Report Overview
Global Molded Interconnect Devices Highlights
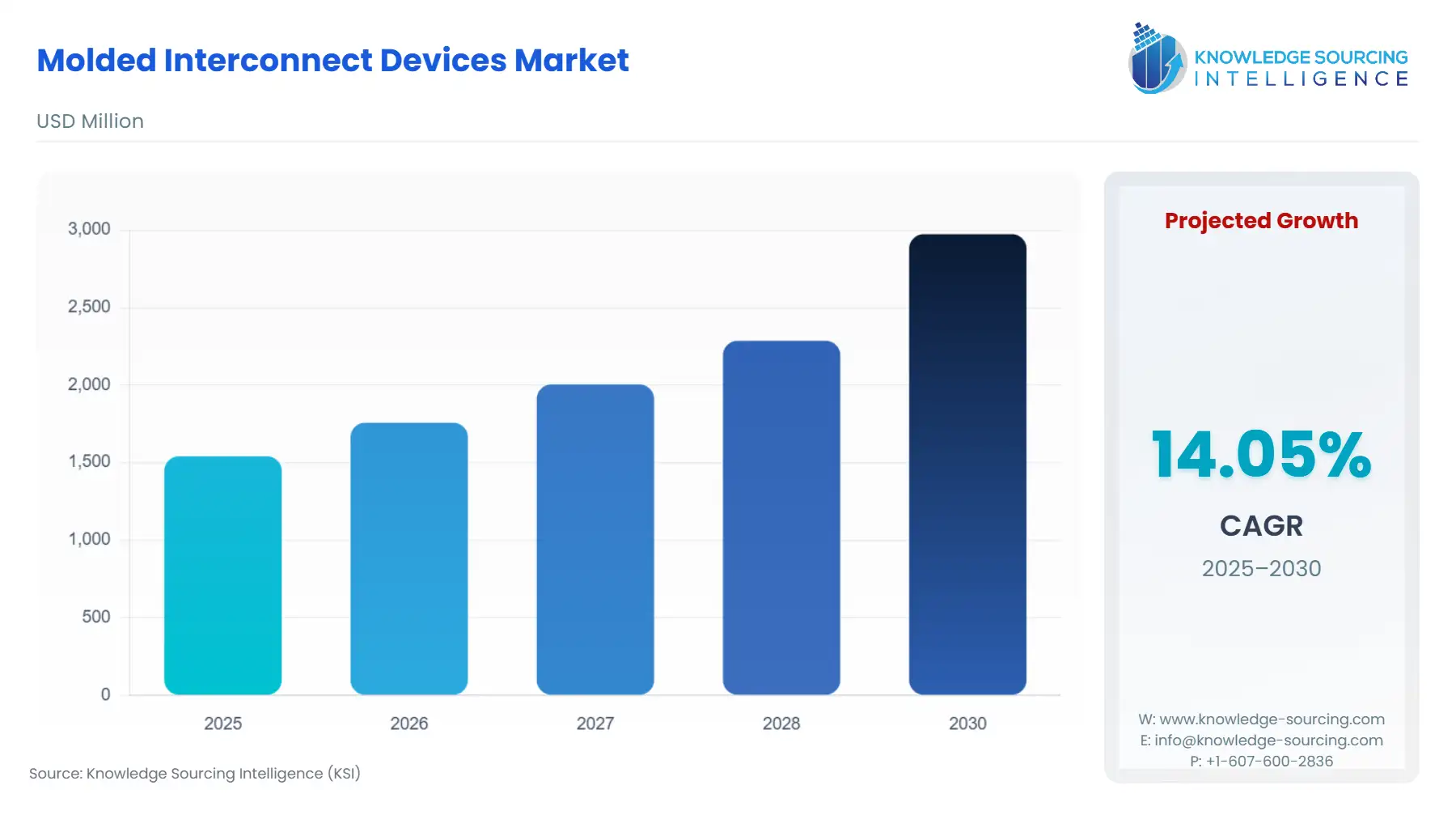
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Size:
The Molded Interconnect Devices Market is anticipated to increase from USD 1.541 billion in 2025 to USD 2.974 billion by 2030, registering a 14.06% CAGR.
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Introduction
Molded Interconnect Devices (MIDs) integrate electrical circuitry onto three-dimensional injection-molded parts, enabling function consolidation (antenna, sensor, connector features) and part count reduction. Industry equipment vendors (e.g., LPKF) and interconnect manufacturers (Amphenol, TE, Molex) position MIDs where miniaturization, RF performance and weight savings converge—notably in telecom and automotive. Regulatory constraints on plastics and plating chemistries further shape OEM sourcing and qualification schedules, making demand for MID-qualified materials a function of both technology adoption and compliance timelines.
Global Molded Interconnect Devices Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Miniaturization and RF integration drive direct demand for MIDs: 5G/mmWave antenna requirements and multi-antenna MIMO arrays favor 3D printed/laser-activated conductors over conventional PCBs, increasing volume for LDS-compatible parts (academic studies on LDS-MIDs for mmWave demonstrate this use case). Automotive electrification and on-vehicle sensing require lighter, integrated interconnects that reduce harness complexity; this pushes OEMs toward MID solutions that replace multi-component assemblies. Finally, materials suppliers (conductive masterbatches, plating chemistries) and equipment vendors expanding capability—documented in company releases—translate into faster OEM adoption because qualification lead times shorten when suppliers offer MID-grade processes and chemistries.
- Challenges and Opportunities
U.S. tariff structures continue to exert measurable pressure on the cost base of molded interconnect device (MID) production, particularly for manufacturers dependent on Asian supply chains for precision-molded plastics, plated components, and electronic subassemblies. Section 301 tariffs on Chinese-origin electronics and plastic components elevate the landed cost of MID inputs, prompting OEMs to shift demand toward suppliers with North American molding and plating capacity to reduce duty exposure and customs-cycle delays. Tariffs applied to various categories of injection-molded plastic parts and electronic connectors increase procurement costs across prototyping, antenna modules, and sensor-integrated MID parts, resulting in tighter sourcing strategies and longer vendor-qualification timelines. These duties also incentivize contract manufacturers to reconfigure sourcing toward Mexico, the U.S., or tariff-neutral jurisdictions, strengthening regional production ecosystems.
Headwinds come from materials regulation and qualification cycles: RoHS/REACH and ECHA flame-retardant initiatives force reformulation of plastics and finishes, delaying supplier approvals and temporarily suppressing demand until replacements are validated. Manufacturing complexity (precision molding + selective metallization) raises initial per-part cost versus PCBs for low volumes, constraining early adoption. Opportunities exist where functionality consolidation delivers system-level cost and weight savings (automotive EV range, mobile handset space savings) and where suppliers offer integrated material+process solutions—companies that supply both MID-grade polymers and plating/activation chemistries can shorten OEM qualification windows, thereby accelerating demand.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
MIDs depend on specialty filled plastics (LDS-activatable polymers, conductive masterbatches) and plating chemistries (copper, nickel, precious-metal finishes). Price volatility in copper and palladium affects plating cost per part; meanwhile, ECHA/REACH actions on some brominated flame retardants and plasticizers drive migration to higher-cost, compliant alternatives. Suppliers that vertically integrate or maintain localized compound and plating capacity reduce exposure to ocean freight and tariff shocks; this shifts OEM demand toward suppliers with regional production footprints to shorten lead times and reduce re-qualification risk. The result: short-term price pressure on compliant polymers and plating materials, but strategic customer lock-in for suppliers that can supply qualified, compliant materials.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The MID supply chain layers: polymer compounders (LDS-capable resins and conductive masterbatches), laser/equipment OEMs (LDS equipment), selective metallizers/plating houses, and MID integrators/contract manufacturers. Key production hubs for polymers and plating are Europe (Germany, France), North America and China; LPKF (Germany) is a central equipment supplier for LDS. Logistical complexity arises from tight coordination of molding schedules, laser activation capacity and plating throughput; long supplier qualification times and regulatory re-testing create bottlenecks when material changes occur. OEMs therefore favor suppliers with multi-region capacity and technical support to reduce qualification cycles and inventory holding costs.
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
RoHS Directive (2011/65/EU & amendments) — European Commission |
Restricts hazardous substances in EEE; forces substitution of certain halogenated flame retardants and heavy-metal finishes. OEMs delay MID rollouts until polymers and plating finishes meet RoHS thresholds, reducing short-term demand for non-compliant materials. |
|
European Union / ECHA |
REACH / ECHA flame-retardant strategy |
Candidate restrictions and group-approach regulation for flame retardants increase re-qualification costs for MID plastics, raising demand for approved, high-performance alternatives and certified suppliers. |
|
United States |
FCC Equipment Authorization (47 CFR Part 2) |
Antenna-integrated MIDs used in wireless devices require equipment authorization; conformity testing and documentation affect time-to-market and favor suppliers who provide design/EMC support. |
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Segment Analysis
- By Technology — Laser Direct Structuring (LDS)
LDS is the dominant MID technology for high-frequency and high-precision applications because it allows fine conductive traces on three-dimensional molded parts. Academically documented work on LDS-MID manufacturing for mmWave antennas demonstrates LDS’s suitability for 5G MIMO and compact RF modules. Demand drivers specific to LDS include telecom operators’ rollouts of mmWave/5G infrastructure (which create volume demand for compact, high-frequency antennas) and OEM product trends toward surface-integrated antennas in consumer devices and IoT nodes. LDS increases OEM demand for compatible polymers and selective metallization partners, because designers require both dimensional stability for high-frequency performance and plating processes with predictable conductivity and adhesion. Equipment availability (LPKF) and established supplier toolchains reduce process risk and shorten adoption cycles; therefore, demand for LDS MIDs is concentrated where suppliers and equipment are co-located or have proven reference designs that meet regulatory and EMC tests.
- By Application — Automotive
Automotive is a high-value application because MIDs replace multi-component harnesses, support embedded antennas and sensors, and reduce weight—directly affecting EV range and assembly cost. Regulatory drivers (UNECE R10 EMC requirements; safety and environmental rules) mean OEMs demand suppliers who can supply MID parts that pass vehicle-level EMC and durability testing. Electrification pushes more electronics into the vehicle body and powertrain, increasing instances where MIDs can combine mechanical and electrical function (e.g., exterior antennas, illumination modules with integrated connectors). Procurement behavior in automotive favors tier-1 suppliers with qualified material chains and regional capacity to satisfy just-in-time assembly. Consequently, MID demand in automotive is not only a function of unit growth (EVs and connected cars) but also of the supplier’s ability to provide certified materials, stable plating processes, and assembly references that reduce integration risk and shorten validation timelines.
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis
U.S. demand is shaped by FCC equipment authorization and rising EV penetration (IEA / EIA data). OEMs require MID suppliers with FCC/EMC support and local qualification capabilities; suppliers with U.S. plating and compounding shorten validation cycles.
- Brazil Market Analysis
Automotive manufacturing clusters drive regional demand for MID materials that support lightweighting; local supply options and proximity to tier-1s reduce logistics and qualification friction.
- Germany (Europe) Market Analysis
Germany’s automotive and industrial electronics sectors create concentrated demand. EU RoHS/REACH require compliant materials; EU-based compounders and metallizers are preferred for faster regulatory alignment.
- Middle East & Africa (UAE) Market Analysis
Telecom infrastructure and smart city projects (UAE operator investments) increase demand for MID antennas in urban deployments; local projects favor suppliers who can meet telecom authorization and deliver localized service.
- China Market Analysis
Massive 5G base-station rollouts (MIIT data: multi-million 5G sites by end-2024) and the largest EV market globally drive high demand for MIDs in antennas, infotainment and sensor modules. Local supply and certification shorten time-to-deployment, favoring manufacturers with China-based compounding and plating.
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
Major companies from the Table of Contents: TE Connectivity, LPKF Laser & Electronics, Molex, Lanxess, MacDermid (Element Solutions / MacDermid Alpha), RTP Company, Amphenol.
- TE Connectivity (profile): TE offers broad interconnect and sensor portfolios and public corporate materials state deep involvement in connectivity solutions across mobility and telecom sectors; TE’s global engineering footprint positions it to supply MID-adjacent systems and device integration support.
- LPKF Laser & Electronics (profile): LPKF manufactures LDS equipment and positions LDS as the enabling process for 3D MID antennas and RF applications; company filings and product pages confirm its central role in supplying laser systems used to activate MID surfaces.
- Amphenol (profile): Amphenol provides RF interconnects, antennas and cable assemblies; the company completed the acquisition of Carlisle Interconnect Technologies in May 2024 (company press release), signaling consolidation and expanded harsh-environment interconnect capabilities that intersect with MID applications (antenna/connector integration).
Molded Interconnect Devices Market Developments
- May 2024 — Amphenol Corporation completes acquisition of Carlisle Interconnect Technologies (CIT). (M&A; Amphenol press release)
- Nov 2024 — LPKF showcases LDS / 3D-MID innovations at electronica 2024. (Product/technology showcase; LPKF press release)
- Apr 2024 — MacDermid Alpha launches Low Alpha Tin plating solutions (product launch targeted at semiconductor and high-reliability interconnects). (Company newsroom press release)
Model-Based Enterprise Market Segmentation
- By Process
- Laser Direct Structuring
- 2-shot molding
- Film Techniques
- By Product Type
- Antennae and Connectivity Modules
- Sensors
- Connectors and Switches
- Lighting
- Others
- By Application
- Telecommunication
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Medical Devices
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Others
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- South Korea
- Taiwan
- Others
- North America