Report Overview
South Korea Private 5G Highlights
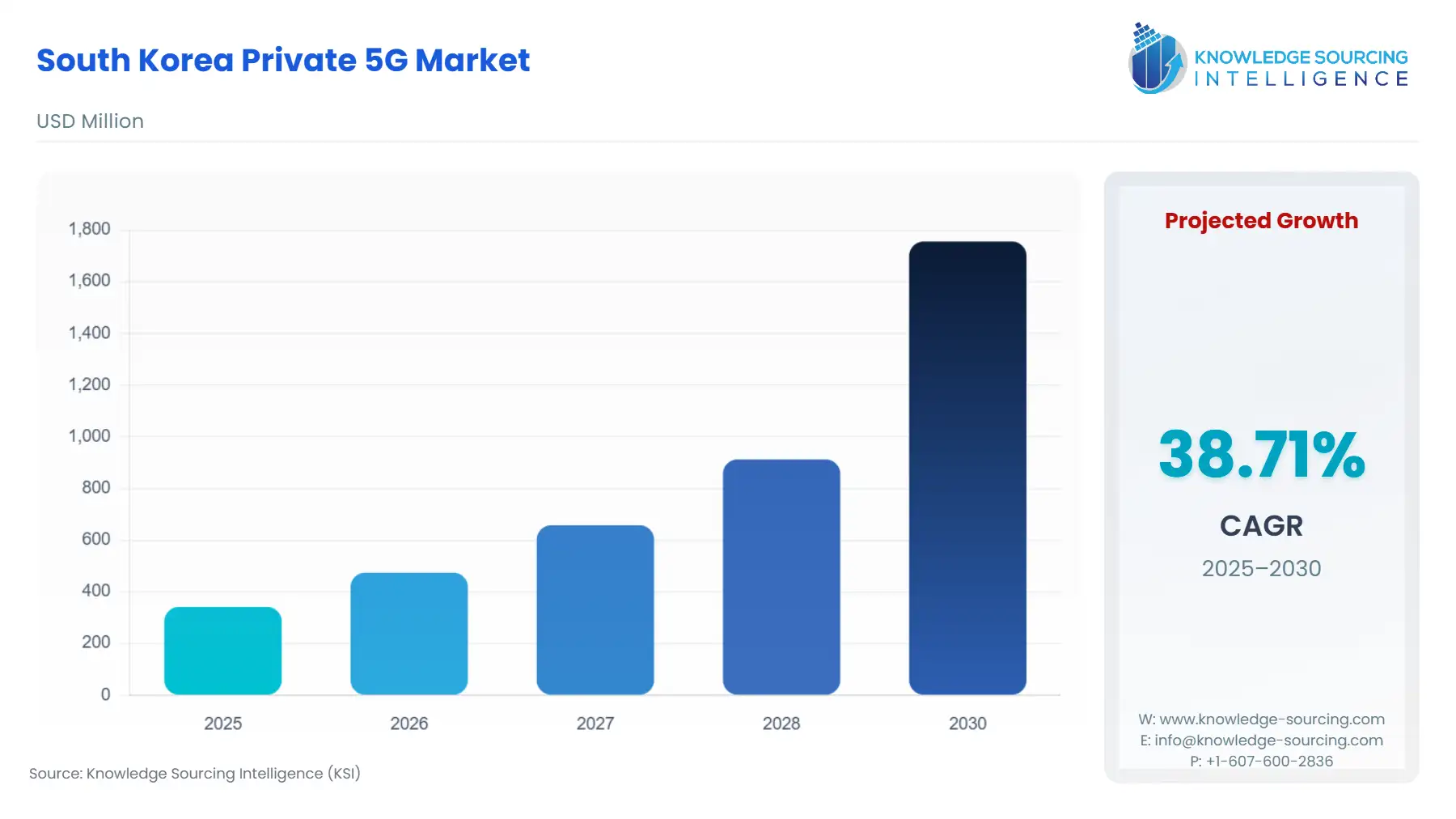
South Korea Private 5G Market Size:
The South Korea Private 5G Market is projected to surge at a CAGR of 38.71%, reaching USD 1.756 billion in 2030 from USD 0.342 billion in 2025.
The South Korean private 5G market represents a strategic inflection point in the nation's digital transformation agenda, moving beyond the consumer-centric public 5G rollout. The market is defined by a unique regulatory framework that empowers non-telecom operators to own and manage their dedicated enterprise networks, thereby bypassing the incumbent Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). This regulatory intervention, combined with South Korea's high concentration of advanced manufacturing and technology-centric enterprises, cultivates a robust demand landscape focused on mission-critical, high-performance applications. The clear distinction between public and private spectrum, particularly the allocation of the mid-band 4.7GHz and high-band 28GHz, signals a national commitment to fostering industry-specific digital innovation, positioning private 5G as an essential utility for realizing the Fourth Industrial Revolution goals within the enterprise vertical.
________________________________________________________________
South Korea Private 5G Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The foundational growth driver is the government's direct spectrum allocation policy. The Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) designated the 4.7GHz and 28GHz bands for non-telecom operators to build their own networks, a policy that instantly creates direct demand by providing the essential resource needed for private network deployment. Enterprises, particularly in manufacturing, face an imperative to integrate Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) for enhanced productivity and safety. This operational shift demands Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) and high-density connectivity that traditional Wi-Fi cannot reliably deliver, thereby forcing a direct adoption of private 5G solutions to meet strict performance requirements for real-time control. Furthermore, government-funded 5G projects and tax credits on capital investment for network deployment substantially reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for enterprises, functioning as a financial catalyst that lowers the barrier to entry and stimulates demand.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A key challenge is the complexity of integrating a private 5G network with existing legacy IT and Operational Technology (OT) systems. The high initial capital expenditure for dedicated hardware components—Radio Access Network (RAN) and 5G Core—creates a significant hurdle for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), which directly constrains market expansion by limiting adoption to large, well-capitalized corporations. However, this challenge simultaneously presents an opportunity in the Managed Private 5G model. Enterprises seeking to mitigate integration complexity and capital risk will increasingly demand managed services, where MNOs or system integrators handle the deployment and operation. This shift creates a burgeoning opportunity for service providers to focus on network management and orchestration solutions, shifting the demand from a purely hardware-centric purchase to an operational expenditure (OpEx) service model. The underutilized 28GHz band, despite technical difficulties, offers an immense opportunity to service ultra-high-capacity applications like augmented reality (AR) and digital twins, creating future high-value demand once technical maturity improves.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The South Korean Private 5G market is fundamentally a physical product market, relying on specialized telecommunications hardware. Key raw materials for the RAN and Edge Server components include semiconductor chipsets, specialized radio frequency (RF) filters, and high-performance processors. Global supply chain constraints in the semiconductor industry create inflationary pressure on the Bill of Materials (BOM) for the 5G Core and RAN hardware, increasing the capital cost of private 5G solutions. This rising hardware cost is a direct factor that restrains enterprise demand. Conversely, the market's pricing dynamics are currently driven by a competition between domestic conglomerates and global vendors, leading to optimization and cost reduction in core software licensing and hardware design, particularly through the adoption of more compact, single-server deployment models (e.g., Samsung's Compact Core), a dynamic that counteracts raw material inflation and helps stabilize enterprise pricing expectations.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The South Korean private 5G supply chain is a high-tech ecosystem centered on advanced domestic manufacturing capabilities, predominantly led by companies like Samsung and LG. Key production hubs for the crucial components—chipsets, network gear, and advanced modules—are located in South Korea and other East Asian nations. This geographical concentration creates logistical complexity and supply dependencies, particularly concerning global semiconductor shortages, which can severely impact delivery timelines and the scalability of deployments for enterprise customers. The market maintains a strong dependency on global technology partners for specialized software and open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) architectures, despite domestic leadership in hardware. This reliance on a global web of intellectual property and component sourcing introduces vulnerability to geopolitical trade shifts, but also ensures access to best-in-class technology, which is an imperative for maintaining the nation's technological edge in manufacturing.
South Korea Private 5G Market Government Regulations:
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) - Private 5G Spectrum Allocation | Directly increases demand by allowing non-telecom companies to acquire dedicated spectrum (4.7GHz and 28GHz) for private use, eliminating reliance on MNOs for core enterprise connectivity. |
| South Korea | National Security Law/Telecommunications Business Act | Imposes stringent security and data localization requirements, which increases the complexity and cost of deployment but simultaneously drives demand for highly secure, on-premises private networks with localized data processing. |
| South Korea | Government 5G+ Strategy | Mandates state investment and provides tax incentives for 5G deployment in strategic industries, directly accelerating enterprise spending on private 5G solutions as a means to achieve national digitalization targets. |
________________________________________________________________
South Korea Private 5G Market Segment Analysis
- By End-User: Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
The Manufacturing and Industrial Automation segment is the central growth engine for the South Korean private 5G market. The imperative for 'Smart Factories' drives the need, as traditional wireless technologies fail to meet the deterministic performance required for advanced manufacturing use cases. Specifically, these environments require Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) to support applications such as precise, real-time control of robotics, synchronizing Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) across large factory floors, and facilitating real-time machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. This necessity is further fueled by the need for massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC) to connect thousands of IoT sensors for predictive maintenance and quality assurance, generating vast amounts of data. Private 5G networks, utilizing both the 4.7GHz mid-band for balanced coverage/capacity and the 28GHz millimeter-wave for localized high-throughput data offload, are the only verifiable technology currently capable of meeting these triple performance requirements—low latency, high reliability, and massive connectivity—directly translating into concrete demand.
- By Components: 5G Core
The 5G Core component is the intellectual and functional heart of a private network, driven by the enterprise requirement for total control and customization. The transition from monolithic telecom cores to cloud-native, virtualized, and miniaturized cores (such as Samsung's Compact Core) directly increases enterprise demand for deployment flexibility. Enterprises demand a 5G Core that can reside on-premises (Edge Server) to enable Mobile Edge Computing (MEC), ensuring all mission-critical data remains local and latency is minimized to below 10 milliseconds, which is critical for real-time applications like digital twins and augmented reality (AR) for field service. Furthermore, the 5G Core facilitates network slicing, a key growth driver, allowing a single physical network to be logically partitioned to dedicate guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS) for specific applications—e.g., separating robotic control traffic from CCTV surveillance traffic. This functionality is an essential demand feature that commercial public networks cannot guarantee, solidifying the need for a dedicated private 5G Core.
________________________________________________________________
South Korea Private 5G Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The South Korean Private 5G market is an oligopoly dominated by the nation's incumbent Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and large domestic equipment vendors, with specialized foreign players acting as technology partners. The competitive landscape is defined by the unique regulatory environment that pits the MNOs' 'Managed Private 5G' service against the 'Enterprise-Owned' network model supported by equipment vendors. MNOs leverage their existing spectrum assets and network deployment expertise to offer simplified, managed services, while domestic industrial conglomerates and hyperscalers (like Naver) push for full self-ownership using the dedicated private spectrum.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Samsung's strategic positioning is as a comprehensive, end-to-end private 5G solutions provider, directly addressing the government's dual-band spectrum allocation. Its key products include the 5G SA Compact Core and Compact Macro/Radios supporting both the 4.7GHz and 28GHz bands. Samsung's strategy is to enable non-telecom enterprises to rapidly deploy and operate their own networks with a compact, fully virtualized core that can run on a single server, significantly reducing the hardware footprint and operational complexity. This direct-to-enterprise model, evidenced by its deployment for Naver's headquarters and its selection by public sectors, positions Samsung as a crucial enabler of the enterprise-owned private network model.
- KT Corporation
KT Corporation, one of the 'Big 3' MNOs, adopts a strategic positioning centered on leveraging its extensive network infrastructure and experience to offer Managed Private 5G services. This approach targets enterprises seeking to avoid the complexity and large initial capital investment of a self-owned network. KT's strategy focuses on vertical integration, combining its 5G network expertise with its Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, and Cloud (ABC) capabilities to deliver high-value, turn-key solutions. Its verified collaborations in the healthcare sector, such as its work with Samsung Medical Center on a 5G smart hospital, and its recent joint deployment with Samsung for the Republic of Korea Navy, underscore its focus on secure, mission-critical, high-availability networks across public and defense sectors.
- SK Telecom Co., Ltd. (network division)
SK Telecom's private 5G strategy is differentiated by its focus on Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) integration and hyper-collaboration. The company aims to lead the industrial revolution by building 5G MEC Centers in multiple locations across South Korea, directly addressing the demand for ultra-low-latency processing required by applications like unmanned delivery robots and telemedicine. SK Telecom's publicly announced plans to deploy a private 5G network at SK Hynix's semiconductor facility demonstrates a clear focus on the high-value manufacturing vertical, where its strategy is to integrate its 5G network with cutting-edge technologies like AI video analytics and AR for smart factory realization, cementing its position as a key enabler for advanced industrial automation.
________________________________________________________________
South Korea Private 5G Market Developments:
- October 2024: Samsung and KT Corporation Selected for ROK Navy Private 5G Project. Samsung Electronics and KT Corporation were selected to deploy a Private 5G network for the Republic of Korea (ROK) Navy's 'Smart Naval Port' project. This collaboration involves building a fully independent network infrastructure to encompass 13 different systems, ranging from uncrewed vehicle operations to armory and ammunition depot management. The deployment utilizes Samsung's private network 5G SA Compact Core and radio solutions supporting the mid-band 4.7GHz spectrum, establishing a significant new capacity addition in the defense and public safety end-user segment.
- August 2022: Samsung Electronics Delivers Private 5G Solutions to Public and Private Sectors. Samsung Electronics announced its selection to provide a diverse range of its 5G solutions to five government agencies and private institutions in South Korea. The company supplied its advanced Private 5G network solutions, including Compact Macro, Compact Core, and radios supporting both the 4.7GHz and 28GHz bands, for applications in energy, safety, water resource management, and medical services/education. This marked a key product launch and capacity addition, expanding Samsung's market footprint in non-telecom vertical segments and furthering the government's private 5G initiative.
________________________________________________________________
South Korea Private 5G Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 0.342 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 1.756 billion |
| Growth Rate | 38.71% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment Model, End-User |
| Companies |
|
South Korea Private 5G Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENTS
- RAN
- 5G Core
- Transport
- Edge Server
- Network Management and Orchestration
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODEL
- On-Premises Private 5G
- Managed Private 5G
- BY END-USER
- Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
- Logistics, Warehousing and Ports
- Energy, Oil and Mining
- Healthcare
- Public Safety and Security
- Other Enterprises