Report Overview
Iron Chelates Market Size, Highlights
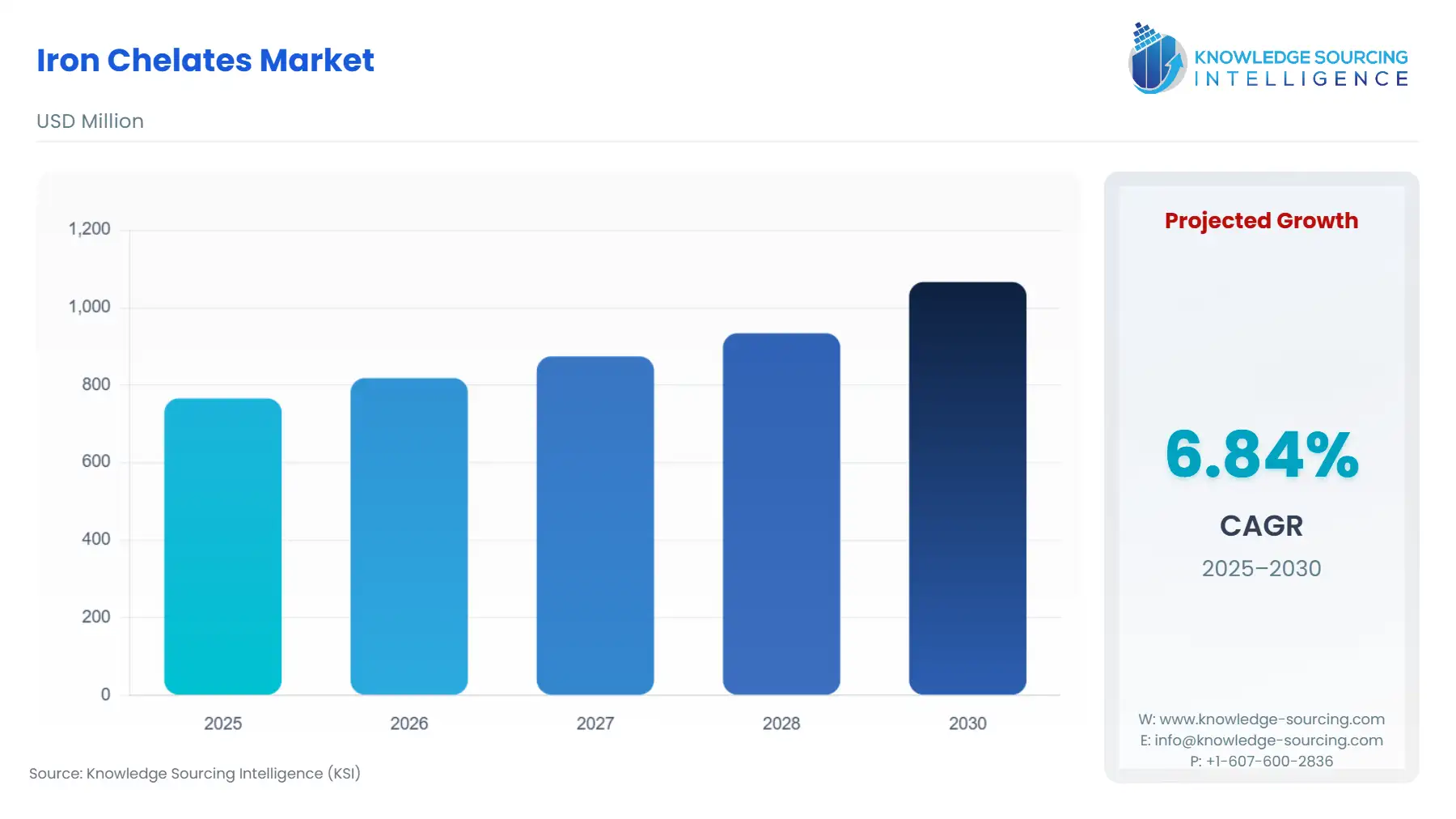
Iron Chelates Market Size:
Iron Chelates Market is projected to expand at a 6.84% CAGR, achieving USD 1,066.213 million by 2030 from USD 765.893 million in 2025.
The Iron Chelates Market is fundamentally driven by the imperative to correct ubiquitous iron deficiency, or chlorosis, across global agricultural land and within livestock nutrition programs. Iron, while abundant in soil, is frequently rendered unavailable to plants, especially in calcareous or alkaline conditions, necessitating the use of synthetic chelating agents (such as EDTA, DTPA, and EDDHA) to maintain the metal ion in a stable, soluble, and bioavailable form. As crop yields and quality face increasing pressure from climate variability and intense farming practices, the prophylactic and corrective application of these specialized chemical compounds has transitioned from a supplemental measure to a critical component of precision Crop Nutrition, extending its reach across high-value Fruits & Vegetables and specialized Cereals & Grains cultivation.
Iron Chelates Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary driver accelerating growth is the pervasive issue of iron chlorosis in high-pH agricultural soils globally, which directly renders simple iron salts ineffective, compelling the shift to stable iron chelates. Approximately 30% of the world’s arable land suffers from calcareous conditions, creating a non-negotiable requirement for high-stability EDDHA chelates, which maintain iron availability up to pH 11. Furthermore, stringent EU and USDA regulations governing Animal Feed Additives for iron content and bioavailability create a captive demand for iron chelates like ferrous glycine, ensuring effective treatment of widespread anemia in high-productivity livestock. This twin-engine of agronomic necessity and nutritional regulation directly translates into demand for superior chelated products.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary obstacle impacting market adoption is the high cost differential between synthesized iron chelates and traditional, lower-efficacy micronutrient salts, constraining their use in lower-value Cereals & Grains. This constraint is compounded by the price instability of petrochemical-derived raw materials, which producers often pass to farmers. The key opportunity, however, is the increasing demand for sustainable chemistry, pushing innovation toward biodegradable chelating agents like IDHA (iminodisuccinic acid). These environmentally superior alternatives, which degrade naturally after use, mitigate the environmental impact concerns associated with persistent compounds like EDTA, thereby opening new market opportunities in Europe and other regions with evolving environmental mandates.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The pricing dynamics of Iron Chelates are structurally tied to the cost of two core chemical inputs: elemental iron salts (ferrous or ferric sulfate) and the organic chelating agents. Ethylenediamine, a petrochemical derivative used to synthesize the backbone of EDTA and EDDHA chelates, represents the most significant source of price volatility. Fluctuations in crude oil and natural gas prices directly translate into changes in the cost of ethylenediamine, with verified price swings impacting manufacturers' cost of goods sold. Since iron chelates are specialty chemicals, they command a high premium over commodity iron salts; thus, any upward pressure on raw materials is frequently passed to the end-user, limiting affordability for large-scale Oilseed & Pulses production.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for Iron Chelates is concentrated, operating on a few key production hubs for the essential chelating agents. China, Germany, and France are major global exporters of finished iron chelates, indicating a dependence on Asian and European chemical manufacturing infrastructure. The process requires specialized reactors and quality control to manage the chelation reaction between the organic agent and the iron ion, leading to high capital costs for producers. Logistical complexity arises from the need to transport highly concentrated Powder & Granules and specialized Liquid formulations globally to meet season-specific agricultural demand across North America and Asia-Pacific, requiring specialized regulatory compliance for agricultural chemicals in transit.
Iron Chelates Market Government Regulations
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1412 |
Compulsory Feed Demand: Authorizes the use of specific chelates, like Iron(III) citrate chelate, as a Feed Additive for piglets. This regulatory approval mandates its use under specific conditions, creating an immediate and continuous procurement demand in the European animal nutrition sector. |
|
European Union |
Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) (2024) |
Supply Chain Transparency: Requires large companies operating in the EU, including major chemical producers, to conduct due diligence on human rights and environmental impacts throughout their supply chain. This drives demand for Iron Chelate producers to adopt auditable traceability systems, favoring suppliers who can verify ethical sourcing of raw materials. |
|
United States |
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) |
Product Registration and Safety: Requires all pesticide and fertilizer products (including many chelated micronutrient formulations) to undergo stringent registration processes under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This increases the barrier to entry for new chelates, favoring established manufacturers with verified safety and efficacy data. |
Iron Chelates Market Segment Analysis
- By Type: EDDHA Iron Chelates
The EDDHA (Ethylenediamine-N, N′-bis(o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid)) segment is defined by its unparalleled chemical stability, making it the most expensive but often non-substitutable iron chelate. Growth is acutely concentrated in regions struggling with alkaline soils (pH> 7.5), which typically render other chelates like EDTA ineffective due to iron precipitation. EDDHA’s high stability ensures the iron remains bioavailable for Fertigation and soil application, delivering essential micronutrients directly to the roots of highly sensitive crops. This attribute is non-negotiable for high-value specialty crops, particularly Fruits & Vegetables such as citrus, grapes, and stone fruits, where chronic iron chlorosis severely compromises yield and market quality. The efficacy of EDDHA in these arduous environments makes its procurement a technical imperative, insulating it from simple price-based competition with lower-grade iron sources.
- By Crop Type: Fruits & Vegetables
The Fruits & Vegetables segment represents a critical and rapidly expanding demand center for the Iron Chelates Market, driven by the high economic value of the crops and their pronounced sensitivity to iron deficiency. Unlike commodity Cereals & Grains, a minor incidence of iron chlorosis in fruits or vegetables directly leads to visible symptoms (interveinal yellowing, stunted growth), resulting in immediate and significant loss of market value and harvestable yield. This economic risk compels producers of high-value crops to integrate iron chelates into their fertilization programs as a preventative measure. The necessity is particularly high for quick-acting Liquid formulations suitable for Foliar Application, providing rapid symptom correction in the event of an acute deficiency, demonstrating a clear focus on product quality and immediacy of effect over simple cost minimization.
Iron Chelates Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis
The US market is highly segmented. In the Western and Southwestern US (California, Arizona), the prevalence of high-pH, calcareous soils creates high-intensity demand for premium EDDHA chelates for high-value Fruits & Vegetables and specialized horticulture. Conversely, the demand in the Midwest is concentrated in bulk Cereals & Grains and Oilseed & Pulses production, favoring cost-effective EDTA and newer biodegradable chelates for less-severe deficiencies. The market is also heavily influenced by the robust domestic Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical sectors, where highly pure chelated iron compounds are procured as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and supplement minerals, driving distinct high-purity demand streams.
- Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil's iron chelate demand is characterized by large-scale mechanized Cereals & Grains and Oilseed & Pulses (soybean) production. The primary growth factor is the sheer scale of the agricultural footprint, which requires massive volumes of micronutrients applied via Fertigation. Demand centers on Powder & Granules forms of EDTA and DTPA for bulk soil applications. The local market places a high value on logistical efficiency and cost-per-hectare, favoring high-concentration products that simplify application in vast, often remote, agricultural zones, although high-value crops (coffee, citrus) still require premium solutions.
- Germany Market Analysis
The German market is distinguished by strict regulatory standards and a strong focus on environmental sustainability. The need for Iron Chelates in agriculture is increasingly shifting away from non-biodegradable EDTA towards eco-friendly alternatives like IDHA, anticipating future regulatory pressure. Furthermore, Germany's sophisticated livestock and companion animal industries create substantial demand for precisely formulated, regulatory-compliant chelated iron Feed Additives, ensuring that compliance with EU nutritional regulations (e.g., Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003) is a non-negotiable procurement criterion, driving demand for high-purity chemicals.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The Saudi Arabian market is driven by the necessity of protected agriculture and specialized high-intensity food production systems (greenhouses, vertical farms) to achieve national food security goals. Given the arid, high-saline, and alkaline soil conditions, the efficacy of EDDHA and other highly stable chelates for Fertigation is essential. The requirement is not subject to high volume but instead focuses on quality and performance within closed-loop systems, where minimizing input waste and maximizing nutrient uptake under extreme environmental stress are the primary procurement drivers.
- China Market Analysis
The Chinese market is characterized by two powerful, contrasting forces: immense volume agricultural output and stringent quality requirements for Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical ingredients. The agricultural sector creates massive demand for commodity EDTA and DTPA for bulk applications. Concurrently, the domestic pharmaceutical industry, under increasing pressure for data integrity and quality control from bodies like the US FDA, drives a demand for exceptionally high-purity chelated iron compounds, requiring suppliers to provide comprehensive regulatory dossiers and guaranteed trace metal limits.
Iron Chelates Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Iron Chelates market exhibits a competitive structure where large, diversified chemical manufacturers coexist with specialized micronutrient producers. Competition is defined by the ability to manage raw material volatility, offer a complete portfolio of chelating agents (EDTA, DTPA, EDDHA) to match varied soil pH requirements, and maintain regulatory compliance across global jurisdictions (EU REACH, US EPA). Differentiation increasingly occurs through the development and marketing of novel, environmentally superior products.
- BASF SE
BASF SE maintains a strategic position as a global leader in integrated chemical production. The company leverages its Verbund network to secure the supply of precursors, such as ethylenediamine, giving it a cost advantage in producing the foundational EDTA and DTPA chelating agents. BASF's strategy focuses on a broad product offering across multiple end-use segments, including agriculture, personal care, and industrial applications. Its extensive global capacity expansion, particularly in Asia-Pacific, ensures it can meet high-volume demand while complying with evolving sustainability standards for its various chemical intermediates.
- Yara International ASA
Yara International ASA strategically focuses on the Fertigation and Foliar Application segments, positioning itself as an integrated crop nutrition specialist. Yara’s demand is directly influenced by its broad portfolio of micronutrient fertilizers, where iron chelates are integrated into proprietary blends to solve specific field-level nutritional problems. The company's competitive advantage stems from its direct relationship with farmers through agronomic services, driving demand for high-performance products that guarantee yield and quality results in high-value Fruits & Vegetables markets globally.
- Dow Chemical Company
Dow Chemical Company maintains a significant, though indirect, influence on the Iron Chelates market through its role as a core manufacturer of chemical building blocks, including ethylene oxide and its derivatives. Dow's strategic strength lies in its ability to supply high-purity chelating agents like EDTA and DTPA to downstream formulators. The company’s focus is on maintaining high-volume, reliable supply of these essential raw materials, positioning it as a foundational provider in the supply chain, ensuring global capacity and material availability for many of the specialized micronutrient producers.
Iron Chelates Market Developments
- November 2025: BASF SE successfully commenced production of initial products from the core of its Zhanjiang Verbund site in China. This major capacity addition is designed to strengthen BASF's core chemical businesses, improving supply reliability and local-for-local product delivery in the rapidly expanding Asia-Pacific markets.
- November 2024: BASF SE opened a new production line for water-based dispersions in Heerenveen, the Netherlands. This capacity addition utilizes green electricity and aims to serve evolving customer demand for sustainable and low-carbon-footprint chemical products within the European region.
Iron Chelates Market Segmentation:
BY TYPE
- EDTA
- DTPA
- EDDHA
- Others
BY FORM
- Liquid
- Powder & Granules
BY APPLICATION
- Foliar Application
- Fertigation
- Soil Injection
- Seed Dressing
- Others
BY CROP TYPE
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Cereals & Grains
- Oilseed & Pulses
- Others
BY GEOGRAPHY
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others