Report Overview
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Highlights
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Size:
The Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market is expected to rise at a CAGR of 20.33%, attaining USD 0.56 billion in 2030 from USD 0.222 billion in 2025.
The Saudi Arabian Additive Manufacturing market is undergoing a rapid, state-backed industrial transition, moving beyond simple prototyping to industrial-scale production. This shift is an explicit directive of Vision 2030, which positions advanced manufacturing, notably Industry 4.0 technologies like AM, as a core enabler for economic diversification and localized high-tech capability building. This strategy is fundamentally altering the procurement landscape in key sectors like Aerospace & Defense, Energy, and Healthcare, creating a protected domestic market for AM hardware, software, and services that prioritize in-Kingdom value addition over traditional importation models. The prevailing demand is therefore less organic and more structurally mandated by national industrial policy.
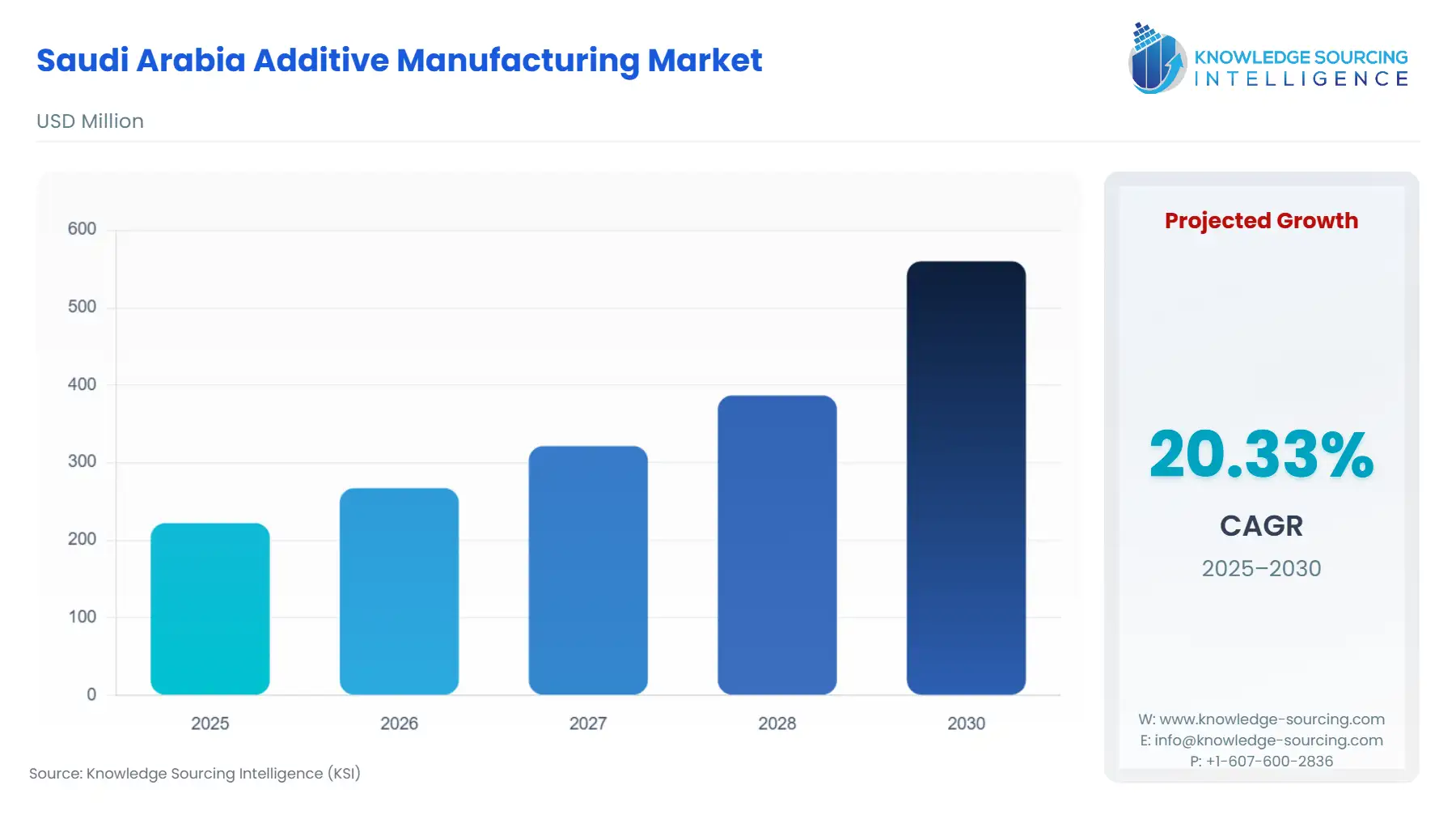
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary catalyst for market growth is the state's strategic intent to reduce international supply chain dependency, directly increasing demand for localized production capabilities.
National Industrial Development and Logistics Program (NIDLP): This program explicitly targets the establishment of high-tech industrial hubs and additive manufacturing labs. This policy directly increases the need for AM hardware and specialized technician services by providing funding and institutional support for domestic technology adoption, particularly in strategic areas like automotive and aviation spare parts, which require cost-effective, on-demand solutions to stabilize supply chains.
Defense Localization Mandate (GAMI): The General Authority for Military Industries (GAMI) aims for a 50% localization of military spending by 2030. This mandate translates directly into a high-value requirement for certified metal AM systems (e.g., Laser Sintering, Electron Beam Melting) capable of producing qualified, lightweight parts for the aerospace and defense sector, driving technology transfer and local joint ventures.
Saudi Aramco's Digital Transformation: Aramco's deployment of AM for industrial applications, such as the on-demand printing of spare parts for oil rigs and refineries, demonstrably increases the need for both material feedstock and printing services. The use of AM reduces equipment downtime and significantly lowers inventory costs, establishing a clear economic incentive that compels further corporate adoption.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The market faces significant human capital and standardization headwinds, yet these constraints simultaneously create substantial commercial opportunities for specialized providers.
Challenges: Digital Skills Gap and Standardization: The rapid adoption of complex AM technologies is constrained by a notable digital skills gap in the local workforce, increasing reliance on expatriate technical expertise. Furthermore, the absence of universally recognized industry-defined standards for 3D-printed metal components, particularly for safety-critical parts in oil & gas, acts as a bottleneck, slowing the demand for full-scale industrial deployment of metal AM.
Opportunities: Service Provider Local Expansion: The localized market gap for advanced AM services creates an opportunity for international technology providers to establish joint ventures, focusing on application development and training facilities. These centers directly address the skill and standardization constraints by providing certified production and application-specific expertise, thereby bolstering customer confidence and driving demand for long-term service contracts.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Additive Manufacturing equipment, materials, and services constitute a physical market, mandating the inclusion of this analysis.
The Saudi AM market's raw material supply chain remains nascent, with a predominant focus on service provision, rather than domestic material production. AM relies on specialized powders (metals, polymers) and resins, which are globally sourced. This dependency on international suppliers introduces price volatility and logistical lead-time risk. For metal AM, materials like Aluminium AlSi10Mg and Nickel Alloys are imported, with their pricing dynamics linked to global commodity markets and proprietary technology licensing. However, the Kingdom’s existing strength in petrochemicals presents an opportunity for local development of high-performance polymer feedstocks, which could stabilize pricing and shorten the supply chain for polymer-based AM applications, thereby encouraging increased demand from the construction and consumer goods sectors.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global AM supply chain is decentralized, with key production hubs for advanced metal AM hardware centered in Europe (Germany) and the US. The Saudi market is highly dependent on inbound logistics from these hubs. This dependency manifests as lengthy lead times for new equipment and specialized spare parts, constraining rapid capacity scaling. Additive manufacturing inherently addresses downstream supply chain complexities by enabling localized, on-demand part production, which significantly reduces the need for large, centralized inventories and mitigates international logistics risks. The supply chain dependency, therefore, is primarily upstream (hardware and high-performance material imports), while the value proposition for the end-user is downstream supply chain disintermediation and resilience.
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Saudi Arabia |
General Authority for Military Industries (GAMI) |
GAMI's localization target of 50% of military spending creates non-price-based demand, compelling defense contractors to invest in local AM capacity, which increases the purchase of certified hardware and software solutions. |
|
Saudi Arabia |
Ministry of Industry and Mineral Resources (MIMR) / National Industry Strategy (NIS) |
The NIS supports the development of an AM ecosystem, which directly facilitates funding for AM adoption. This lowers the barrier to entry for local manufacturers, thereby increasing the market demand for AM services and materials. |
|
Saudi Arabia |
Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization (SASO) |
The current developmental phase of local AM standards for industrial use creates regulatory uncertainty. This slows the adoption of AM for critical, high-risk applications until clear quality and certification protocols are established, constraining growth in the short term. |
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Segment Analysis:
- By Technology: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
The Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) segment holds a dominant market share in Saudi Arabia primarily due to its cost-effectiveness, material versatility (using various thermoplastic materials), and robust adoption in prototyping and tooling applications. The need for FDM is directly driven by the Kingdom's acceleration of product development cycles within the automotive, consumer, and education sectors, which require rapid, iterative prototyping. Unlike advanced metal technologies, FDM systems have a comparatively lower initial capital expenditure and operating cost, making them highly accessible to Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) that are critical to the Vision 2030 economic diversification agenda. The technology's simplicity and reliability in non-critical applications, such as jigs, fixtures, and conceptual models, minimize the local skills barrier, promoting widespread demand for FDM hardware and standard polymer materials across a broad industrial base.
- By End-User Industry: Aerospace & Defense
The Aerospace & Defense sector is a critical, high-value demand segment for advanced metal Additive Manufacturing (AM) technologies in Saudi Arabia. This growth is driven by the state's military localization target, which compels Saudi Arabian Military Industries (SAMI) and its international partners to integrate AM into their supply chains for high-performance, lightweight components. The use of AM in this sector facilitates the production of geometrically complex parts that offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, directly supporting fuel efficiency and operational readiness goals for aircraft and other platforms. The requirement for supply chain resilience means that the primary requirement is for certified, high-end AM systems (e.g., Electron Beam Melting) capable of processing advanced alloys like Titanium and Nickel, and is not price-sensitive but rather performance- and certification-driven.
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Competitive Analysis:
The Saudi Arabian Additive Manufacturing competitive landscape is defined by strategic joint ventures (JVs) between major global technology providers and powerful local industrial investment companies, positioning domestic entities as key service providers and distributors. This model prioritizes technology transfer and localization over pure open-market competition.
- 3D Systems (Joint Venture with Dussur)
3D Systems, a leading global additive manufacturing solutions provider, operates through a joint venture with the Saudi Arabian Industrial Investments Company (Dussur). This partnership established the Center for Innovation and Additive Manufacturing, focusing initially on the energy segment but with planned expansion into healthcare and aerospace. Their strategic positioning is to leverage 3D Systems’ comprehensive portfolio of hardware, software, materials, and application expertise—particularly in Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)—to act as the foundational technology enabler for Saudi Arabia’s industrialization. The JV directly addresses the localization imperative by providing in-Kingdom manufacturing capabilities and technical training.
- EOS GmbH
EOS is a prominent global supplier of industrial 3D printing solutions, specializing in Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF) technologies for both polymers and metals. EOS's strategic focus is on high-performance applications in the aerospace and defense sectors, which align with the Kingdom’s defense localization goals. Their core offering includes the EOS M series for metal AM and the EOS P series for polymer AM, targeting serial production of end-use parts. The company’s emphasis on responsible manufacturing and materials development, such as the introduction of certified aluminum materials, positions them to meet the stringent quality and sustainability demands of key Saudi industries.
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Developments:
- September 2025: Localized Metal Component Production for Aerospace & Defense: The National Additive Manufacturing and Innovation Company (NAMI) partnered with Lockheed Martin to begin producing 3D-printed aluminum components for the aerospace and defense sector within Saudi Arabia. This is a clear capacity addition focused on qualifying parts for integration into a major international defense firm's global supply chain.
- February 2023: Construction Sector Capacity Addition: Aramco successfully constructed its first 3D-printed concrete industrial building in Hawiyah as part of its Hawiyah Unayzah Gas Reservoir Storage (HUGRS) Program. The structure, a radio shelter, used a cantilevered arm-type printer and achieved a significant reduction in construction time, demonstrating the adoption of 3D Construction Printing (3DCP) for commercial, industrial-grade projects.
- March 2022: Joint Venture and Facility Establishment: 3D Systems and the Saudi Arabian Industrial Investments Company (Dussur) finalized an agreement to create a joint venture for the expansion of additive manufacturing in Saudi Arabia. The purpose was to enable the development of domestic AM production capabilities, with an initial focus on the energy segment, marking a pivotal merger/acquisition and a planned capacity addition.
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.222 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 0.56 billion |
| Growth Rate | 20.33% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Saudi Arabia Additive Manufacturing Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
- Material
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Laser Sintering (LS)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Fused Disposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- BY END-USER INDUSTRY
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Construction
- Consumer
- Others