Report Overview
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market - Highlights
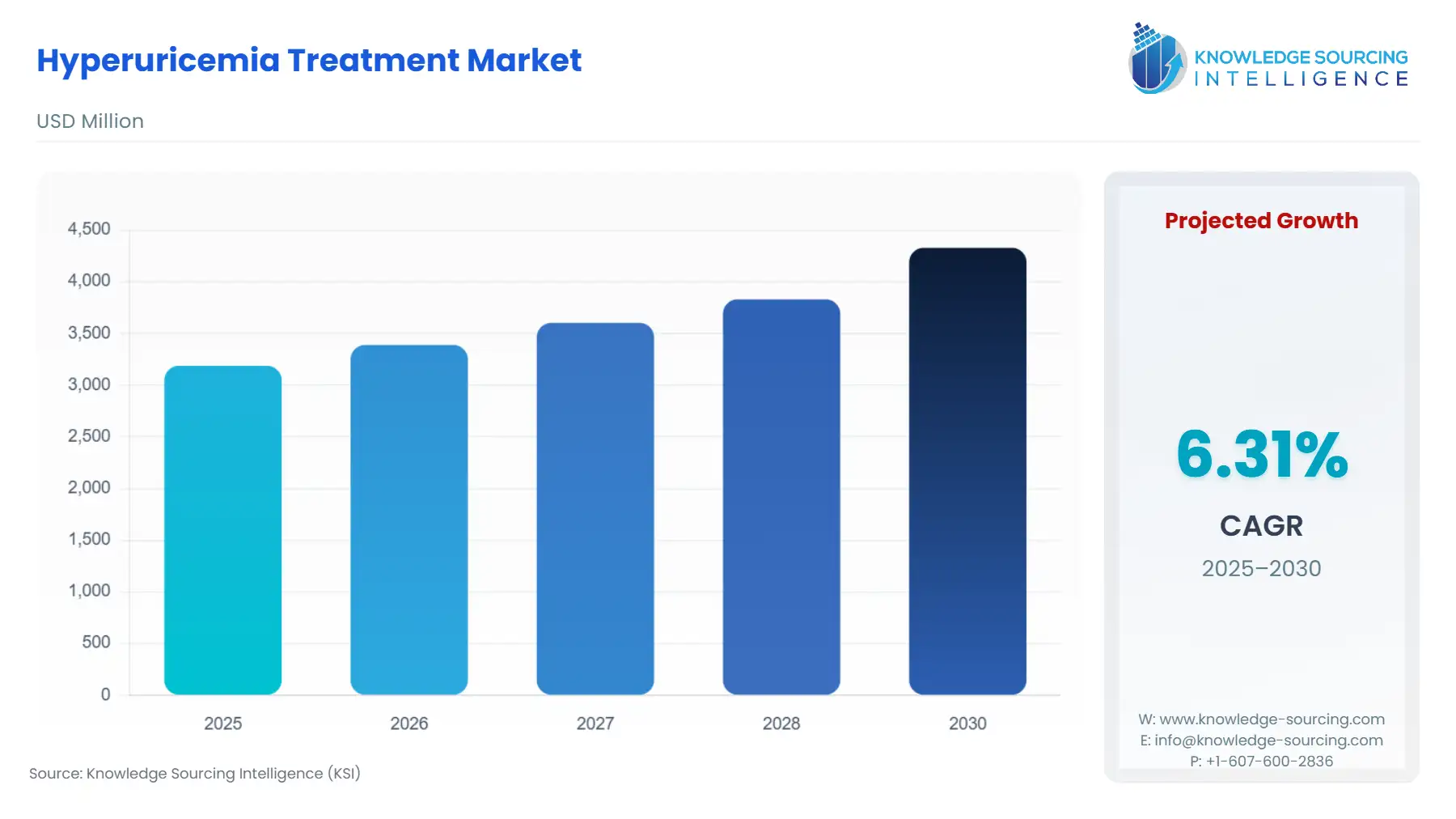
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Size:
The Hyperuricemia Treatment Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.31%, reaching a market size of US$4.329 billion in 2030 from US$3.188 billion in 2025.
The Hyperuricemia Treatment Market is a critical segment of the global pharmaceutical and healthcare industry, addressing the growing prevalence of hyperuricemia—a condition characterized by elevated serum uric acid (SUA) levels in the blood. Hyperuricemia is a significant risk factor for gout, chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome, impacting quality of life and increasing healthcare costs. The market encompasses pharmacological interventions, such as xanthine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., allopurinol, febuxostat), uricosuric agents (e.g., lesinurad), and recombinant uricase (e.g., rasburicase), as well as non-pharmacological approaches, including lifestyle modifications. Driven by increasing global incidence, advancements in therapeutics, and heightened awareness of associated comorbidities, the market is poised for growth.
Hyperuricemia arises from an imbalance between uric acid production and excretion, often influenced by genetic predisposition, obesity and hyperuricemia, purine-rich diet, and chronic kidney disease. The condition affects approximately 38 million Americans, with prevalence rising globally due to lifestyle changes and an aging population. In contrast, symptomatic hyperuricemia manifests as gout or nephrolithiasis, and asymptomatic hyperuricemia—where elevated SUA levels present without clinical symptoms—is increasingly recognized for its potential to contribute to long-term cardiovascular and renal risks. The market addresses both symptomatic and, in specific cases, asymptomatic cases, with a focus on personalized medicine and innovative therapies to manage uric acid levels effectively.
The market is primarily driven by:
Increasing Prevalence of Risk Factors: The global rise in obesity and hyperuricemia, coupled with purine-rich diets (e.g., red meat, seafood, and fructose-rich beverages), is a primary driver. Obesity exacerbates uric acid production and impairs excretion, contributing to hyperuricemia. The aging population further amplifies prevalence, as renal function declines with age, reducing uric acid clearance.
Advancements in Therapeutics: Innovations in urate-lowering therapies, such as novel xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosurics, are expanding treatment options. For example, Shanghai Institute of Biological Products initiated Phase 1 trials for pegloticase, a promising therapy for asymptomatic hyperuricemia, aiming to enhance safety and tolerability. Such developments drive market growth by addressing unmet needs in refractory hyperuricemia and gout.
Rising Awareness of Comorbidities: Growing evidence linking hyperuricemia to chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases is increasing demand for proactive treatment. In Japan, guidelines recommend treating asymptomatic hyperuricemia in patients with high-risk comorbidities, such as chronic kidney disease, to prevent disease progression. This trend is fostering market expansion as healthcare providers prioritize early intervention.
The market faces challenges such as:
Limited Treatment for Asymptomatic Cases: The lack of consensus on treating asymptomatic hyperuricemia restricts market growth, as most guidelines recommend lifestyle changes over pharmacotherapy due to insufficient evidence of long-term benefits versus risks. This limits the market’s scope for a significant portion of the patient population.
High Treatment Costs: Advanced therapies, such as recombinant uricase, are expensive, and the need for chronic management in conditions like chronic kidney disease increases financial burdens. This can deter adoption, particularly in low-resource settings, constraining market penetration.
Management of Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia, defined as elevated SUA levels without gout or kidney stones, is generally not treated with pharmacotherapy unless specific risk factors are present. Management primarily focuses on non-pharmacological interventions, including:
Lifestyle Modifications: Reducing consumption of purine-rich diets (e.g., red meat, seafood, alcohol, and fructose-rich beverages) is critical. Weight loss to address obesity and hyperuricemia can lower SUA by 10–15%, as noted in a 2022 study. Regular exercise and hydration are also recommended to enhance uric acid excretion.
Dietary Supplements: Folic acid and vitamin C have shown potential to reduce SUA levels. A DASH or Mediterranean diet, rich in vegetables and low-fat dairy, is advised, particularly for older adults, as evidenced by a 2022 study confirming its SUA-lowering effects in men.
Pharmacotherapy in High-Risk Cases: In patients with chronic kidney disease, hypertension, or undergoing chemotherapy (at risk of tumor lysis syndrome), xanthine oxidase inhibitors like allopurinol may be prescribed preventively. Japanese guidelines advocate for treatment when SUA exceeds 8 mg/dL in such cases to mitigate cardiovascular and renal risks.
Asymptomatic hyperuricemia is included in the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market, but its contribution is limited due to the preference for non-pharmacological approaches. The market primarily focuses on symptomatic cases (e.g., gout, nephrolithiasis) and high-risk asymptomatic patients, where pharmacotherapy is justified. For instance, clinical trials like those for pegloticase target asymptomatic hyperuricemia in specific populations, indicating a growing but niche market segment.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Trends:
The Hyperuricemia Treatment Market is experiencing transformative trends driven by advancements in personalized medicine and a robust pipeline analysis. Clinical trials of hyperuricemia are focusing on novel urate-lowering therapies, such as URAT1 inhibitors, to address unmet medical needs in patients with refractory gout or asymptomatic hyperuricemia. For instance, in March 2025, Shanton Pharma reported promising Phase 2b results for SAP-001, a urate-lowering therapy showing superior outcomes for patients unresponsive to standard treatments. This reflects a shift toward therapies tailored to individual genetic predispositions and comorbidities.
Drug approvals in 2025 are anticipated to reshape the market, with candidates like ABP-671, a URAT1 inhibitor by Jiangsu Atom Bioscience, advancing through Phase III trials for enhanced efficacy and safety. These developments aim to improve patient adherence by offering simplified dosing regimens, such as once-daily oral therapies, compared to traditional options like allopurinol. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches are gaining traction, leveraging genetic profiling to optimize treatment outcomes. In December 2024, Atom Therapeutics partnered with China Medical System Holdings to commercialize lingdolinurad (ABP-671), targeting unmet medical needs in chronic gout management. These trends underscore a market evolving toward precision, efficacy, and patient-centric care.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Drivers:
Increasing Prevalence of Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors: The Hyperuricemia Treatment Market is propelled by the rising prevalence of lifestyle-related risk factors, particularly obesity and purine-rich diets, which significantly contribute to elevated serum uric acid levels. Obesity impairs uric acid excretion, while diets high in red meat, seafood, and fructose exacerbate hyperuricemia, increasing gout and chronic kidney disease risks. The global shift toward sedentary lifestyles and high-calorie diets has amplified these issues, particularly in urban populations. A 2024 study highlighted the growing burden of gout due to dietary and lifestyle changes, emphasizing the need for effective treatments. This trend drives demand for urate-lowering therapies and lifestyle interventions, as healthcare providers seek to address comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes, which are closely linked to hyperuricemia, thereby expanding the market for both pharmacological and non-pharmacological solutions.
Aging Population and Associated Comorbidities: The aging population is a key driver of the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market, as older adults are more susceptible to hyperuricemia due to declining renal function and chronic kidney disease. Age-related reductions in uric acid clearance elevate risks of gout and cardiovascular complications, necessitating proactive treatment. The global increase in life expectancy, particularly in developed nations, amplifies this demand. A recent study noted that hyperuricemia prevalence rises significantly in individuals over 60, particularly those with comorbidities like hypertension. This demographic shift encourages the adoption of xanthine oxidase inhibitors and emerging therapies like URAT1 inhibitors to manage both symptomatic and asymptomatic hyperuricemia, driving market growth as healthcare systems prioritize early intervention to mitigate long-term health risks in aging populations.
Advancements in Therapeutic Options: Advancements in therapeutic options, particularly in personalized medicine, are fueling the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market. Novel urate-lowering therapies, such as URAT1 inhibitors and improved xanthine oxidase inhibitors, offer enhanced efficacy and safety for patients with refractory gout or asymptomatic hyperuricemia. In March 2025, Shanton Pharma reported positive Phase 2b results for SAP-001, a URAT1 inhibitor addressing unmet medical needs in patients unresponsive to allopurinol. These innovations, coupled with ongoing clinical trials for hyperuricemia, are expanding treatment options and improving patient adherence through simplified dosing regimens. The focus on personalized medicine, leveraging genetic profiling to tailor therapies, further drives market growth by addressing individual variations in genetic predisposition and treatment response.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Restraints:
Limited Consensus on Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia Treatment: A significant restraint in the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market is the lack of consensus on treating asymptomatic hyperuricemia, which limits the market scope. Most guidelines, including those from the American College of Rheumatology, recommend lifestyle modifications over pharmacotherapy for asymptomatic hyperuricemia due to insufficient evidence of long-term benefits versus risks like drug side effects. This restricts the use of urate-lowering therapies to symptomatic cases or high-risk patients with chronic kidney disease or cardiovascular issues. A 2022 study emphasized that treating asymptomatic hyperuricemia remains controversial, with non-pharmacological approaches preferred. This lack of standardized protocols hinders market growth, as a significant portion of the hyperuricemic population is managed outside the pharmacological market, reducing demand for therapies in this segment.
Report Metric Details Total Market Size in 2025 USD 3.188 billion Total Market Size in 2030 USD 4.329 billion Forecast Unit Billion Growth Rate 6.31% Study Period 2020 to 2030 Historical Data 2020 to 2023 Base Year 2024 Forecast Period 2025 – 2030 Segmentation Type of Disease, Treatment Method, End-User, Geography Geographical Segmentation North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific Companies - Amgen Inc.
- Atom Therapeutics Co.
- Ltd.
- Shanton Pharma Co.
- Ltd.
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Teijin Pharma Limited
High Costs of Advanced Therapies: The high cost of advanced therapies, such as recombinant uricase and novel URAT1 inhibitors, poses a significant restraint on the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market. These treatments, often required for refractory gout or chronic kidney disease-associated hyperuricemia, involve substantial development and production costs, making them expensive for patients and healthcare systems. For instance, therapies like pegloticase, used in severe cases, are cost-prohibitive, particularly in low-resource settings, limiting accessibility. A 2024 analysis highlighted the economic burden of biologics in gout management, noting challenges in widespread adoption. Additionally, the need for chronic management in patients with comorbidities increases financial strain, deterring patient adherence and constraining market penetration, especially in regions with limited healthcare funding or insurance coverage.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Segmentation Analysis:
The increasing prevalence of Gout is boosting the market expansion: The Gout segment dominates the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market due to its high prevalence and direct association with elevated serum uric acid levels, which characterize hyperuricemia. Gout, a painful form of inflammatory arthritis caused by urate crystal deposition in joints, drives significant demand for both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. It affects millions globally, with risk factors like obesity, purine-rich diets, and chronic kidney disease exacerbating its incidence. In July 2024, it was reported by The Lancet that gout is a leading comorbidity of hyperuricemia, with a male-to-female prevalence ratio of 3.26:1, underscoring its market significance. Treatments such as xanthine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., allopurinol, febuxostat) and anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., colchicine) are widely prescribed to manage acute flares and prevent chronic progression. The segment’s dominance is further fueled by advancements in personalized medicine, such as URAT1 inhibitors, addressing unmet medical needs in refractory cases, ensuring gout remains the primary focus of therapeutic innovation.
By Treatment Method, Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors are rising in demand: Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors (XOIs), such as allopurinol and febuxostat, are the leading treatment method in the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market due to their widespread use and efficacy in lowering serum uric acid levels. By inhibiting xanthine oxidase, these drugs reduce uric acid production, making them a cornerstone for managing gout and preventing complications like chronic kidney disease. Their dominance is driven by established safety profiles, cost-effectiveness (particularly generics), and applicability across both symptomatic and high-risk asymptomatic hyperuricemia cases. In January 2024, Lupin received FDA approval for generic febuxostat tablets, enhancing accessibility and patient adherence through affordable options. Ongoing clinical trials on hyperuricemia are exploring next-generation XOIs with improved dosing regimens, further solidifying this segment’s market leadership. Their versatility and alignment with personalized medicine trends make XOIs the preferred choice for long-term hyperuricemia management.
North America is expected to lead the market expansion: North America, particularly the USA, holds the largest share of the Hyperuricemia Treatment Market due to its high prevalence of gout and chronic kidney disease, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and robust pharmaceutical innovation. The region’s aging population, coupled with lifestyle factors like obesity and purine-rich diets, contributes to hyperuricemia’s prevalence, affecting over 38 million Americans. The USA leads in drug approvals in 2025, with companies like Amgen advancing therapies like pegloticase for chronic gout. North America’s market dominance is further supported by high healthcare expenditure, widespread adoption of personalized medicine, and active clinical trials for hyperuricemia, such as those for URAT1 inhibitors. The region’s focus on early diagnosis and treatment, driven by awareness of hyperuricemia’s comorbidities, ensures its leadership in addressing unmet medical needs and driving therapeutic advancements.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Key Developments:
URECE® (Dotinurad) Launch in China: URECE (Dotinurad) is a selective urate reabsorption inhibitor (SURI) that works by selectively inhibiting the urate transporter (URAT1) in the kidney, thereby promoting the excretion of uric acid and lowering serum uric acid levels. The drug was approved by China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in December 2024 and subsequently launched in July 2025. This launch is significant as it introduces a new class of urate-lowering therapy (ULT) to the estimated 23 million gout patients in China, providing an alternative to traditional xanthine oxidase inhibitors like allopurinol and febuxostat.
URECE® (Dotinurad) Approval and Launch in the Philippines: Following its approval in Thailand in late 2024, URECE (Dotinurad) received approval in the Philippines in February 2025. As a potent URAT1 inhibitor, this uricosuric agent is crucial for patients with gout and hyperuricemia who have an underexcretion of uric acid. Its introduction expands the modern ULT options in Southeast Asia, offering a potentially safer and more effective path to achieving target serum uric acid levels for patients who have limited options or contraindications to other treatments.
Gloperba® (Colchicine Oral Solution) Launch: Gloperba is a low-dose, 0.6 mg colchicine in a ready-to-use oral solution format, approved by the U.S. FDA in August 2024 for the prophylaxis of gout flares in adults. While colchicine is an old drug, this new liquid formulation is significant for patients who have difficulty swallowing tablets or those who require precise, lower-dose adjustments, particularly in the presence of comorbid conditions like chronic renal impairment. This format aims to improve adherence and potentially reduce the gastrointestinal side effects common with the tablet form.
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Scope:
Hyperuricemia Treatment Market Segmentation:
By Type of Disease
Gout
Chronic Kidney Diseases
Others
By Treatment Method
Uricosuric agents
Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors
Recombinant Uricases
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Others
By End-User
Hospitals
Clinics
Others
By Geography
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
United Kingdom
Germany
France
Spain
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Others
Asia Pacific
China
Japan
South Korea
Australia
India
Indonesia
Thailand
Others