Report Overview
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Highlights
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Size:
The Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market is expected to climb at a CAGR of 15.80%, reaching USD 5.111 billion in 2030 from USD 2.454 billion in 2025.
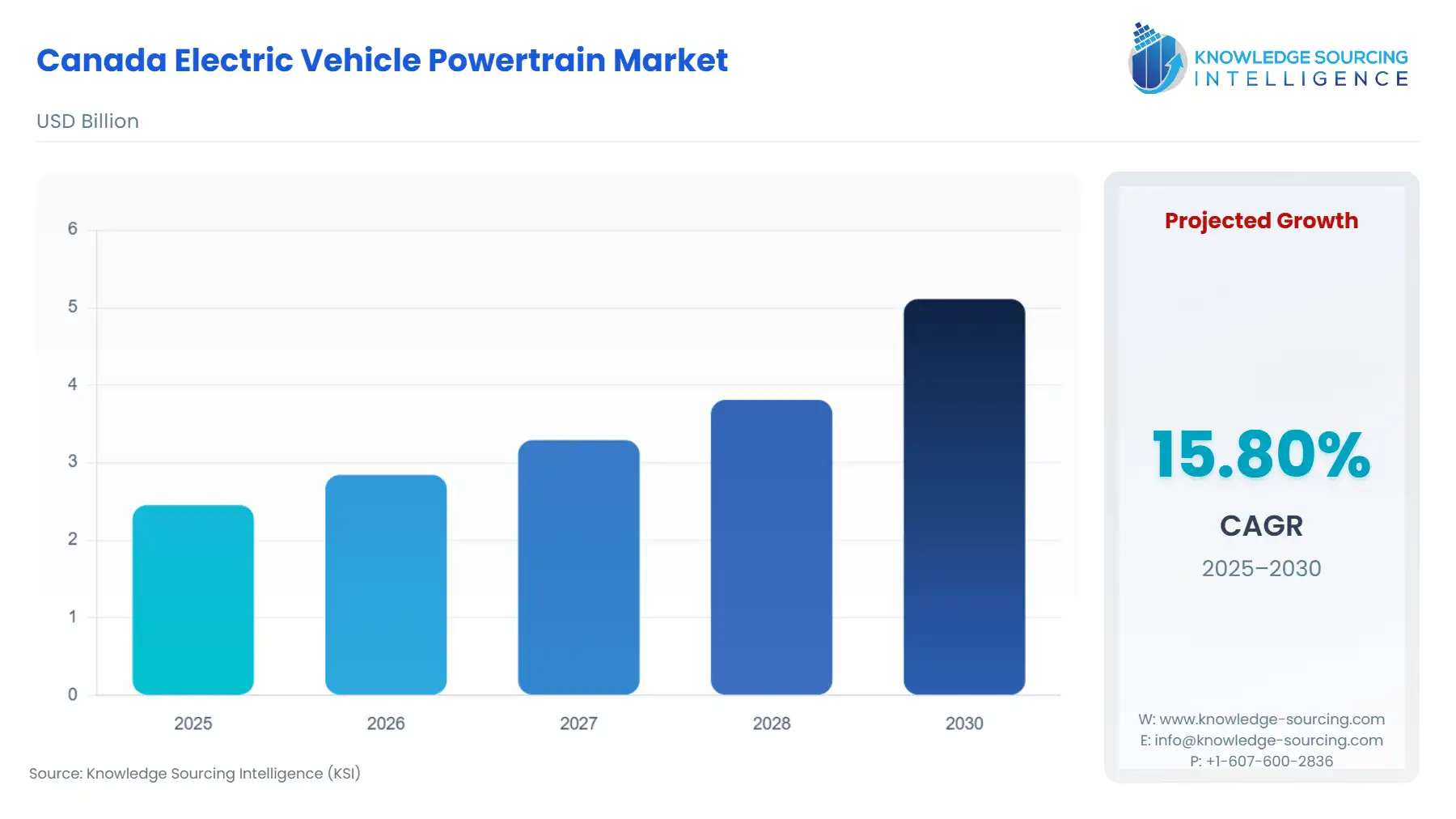
Canada's electric vehicle powertrain market is entering a pivotal phase of industrial localization and policy-driven demand saturation. The sector’s immediate trajectory is shaped less by organic consumer adoption rates and more by top-down regulatory frameworks that compel manufacturers to re-engineer their Canadian production footprints. Substantial public and private capital injections into the Ontario automotive cluster are establishing a complete, vertically integrated supply chain, spanning from cathode active materials to final vehicle assembly. This strategic pivot ensures the long-term, sustained demand for advanced powertrain components, including integrated drive units, power electronics, and sophisticated thermal management systems, by mitigating reliance on complex, long-haul international logistics.
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary catalyst propelling the market is the regulatory certainty provided by the federal Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) sales mandate. This legislation compels automakers to progressively increase the share of ZEVs sold, beginning with a 20% target by 2026 and culminating in 100% by 2035. This supply-side regulation directly translates into guaranteed, escalating demand for complete EV powertrains, including the battery pack, e-axle, and Power Electronics, irrespective of quarterly sales fluctuations in non-mandated provinces. Concurrently, the electrification of the commercial fleet acts as a powerful growth accelerant. Government funding programs specifically targeting medium- and heavy-duty vehicles (MHDVs), combined with fleet operators’ recognition of lower total cost of ownership (TCO) from reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, generate strong, sustained demand for heavy-duty electric motor and battery pack solutions tailored for bus, truck, and van applications.
- Challenges and Opportunities
A key constraint facing the market is the fragmentation of consumer adoption across the provinces, where significant portions of the country, outside of Quebec and British Columbia, exhibit a preference for full hybrids over Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs). This hesitation, driven by high interest rates, affordability concerns, and persistent range anxiety, creates a demand challenge for pure BEV-specific powertrains while simultaneously opening an opportunity for suppliers of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) powertrains. The PHEV, utilizing a smaller battery and electric motor in conjunction with an internal combustion engine, serves as a transitional technology, allowing component suppliers to capture a demand segment from risk-averse consumers and automakers seeking to meet initial ZEV compliance targets. The second significant opportunity lies in addressing the local skills gap. As multi-billion-dollar facilities for battery cell production and EV assembly come online, a specialized workforce for high-voltage systems manufacturing, battery management systems, and advanced power electronics is critically needed.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The electric vehicle powertrain, being a physical hardware system, is fundamentally constrained by the supply and pricing dynamics of its constituent critical minerals. An electric vehicle requires significantly higher quantities of key materials—specifically lithium, nickel, cobalt, and graphite—compared to a traditional internal combustion engine vehicle. Canada's response, the federal Critical Minerals Strategy, channels substantial investment into domestic exploration and processing capacity, directly influencing pricing stability and supply security for local manufacturers. The primary pricing imperative is to reduce the long-term cost of the battery pack, which represents the largest single cost component of the powertrain. Fluctuations in global lithium and nickel commodity pricing translate directly into the final price and demand elasticity of the complete powertrain, with localized processing acting as a crucial hedge against global geopolitical and logistical volatility.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The Canadian EV powertrain supply chain is undergoing a rapid geographical transformation from a purely import-reliant model to a nascent, integrated North American ecosystem, primarily centered in Ontario and Quebec. Key production hubs are emerging in Southern Ontario, following massive OEM commitments to retool existing assembly plants for EV production and the establishment of new battery cell and cathode active material (CAM) manufacturing facilities. Logistical complexities stem from the global sourcing of highly specialized sub-components, such as silicon carbide power semiconductors, which are essential for high-efficiency inverters. The domestic industry's dependency on key international partners for advanced battery cell technology remains high, necessitating strategic government and private sector collaborations to build out full-cycle production, from mined minerals to finished battery packs, thereby strengthening the regional supply chain's resilience and reducing en route time to assembly.
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Canada (Federal) |
Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Sales Mandate |
Creates a non-negotiable supply-side obligation for automakers, guaranteeing a minimum level of demand for electric vehicle powertrains to meet required annual sales targets. |
|
Ontario |
Provincial Investments and Support |
Direct financial support to OEMs (e.g., Stellantis, Honda, GM) for retooling assembly plants and establishing battery manufacturing, creating a regional demand cluster for powertrain components. |
|
Quebec |
ZEV Act |
Imposed earlier sales targets, significantly accelerating regional BEV adoption and establishing Quebec as a stronghold for early, high-volume demand for electric powertrain components in the Canadian market. |
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segment Analysis:
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
The BEV segment constitutes the foundational growth driver for the most complex and high-value components within the electric vehicle powertrain market. The specific requirement is driven by the imperative for maximum energy density and superior system integration. Automakers require sophisticated, high-voltage Battery Management Systems (BMS) to manage larger battery packs and liquid-based Thermal Management Systems (TMS) to ensure optimal operating temperatures for extended range and faster charging. This growth is further concentrated on highly efficient, integrated e-axles, which combine the electric motor, power electronics, and transmission into a single, compact unit. This integration reduces overall vehicle weight, improves efficiency, and reduces assembly complexity for OEMs, directly increasing demand for advanced, compact permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs). Federal mandates and consumer expectation for long-range travel sustain the high-specification component demand within this segment.
- By Vehicle Type: Commercial Vehicle
The commercial vehicle segment is driven by fundamental business economics, fleet renewal cycles, and public sector mandates. Unlike passenger cars, the growth catalyst here is the measurable operational cost saving derived from reduced maintenance and lower energy costs over the TCO, directly increasing demand for durable, heavy-duty powertrain components. Specifically, commercial operators require robust, high-torque electric motors and rugged, modular battery packs capable of sustained, high-duty-cycle operation. Government initiatives, such as funding for the deployment of electric transit buses and last-mile delivery vans, create guaranteed procurement streams, notably for components like electric drive systems built on General Motors’ Ultium platform, which is being produced for its BrightDrop commercial line in Canada. This focus on utility and cost-effectiveness shifts demand toward reliability and power output rather than merely long-distance range.
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Competitive Analysis:
The Canadian Electric Vehicle Powertrain market's competitive landscape is defined by the strategic presence of multinational automotive OEMs and their Tier 1 suppliers, who are establishing localized manufacturing capacity. Competition centers on securing intellectual property around high-efficiency motor design, battery cell chemistry, and power electronics integration.
- Stellantis N.V. has committed billions to retooling its Canadian assembly plants, notably the Windsor Assembly Plant, to produce vehicles utilizing the new STLA Large BEV platform. This strategic move creates direct, substantial, and long-term demand for the company’s internal and joint venture-sourced battery packs and integrated drive units, positioning the company as both a major customer and a manufacturing anchor. Stellantis’ joint venture with LG Energy Solution, NextStar Energy, to construct a large-scale battery manufacturing facility in Windsor is crucial to securing the domestic supply of the most valuable powertrain component.
- General Motors of Canada Company (GM) is leveraging its existing footprint, transforming the CAMI Assembly Plant in Ingersoll into the country’s first large-scale electric commercial vehicle production facility for its BrightDrop line. This transformation creates immediate, targeted demand for its proprietary Ultium battery platform components—including cells, modules, and drive units—with a focus on the commercial (van and truck) segment. The company's co-investment in a cathode active material (CAM) plant in Bécancour, Quebec, with POSCO Chemical, further fortifies its vertically integrated supply chain for core battery powertrain components.
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Developments:
- September 2025: NextStar Energy (Stellantis/LGES Joint Venture) marked the official completion of construction for its $5 billion EV battery plant in Windsor, Ontario. The achievement of the occupancy permit signals the transition from the construction phase to the final preparations for full-scale cell production, representing a critical capacity addition to the domestic supply of the EV powertrain's key component.
- April 2024: Honda Canada announced a $15 billion investment to build a new electric vehicle manufacturing ecosystem in Ontario, including an EV assembly plant and a battery manufacturing facility. This is a significant capacity addition that will create new, long-term demand for a full suite of localized powertrain components to support multiple new electric vehicle models.
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.454 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 5.111 billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.80% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Propulsion Type, Vehicle Type |
| Companies |
|
Canada Electric Vehicle Powertrain Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Battery Pack
- Transmission
- Power Electronics
- Battery Management System
- Thermal Management System
- Others
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Car
- Commercial Vehicle
- Others