Report Overview
UK 5G Base Station Highlights
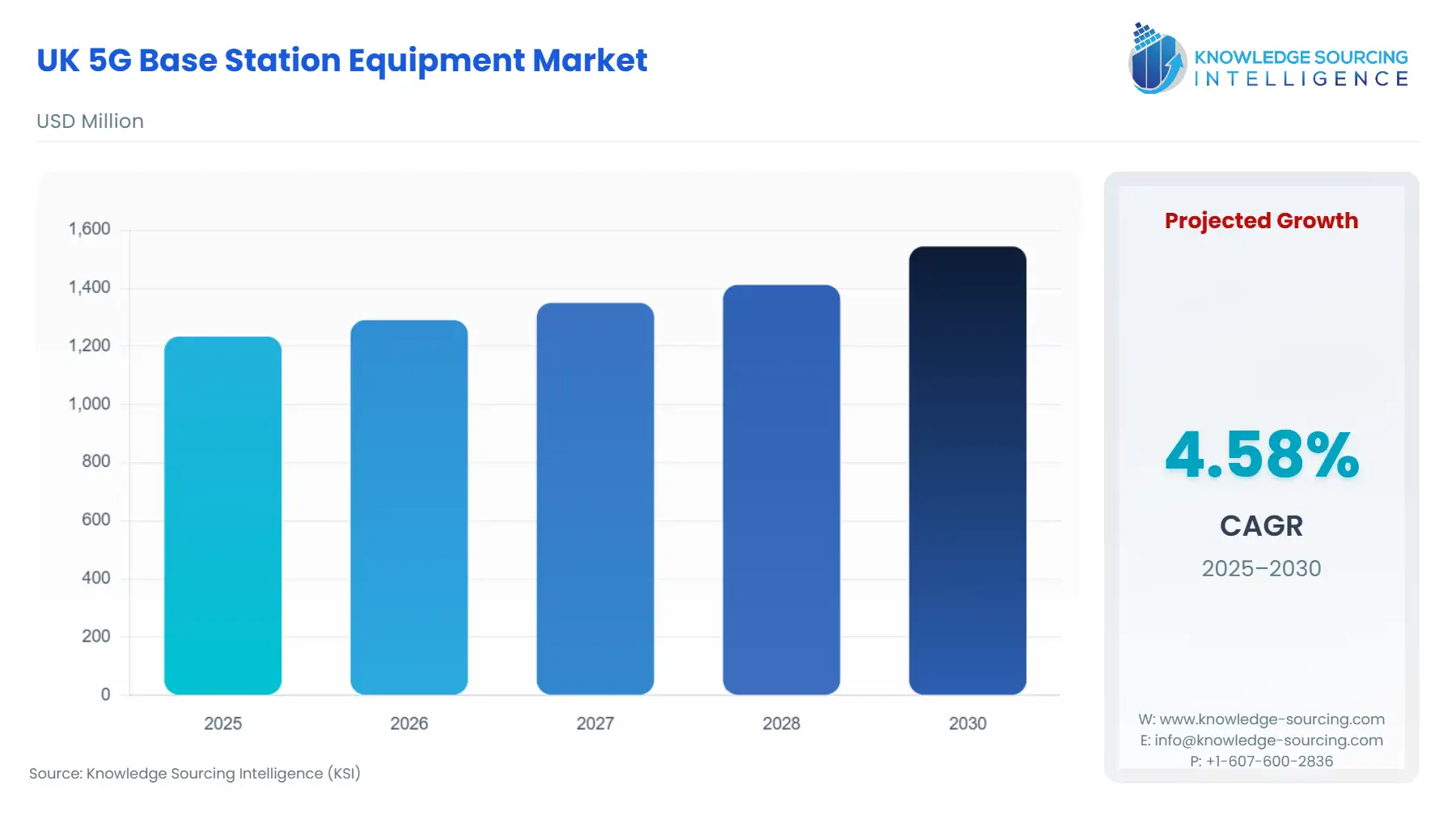
UK 5G Base Station Equipment Market is set to progress from USD 1.234 billion in 2025 to USD 1.544 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 4.58%.
UK 5G Base Station Equipment Market Key Highlights
The UK 5G Base Station Equipment Market is undergoing a fundamental transformation, driven by an ambitious national coverage agenda and profound regulatory shifts. Following initial Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G rollouts that leveraged existing 4G core infrastructure, the market imperative has decisively shifted toward 5G Standalone (SA) deployment and vendor diversification. This dual focus necessitates significant capital expenditure in the Radio Access Network (RAN) layer—specifically new Baseband Unit (BBU) and Radio Unit (RU) hardware—to support advanced capabilities such as network slicing and ultra-low latency. Furthermore, the commercial and legislative environment mandates a greater focus on supply chain resilience and security, fundamentally restructuring procurement decisions and driving the adoption of new, flexible technologies like Open RAN across the network, positioning the UK as a primary market for this architectural evolution in Europe.
UK 5G Base Station Equipment Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The primary catalyst for equipment demand is the mandated removal of high-risk vendor technology, compelling MNOs to replace core and RAN hardware, thereby creating immediate, non-discretionary procurement cycles for Radio Units and Baseband Units. Concurrently, the proliferation of data traffic, which reached 151 Petabytes (PB) in 2023, up 140% from 2022, structurally increases the need for high-capacity Massive MIMO Antennas capable of handling dense user loads in mid-band and urban environments. Additionally, government initiatives like the Shared Rural Network (SRN) indirectly fuel demand for Macrocell Base Stations in underserved rural geographic areas to meet coverage obligations, expanding the market footprint beyond dense urban centers. This regulatory pressure and data explosion collectively ensure sustained investment in RAN hardware refresh and greenfield sites.
Challenges and Opportunities
A critical challenge is the significant capital outlay and complexity associated with migrating from Non-Standalone (NSA) to Standalone (SA) 5G architectures, which requires a complete overhaul of the core and an upgrade of RAN infrastructure, creating a financial constraint on MNOs. However, this same challenge presents a significant opportunity: the government's push for Open RAN adoption to enhance supply chain resilience has become a major growth avenue. Open RAN Base Stations and disaggregated Radio/Baseband equipment allow for multi-vendor interoperability and a faster introduction of new players like Mavenir, increasing the addressable market for non-traditional vendors. Furthermore, the availability of new mmWave spectrum from Ofcom unlocks a high-value opportunity to deploy Small Cells in dense urban spots and private enterprise networks where ultra-high throughput is paramount.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
5G Base Station Equipment, being a physical product, is intrinsically linked to the global semiconductor and rare earth element supply chains. The Radio Unit (RU) and Baseband Unit (BBU) rely heavily on high-performance semiconductors, including specialized System-on-Chip (SoC) technology, which have experienced persistent supply volatility. Pricing dynamics are complex; while global scale allows vendors like Ericsson and Nokia to achieve competitive manufacturing costs, the UK-specific demand is influenced by the mandated replacement cycle under the Telecoms (Security) Act. This regulatory obligation creates inelastic demand, allowing vendors that meet compliance standards to maintain favorable pricing structures for new or replacement RAN equipment in the short to medium term. The cost of advanced components like gallium nitride (GaN) power amplifiers, essential for Massive MIMO efficiency, remains a core cost driver.
Supply Chain Analysis
The UK 5G base station equipment supply chain is characterized by a high degree of global centralization, with key production hubs located in East Asia (semiconductor fabrication and electronic assembly) and, to a lesser extent, Northern Europe and the US (high-value R&D and core software). The logistical complexity stems from the need to secure high-performance, specialized components for Massive MIMO Antennas and RUs. A critical dependency is the availability of precision-engineered components, which are subject to global geopolitical and trade friction. This reliance necessitates a 'just-in-case' inventory strategy rather than 'just-in-time,' especially following the supply chain disruptions of the preceding years. The government’s security focus amplifies this, forcing MNOs to undertake lengthy certification and vetting processes to ensure the security and provenance of all physical hardware entering the UK network.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| UK | Telecommunications (Security) Act 2021 | Mandates a structural shift in the vendor landscape, directly driving demand for new, compliant equipment from approved suppliers (e.g., Ericsson, Nokia). The associated high-risk vendor removal deadlines create predictable, high-volume replacement cycles for existing Radio Unit and Baseband Unit inventory. |
| UK | Ofcom Spectrum Allocation (mmWave) | The decision to auction high-frequency 26 GHz and 40 GHz bands directly catalyzes immediate, high-density demand for specialized High-Band Base Station Equipment, particularly Small Cells and Massive MIMO Antennas, in urban and high-traffic areas. |
| UK | Shared Rural Network (SRN) Initiative | While primarily focused on 4G, the initiative provides the financial and planning framework (reformed planning and land access rules) to erect new shared mast infrastructure, creating the physical sites for future and concurrent Macrocell Base Station 5G deployment in rural geographies. |
In-Depth Segment Analysis
By Technology: Open RAN Base Stations
The Open RAN segment is the fastest-growing technology driver for the UK equipment market, propelled by both government mandate and MNO strategy to reduce vendor lock-in. The Telecoms Diversification Taskforce specifically promoted an Open RAN approach, creating a direct demand signal for Open RAN-compliant hardware, including O-RUs, O-DUs, and O-CUs. This shift immediately increases the need for virtualized Baseband Unit (BBU) software solutions and specialized hardware running on Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS) servers, moving away from monolithic proprietary solutions. Mavenir's work with MNOs, including a collaboration with Three UK and Red Hat to double 5G speeds in Glasgow using Open RAN small cells, demonstrates live commercial adoption. This architectural change dictates that procurement will increasingly favour disaggregated and modular equipment, enabling MNOs to mix and match RU and BBU components from different, compliant suppliers. The resulting ecosystem fosters competition, lowers the barriers to entry for specialized hardware providers, and rapidly increases demand for software-centric RAN solutions.
By End User: Enterprise 5G Networks
The Enterprise 5G Networks segment represents a distinct, high-growth vector, moving beyond traditional Telecom Operator deployment models. Its necessity is driven by the intrinsic capability of 5G Standalone (SA) and Mid-Band/High-Band spectrum to deliver use cases requiring Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), such as industrial automation, smart port logistics, and remote healthcare. Enterprises in the manufacturing and logistics sectors require dedicated, secure, and localized connectivity that standard public networks cannot guarantee. This requirement directly fuels demand for private 5G network equipment, predominantly Small Cells and dedicated Mid-Band RUs, capable of high-density indoor coverage and multi-access edge computing (MEC) integration. Ofcom’s policy of supporting shared use licenses further lowers the barrier for enterprises to acquire spectrum, accelerating the deployment of localized 5G base stations. This segment necessitates smaller, more adaptable equipment form factors compared to traditional Macrocell deployments, focusing on the high-value features of 5G rather than purely population coverage.
Competitive Environment and Analysis
The UK market is characterized by intense competition between the major traditional European vendors and aggressive positioning by specialized Open RAN disruptors. The landscape is fundamentally shaped by the Telecommunications (Security) Act 2021, which effectively restricts one major vendor and forces MNOs to pivot to compliant alternatives. This dynamic has created a procurement surge favoring European and US-headquartered suppliers.
Ericsson: The company is strategically positioned as a primary beneficiary of the vendor diversification mandate. Ericsson secured a major contract in September 2025 to supply the majority of the merged VodafoneThree’s next-generation UK mobile network, including becoming the sole core network vendor. This agreement leverages their Radio System hardware and software, focusing on a robust, performance-led deployment of 5G Standalone (5G SA) technology. Their strategic positioning emphasizes end-to-end network control and guaranteed security compliance, driving demand for their Macrocell Base Stations and Core Network solutions.
Nokia: Nokia is operating with an equally strong competitive posture, also capturing a significant portion of the mandated network transition. In September 2025, Nokia won a separate, significant 5G deal with VodafoneThree, committing to supply equipment from its energy-efficient AirScale RAN portfolio to approximately 7,000 sites nationwide. This deal includes the latest generation of ultra-performance Habrok Massive MIMO radios and multiband Pandion Remote Radio Heads. Nokia’s strategy focuses on energy efficiency, its ReefShark System-on-Chip technology, and providing solutions for large-scale, high-capacity coverage, directly driving demand for their advanced Massive MIMO Antennas.
Mavenir: As a cloud-native software provider, Mavenir is the key challenger in the Open RAN segment, benefiting directly from MNOs’ long-term desire for a multi-vendor, lower-cost RAN architecture. Mavenir’s positioning is centred on its Open vRAN solution, which enables network operators to deploy virtualized Baseband Units (BBUs) on COTS hardware. A notable development is their successful collaboration with Three UK and Red Hat to roll out Open RAN small cells in Glasgow (May 2025/September 2025), which demonstrated a significant reduction in urban traffic congestion. Mavenir’s success drives demand for O-RAN compliant Radio Units (O-RUs) from various third-party suppliers, fundamentally disrupting the traditional closed system procurement model.
Recent Market Developments
- September 2025: Ericsson secured a multi-billion SEK contract to supply the majority of the merged VodafoneThree’s new UK mobile network. The partnership includes supplying the Radio System hardware and software to power the upgraded radio network and involves the deployment of 5G Standalone (5G SA) technology, making Ericsson the sole core network vendor for the newly merged entity.
- September 2025: Nokia announced a significant deal with VodafoneThree to supply equipment for the network modernization drive. The agreement will see Nokia providing its AirScale RAN portfolio, including Habrok Massive MIMO radios and Remote Radio Heads, to approximately 7,000 sites nationwide, supporting the accelerated deployment of a secure, future-proof network across the UK.
- May 2025: Mavenir and Three UK successfully completed the UK's first trial of O-RAN compliant small cells working alongside legacy macro cells in a dense urban environment in Glasgow city centre. The deployment utilized Mavenir's Open vRAN solution and doubled 5G speeds, demonstrating the technological and commercial viability of open, multi-vendor architectures for urban capacity additions.
UK 5G Base Station Equipment Market Segmentation
- BY TYPE OF BASE STATION
- Macrocell Base Stations
- Small Cells
- Open RAN Base Stations
- BY PRODUCT TYPE
- Radio Unit (RU)
- Baseband Unit (BBU)
- Massive MIMO Antennas
- Power Systems & Supporting Equipment
- BY DEPLOYMENT MODE
- Standalone
- Non-Standalone
- BY FREQUENCY BAND
- Low-Band
- Mid-Band
- High-Band
- BY END USER
- Telecom Operators
- Government & Defense
- Enterprise 5G Networks