Report Overview
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Highlights
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Size:
The Japan Additive Manufacturing Market is anticipated to advance at a CAGR of 18.93%, reaching USD 1.88 billion in 2030 from USD 0.79 billion in 2025.
The Japanese Additive Manufacturing (AM) market is transitioning from a prototyping-centric industry to a key enabler of advanced, low-volume production across critical industrial verticals. This shift is predicated on the technology’s capacity to deliver complexity without tooling costs, a significant advantage for Japan’s high-mix, low-volume manufacturing ethos. The nation's sustained emphasis on precision engineering, coupled with a national mandate for supply chain resilience, positions AM as a strategic imperative rather than a mere technological upgrade. The market's evolution is inherently linked to macro-level industrial strategies, particularly those targeting carbon neutrality and next-generation product development, which amplify the core demand for AM processes that minimize material waste and optimize component weight.
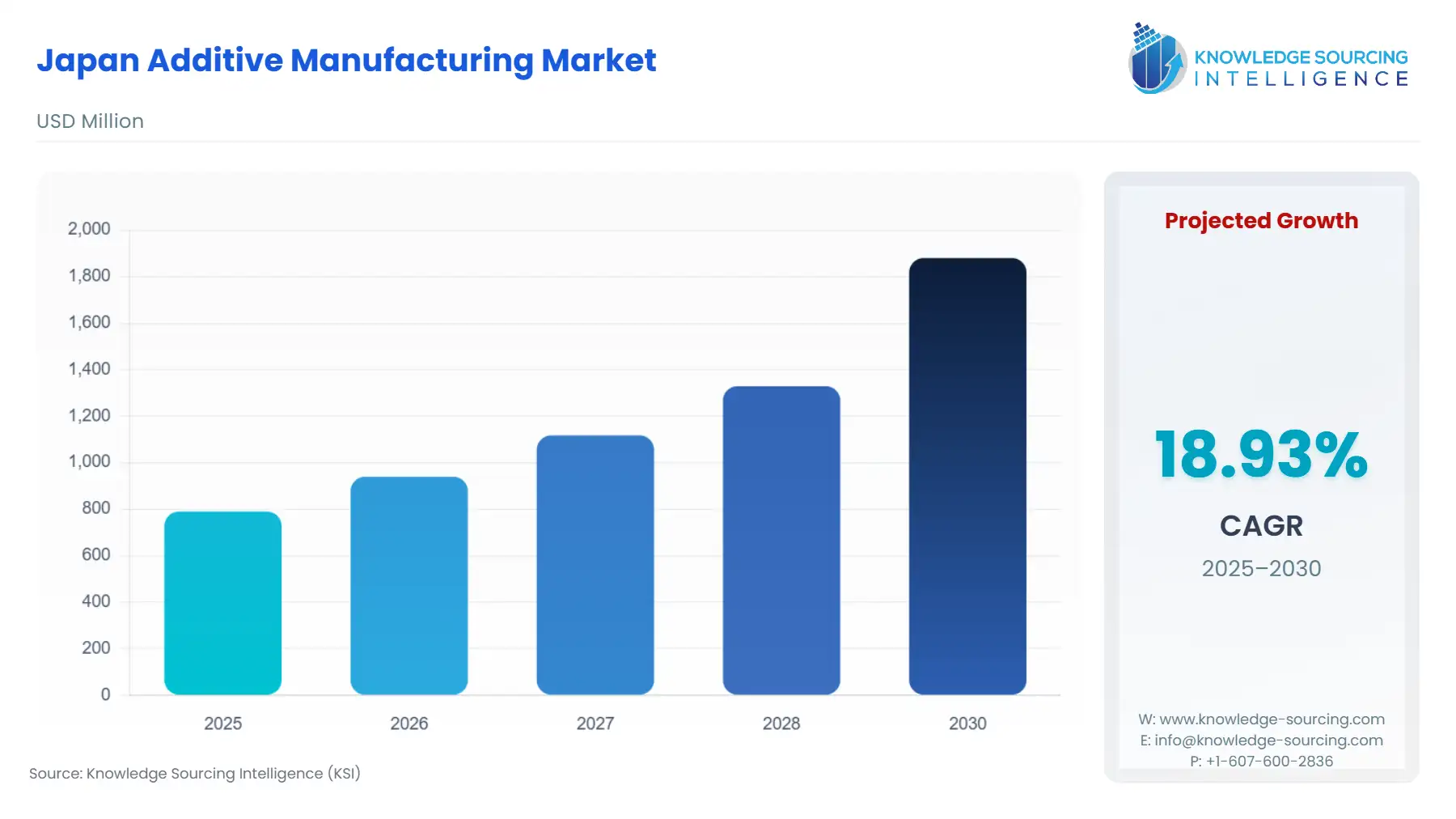
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Government-led industrial digitalization initiatives serve as a foundational catalyst, explicitly generating demand for AM integration. Programs that encourage the deployment of smart manufacturing technologies accelerate the procurement of AM hardware and related software by Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) aiming to enhance global competitiveness. Concurrently, the robust automotive sector's imperative for vehicle lightweighting directly increases the need for high-strength, low-density components achievable through metal AM. This trend specifically favors the adoption of metal 3D printing systems for rapid tooling and the production of electric drivetrain and battery cooling parts, where intricate, thermally-efficient designs are non-negotiable for performance gains.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A significant constraint is the lack of standardized materials and limited interoperability across industrial AM platforms. This challenge directly impacts demand by complicating supply chain integration and increasing quality assurance costs, particularly for certified aerospace and medical components where material consistency is paramount. This necessitates longer validation cycles, dampening the adoption rate among risk-averse, highly regulated end-users. Conversely, the opportunity lies in the rapid expansion of healthcare applications, especially for customized prosthetics, dental implants, and patient-specific surgical tools. The technology's ability to create bespoke, patient-specific solutions drives a clear, inelastic demand for both AM hardware and the associated design and post-processing services, making this sector a high-growth opportunity.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Additive Manufacturing is a physical product market encompassing hardware, materials, and services. The raw material segment, predominantly metal and polymer powders, features a supply chain centered on specialized production for materials like Titanium Alloys (e.g., Ti6Al4V) and Nickel-based Superalloys (e.g., Inconel718). These high-performance materials are often sourced from specialized domestic and international suppliers. The primary pricing dynamic is the high cost of these certified metal powders, driven by stringent quality control requirements for aerospace and medical grades and the specialized gas-atomization processes needed for powder production. However, the high material utilization rates achievable in powder-bed fusion processes, where unused powder is recovered and reused, partially mitigates the overall cost relative to subtractive manufacturing for complex parts.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The Japanese AM supply chain is characterized by a reliance on global production hubs for industrial hardware, while the specialized material production and application expertise are highly concentrated domestically. Logistical complexities arise from the necessity of importing high-value, industrial-grade metal AM systems and then ensuring a consistent supply of certified raw materials. A notable domestic dependency exists for post-processing and finishing services, such as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) and advanced machining. A common supply chain model involves the AM build process being completed by one supplier, with subsequent heat treatments and finishing often outsourced to different specialized providers, increasing the number of logistical handoffs and quality inspection points.
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Government Regulations:
The regulatory environment plays a definitive role in shaping AM market expansion, primarily through state-sponsored R&D and quality standards.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Japan |
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) Strategy |
Promotes R&D and private investment, creating demand for advanced industrial AM equipment to support next-generation semiconductor and robotics manufacturing infrastructure. |
|
Japan |
Japan Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) |
The development and establishment of new industry standards for AM processes and materials are crucial. Clear standards increase end-user confidence, reducing the barrier to adoption and thereby accelerating demand for certified materials and equipment, especially in critical applications. |
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis:
- By Technology: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
The Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technology segment in Japan is driven by its ability to produce highly functional, complex plastic parts without the need for support structures, making it exceptionally efficient for low-to-medium-volume production. This efficiency directly increases demand for SLS systems, especially in the automotive sector, for creating durable, lightweight plastic components for interiors and functional prototypes. The high material versatility, particularly with Polyamide-based powders, provides designers with substantial flexibility, directly correlating to an increase in industrial prototyping demand. As manufacturers seek to consolidate multiple parts into single, complex 3D-printed assemblies, the unique design freedom of SLS reduces assembly costs and part count, further cementing its demand for end-use part manufacturing in non-critical applications and tooling fabrication. The rapid cycle time for batch production solidifies SLS's role as a cornerstone of agile manufacturing strategies.
- By End-User Industry: Aerospace & Defense
The Aerospace & Defense sector’s necessity for AM is an essential driver, characterized by mission-critical requirements for weight reduction and high thermal resistance. The imperative to build lighter, more fuel-efficient aircraft and spacecraft components creates a non-negotiable demand for metal AM processes like EBM and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). These technologies enable the fabrication of complex, high-performance engine parts and satellite components from advanced materials such as titanium aluminide (TiAl) and high-strength nickel superalloys. Government and private investment in next-generation aerospace programs, including indigenous aircraft development and space exploration efforts, specifically fuels the procurement of AM systems capable of meeting stringent quality and structural integrity benchmarks. The technology’s capacity to achieve optimal strength-to-weight ratios through lattice structures and topology optimization directly addresses the sector's performance and sustainability goals.
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape in Japan's AM market is a blend of global hardware giants and domestic industrial conglomerates leveraging deep manufacturing expertise. Japanese companies often focus on vertical integration and providing specialized AM solutions for high-performance industrial applications.
- Canon Inc.
Canon is strategically positioned in the AM ecosystem primarily through its optical and precision manufacturing heritage, leveraging its strengths in fine inkjet technology, materials development, and process control. The company is actively focused on expanding its production inkjet portfolio, which aligns conceptually with high-throughput 3D printing systems. While Canon's recent press releases highlight advancements in large-format 2D printing and UVgel technology, its strategic thrust into the wider AM space capitalizes on its core competency in high-precision, industrial-grade imaging and material deposition systems, targeting applications where accuracy and consistency are paramount.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) Group
MHI, a diversified heavy industry leader, positions AM as a critical technology for its high-value sectors, including power generation and defense. MHI’s strategy involves internal adoption and external commercialization of advanced metal AM technologies like powder-bed fusion and Directed Energy Deposition (DED) to produce large, complex, and high-temperature-resistant components such as turbine blades. The company is actively integrating AM into its existing manufacturing workflow to optimize production processes and enhance the performance of core products, aligning its AM development with its broader energy transition and decarbonization goals, where highly efficient, custom-made parts are essential.
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Developments:
- July 2025: Global 3D printing innovator PioCreat introduced two advanced machines to the Japanese market at the Additive Manufacturing Expo Tokyo. The debut included the G5Ultra Pellet 3D Printer, notable for its large build volume and high-speed pellet extrusion, which aims to lower material costs for industrial prototyping and small-batch production. Alongside this, the HALOT-X1 16K Resin 3D Printer was showcased, drawing attention for its ultra-high resolution and consumer accessibility for high-precision resin printing applications.
- February 2025: Nikon, building on its 2023 acquisition of metal AM leader SLM Solutions, opened the Nikon AM Technology Center Japan in Gyoda City, Saitama, in 2025. This facility serves as a major hub for advanced metal additive manufacturing development and customer solutions. Equipped with both Nikon's existing Directed Energy Deposition (DED) systems and Nikon SLM Solutions' large-scale Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) systems, the center is focused on accelerating the application of metal 3D printing, especially in the growing aerospace sector, including projects with JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency).
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.79 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.88 billion |
| Growth Rate | 18.93% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Japan Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
- Material
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Laser Sintering (LS)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Fused Disposition Modeling
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Construction
- Consumer
- Others