Report Overview
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
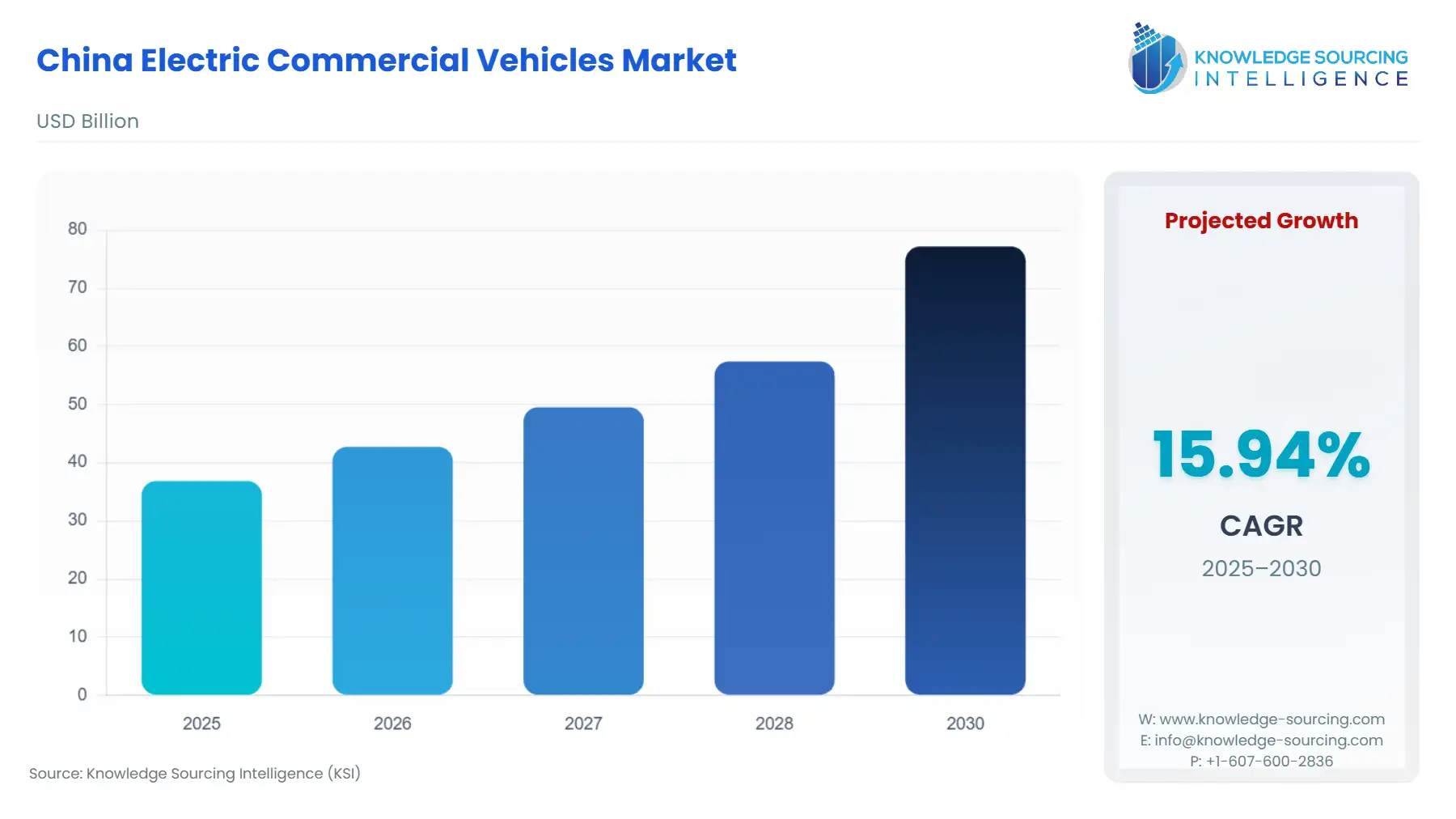
The China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is projected to rise at a CAGR of 15.94%, increasing to USD 77.188 billion in 2030 from USD 36.85 billion in 2025.
The Chinese Electric Commercial Vehicles (eCV) market has transitioned from a subsidized, policy-driven experiment to a commercially viable sector, establishing China as the undisputed global leader in the production and deployment of electrified fleets. This rapid evolution, underpinned by a strategic national ambition for a low-carbon economy, has resulted in profound shifts across vehicle segments. The initial focus on public transit is yielding to a broad-based electrification effort now encompassing logistics, construction, and specialized industrial vehicles. This shift is not merely a quantitative expansion but a qualitative change, with technological advancements like battery swapping and high-density lithium iron phosphate (LFP) chemistries emerging to meet the rigorous operational requirements of commercial end-users. The market's current phase is characterized by a drive for operational efficiency and total cost of ownership (TCO) parity with internal combustion engine counterparts, setting the stage for global technological leadership.
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Strict governmental enforcement of carbon reduction targets and stringent urban emission standards acts as the principal catalyst propelling the demand for eCVs. These regulations compel municipal fleet operators and major logistics corporations to aggressively transition away from diesel vehicles during scheduled fleet renewal cycles, immediately increasing purchase orders for electric buses, light-duty trucks, and vans. Furthermore, significant tax incentive packages, such as the RMB 520 billion tax break package spanning 2024-2027, directly lower the total acquisition cost for fleet buyers, making eCVs financially more competitive against traditional vehicles and thus creating direct, price-elastic demand. The continuously improving energy density and durability of battery packs also increase the vehicle's real-world operational range, mitigating range anxiety and increasing the demand for ECVs in longer-haul applications that were previously unsuitable.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary constraint facing the eCV market is the persistent high and volatile cost of critical battery raw materials—lithium, cobalt, and nickel—which can account for over 40% of a battery-electric vehicle's manufacturing cost. This pricing volatility creates uncertainty in the long-term TCO calculation for large-scale fleet procurements, thereby decreasing purchase certainty and acting as a headwind against demand. Concurrently, a significant market opportunity exists in establishing comprehensive public charging infrastructure. Despite the increasing proliferation of private charging piles, the charging gap remains a critical issue for high-utilization commercial vehicles. Developing and standardizing battery swapping technology and building out a dense network of high-power charging stations directly unlock higher asset utilization rates, which is a key commercial imperative, and substantially increases the addressable demand for electric trucks and vans in intercity logistics.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The ECV market, being a physical product centered on the battery-electric powertrain, is highly sensitive to the supply chain of lithium-ion battery components. The cost of battery packs is significantly affected by the scarcity and geopolitical concentration of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Although technological innovations and economies of scale continue to exert downward pressure on manufacturing costs, the material cost of the Lithium-ion battery (LIB) is fundamentally driven by finite material reserves. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) chemistry, a technology dominated by Chinese firms, due to its lower cost and greater safety profile compared to nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) alternatives. This material shift directly impacts ECV pricing, making certain vehicle segments, particularly medium-duty and city buses, more cost-competitive and accessible to a wider pool of buyers, consequently boosting unit demand.
- Supply Chain Analysis
China holds a dominant position across the global ECV supply chain, particularly in the midstream segment of battery manufacturing, exemplified by companies like Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd. (CATL). Production hubs for cells and packs are highly concentrated within China. The upstream segment, however, is characterized by geographical disequilibrium, with raw material mines for lithium, nickel, and cobalt heavily concentrated in a few countries (e.g., Australia, Chile). This creates a fragile linkage between raw material sourcing and the major battery manufacturing centers in China. Logistical complexity is managed through deep integration between domestic ECV manufacturers and battery suppliers, allowing for accelerated technology deployment, such as the rapid adoption of LFP batteries and battery-swapping architectures, creating a critical dependency for global automakers.
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
Key government regulations are systematically engineering market expansion:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
China (National) |
New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2021-2035) |
Establishes a long-term national roadmap, instilling confidence in manufacturers and investors, thereby encouraging the capacity expansion necessary to meet future demand. |
|
China (National) |
Tax Exemption for NEVs (2024-2027) |
Provides a complete exemption from the purchase tax for NEVs, directly reducing the upfront capital expenditure for fleet operators and strongly driving short-to-medium term purchasing demand. |
|
China (Local, e.g., Shenzhen) |
Emission and Fleet Renewal Mandates |
Local policies enforcing a 100% electrification target for urban bus fleets (as completed by Shenzhen) create guaranteed, immediate, and localized demand for electric buses and coaches. |
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Public Transportation
The Public Transportation segment, encompassing city buses and coaches, represents the most mature and saturated part of the Chinese eCV market. The need for electric buses is now almost exclusively driven by scheduled fleet replacement cycles and the operational TCO advantage they hold over diesel counterparts, rather than initial policy mandates. Cities like Shenzhen, which achieved 100% bus electrification, serve as an operational proof point, demonstrating the long-term reliability and lower maintenance costs of large-scale e-bus fleets. Furthermore, the fixed-route nature of public transport simplifies the necessary charging infrastructure planning and execution, further solidifying the BEV as the superior TCO choice. The focus for demand is shifting toward technology upgrades, such as longer-range batteries for coaches and the integration of smart-charging systems to manage power consumption and grid integration.
- By Propulsion Type: Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
The BEV segment dominates eCV demand, particularly in the light-duty and urban vehicle categories, due to its zero-tailpipe emission profile, which aligns perfectly with dense city center regulations. BEV demand is primarily catalyzed by a high degree of technological maturity in Chinese battery manufacturing, which has driven down cell costs and allowed for segment-specific optimization (e.g., LFP for energy density-sensitive trucks). The rapid deployment of battery swapping infrastructure, especially for heavy-duty applications in steel, port, and mining logistics, is a key demand stimulant. This technology minimizes non-revenue-generating downtime, an essential factor for commercial operations, directly addressing the core drawback of BEVs and substantially increasing their economic viability and adoption rate across the logistics and construction application segments.
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis
The Chinese eCV market's competitive landscape is defined by the vertical integration capabilities of domestic manufacturers, particularly those that control the entire value chain from battery cell to vehicle assembly. Competition is centered on TCO advantages, range extension, and charging/swapping flexibility.
- BYD Company Limited: BYD stands as a dominant force, utilizing its proprietary expertise in battery development, specifically the Blade Battery, to gain a strategic advantage. The company offers a comprehensive range of commercial vehicles spanning buses, coaches, sanitation vehicles, and logistics trucks. Its strategy, based on the "7+4 Full Market EV Strategy" released in April 2015, targets electrification across ten market segments including public transport, logistics, and specialized airport/port operations, underscoring its commitment to end-to-end commercial solutions.
- CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Ltd.): Although primarily a battery manufacturer, CATL's strategic positioning fundamentally shapes the ECV competitive environment. CATL's focus on technological leadership, evidenced by its aggressive capacity expansion in LFP and the development of new chemistries like sodium-ion batteries, directly influences the cost and performance metrics of nearly all ECV original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Its dominance as the largest battery supplier to the market gives it critical leverage and allows it to drive down the cost curve for the entire sector.
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments
- March 2025: Heavy-Duty Battery Electric Truck Sales Peak. Sales of battery electric heavy trucks in China soared to over 14,700 units, reaching a new high market share of 22% in December 2024. This market penetration, more than double the volume recorded in January 2024, reflects the commercial viability of electric powertrains in the high-utilization logistics and infrastructure sectors.
- February 2022: BYD Secures Major US Truck Order. BYD announced that Swedish freight technology company Einride purchased 200 units of its Class 8 8TT battery-electric day cab trucks for deployment in the United States. This order, described as the largest outside of Asia, confirmed the export-readiness and global competitive quality of Chinese-assembled electric heavy trucks.
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 36.85 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 77.188 billion |
| Growth Rate | 15.94% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
China Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others