Report Overview
Germany AI in Workforce Highlights
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Size:
The Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 14.83%, reaching USD 10.637 billion in 2030 from USD 5.329 billion in 2025.
The German market for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Workforce Automation is undergoing a structured transformation, driven less by speculative technological hype and more by a strategic confluence of government investment, industrial modernization imperatives, and a stringent regulatory environment. This market centers on deploying AI solutions—including Process Mining, Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Conversational AI—to augment human tasks, optimize operational efficiency, and address the nation's persistent skilled labor shortage (Fachkräftemangel). Unlike markets prioritizing rapid, unregulated deployment, the German ecosystem operates under a dual mandate: achieving global technological leadership ("AI made in Germany") while rigorously upholding ethical and employee-centric principles established by the GDPR and national labor laws.
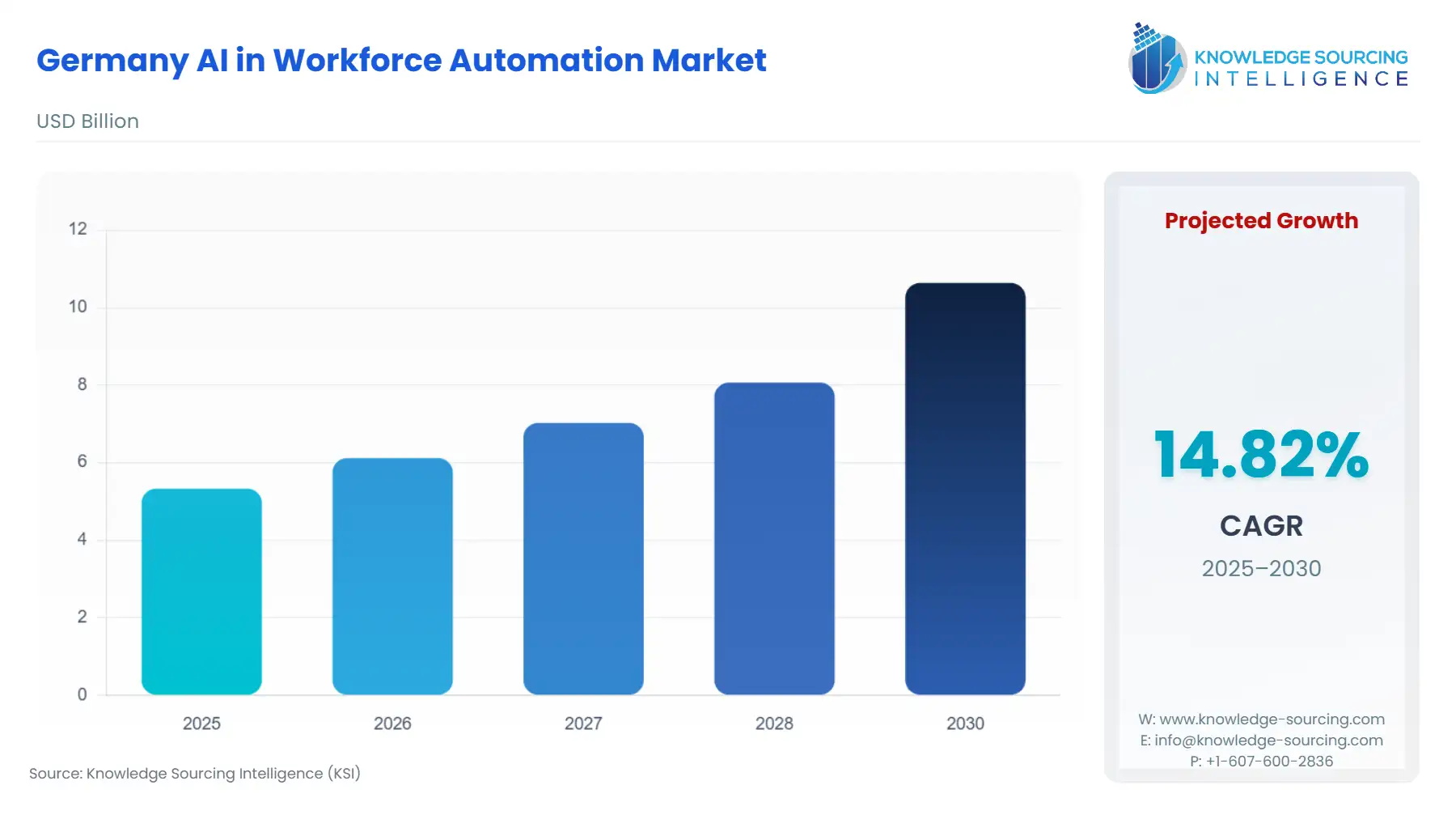
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
The German Federal Government's commitment of EUR 5 billion toward the national AI Strategy directly acts as a significant growth catalyst. This funding supports AI competence centers and promotes the transfer of AI into value creation, prompting large enterprises and Mittelstand firms to procure automation software to qualify for state-backed programs. Simultaneously, the manufacturing sector's ongoing push toward Industry 4.0 mandates the digitalization of complex production and supply chain workflows. This creates an immediate, acute demand for Process Intelligence platforms like Celonis, which map out opaque, existing processes, enabling the subsequent, targeted deployment of AI-driven automation solutions to address inefficiencies identified by the data.
Challenges and Opportunities
A primary challenge is the mandatory works council co-determination under the Works Constitution Act for monitoring-capable AI systems, which introduces a time-consuming negotiation layer and elevates the cost of deployment, constraining immediate demand for opaque black-box AI tools. This challenge, however, generates a substantial market opportunity: a verifiable increase in demand for highly transparent, explainable AI (XAI) solutions and sophisticated AI governance software designed specifically to satisfy co-determination rights by providing clear, auditable insights into their impact on work practices and employee metrics, thus shifting demand toward responsible AI providers.
Supply Chain Analysis
The AI software supply chain is predominantly digital and geographically diversified, with key dependencies resting on cloud infrastructure providers (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud), which host the models, and the availability of AI talent (data scientists, ML engineers). German demand is heavily reliant on a global pool of Generative AI (GenAI) models, creating a geopolitical dependency on US-based foundational model developers. However, the German market, due to privacy regulations, demonstrates a concentrated demand for regionalized or on-premises deployment models, thereby increasing the supply-side complexity for providers who must offer secure, EU-hosted data processing and cloud solutions to meet stringent German enterprise and public sector requirements.
Government Regulations
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | The regulation creates an urgent, compulsory demand for AI automation systems that are privacy-by-design, enforce explicit consent, and facilitate the "right to erasure" and data minimization, especially in HR and customer data applications. |
| European Union | EU AI Act (High-Risk) | AI systems used in recruitment, performance evaluation, and task allocation are classified as 'high-risk,' demanding compliance with stringent requirements for risk management systems, data governance, human oversight, and mandatory record-keeping, directly increasing demand for specialized governance and audit software. |
| Germany | Works Constitution Act (Betriebsverfassungsgesetz) (Art. 87 (1) No. 6) | Grants works councils co-determination rights on technical monitoring devices. This constrains rapid, non-transparent deployment, but directly compels demand for AI systems that can provide transparent data and XAI to justify their use and impact during the mandatory co-determination process. |
| Germany | Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) | Funds initiatives like the AI Strategy and AI Service Centres, creating a public-sector demand for AI tools and increasing the supply of technically trained personnel, which in turn lowers the cost barrier for companies adopting automation. |
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Segment Analysis:
By Component: Software & Services
The Software & Services segment acts as the foundational layer driving the market's utility, catalyzed by the continuous functional obsolescence of legacy enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. German firms do not replace these large systems easily; instead, they seek non-invasive automation layers to extract latent value. This drives demand for modular software that can execute specific, cross-system tasks, such as intelligent document processing (IDP) and low-code/no-code RPA platforms. The shift is from monolithic IT procurement to agile API-driven service integration. This imperative is amplified by the scarcity of skilled IT labor capable of complex system integration, thereby increasing the need for 'as-a-service' and cloud-based models that transfer operational complexity and maintenance obligations to the vendor. The recent focus on Agentic AI further drives this demand, as companies seek software solutions capable of autonomous, multi-step orchestration across multiple business applications.
By Industry Vertical: Manufacturing
The Manufacturing vertical, the cornerstone of the German economy, exhibits high structural demand for AI in workforce automation, specifically in the areas of logistics, predictive maintenance, and quality assurance. The key growth driver is the margin imperative and the need for precision automation in high-complexity, low-margin processes. AI tools are not simply replacing human labor; they are augmenting and coordinating complex supply chains, which are particularly critical for the Mittelstand with its global dependencies. The verified trend of high-mix, low-volume production creates a specific demand for AI solutions that can rapidly adapt automation workflows, unlike rigid, traditional robotics. Process Mining platforms are highly sought after in this vertical to first benchmark "as-is" processes in logistics and production—a critical pre-requisite before any subsequent deployment of RPA or conversational AI for back-office functions like procurement and invoicing can be justified and implemented.
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The German AI in Workforce Automation market is characterized by a dual structure: a presence of global hyper-scale providers and a significant cluster of highly specialized, often B2B-focused, domestic champions. Competition centers on demonstrating regulatory compliance, seamless integration with European enterprise systems (SAP, for instance), and delivering industry-specific vertical expertise, particularly in the manufacturing and financial services sectors.
Celonis
Celonis, with headquarters in Munich and New York, is a global leader in Process Mining and Process Intelligence. Its strategic positioning centers on providing a "living digital twin" of a company's operations, a crucial prerequisite for effective automation. The firm's core value proposition is not automation itself but intelligence that guides highly targeted, value-driven automation, which directly addresses the cautious, data-driven investment culture of German enterprises. Celonis' platform uses AI to analyze event logs from IT systems (like SAP or Oracle) to visualize process execution gaps and compliance violations. This diagnostic capability creates demand by substantiating the return on investment for subsequent AI automation deployments, positioning Celonis as a platform-agnostic orchestrator.
Cognigy
Cognigy, headquartered in Düsseldorf, specializes in Conversational and Agentic AI platforms for customer service and contact center automation. The company's strategic focus is on delivering end-to-end customer experience (CX) and employee experience (EX) automation via AI Agents that can handle complex, multi-step interactions across voice and digital channels. Its Cognigy.AI platform emphasizes deep integration capabilities, enabling AI agents to connect seamlessly with existing enterprise systems. The company's focus on Agentic AI—AI capable of thinking, reasoning, and acting independently—is a direct response to the escalating labor costs and workforce shortages in German service-oriented industries, driving demand for self-service automation that requires minimal human intervention.
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Recent Developments:
- August 2025: Cognigy's product updates for the Cognigy.AI 2025.17 release included new EU-hosted speech support features. This product launch is a direct response to the high German demand for GDPR-compliant, voice-based AI solutions, ensuring that sensitive speech data processing remains within the European Economic Area, thereby minimizing cross-border data transfer risks and catering specifically to enterprise privacy mandates.
- July 2025: NiCE (NASDAQ: NICE) announced a definitive agreement to acquire German-based conversational and agentic AI provider Cognigy for approximately $955 million (transaction expected to close in Q4 2025). The acquisition is intended to combine NiCE's CXone Mpower platform with Cognigy's AI-powered capabilities, accelerating the adoption of AI-first customer service and orchestrating AI agents across both front and back-office operations, demonstrating significant foreign investment and validation of German AI technology.
- June 2025: Celonis announced an expanded collaboration with global fashion destination ASOS to optimize its supply chain operations, powered by its Process Intelligence platform. This development illustrates the deployment of German-rooted process mining technology for enterprise-level supply chain management—a critical segment of workforce automation that drives efficiency in logistics, procurement, and fulfillment planning processes across Europe.
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 5.329 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 10.637 billion |
| Growth Rate | 14.83% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Deployment, Size of Organisation, Industry Vertical |
| Companies |
|
Germany AI in Workforce Automation Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT
- Software & Services
- Hardware
- BY DEPLOYMENT
- On-Premises
- Cloud-based
- BY SIZE OF ORGANISATION
- Small & Medium Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
- BY INDUSTRY VERTICAL
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- Banking & Finance
- Supply Chain
- Others