Report Overview
Global Electric Motorcycles & Highlights
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Size:
The Global Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market is expected to grow from USD 7.940 billion in 2025 to USD 16.764 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 16.12%.
The global shift towards sustainable transportation is fundamentally reshaping the two-wheeler market, creating a pivotal role for electric motorcycles and scooters. These vehicles are emerging as a critical solution to the twin challenges of urban congestion and air pollution. They offer a quieter, more efficient, and lower-emission alternative to their gasoline-powered counterparts. The market is moving beyond early adoption to become a mainstream segment of the mobility industry, driven by a convergence of technological innovation, supportive government policy, and evolving consumer preferences.
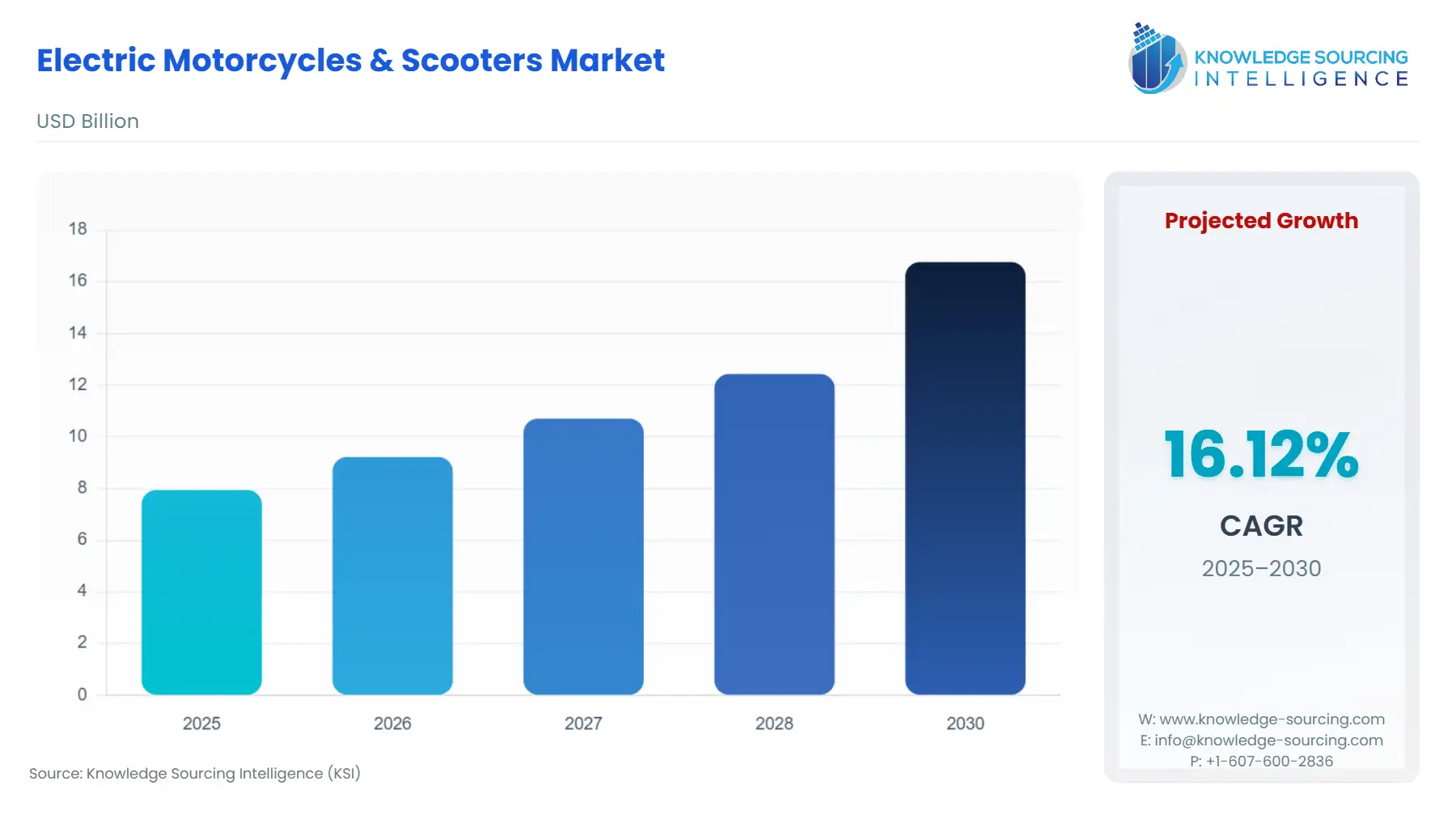
The core demand for electric two-wheelers is being driven by a powerful combination of regulatory push and market pull. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions standards and offering significant financial incentives to encourage adoption. At the same time, consumers are being drawn to the lower operating costs and improving performance of electric models. However, the industry is also navigating significant headwinds. These include the high upfront cost of vehicles, the need for widespread and reliable charging infrastructure, and the supply chain complexities associated with battery production.
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling demand for electric motorcycles and scooters is a global and increasingly stringent regulatory push towards decarbonizing transportation. Governments, particularly in Europe and Asia, are implementing policies aimed at phasing out internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to combat urban air pollution and meet climate targets. These policies create direct demand for electric alternatives through measures such as outright bans on the sale of new ICE two-wheelers in certain cities. Other measures include the establishment of low-emission zonesubstantial consumer subsidies and tax credits that reduce the upfront cost of electric models.
This regulatory push is amplified by favorable economic factors for consumers. Persistently high and volatile gasoline prices make the lower "cost-per-kilometer" of electric vehicles, which benefit from cheaper electricity, a compelling value proposition. This is particularly impactful in the high-volume markets of Asia and South America, where two-wheelers are a primary mode of daily transportation for millions of commuters. The simpler mechanical design of electric vehicles, which lack engines, exhaust systems, and complex transmissions, also results in significantly lower maintenance requirements, further strengthening their total cost of ownership advantage and driving consumer demand.
Furthermore, continuous advancements in battery technology are a critical growth driver. Innovations in lithium-ion battery chemistry are leading to higher energy densities, which translates directly to longer vehicle ranges—a key factor in overcoming consumer "range anxiety." Simultaneously, economies of scale in battery manufacturing are driving down costs, making electric motorcycles and scooters progressively more affordable and accessible to a broader segment of the population.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The most significant challenge constraining the growth of the electric motorcycle and scooter market is the high initial purchase price compared to conventional ICE equivalents. The lithium-ion battery pack is the single most expensive component of an electric two-wheeler, and despite falling costs, it still results in a retail price that can be a significant barrier for price-sensitive consumers, particularly in emerging markets. This pricing disparity slows the rate of mass-market adoption and makes the industry heavily reliant on government subsidies to remain competitive.
Another major challenge is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. While many scooter users can charge their vehicles at home, the absence of a dense network of public charging stations creates "range anxiety" and limits the practicality of electric two-wheelers for longer trips or for consumers living in apartments without dedicated charging access. The time required to fully charge a battery, which can take several hours, is also a significant drawback compared to the few minutes needed to refuel a gasoline-powered vehicle.
These infrastructure challenges, however, are creating a major market opportunity for innovative solutions, most notably battery-swapping technology. Companies like Gogoro have pioneered a model where users do not own their batteries but subscribe to a service that allows them to swap depleted batteries for fully charged ones at a network of automated stations in seconds. This model effectively eliminates both charging time and range anxiety, and by separating the cost of the battery from the vehicle, it can significantly lower the upfront purchase price. This is creating a powerful opportunity for companies that can build out these battery-as-a-service ecosystems, which is becoming a dominant and high-growth segment of the market, particularly in dense urban environments.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The pricing structure of the electric motorcycle and scooter market is fundamentally dictated by the cost of the raw materials used in their most critical component: the lithium-ion battery. The key materials that determine the cost of a battery cell are lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. The prices of these metals are traded on global commodity markets and are subject to significant volatility based on geopolitical factors, mining output, and surging demand from both the electric vehicle and consumer electronics industries. According to data from Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, the price of lithium carbonate, a key precursor, has experienced extreme fluctuations, which directly impacts the cost of battery cells and, consequently, the final price of the electric vehicle.
Cobalt, which is a critical material for the cathode in many high-performance lithium-ion batteries, presents a particular challenge due to its price volatility and a supply chain that is heavily concentrated in the Democratic Republic of Congo. This has created a strong market incentive for battery manufacturers and vehicle OEMs to invest in R&D for low-cobalt or cobalt-free battery chemistries, such as Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), to mitigate this cost and supply chain risk.
Beyond the battery, electric motors rely on high-strength rare earth magnets (primarily neodymium and dysprosium) to achieve high efficiency and power density. The prices of these rare earth elements are also volatile and their supply is dominated by China, creating another layer of supply chain complexity and cost uncertainty for manufacturers.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The supply chain for electric motorcycles and scooters is a complex global network centered on battery manufacturing. The chain begins with the mining and refining of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, a process concentrated in a few key countries such as Australia, Chile, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. These refined materials are then processed into precursor materials and active cathode and anode materials, a step that is overwhelmingly dominated by Chinese chemical companies.
These advanced materials are then supplied to battery cell manufacturers, who assemble them into individual cells. This stage of the supply chain is also heavily concentrated in Asia, with companies like CATL, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic being major global suppliers. These cells are then assembled into complete, managed battery packs by either specialized pack assemblers or the vehicle OEMs themselves. In parallel, electric motors and controllers are sourced from another set of specialized suppliers. The final stage involves the vehicle OEMs, who integrate the battery pack, motor, and other components into the final chassis for assembly. The finished vehicles are then distributed through a network of dealerships and, increasingly, through direct-to-consumer online sales channels.
- Government Regulations
The global electric motorcycle and scooter market is profoundly shaped by government policies. These regulations are a primary force driving market demand, as they are designed to both penalize the use of polluting vehicles and incentivize the adoption of electric alternatives.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
China |
Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) |
Implements stringent national standards for e-bikes and scooters, including limits on speed and weight. More importantly, many major cities have outright banned or heavily restricted the use of gasoline-powered scooters, which has created a massive, captive market and is the single largest driver of demand for electric two-wheelers in the country. |
|
India |
Department of Heavy Industry (under the FAME-II Scheme - Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles) |
Provides significant upfront subsidies to consumers who purchase electric two-wheelers. The FAME-II scheme has been a critical driver of demand by making electric scooters more price-competitive with their gasoline counterparts in this highly price-sensitive market. |
|
European Union |
European Commission (under Euro emission standards and various national subsidy programs) |
While the EU-wide "Euro" standards set emission limits for ICE motorcycles, the primary market impact comes from individual member states. Countries like France and Germany offer substantial "eco-bonuses" or purchase premiums for electric two-wheelers, which directly stimulates consumer demand. |
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Segment Analysis:
- Analysis by Product: E-Scooter
The e-scooter segment is the largest and most dynamic component of the global electric two-wheeler market. The demand for e-scooters is overwhelmingly driven by their utility in urban transportation. Their small footprint, light weight, and ease of operation make them an ideal solution for navigating congested city streets and for "last-mile" commutes from public transit hubs to homes or offices. This is creating immense demand in the densely populated megacities of Asia, such as Shanghai, Delhi, and Taipei, where e-scooters are often the fastest and most cost-effective mode of personal transport.
The demand is further amplified by the significantly lower operating costs of e-scooters compared to both cars and gasoline-powered scooters. The cost of electricity to charge an e-scooter is a fraction of the cost of gasoline for an equivalent distance, and their simple electric powertrains require minimal maintenance. This economic advantage is a powerful driver of demand for both private consumers and commercial users, such as last-mile delivery and logistics companies. The rise of shared mobility services, which deploy large fleets of rentable e-scooters in city centers, has also been a major source of demand for the vehicles themselves and has served to introduce a wide consumer base to the benefits of electric mobility.
- Analysis by Battery: Lithium-ion
The lithium-ion battery segment is the dominant and most critical enabling technology in the electric motorcycle and scooter market. The demand for lithium-ion batteries is a direct function of the demand for viable, long-range electric vehicles. Older battery technologies, such as sealed lead-acid, are heavy, have a short lifespan, and offer limited range, which severely restricts the utility and consumer appeal of the vehicles they power. The superior characteristics of lithium-ion technology are directly responsible for making mass-market electric two-wheelers a practical reality.
The primary demand driver for lithium-ion technology is its high energy density. This means that for a given weight, a lithium-ion battery can store significantly more energy than a lead-acid battery, which directly translates into longer vehicle range—the single most important factor for many consumers. Furthermore, lithium-ion batteries have a much longer cycle life, meaning they can be charged and discharged many more times before their capacity degrades, which improves the long-term reliability and value of the vehicle. According to reports from BloombergNEF, the price of lithium-ion battery packs has fallen by over 85% in the last decade due to massive economies of scale in manufacturing. This dramatic cost reduction is the single most important factor that is making electric two-wheelers increasingly price-competitive and is the key driver of their accelerating adoption.
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Geographical Analysis:
China Market Analysis
China is, by an overwhelming margin, the largest and most mature market for electric two-wheelers in the world. This dominance is the direct result of government policy. Strict municipal regulations in many of China's largest cities that ban or heavily restrict gasoline-powered scooters have created a massive captive market for their electric counterparts. This policy-driven demand is supported by a vast domestic manufacturing ecosystem, making China the global hub for both the production and consumption of e-scooters and e-bikes.
India Market Analysis
India represents the market with the highest growth potential for electric two-wheelers. The country has the largest traditional motorcycle and scooter market in the world, and the government is aggressively promoting a transition to electric mobility through its FAME-II subsidy scheme. This is creating a surge in demand, particularly for electric scooters, as consumers are drawn to the lower operating costs and government incentives. A host of domestic startups are competing fiercely in this rapidly growing market.
Germany Market Analysis
As a key market in Europe, demand in Germany is driven by strong consumer environmental awareness and supportive government policies. Generous federal and municipal subsidies, known as the "Umweltbonus," reduce the purchase price of electric scooters and motorcycles, directly stimulating demand. The market is characterized by a strong preference for high-quality, well-engineered products from both established European brands and premium new entrants.
US Market Analysis
The electric two-wheeler market in the United States is smaller than in Asia or Europe but is growing steadily. The demand is segmented, with a high-end market for premium, high-performance electric motorcycles from brands like Zero and Harley-Davidson's LiveWire. In urban areas, the demand is largely driven by the proliferation of scooter-sharing services, which have introduced a wide audience to electric mobility. The consumer ownership market for e-scooters is growing, but is less established than in other regions.
Brazil Market Analysis
In Brazil, motorcycles and scooters are a primary mode of transportation, creating a vast potential market for electrification. The demand is currently in its early stages but is being driven by the need for lower-cost transportation solutions in the face of high fuel prices. The commercial sector, particularly last-mile delivery services in large cities like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, is an early adopter and a key driver of demand for durable and efficient electric scooters.
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape of the electric motorcycle and scooter market is a dynamic mix of legacy automotive giants, established two-wheeler manufacturers, and a new wave of agile, technology-focused startups.
- Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd.: As a major global manufacturer of traditional motorcycles and scooters, Yamaha's strategy is to leverage its immense brand recognition, engineering expertise, and extensive global distribution network to transition into the electric era. They are methodically introducing electric scooters into key markets, particularly in Asia and Europe. Their competitive advantage lies in their reputation for quality and reliability, which allows them to capture demand from consumers who may be wary of unfamiliar startup brands.
- NIU Technologies: NIU is a prime example of a digital-native company that has become a global leader in the "smart scooter" segment. Based in China, their strategy is centered on integrating connectivity and technology into their vehicles. All NIU scooters are equipped with IoT sensors that connect to a cloud platform, allowing users to track their vehicle, monitor battery health, and receive over-the-air software updates via a mobile app. This technology focus, combined with a strong emphasis on modern design, allows them to capture demand from a younger, more tech-savvy urban demographic.
- Zero Motorcycles, Inc.: This California-based company is a pioneer and leader in the high-performance electric motorcycle segment. Their strategy is to compete directly with high-end gasoline-powered motorcycles on the basis of performance. They design and manufacture their own proprietary electric powertrains, including high-output motors and high-density battery packs. Their competitive advantage lies in their dedicated focus on the electric motorcycle, which has allowed them to achieve a level of performance and range that is highly attractive to enthusiast riders, capturing demand in the premium segment of the market.
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Recent Developments:
- June 2025: Finland banned e-scooters for children and introduces stricter rental regulations. This move prioritized public safety by addressing rising accidents among minors and rental misuse. It set a precedent for other European nations to adopt stricter micromobility rules.
- March 2025: Segway recalled over 220,000 Ninebot scooters due to folding mechanism failures. The recall highlights persistent safety concerns in the e-scooter industry. It pressures manufacturers to invest more in design reliability and after-sales accountability.
- May 2025: Seattle launched LimeGlider, a seated electric scooter model. The innovation expands accessibility for older riders and those less comfortable on stand-up scooters and signals a shift toward inclusive micromobility solutions in urban transport planning.
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 7.940 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 16.764 billion |
| Growth Rate | 16.12% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product, Battery, Application, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Electric Motorcycles & Scooters Market Segmentation:
- By Product:
- E-Motorcycle
- E-Bicycle
- E-Scooter
- By Battery:
- Sealed-ion lead acid
- Lithium-ion
- Nickel metal hydride
- By Application:
- Personal Use
- Commercial Use
- By Geography:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Others
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Others
- North America