Report Overview
Sweden Private 5G Market Highlights
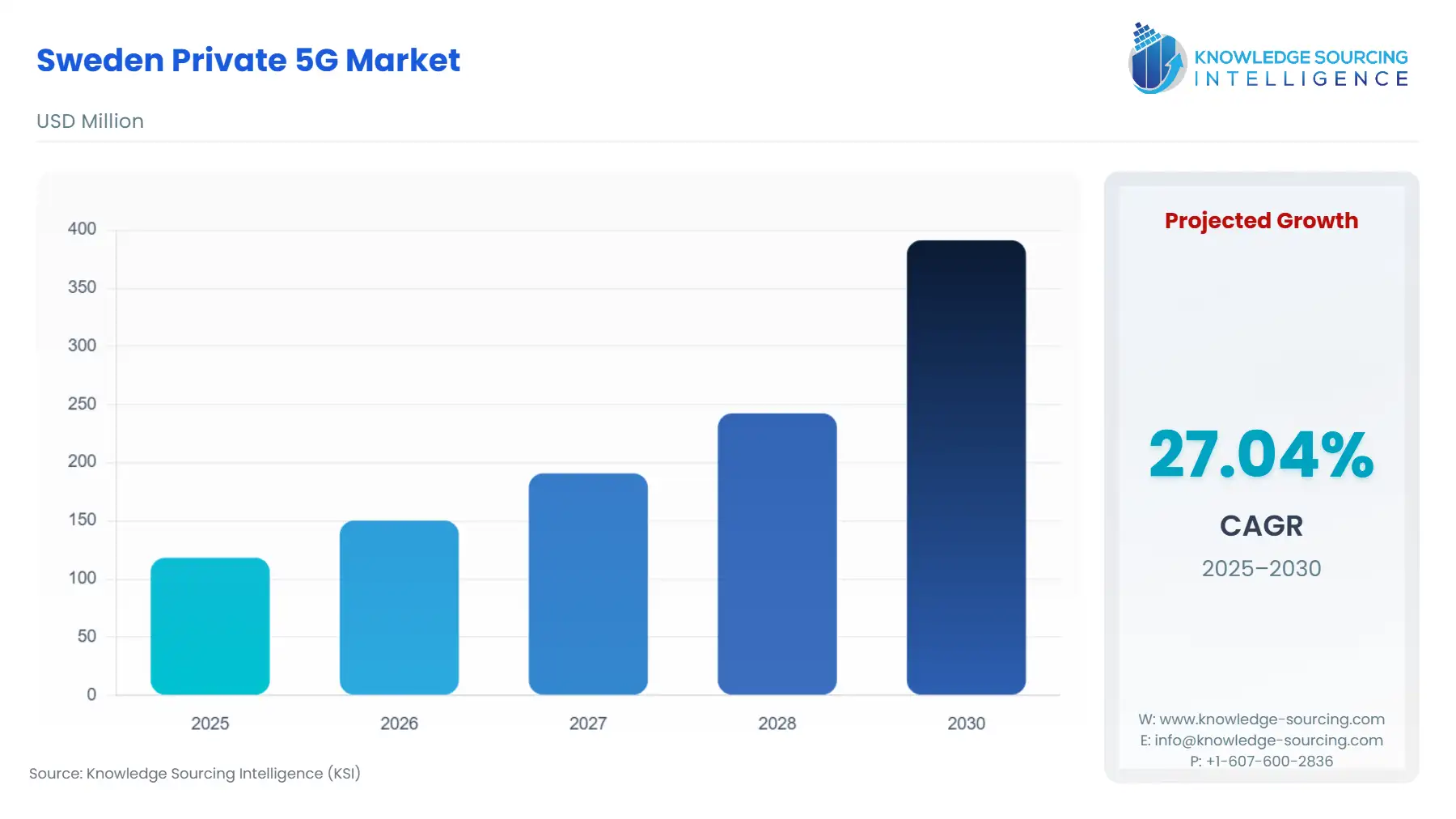
Sweden Private 5G Market Size:
The Sweden Private 5G Market is forecast to expand rapidly at a CAGR of 27.04%, attaining USD 391.276 million in 2030 from USD 118.247 million in 2025.
The Swedish Private 5G market is navigating a decisive transition, shifting from initial public network deployments to enterprise-specific Non-Public Networks (NPNs). This evolution is fundamentally influenced by a forward-thinking regulatory environment that prioritizes spectrum liberalization for local use and a strong national imperative toward industrial digitalization. Enterprises across Sweden, home to globally significant manufacturing and resource sectors, now seek dedicated, high-performance wireless connectivity. The market's trajectory is dictated by the confluence of robust industrial demand for critical machine-to-machine (M2M) communication and a unique political and security landscape that favors a distinct set of global and regional technology providers.
________________________________________________________________
Sweden Private 5G Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The liberalization of radio spectrum by the PTS acts as the singular most powerful growth catalyst. By opening the 3.7 GHz and 26 GHz bands for local licensing, the authority eliminated the dependence on MNOs for critical network ownership, enabling industries to procure spectrum directly. This control is an imperative for the manufacturing and energy sectors, as it allows for deterministic network slicing and guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS) for mission-critical applications, directly propelling the demand for dedicated Private 5G solutions. Simultaneously, the Swedish government's emphasis on industrial digitalization—aligned with the European Union's Industry 4.0 framework—mandates the deployment of high-throughput, low-latency networks. This necessitates private 5G for applications such as robotic control, predictive maintenance via Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC), and real-time Augmented Reality (AR) tools for field workers, where network reliability cannot be compromised by public network congestion.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A principal challenge constraining immediate market expansion is the technical complexity and high initial capital expenditure associated with Standalone Private 5G deployments, coupled with a national shortage of specialized radio frequency (RF) and cloud-native network engineering talent. This challenge shifts demand toward managed and 'as-a-service' deployment models, favoring vendors with strong professional services arms. Furthermore, spectrum co-existence limitations in the crucial mid-band 3.7 GHz range, particularly in coastal regions where the frequency overlaps with aviation radar systems, pose an immediate constraint on deployment scale and location flexibility, necessitating alternative solutions like millimetre-Wave (mmWave) for indoor industrial campuses. Conversely, a significant opportunity emerges from the regulatory push to adopt the global MCC 999 framework for SNPNs, which simplifies inter-network mobility and eliminates the administrative burden of unique Swedish Mobile Network Code (MNC) allocation, thereby substantially reducing the complexity of multi-site or internationally scaled private network deployments and accelerating enterprise adoption.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The Private 5G supply chain for Sweden is highly sophisticated and globally interdependent, yet strategically constrained. Component manufacturing for Radio Access Network (RAN) hardware (base stations, antennas) is primarily concentrated in Asia-Pacific fabrication hubs, introducing geopolitical and logistical complexities that impact lead times. The 5G Core and Network Management and Orchestration layers, however, are dominated by software and intellectual property developed by European and North American technology firms. The non-negotiable national security regulation, which mandates the exclusion and phase-out of specified Chinese vendor equipment from central network functions, fundamentally alters the supply dynamics within Sweden. This requirement places a premium on resilient supply chains from trusted vendors like Ericsson and Nokia, who operate production and development facilities within the Nordic and broader Western geopolitical spheres, directly translating into higher demand for their specific hardware and software portfolios. Logistical complexities revolve around the secure, timely deployment of specialized, certified hardware components that must conform to the stringent national security parameters set by the PTS.
Sweden Private 5G Market Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Sweden | Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) – Local Spectrum Assignment (3.7 GHz and 26 GHz) | The directive enables self-owned NPNs, creating demand for equipment and system integrators. It allows enterprises to guarantee latency and capacity, a critical factor for industrial adoption, directly bypassing MNO reliance. |
| Sweden | PTS – Security Requirements for 5G Networks (Exclusion of products from Huawei/ZTE) | This regulation drastically limits the competitive field, reducing the pool of available, lower-cost network equipment. It mandates demand for technology and services from compliant European and other non-prohibited vendors, reinforcing the market positions of Ericsson and Nokia in their home region. |
| Sweden | PTS – Study on Mobile Network Code (MNC) Administration (MCC 999 for SNPNs) | PTS's endorsement of un-coordinated MNCs for SNPNs standardizes network identification, simplifying the technical deployment of private 5G across multiple enterprise locations and promoting a scalable, future-proof network architecture, thereby reducing barriers to entry. |
________________________________________________________________
Sweden Private 5G Market Segment Analysis
- By Components: RAN (Radio Access Network)
The RAN segment constitutes the principal hardware investment within a Private 5G deployment, acting as the immediate growth driver for physical components. In the Swedish market, the need for RAN is fundamentally tied to the industrial requirement for ubiquitous and high-density connectivity within large, complex environments like factories and ports. Unlike public networks, private networks necessitate a highly granular distribution of small cells and radio units to achieve the desired in-building penetration and guaranteed signal integrity around heavy machinery. The necessity here is not merely for volume, but for specialized RAN technology, specifically Massive MIMO and millimeter-Wave (mmWave) Radio Units (RUs) that can handle the dense concentration of endpoints (mMTC) and provide the extreme throughput required for high-definition video monitoring or holographic maintenance guides. The security mandate further concentrates this demand toward European and North American suppliers, who must also demonstrate compliance with Open RAN principles to accommodate the increasing interest from enterprises seeking multi-vendor interoperability and competitive pricing on hardware modules. Therefore, demand focuses on modular, security-compliant, and high-performance RUs that can be integrated flexibly into the enterprise's existing edge computing infrastructure.
- By End-User: Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
The manufacturing sector forms the foundational demand base for Private 5G in Sweden, given the country's extensive footprint in high-value, automated industrial production. The sector's migration to Industry 4.0 paradigms—characterized by hyper-automation, digital twins, and flexible manufacturing—directly dictates the necessity for Private 5G. Traditional wireless technologies (Wi-Fi) cannot deliver the sub-10ms latency and high connection density required to manage fleets of collaborative robots, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication protocols on a single, deterministic network. The implementation of AGVs for material handling, for example, is a direct growth driver, as these systems require constant, ultra-reliable network handovers and real-time control loops to ensure safety and efficiency, functions that only the 5G core's URLLC functionality can reliably enable. Consequently, Swedish manufacturing enterprises are increasingly issuing demand for Private 5G solutions that are pre-integrated with industrial control systems (ICS) and can guarantee network segmentation for mission-critical operations, establishing this segment as the primary revenue generator for solution providers.
________________________________________________________________
Sweden Private 5G Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Swedish Private 5G market is fundamentally a duopoly at the infrastructure level, heavily favoring Ericsson and Nokia due to the national security ban on specific foreign vendors. This geopolitical constraint ensures that the competitive focus centers on product differentiation in software, cloud-native core technology, and professional services, rather than a price war on commodity hardware. While Cisco Systems and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) compete aggressively in the 5G Core, edge server, and network management layers, the market is structurally biased toward the two Nordic vendors who can provide end-to-end, politically palatable solutions.
- Ericsson AB
As the domestic champion, Ericsson leverages its global leadership in 5G RAN and Core networks. The company's strategic positioning revolves around providing high-performance, cloud-native solutions, notably its Compact Packet Core, which facilitates the modernization of a service provider's Packet Core to a cloud-native platform, serving both 4G and 5G connectivity. Ericsson is strategically advancing its enterprise focus through specialized offerings and partnerships, reporting an accelerated 19% year-on-year sales growth in its enterprise wireless solutions. Its involvement in the local launch of Sferical AI in August 2025 demonstrates a commitment to integrating advanced AI directly into its enterprise wireless portfolio, aiming to boost network scalability, efficiency, and Swedish industrial competitiveness.
- Nokia Solutions and Networks AB
Nokia maintains a robust competitive stance through its extensive global installed base in the private wireless segment, claiming over 850 customers globally by the end of 2024. Nokia's strategy emphasizes its Core Enterprise Solutions and its Digital automation for industrial campus offerings, focusing on comprehensive, secure, and future-ready networks. Its product portfolio includes specialized industrial devices like the world's first 5G 360° camera for industrial use, demonstrating a vertical-specific product development approach. Nokia's competitive advantage lies in its focus on multi-site, multi-country deployments and its strong track record in critical industrial sectors like mining and ports, making it a powerful contender for large, multinational Swedish enterprises.
________________________________________________________________
Sweden Private 5G Market Developments
- August 2025: Ericsson and Partners Launch Sferical AI to Drive Competitiveness. Ericsson, in collaboration with a consortium of leading Swedish companies, officially launched Sferical AI, an advanced AI company. This capacity addition is explicitly designed to drive Swedish competitiveness through the development of generative Artificial Intelligence solutions. The move directly supports the core value proposition of private 5G by providing sophisticated, locally developed AI tools that can operate on the massive data streams generated by private networks in the manufacturing and industrial sectors. The company's focus on AI is a strategic development that elevates the value of Ericsson's core network and automation platforms.
- August 2025: Ericsson Completes Sale of iconectiv. Ericsson completed the sale of iconectiv to Koch Equity Development LLC. This strategic divestiture signifies Ericsson's ongoing portfolio simplification and focused commitment toward its core business lines, specifically 5G network infrastructure and enterprise wireless solutions. By divesting non-core assets, the company frees capital and internal resources for greater investment in its leading private 5G and core network technology, strengthening its competitive positioning against global rivals.
________________________________________________________________
Sweden Private 5G Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 118.247 million |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 391.276 million |
| Growth Rate | 27.04% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment Model, End-User |
| Companies |
|
Sweden Private 5G Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENTS
- RAN
- 5G Core
- Transport
- Edge Server
- Network Management and Orchestration
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODEL
- On-Premises Private 5G
- Managed Private 5G
- BY END-USER
- Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
- Logistics, Warehousing and Ports
- Energy, Oil and Mining
- Healthcare
- Public Safety and Security
- Other Enterprises