Report Overview
Global Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Highlights
Global Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Size:
The Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market is expected to grow from US$5.929 billion in 2025 to US$7.923 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 5.97%.
The Global Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market provides a critical industrial solution for extending the shelf life of liquid food products, primarily through the rapid heating of products like milk or juices to temperatures of 135°C to 150°C for a very short duration (1-4 seconds). This stringent thermal treatment effectively achieves commercial sterility by inactivating nearly all spores, microorganisms, and enzymes, fundamentally changing the product's logistical and distribution profile. The strategic value of UHT processing equipment lies not in the treatment itself, but in its ability to decouple product perishability from cold-chain logistics, thereby facilitating broad geographical distribution and lowering operating expenses for manufacturers. The technology is an infrastructural imperative for manufacturers targeting mass markets, especially those expanding into regions with underdeveloped or unreliable refrigeration networks.
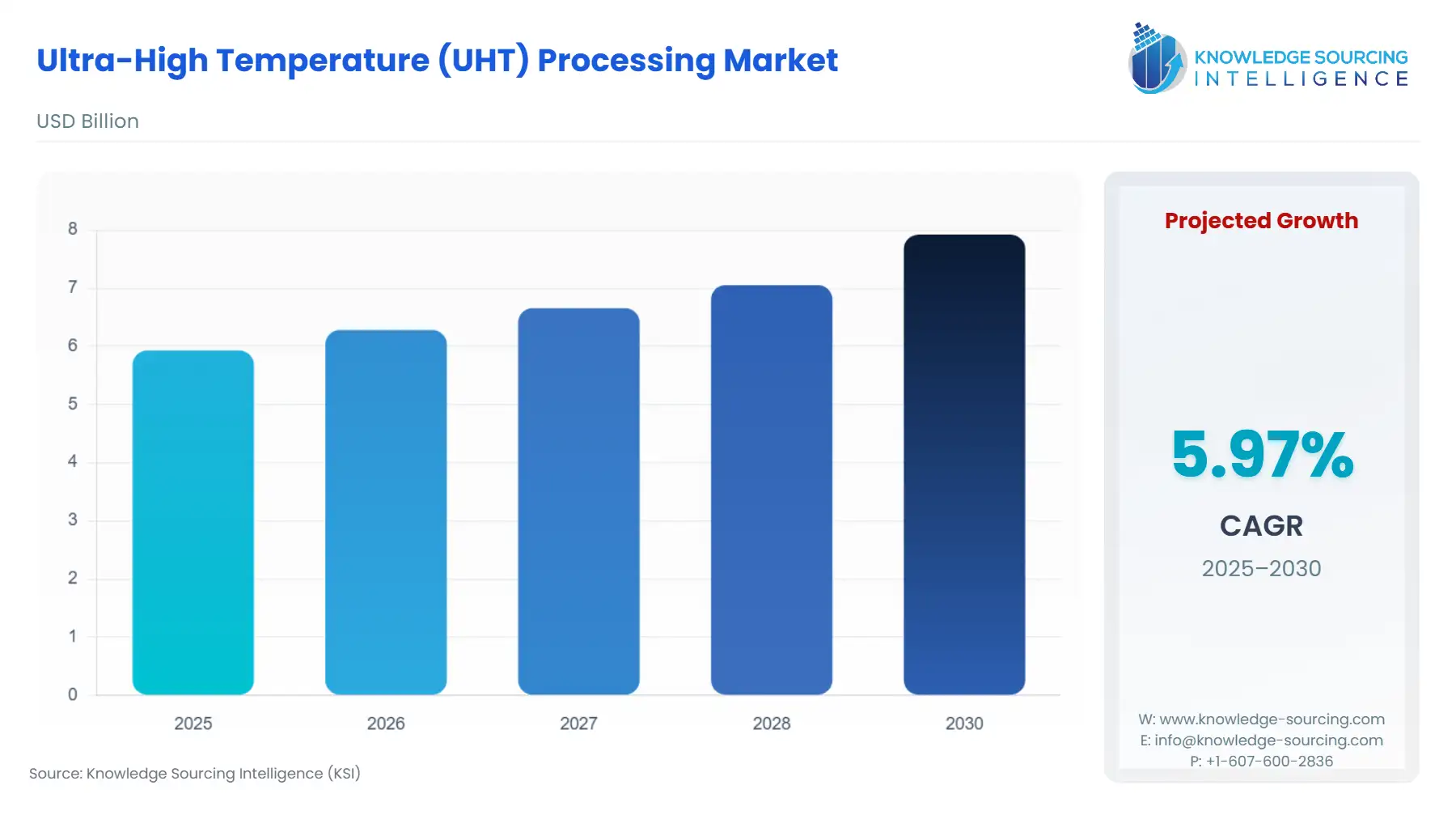
Global Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
Extended shelf life, achievable without refrigeration, forms the primary catalyst, directly increasing demand for UHT processing equipment by enabling manufacturers to penetrate geographically distant markets and reduce cold-chain infrastructure investment. Rapid urbanization in developing economies, coupled with a corresponding rise in disposable income and a growing demand for packaged, ready-to-consume liquid foods, compels food and beverage processors to adopt UHT technology to meet mass-market convenience demand. Additionally, global regulatory bodies' and consumers' stringent focus on verifiable food safety and microbiological stability compels producers of perishable liquids like milk and juices to invest in the UHT process to meet safety and quality compliance standards, thereby securing consumer trust.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge is the unavoidable impact of high temperatures on the organoleptic and nutritional quality of some liquid foods, which can reduce consumer acceptance in markets prioritizing fresh flavor profiles. This quality constraint can limit demand for UHT-treated products in high-value, quality-sensitive segments. However, a key opportunity lies in the burgeoning market for plant-based beverages (e.g., oat, almond, soy milk). As these non-dairy segments expand, UHT technology is essential for ensuring their microbiological stability and achieving ambient-temperature distribution, directly increasing demand for adaptable UHT systems capable of processing diverse viscosities and compositions with minimal thermal degradation.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The UHT processing market centers on specialized hardware and is consequently subject to raw material and component pricing dynamics. Key materials include high-grade stainless steel (specifically AISI 304 and 316) for plate, tubular, and shell-and-tube heat exchangers, and associated piping, as this material is mandated for hygienic and corrosion-resistant contact surfaces. Price volatility in the global nickel and chromium markets, essential alloying elements for stainless steel, directly impacts the capital expenditure for new UHT lines. Furthermore, advanced sensor technology and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) represent key high-value electronic components whose global supply chain constraints and pricing influence the final cost and sophistication of automated UHT systems.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain is highly concentrated in specialized equipment manufacturing centers in Europe (Germany and Sweden) and Asia (China). This model is characterized by long lead times, as UHT systems are complex, custom-engineered solutions incorporating high-precision components like heat exchangers, homogenizers, and aseptic valves. Logistical complexities arise from the necessity of transporting large, heavy, and often modular stainless steel machinery globally, requiring specialized freight. The market’s dependency on a limited number of specialized engineering firms for complex aseptic components (valves, pumps) creates a potential choke point, impacting the speed and cost of capacity additions for global food processors.
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
Grade "A" Pasteurized Milk Ordinance (PMO) / FDA |
The PMO defines the standards for all aspects of UHT milk processing, sanitation, and packaging. This standardization drives demand for equipment compliance, ensuring UHT systems meet verifiable microbiological standards required for interstate commerce. |
|
European Union |
Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 (Food Hygiene) |
This regulation specifies the precise temperature and time parameters (135°C for 1 second) necessary for UHT treatment to achieve commercial sterility, directly setting the functional requirements and performance envelope for all UHT equipment used in EU food production. |
|
India |
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) Regulation |
FSSAI regulations define the required microbiological standards for UHT milk and other products, compelling Indian dairy and juice processors to invest in validated UHT lines to meet domestic quality assurance and shelf-life claims, thus accelerating capital investment. |
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Segment Analysis
- By Method: Direct
The Direct UHT processing method, which encompasses both steam injection and steam infusion, constitutes a high-value, albeit smaller, segment of the market. This technology drives specific demand from processors focused on premium liquid foods. The direct method involves mixing steam directly into the product, achieving ultra-high temperatures almost instantaneously and cooling the product just as quickly via flash cooling in a vacuum. This rapid heating and cooling cycle is the critical demand driver, as it results in minimal thermal load exposure on the product. This minimal thermal stress reduces flavor deterioration and preserves the nutritional quality (e.g., vitamins) of temperature-sensitive ingredients more effectively than indirect methods, making it the preferred choice for specialty milks, high-viscosity creams, and high-value nutritional drinks where organoleptic integrity is a competitive differentiator.
- By Food Type: Milk and Dairy Products
The milk and dairy products segment represents the foundational and most robust application for UHT processing technology. The primary growth driver is the critical need for a stable, long-life milk product that bypasses the logistical and cost constraints of the cold chain. UHT treatment transforms perishable raw milk, which has a shelf life of days, into a commercially sterile product with a shelf life extending to months. This capability directly enables dairy processors to stabilize supply in high-demand, high-risk environments, and to efficiently transport product across vast distances, particularly in developing countries with fluctuating power supply and inadequate refrigeration. Furthermore, the growth of value-added products like flavored milk and single-serve nutritional milk shakes also necessitates UHT processing to ensure both safety and extended retail viability.
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis
The US UHT processing market experiences growth primarily driven by the increasing consumer preference for convenience and specialty milk products (e.g., organic, lactose-free, and plant-based beverages). Local demand factors include the established Grade "A" Pasteurized Milk Ordinance (PMO) standards, which require strict equipment validation and operational protocols, maintaining a high entry barrier for new processors but ensuring quality. UHT milk is also critical for institutional feeding programs and emergency relief supplies, where ambient storage is a logistical necessity. Growth is characterized by processors seeking high-throughput, automated systems that integrate seamlessly with existing sophisticated packaging lines.
- Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil represents a significant demand center due to its vast geographical distances and uneven refrigeration infrastructure, making UHT processing an economic imperative for dairy and juice distribution. Local factors include strong regulatory oversight by ANVISA (National Health Surveillance Agency) on food safety, which ensures market stability but requires compliant technology investment. The high domestic consumption of UHT milk, favored for its long shelf life in a climate where power outages can compromise chilled products, sustains high equipment utilization and steady investment in new UHT lines by domestic and multinational food processors.
- United Kingdom Market Analysis
The UK market is mature, but continuous investment is driven by the dynamic shift in consumer preferences, particularly the explosive growth of fortified and plant-based milk alternatives (oat, soy, almond). While chilled milk dominates, UHT is essential for specialty product exports and for the supply of aseptic, single-serve formats for the on-the-go consumption segment. Compliance with stringent FSA (Food Standards Agency) and EU-derived hygiene regulations necessitates investment in the latest-generation, traceable UHT technology, driving a preference for highly automated and energy-efficient indirect systems.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The Saudi Arabian UHT market is governed by the need for logistical resilience in an extremely hot environment where cold-chain integrity is challenging and expensive to maintain. Local demand factors include the high reliance on imported dairy and beverages, where UHT is the non-negotiable processing standard for ambient sea-freight transport and storage. The Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) enforces strict halal and safety standards, directly compelling manufacturers to adopt verifiable, globally certified UHT systems to meet national import and domestic production requirements for essential goods.
- China Market Analysis
China is a critical and rapidly expanding market for UHT processing, spurred by accelerating urbanization and the massive scale required for milk and beverage production. Local demand is critically driven by a high-profile historical focus on food safety, which mandates robust, highly reliable sterilization techniques like UHT to restore consumer confidence. The market requires large-scale, high-capacity UHT production lines, and domestic manufacturers are rapidly increasing their capacity for complex systems, often focusing on advanced automation to lower operational human-error risks in mass production environments.
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Global UHT Processing Market exhibits a highly competitive landscape dominated by a few multinational conglomerates that command superior market share through technological leadership and integrated offerings. The competitive edge is derived from offering complete, verifiable aseptic solutions, including processing, packaging, and service, rather than just standalone UHT units. Firms compete on energy efficiency (e.g., heat regeneration rates), the minimization of fouling, automation capabilities (Industry 4.0 integration), and the ability to process a broader array of food viscosities with minimal quality degradation.
- Tetra Laval International S.A
Tetra Laval International S.A., through its subsidiary Tetra Pak, is the undeniable market leader, strategically positioning itself as a comprehensive provider of integrated food processing and packaging solutions. Their competitive advantage stems from the seamless, proprietary integration of UHT processing equipment with their universally recognized aseptic carton packaging systems. Key offerings include the Tetra Therm Aseptic processing units, which utilize both indirect and direct heating, tailored for high-volume dairy and juice processing. This end-to-end control of the aseptic chain—from sterilization to packaging—creates a significant switching barrier for customers and ensures product safety compliance across global markets.
- GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft
GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft maintains a dominant position as a technology provider focused on high-specification process engineering, particularly in the dairy and beverage sectors. GEA competes by offering a broad, highly customizable portfolio of UHT systems, including the GEA Vaporator for direct heating and advanced plate and tubular heat exchangers for indirect heating. The company’s strategic focus is on maximizing production efficiency, minimizing product loss, and offering advanced automation and cleaning-in-place (CIP) technology. GEA’s strength lies in serving large-scale, complex food processing plants that require bespoke engineering solutions for varied product ranges, from milk to specialized infant formula.
- SPX Flow
SPX Flow is a key competitor specializing in the design and manufacture of highly engineered components and systems for the industrial and process markets, including a strong presence in UHT technology. Their strategic positioning focuses on the APV brand of UHT systems, emphasizing robust, modular designs, particularly tubular and plate heat exchangers known for flexibility in handling a wide range of liquid food products. SPX Flow targets processors demanding reliable, easy-to-maintain equipment with excellent heat recovery capabilities. Their product differentiation centers on advanced thermal processing technology that provides verifiable performance with optimized capital and operational expenses.
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Developments
- November 2025: Tetra Pak introduced its next-generation automation and digital portfolio, Tetra Pak® Factory OS™. This system is designed to create AI-ready, digitally connected food and beverage factories. The platform provides real-time, contextualized insights for smarter, faster decision-making, aiming to boost operational efficiency in UHT processing and beyond.
- April 2025: Malo Dairy, a subsidiary of SILL Enterprises in France, migrated its UHT milk line to Elopak's sustainable Pure-Pak® cartons. This move was made to enhance Malo's operational efficiency and support its sustainability goals. The switch reflects a growing trend towards eco-friendly packaging solutions for long-life UHT products.
Global Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) Processing Market Segmentation
By Method
- Direct
- Indirect
By Food Type
- Milk and Dairy Products
- Juices
- Wine
- Others
By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Israel
- Saudi Arabia
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- South Korea
- India
- Others