Report Overview
Electric Tractors Market - Highlights
Electric Tractors Market Size:
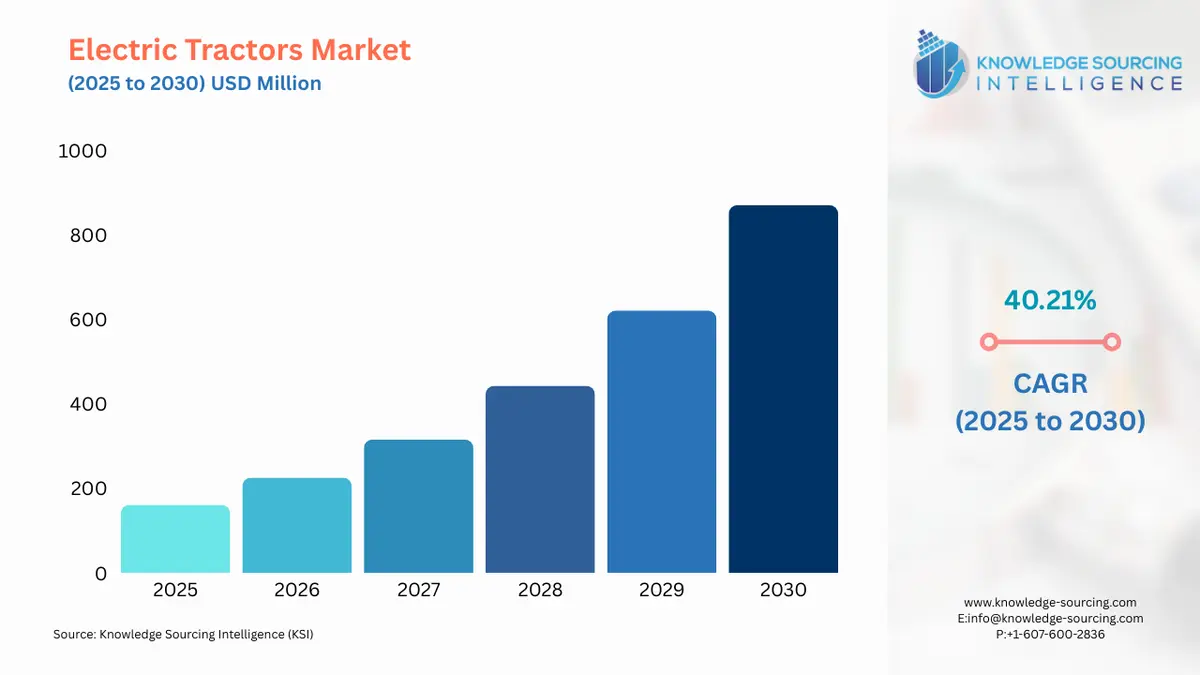
The Electric Tractors Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 40.21%, reaching USD 870.767 million in 2030 from USD 160.675 million in 2025.
The electric tractors market is transitioning from a niche segment to a viable alternative in the agricultural and landscaping sectors. This shift is predicated on the imperative for sustainable farming practices and the long-term economic advantages of electric machinery. While numerous factors are driving the nascent demand for electric tractors, the industry's progression is contingent on overcoming substantial barriers related to capital investment and infrastructure.
Electric Tractors Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The market for electric tractors is propelled by factors that directly impact farmer and commercial operator demand by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and aligning with global sustainability initiatives. A primary driver is the rising cost of diesel fuel, which makes the lower operational cost of an electric tractor—due to cheaper electricity and fewer moving parts—a compelling economic proposition. This operational cost advantage directly increases the demand for electric models as a more financially sustainable alternative for long-term use.
Additionally, stringent environmental regulations on emissions serve as a significant catalyst. Many jurisdictions are implementing policies aimed at reducing carbon footprints in agriculture. For example, policies that tax carbon emissions or provide incentives for low-carbon technologies directly influence purchasing decisions. The zero tailpipe emissions of electric tractors make them an attractive solution for compliance, thereby increasing their demand. This is particularly relevant in controlled environments such as vineyards, greenhouses, and municipal fleets, where air quality and noise pollution are key concerns.
Technological advancements in battery and charging infrastructure also directly boost demand. As battery capacities increase, the range and operational duration of electric tractors expand, addressing a primary concern for farmers who require equipment capable of working extended hours. Innovations like fast-charging and battery-swapping technologies reduce downtime, making electric models more competitive with their diesel counterparts and thereby catalyzing demand. The integration of precision agriculture technologies, such as IoT and AI, further enhances the appeal of electric tractors by offering data-driven insights that optimize operations and crop yields. This integration transforms the tractor from a simple machine into a data-gathering platform, creating a new layer of value that stimulates demand from technologically forward operators.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The electric tractor market faces significant challenges, primarily rooted in economic and infrastructural constraints. The high initial capital cost of electric tractors presents a major hurdle for widespread adoption, especially for small and medium-sized farms with limited capital. This financial barrier directly suppresses demand, as many operators are unable to justify the large upfront investment despite the long-term operational savings. The cost is a direct function of the expensive battery technology and the research and development investments required to bring these machines to market.
A second critical challenge is the lack of a robust charging infrastructure in rural and remote agricultural areas. The absence of readily available fast-charging stations creates range anxiety and logistical difficulties for farmers, limiting the usability of electric tractors for large-scale operations and reducing their perceived value. This infrastructural gap directly constrains demand by making electric models impractical for many potential end-users.
However, these challenges also create opportunities. The high upfront cost can be mitigated through supportive government policies, such as subsidies, grants, and low-interest loans. These incentives directly stimulate demand by making electric tractors more financially accessible. The infrastructural deficit presents an opportunity for public-private partnerships to develop and deploy charging networks in agricultural regions. Manufacturers and energy companies can collaborate on scalable charging solutions, including mobile charging units and solar-powered stations, which would expand the practical applications of electric tractors and drive market penetration. The increasing demand for sustainable and quiet machinery, especially in niche markets like horticulture, viticulture, and municipal landscaping, also offers a significant opportunity for manufacturers to specialize and capture market share.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The electric tractor is a physical product, and its pricing is inextricably linked to the raw materials and manufacturing costs of its primary components, particularly the battery. Lithium-ion batteries, which power the majority of current models, rely on critical raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel. The price and supply of these materials are subject to geopolitical factors, mining constraints, and environmental regulations, leading to significant price volatility. The price of cobalt, for instance, has historically been volatile due to its concentrated supply in a few regions. These fluctuations directly impact the final production cost of the battery and, consequently, the retail price of the electric tractor.
The supply chain for these materials is complex and highly concentrated. A limited number of countries and companies control the extraction and processing of these key battery components. This concentration creates a supply chain vulnerability, making the market susceptible to disruptions from trade disputes, export restrictions, and labor issues. Manufacturers must navigate this complexity to secure a stable and cost-effective supply, a challenge that can lead to increased product pricing or production delays, thereby dampening consumer demand.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for electric tractors is characterized by its dependence on a diverse network of specialized component manufacturers. The process begins with the extraction of raw materials for batteries and semiconductors, which are then processed and assembled into finished components. Key production hubs for batteries and electronic controls are predominantly located in the Asia-Pacific, particularly in countries like China and South Korea. This concentration creates logistical complexities and dependencies, as manufacturers in North America and Europe must rely on imports for these high-value components.
The supply chain faces several bottlenecks. The global semiconductor shortage has had a direct impact, as modern electric tractors rely heavily on sophisticated electronic systems for battery management, navigation, and autonomous controls. This shortage has increased production costs and extended lead times. Furthermore, the transportation of large, heavy battery packs and other components across international borders adds to logistical costs and carbon footprint, presenting a counterpoint to the product's zero-emission benefit. A critical challenge for the industry is to localize the supply chain where possible, from battery cell manufacturing to final vehicle assembly, to reduce these dependencies and enhance resilience against future disruptions.
- Government Regulations
Government regulations play a decisive role in shaping the demand for electric tractors by creating both mandates and incentives. These policies directly influence the economic viability and environmental attractiveness of the technology.
- United States: Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
The IRA provides tax credits and other financial incentives for the purchase of electric vehicles, including off-road machinery. This directly reduces the high upfront cost of electric tractors, thereby boosting demand. EPA regulations on diesel emissions for agricultural equipment compel manufacturers to develop cleaner alternatives, which increases the R&D and market focus on electric models. - Europe: European Green Deal, Common Agricultural Policy (CAP)
The European Green Deal sets ambitious targets for climate neutrality, promoting sustainable farming practices. CAP reforms link farm payments to environmental performance, providing a financial incentive for farmers to adopt electric machinery. This regulatory framework drives demand by making sustainability a financial and regulatory imperative. - India: Subsidies and Rural Credit Programs
The Indian government provides subsidies on agricultural machinery and offers low-interest loans to farmers. While not exclusively for electric tractors, these programs lower the financial barrier to entry for modern equipment. Specific policies supporting clean technology, such as the FAME II scheme, also apply, making electric tractors a more accessible option and thereby increasing their market potential.
Electric Tractors Market Segment Analysis
- By Application: Farming
The farming segment represents the foundational and largest application for electric tractors. Demand within this segment is driven by a focus on operational efficiency, cost reduction, and environmental stewardship. For small to medium-sized farms, the demand for compact electric tractors is particularly pronounced. These operators are motivated by the direct cost savings from the elimination of diesel fuel and reduced maintenance requirements. With fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes or traditional engine servicing, the total cost of ownership over the lifespan of the equipment becomes significantly lower than that of a diesel equivalent. This economic benefit directly translates into increased demand.
Furthermore, electric tractors address critical challenges faced by farmers, such as noise pollution and air quality. In controlled agricultural environments like greenhouses, barns, and vertical farms, the zero-emission and quiet operation of electric tractors is not just a benefit but a necessity. This creates a specific and inelastic demand from this niche, high-value farming sub-segment. The integration of autonomous features, such as those that can automate tasks like tillage, spraying, and harvesting, further enhances their appeal by addressing a major pain point: the chronic shortage of skilled farm labor. The ability of a single operator to manage a fleet of autonomous electric tractors increases productivity and creates a powerful demand driver for larger commercial operations.
- By End-User: Agriculture
The agriculture end-user segment is the primary consumer of electric tractors, with demand dynamics shaped by farm size, crop type, and regional regulatory pressures. The demand for electric tractors is particularly strong among organic and specialty crop farmers who are committed to sustainable practices and often operate in proximity to residential areas. For these users, the zero-emissions and quiet operation of electric tractors are a key selling point that aligns with their brand values and meets local ordinances. The shift towards precision agriculture also catalyzes demand. Farmers are increasingly adopting technology that improves yield and resource efficiency. Electric tractors, with their advanced electronics and sensor integration, are a natural fit for these applications.
While the market for large-scale, high-horsepower electric tractors is still nascent due to battery range and power constraints, a clear demand exists in the smaller, utility-focused segment. This is where electric tractors compete directly with diesel models on a performance basis, particularly for tasks such as material handling, mowing, and light tilling. The demand from agricultural end-users is also influenced by their access to renewable energy sources, such as solar power. Farmers who can generate their own electricity can further reduce their operational costs by "fueling" their tractors for free, creating a powerful economic incentive that directly increases demand for electric models. The growing prevalence of on-farm solar installations is therefore a key market enabler.
Electric Tractors Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis: The US electric tractor market is characterized by strong demand drivers rooted in government policy and a shift towards sustainable agriculture. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and other federal and state-level incentives provide substantial tax credits and subsidies for electric farm equipment, directly lowering the financial barrier for operators. This has catalyzed initial adoption, particularly for compact utility models used in vineyards, orchards, and small-scale farms where zero emissions and low noise are highly valued. The need for these tractors is also increasing as large agricultural conglomerates and corporate farms seek to meet their own sustainability targets. The US market benefits from a robust ecosystem of technology startups and established manufacturers that are heavily investing in R&D, which accelerates product development and expands the range of available electric models. However, the vast size of the country's agricultural regions and the dominance of large-scale row-crop farming present a significant challenge for battery-powered tractors due to range and operational duration limitations.
- Brazil Market Analysis: In Brazil, the demand for electric tractors is growing, fueled by a strong push for agricultural modernization and government-backed rural credit programs. The nation is a global leader in agricultural production, and a confluence of factors, including increasing mechanization and a need to improve productivity, propels the overall tractor market. While diesel models still dominate, the demand for electric alternatives is emerging, particularly in the specialty crop sector. The Brazilian government's Moderfrota program, which provides low-interest loans for the purchase of new agricultural machinery, indirectly supports the market by making equipment acquisition more financially feasible. This program, combined with a national focus on biofuel production and sustainability, creates a favorable environment for the eventual adoption of electric technology. The market is still in its early stages, but a clear opportunity exists for manufacturers to introduce models tailored to the specific needs of Brazilian agriculture, such as those suitable for sugarcane and coffee plantations.
- France Market Analysis: The French electric tractor market is expanding, driven by the European Union's stringent environmental policies and a national commitment to green farming. The European Green Deal and associated Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) reforms incentivize farmers to adopt low-emission technologies, creating a direct demand for electric tractors. France, with its significant agricultural sector, is at the forefront of this transition. It is sought after in regions that produce valuable crops, such as wine grapes. In these areas, silent and zero-emission tractors are preferred because they can operate near residential neighborhoods and excel in precision tasks. The instant torque and fine control offered by electric motors make them particularly suitable for these applications. The government provides various grants and subsidies for environmentally friendly equipment, which helps to mitigate the high initial purchase price. The market is characterized by a mix of major international players and innovative local start-ups, fostering a competitive landscape that encourages rapid technological advancement.
- South Africa Market Analysis: The electric tractor market in South Africa is nascent but poised for growth. The primary demand drivers are centered on improving agricultural productivity, reducing operational costs due to volatile fuel prices, and addressing labor shortages through mechanization. While the market for conventional tractors is well-established, the shift to electric models is in its infancy. A key challenge is the lack of a reliable and widespread electrical grid in many rural areas, which complicates charging infrastructure. However, opportunities exist in specific agricultural segments, such as horticulture and viticulture, where operators are more financially capable and can invest in on-site solar power to charge their equipment. Corporate sustainability initiatives from large agricultural firms and food producers who seek to reduce their carbon footprint and demonstrate environmental responsibility also influence market expansion.
- China Market Analysis: China’s electric tractor market is growing rapidly, propelled by a national imperative for agricultural modernization and a strong policy push for electrification. The government provides significant subsidies for the purchase of new, technologically advanced agricultural machinery, with a particular focus on electric and autonomous systems. This policy directly stimulates demand and accelerates the adoption curve. The market is also driven by labor shortages in the agricultural sector, which makes the autonomous capabilities of advanced electric tractors an attractive solution for increasing productivity. The Chinese market benefits from a robust domestic supply chain for batteries and electronic components, which helps to keep production costs lower than in other regions. While diesel tractors still dominate the market, the government's long-term strategic focus on transitioning to clean energy and smart farming technologies ensures a sustained and powerful demand for electric models in the coming years.
Electric Tractors Market Competitive Analysis
The electric tractors market is marked by a dynamic competitive landscape featuring both established agricultural machinery giants and innovative technology-focused startups. The major players are leveraging their deep industry expertise and existing distribution networks, while new entrants are disrupting the market with advanced, purpose-built electric and autonomous solutions.
- John Deere: John Deere, a global leader in agricultural machinery, is strategically positioning itself in the electric tractor market by integrating electrification within its broader "Smart Industrial" strategy. The company's approach is not merely to create electric versions of its existing machines but to deliver "intelligent, connected machines and applications" that enhance customer value. John Deere is developing a fully autonomous, battery-powered electric agricultural tractor with up to 130 horsepower, which demonstrates a commitment to both electrification and autonomy. This product aligns with its objective to help customers optimize their operations and achieve sustainability goals. The company also offers electric turf and compact utility products, such as the electric Gator™ TE 4x2 utility vehicle, showcasing a phased approach to electrification across its product families. John Deere's strategy is to leverage its extensive R&D capabilities and integrate electric technology with its precision agriculture solutions, such as See & Spray, to provide a holistic and data-driven farming experience.
- Kubota Corporation: Kubota, a prominent manufacturer of agricultural and construction machinery, is strategically expanding its presence in the electric and autonomous machinery space. The company's positioning is rooted in providing a wide range of compact and utility tractors that are well-suited for smaller farms, orchards, and landscaping. Kubota is actively engaged in developing and promoting "AgriRobo" unmanned autonomous agricultural machinery. These systems, which use advanced GPS and automatic driving technology, are designed to increase efficiency and save labor. While Kubota has a strong portfolio of diesel-powered tractors, its focus on smart farming and automation technologies, such as the Kubota Smart Agriculture System (KSAS), indicates a clear direction toward integrating electric and robotic solutions into its product line. The company's strategic move to acquire companies and form partnerships in the smart farming space reinforces its commitment to capturing a significant share of the evolving market.
- Monarch Tractor: Monarch Tractor has emerged as a disruptive force in the market, focusing exclusively on a fully electric, driver-optional, smart tractor. The company's flagship product, the MK-V, is a direct challenge to conventional models by combining electrification, autonomy, and data analytics into a single platform. Monarch’s strategic positioning is centered on providing an all-in-one solution that addresses labor shortages, sustainability, and operational efficiency for small and specialty farmers. The MK-V features a mobile power wall, 360-degree cameras for safety, and an operational intelligence platform that provides real-time and historical insights. The company is not just selling a tractor but a complete data-driven ecosystem. Monarch Tractor's strategic partnership with Foxconn and other manufacturers to scale production and its rollout of the Monarch® Autodrive™ technology for commercial use in dairy farms demonstrates a rapid and focused approach to market entry.
Electric Tractors Market Developments
- August 2025: Monarch Tractor announced the commercial launch of its MonarchOne™ platform, which is the underlying AI-powered software stack that enables autonomy, assisted driving, and energy management for off-highway vehicles. The platform, which powers the company’s MK-V electric tractor, is now being offered to other original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), signifying a strategic shift to a platform-as-a-service model.
- February 2025: Monarch Tractor began the commercial rollout of its Monarch® Autodrive™ technology, making a fully autonomous feature in a driver-optional tractor commercially available for dairies for the first time. The technology, which automates tasks such as feed pushing, is designed to improve operational efficiency and address labor shortages in the dairy industry.
Electric Tractors Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Electric Tractors Market Size in 2025 | USD 160.675 million |
| Electric Tractors Market Size in 2030 | USD 870.767 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 40.21% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Electric Tractors Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Electric Tractors Market Segmentation:
- By Power Output
- <30 kW
- 30-100 kW
- 100 kW
- By Propulsion
- Battery Electric Tractor
- Hybrid Electric Tractor
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Tractor
- By Application
- Farming
- Construction
- Landscaping
- Municipalities
- Others
- By Battery Type
- Lithium-Ion
- Lead-Acid
- By Driveline
- FWD
- RWD
- 4WD
- By Automation
- Manual
- Semi-Autonomous
- Autonomous
- By End-User
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Industrial
- Residential
- By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Navigation:
- Electric Tractors Market Size:
- Electric Tractors Market Key Highlights:
- Electric Tractors Market Analysis
- Electric Tractors Market Segment Analysis
- Electric Tractors Market Geographical Analysis
- Electric Tractors Market Competitive Analysis
- Electric Tractors Market Developments
- Electric Tractors Market Scope:
- Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Page last updated on: September 22, 2025