Report Overview
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Highlights
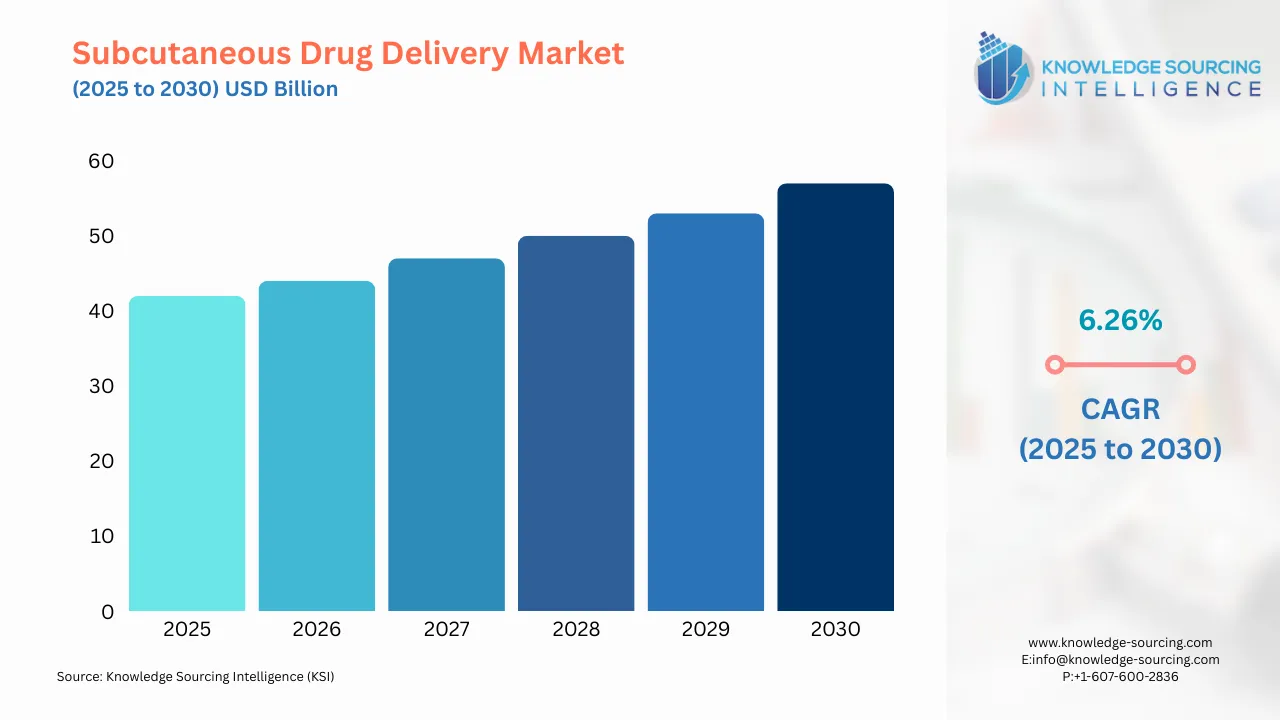
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Size:
The subcutaneous drug delivery market is estimated at USD41.704 billion in 2025 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.26% during the forecast period and reach USD56.503 billion in 2030.
The market for subcutaneous drug delivery devices is growing rapidly, primarily due to increasing demand for advanced minimally invasive solutions. The increase in the prevalence of chronic conditions such as CVD and diabetes, along with advancements in biological drug development, are transforming the modern healthcare landscape.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Growth Drivers:
- The role of Drug-Device Systems in Chronic Disease Management is anticipated to fuel market growth in the projected period.
Major global health challenges that arise from chronic diseases include asthma, multiple sclerosis, cardiovascular conditions, and diabetes. For instance, Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, asthma affects an estimated nearly 28 million people in the United States or about 1 in 12. Within this population, nearly 23 million adults aged 18 years and older have ever been diagnosed with asthma.
Adopting drug-device delivery systems such as prefilled syringes and autoinjectors seems to be an encouraging step forward for improving the outcome of a patient and diminishing healthcare burdens. The systems also help improve convenience for patients while delivering accurate doses, thus saving on the visits made to hospitals for clinical procedures, filling significant gaps in managing chronic diseases.
The diabetes patient population has been increasing over the years, and companies have innovated and executed strategic initiatives to introduce advanced subcutaneous drug delivery devices. Prefilled syringes, especially insulin autoinjectors, have emerged as game-changing solutions, allowing patients to self-administer drugs efficiently and with minimal discomfort. For instance, according to the IDF Diabetes Atlas (2021) says that 10.5% of the adult population, aged between 20 and 79 years, has diabetes and that nearly half of the cases are not even aware that they are living with the condition. As of 2045, according to IDF projections, 1 in 8 adults will be living with diabetes, which will have increased by 46% to an estimated 783 million. Over 90% of people living with diabetes have type 2 diabetes, largely driven by socio-economic, demographic, environmental, and genetic factors.
- Increasing number of geriatric population is expected to increase the demand for subcutaneous drug delivery in the coming years.
Another key factor that has been fuelling the need for subcutaneous drug delivery devices is an increase in the geriatric population. Old age makes the individual vulnerable to chronic conditions such as diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, respiratory infections, asthma, and heart disease. Global health studies reveal that a higher population above 65 years of age is prone to these diseases. Effective and less invasive treatment would be necessary for the above population group. For instance, according to the World Bank, demographic change is increasingly shaping our future. Around the world, people aged 65 and over outnumber children under 5, and over two-thirds of them live in less developed regions of the world. In less developed regions, there will be 1.25 billion people who are 65 and over 2050-around 757 million more than in 2020.
The demand is fulfilled by subcutaneous drug delivery systems as these provide stable, user-friendly devices that assist in the treatment and diagnosis of chronic diseases. This demographic pattern underscores the necessity of innovation in drug delivery systems, but also the crucial role such devices play in the reduction of hospital admissions among the elderly, as well as improved quality of life.
- Biologic Drug Development and Subcutaneous Administration
Biologic drugs have the characteristic advantage of high selectivity for their target disease mechanism. Subcutaneous delivery of these drugs achieves optimal efficacy; however, their development has correspondingly increased demand for delivery systems that can administer these advanced therapies. Subcutaneous delivery devices, including autoinjectors and wearable injectors, are thus being developed in response to these biologic-specific properties, like higher viscosities and dosing intervals.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Segment Analysis:
- By product type, the pen injector segment is anticipated to hold a major market share in the projected period.
Pen injectors will continue to have the largest share of revenue as they are the most convenient, easy to use, and a major player in enhancing compliance by patients. This product category is widely used for diabetes management for insulin injections as well as in other chronic disease management. The growing prevalence of chronic diseases, combined with constant improvements in pen injector technology, is driving the market. Regulatory approvals are becoming increasingly common, and the increasing demand for home-based treatments increases the preponderance of pens within the subcutaneous drug delivery market, providing them with a strong market position. Additionally, increasing product launches for the same are expected to positively influence the pen injector segment in the coming years.
For instance, in February 2023, Phillips-Medisize, a Molex company, and leader in the design and manufacture of drug delivery, diagnostic, and MedTech devices, expanded its product portfolio with the introduction of a disposable pen injector. Ideally suited for high-volume manufacturing, Phillips-Medisize offers pharmaceutical companies a familiar highly competitive pen injector to facilitate faster, more efficient, and cost-effective market entry.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Geographic Analysis:
- The North American subcutaneous drug delivery devices market is anticipated to hold a larger share in the projected period.
The North American region is anticipated to hold a major market share, due to the well-developed healthcare infrastructure, strong emphasis on innovation, and high-end technological capabilities. A healthy health sector is enjoyed in North America due to highly developed medical facilities with superior care, making advanced drug delivery technologies available widely. In addition, heavy investment in research and development for the region fuels continuous innovation of subcutaneous drug delivery devices, which drives market growth along with technological advancement.
The significant prevalence of chronic conditions, including diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, is a primary driver of the market in North America. The Centre for Disease Control and Prevention has estimated that nearly 29.7 million people in the United States, about 8.9% of the population, had diabetes in 2022, making an effective and accessible treatment option extremely important. Devices for subcutaneous drug delivery, including insulin pens, auto-injectors, and wearable injectors, are thus becoming indispensable management tools for such chronic conditions. These devices are far more convenient, precise, and patient-friendly drug administration, particularly for those in need of continuing, long-term treatments. With an aging population and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, the market for these devices is likely to expand even more, cementing North America's position as a leader in the global subcutaneous drug delivery market.
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Recent Development:
- In April 2024, Ypsomed entered into a partnership with Ten23 Health, a global Swiss contract development and manufacturing organization. This partnership aims at advancing the commercialization of the YpsoDose wearable injector for subcutaneous self-injection of large-volume doses. The ten23 drug development, filling, and device assembly will significantly contribute to the product offering.
List of Top Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Companies:
- Gerresheimer AG
- Ypsomed AG
- Medtronic Plc
- Sanofi
- Novo Nordisk
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Size in 2025 | US$41.704 billion |
| Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Size in 2030 | US$56.503 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.26% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Subcutaneous Drug Delivery Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type:
- Prefilled syringes
- Pen injector
- Auto injectors
- Wearable injectors
- Needle-free Injectors
- By Application:
- Diabetes
- Fertility
- Oncology
- Others
- By End-Users:
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Homecare Settings
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- By Geography:
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America