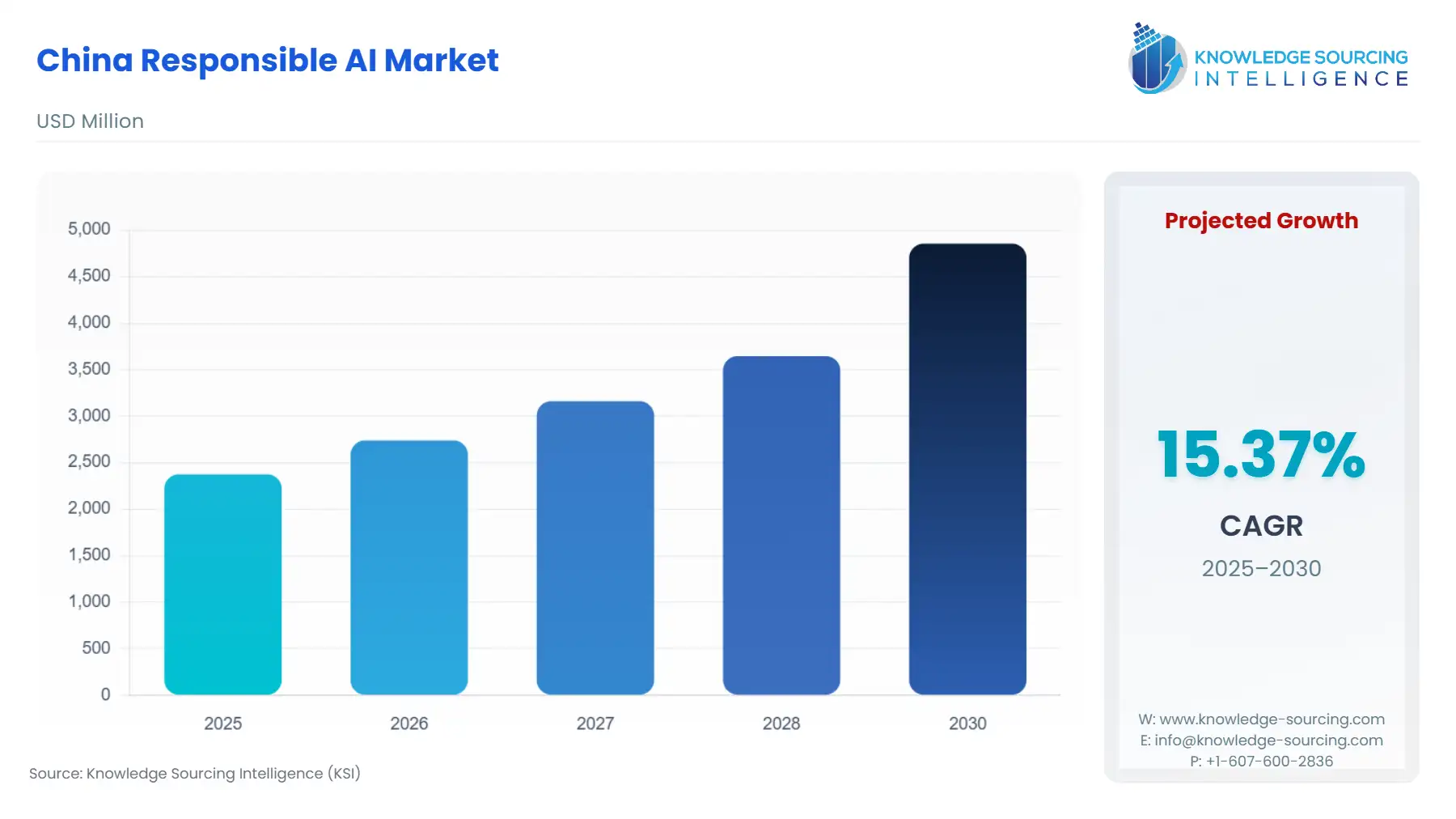
China Responsible AI Market Size:
The China Responsible AI Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.37%, reaching a market size of USD 4.855 billion in 2030 from USD 2.375 billion in 2025.
The Chinese Responsible AI Market is emerging not as a consequence of self-regulation but as a direct and compulsory response to a unique, state-driven governance model. Unlike other global markets where the push for ethical AI originates from a mix of public concern and corporate social responsibility, the Chinese market is fundamentally shaped by a series of targeted, legally binding regulations. These regulations, enacted by the central government, cover specific facets of AI, including recommendation algorithms, deep synthesis technologies, and generative AI services. This regulatory imperative creates a clear demand signal for products and services that help companies achieve compliance. The market's trajectory is defined by the efforts of major technology companies to operationalize these rules, turning a regulatory burden into a new business segment.
China Responsible AI Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The responsible AI market in China is primarily propelled by the government's comprehensive and granular regulatory approach. The Interim Measures for the Management of Generative Artificial Intelligence Services, effective since August 2023, mandate that providers of generative AI services must adhere to socialist core values and prevent content that endangers national security. This regulation creates a non-negotiable demand for software tools and services that can effectively moderate content and align AI outputs with a specific ideological and social framework. Similarly, the Provisions on the Administration of Deep Synthesis Internet Information Services, in effect since January 2023, require deep synthesis service providers to label synthetically generated content. This directly drives demand for technologies like digital watermarking and content provenance tools. The market responds to these rules by developing and implementing the necessary software platforms and services to meet these technical and ethical requirements.
The emphasis on data privacy is another critical driver. China's Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), in force since November 2021, imposes strict obligations on companies to protect personal information and requires specific protocols for automated decision-making. This legal framework directly creates demand for responsible AI solutions that ensure data anonymization, robust privacy-preserving techniques, and transparent user data handling. Companies must invest in these tools to mitigate legal and financial risks, making responsible AI an essential part of their operational and compliance budgets.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge facing the Chinese Responsible AI Market is the technical complexity and high cost associated with meeting regulatory requirements. The sheer computational power and vast datasets needed to build and train large-scale AI models that are simultaneously compliant and performant can be a significant barrier for smaller companies. The ongoing need for model auditing, real-time content moderation, and algorithm explainability requires specialized expertise and infrastructure, which can present a substantial financial burden. This creates a headwind that may concentrate market power in the hands of large corporations with the resources to invest in comprehensive, responsible AI platforms.
This challenge, however, presents a distinct opportunity for a specific market segment: Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms that offer responsible AI tools. Companies that can provide a scalable, accessible, and cost-effective way for enterprises to manage their compliance needs will find a receptive audience. There is an opportunity to develop standardized software and services that help companies with everything from automated data anonymization to regulatory-compliant content filtering and algorithmic bias detection. These platforms reduce the barrier to entry for smaller players, allowing them to innovate within the regulatory confines without needing to build a full-stack responsible AI team from scratch.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for China's Responsible AI Market is largely intangible, consisting of software, services, and human expertise. It is not a physical supply chain reliant on raw materials. Instead, the "producers" are the major technology firms and specialized startups that develop responsible AI tools and services. The key "inputs" are high-quality, ethically sourced data for training models; highly specialized AI talent; and computational resources, primarily from cloud providers. The logistical complexities are not about shipping physical goods but about securing access to clean data, recruiting and retaining top-tier AI researchers, and ensuring the seamless integration of responsible AI software into existing IT infrastructures. The central dependency is on the availability of domestic AI talent and a reliable, high-performance computing infrastructure, which are both priorities of the Chinese government's strategic plans.
- Government Regulations:
The Chinese government has established a clear and enforceable regulatory framework that is the single most important factor shaping the demand for responsible AI.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
National |
Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) - Interim Measures for the Management of Generative AI Services |
This regulation is the primary growth catalyst. It requires generative AI service providers to adhere to content and data security standards. This mandates a market for content filtering tools, data security platforms, and model auditing services that ensure compliance with state-defined "core socialist values" and prevent the dissemination of "illegal information." |
|
National |
Provisions on the Administration of Deep Synthesis Internet Information Services |
This rule directly creates demand for specific technological solutions. By requiring that deepfakes and other synthetically generated content be clearly labeled, the regulation compels companies to adopt and integrate digital watermarking and content provenance tools. This shifts the market trend from purely creative AI tools to those that are transparent and verifiable. |
|
National |
Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) |
PIPL directly impacts the BFSI and Healthcare sectors by imposing strict rules on the collection, processing, and use of personal data. This legislation creates a strong demand signal for responsible AI tools focused on data anonymization, privacy-preserving machine learning, and transparent algorithmic decision-making, as companies in these sectors must demonstrate legal compliance to operate. |
China Responsible AI Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component: Software Tools & Platforms
The software tools and platforms segment is a primary driver of the Chinese Responsible AI market, stemming directly from the need for companies to operationalize regulatory compliance. This segment is not about the AI models themselves but the supplementary software that ensures their responsible deployment. The trend is focused on tools for data governance, including platforms that automate data anonymization and manage consent for data usage, which is a key requirement of the PIPL. Furthermore, there is a strong demand for algorithm auditing software, which allows companies to test their AI models for bias, fairness, and transparency, as required by regulators. These platforms provide a critical layer of assurance, enabling companies in sectors like BFSI and healthcare to deploy AI systems that process sensitive personal data without violating stringent privacy laws. As government mandates become more prescriptive, the demand for these specialized, compliance-focused software tools will continue to accelerate, making this segment the most dynamic and commercially significant part of the market.
- By End-User: Government and Public Sector
The government and public sector is a significant and growing end-user segment for responsible AI. The growth is driven by two key imperatives: using AI to enhance public services and ensuring this technology is deployed in a manner that maintains public trust and national security. Government agencies are deploying AI for smart city management, public security, and administrative efficiency. The demand for responsible AI in this context is centered on ensuring that these systems are transparent, accountable, and free from bias, particularly in applications that affect citizens directly. For example, AI systems used in urban planning or traffic management must be auditable and their decisions explainable to maintain public confidence. The government's own regulatory bodies, such as the CAC, are also end-users of responsible AI tools, as they require sophisticated software to monitor and enforce compliance across the digital landscape. This dual role—as both a regulator and an adopter—makes the public sector a major force in shaping and stimulating demand.
China Responsible AI Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape for responsible AI in China is dominated by the country's technology giants, which possess the resources and technical expertise to integrate compliance into their core offerings.
- Alibaba Group: Alibaba's strategic positioning in responsible AI is deeply integrated with its cloud services. The company's ESG report highlights its focus on "Responsible Technology," which includes using AI to promote sustainability and digital inclusion. Alibaba Cloud offers tools and platforms that help its clients develop and deploy AI models in a compliant manner. This strategy leverages its dominant cloud infrastructure to create a comprehensive ecosystem for its clients. By embedding responsible AI features directly into its cloud products, Alibaba creates a demand for its services by making it easier for customers, particularly those in BFSI and healthcare, to meet their regulatory obligations without having to build the infrastructure themselves.
- Tencent Holdings: Tencent's approach to responsible AI is centered on its dual role as a consumer platform giant and a B2B cloud provider. The company's recent developments, such as the global rollout of its Agent Development Platform (ADP) in September 2025, show a focus on providing AI tools that are not only powerful but also "business-aligned." This implies a focus on integrating security, stability, and ethical considerations into the core of their offerings. Tencent’s strategy is to address the demand for compliant, scalable AI by offering a suite of intelligent agent applications and "SaaS+AI" solutions that can be customized for specific industry needs, thereby positioning itself as a leader in providing responsible AI tools for enterprise use.
China Responsible AI Market Developments:
- September 2025: Tencent announced the global rollout of its new scenario-based AI capabilities and the Agent Development Platform 3.0 (ADP), which empowers enterprises to build and integrate intelligent, autonomous AI agents into their workflows. This development signifies a major move by a Chinese tech leader to provide responsible, business-aligned AI solutions on a global scale.
China Responsible AI Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.375 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 4.855 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR during the forecast period |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment, End-User |
| Companies |
|
China Responsible AI Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Software Tools & Platforms
- Services
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- On-Premises
- Cloud
- BY END-USER
- Healthcare
- BFSI
- Government and Public Sector
- Automotive Industry
- IT and Telecommunication
- Others