Report Overview
Global Inkjet Coders Market Highlights
Global Inkjet Coders Market Size:
The Global Inkjet Coders Market is expected to grow from USD 4.499 billion in 2025 to USD 6.124 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 6.36%.
The global inkjet coders market consists of a wide range of industrial equipment used for printing variable data, such as dates, batch codes, barcodes, and logos, directly onto products and packaging. These devices are an essential component of modern manufacturing and logistics, providing a direct link between physical products and their digital data for purposes of traceability, inventory management, and consumer information. Unlike traditional labeling systems, inkjet coders apply codes without contact, offering a flexible and efficient solution for high-speed production lines and a variety of substrates, including glass, plastic, metal, and cardboard. The market's trajectory is intrinsically tied to the operational needs of the manufacturing sector, where the demand for efficiency, compliance, and product security is a continuous and escalating imperative.
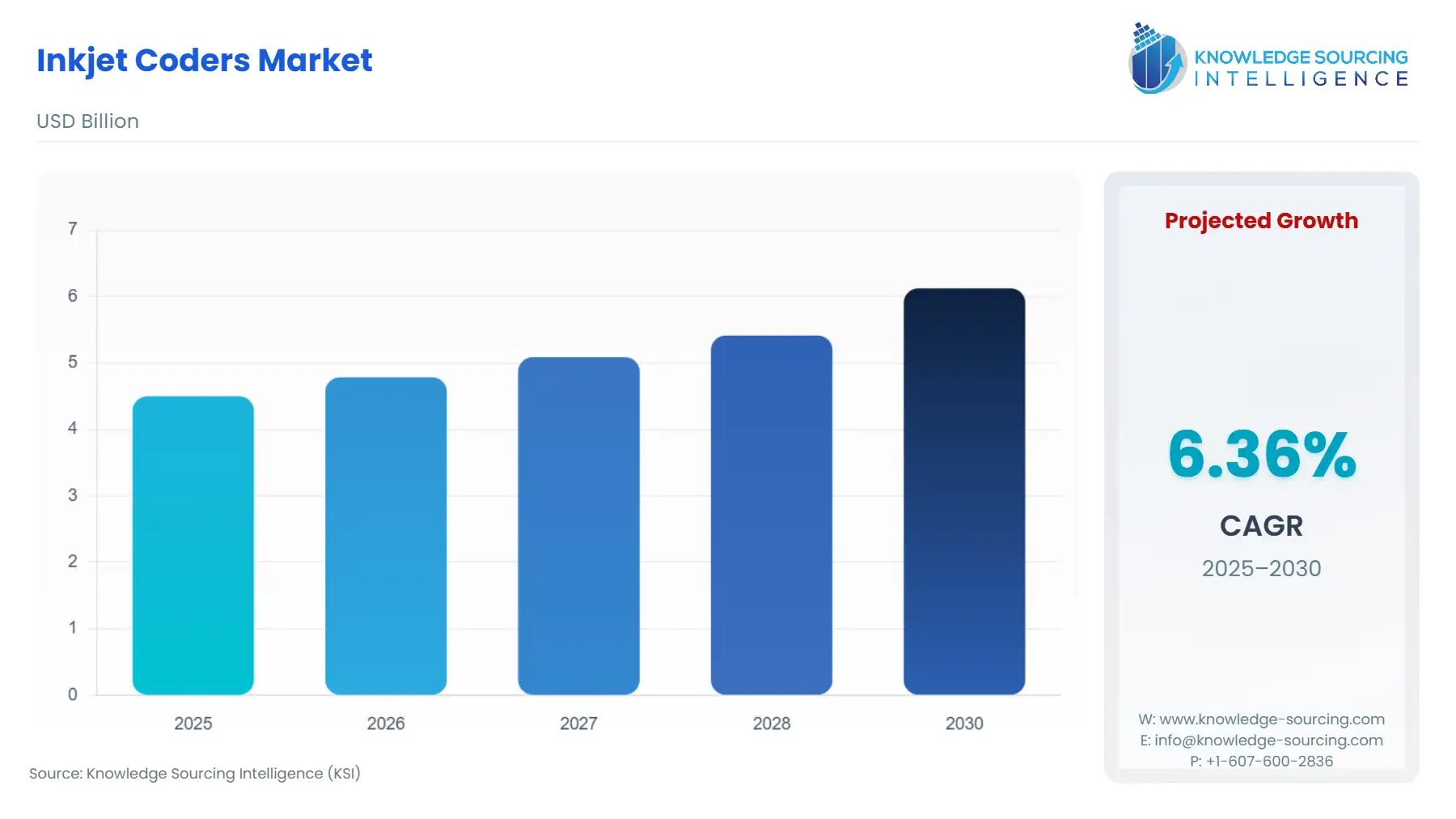
Global Inkjet Coders Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The inkjet coders market is primarily propelled by two powerful and interconnected drivers: the global enforcement of product traceability regulations and the continuous automation of industrial production lines. Regulatory bodies around the world are increasingly mandating that products, particularly in the food and beverage and pharmaceutical sectors, carry specific, legible, and verifiable codes. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), for example, have implemented stringent serialization and traceability requirements to combat counterfeiting and facilitate product recalls. These mandates directly compel manufacturers to invest in coding equipment to achieve compliance. Inkjet coders, especially Continuous Inkjet (CIJ) and Thermal Inkjet (TIJ) systems, provide a flexible and reliable method for applying these codes at high speeds, directly increasing their adoption.
Simultaneously, the widespread automation of manufacturing and packaging processes serves as a fundamental catalyst for demand. Companies are investing in automated production lines to increase throughput, reduce manual labor, and improve operational efficiency. Inkjet coders are designed to integrate seamlessly with these high-speed lines, applying codes without slowing down the process. The need to code thousands of items per hour on a conveyor belt is a core requirement that continuous inkjet technology is specifically engineered to meet. This automation trend is prevalent across all major industrial sectors, from automotive to electronics, and it creates a persistent and growing demand for inkjet coding solutions that can keep pace with faster and more complex production environments.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The market for inkjet coders faces a notable challenge from the rising prevalence of competing technologies, particularly laser coders. Laser coding systems offer the distinct advantage of creating permanent, highly durable marks that do not require consumables like ink. This can be a significant draw for end-users concerned about ongoing ink costs, maintenance, and the potential for code smudging or fading. The high initial capital investment for laser systems, however, acts as a barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), but as laser technology costs decrease and efficiency increases, it presents a significant headwind to the inkjet market.
Despite this, the challenges also illuminate significant opportunities. The demand for more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions is a key opportunity. This is driving innovation in ink formulations, with a growing focus on water-based and UV-curable inks that contain fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Companies that develop and market these greener ink solutions can appeal to a new segment of environmentally conscious consumers and corporate clients. Furthermore, the opportunity exists in providing integrated solutions that move beyond simple coding. The adoption of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) creates a demand for "smart" coders with enhanced connectivity and data analytics capabilities. By integrating inkjet coders with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, manufacturers can offer end-users real-time traceability data, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance alerts. This transformation from a hardware-centric model to a connected, data-driven service model provides a pathway for growth and differentiation.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
The pricing and profitability of inkjet coders are closely linked to the supply and cost of their critical components and consumables. The primary consumables are the specialty inks and solvents, which are chemical compounds whose prices are subject to fluctuations in the global chemical and petroleum markets. The cost of these consumables represents a significant portion of a customer's total cost of ownership over the life of the machine, making it a critical competitive factor. Furthermore, the hardware itself relies on a supply chain of electronic components, including print heads, sensors, and circuit boards. Global supply chain disruptions and shortages of semiconductor components, for instance, can directly impact the manufacturing costs and lead times for inkjet coder producers. This volatility in the raw material and component supply chain can pressure profit margins and challenge manufacturers' ability to maintain stable pricing for their products.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for inkjet coders is a complex network of raw material suppliers, component manufacturers, and final product assemblers. The chain begins with the sourcing of chemical compounds for inks, along with the manufacturing of electronic components and precision mechanical parts. Key production hubs for electronic components are largely concentrated in Asia, particularly in China and Japan. The final assembly, testing, and quality control of the inkjet coding machines often take place in facilities located in Europe, North America, and Asia.
A critical logistical complexity is the handling and distribution of the inks and solvents, which may be classified as hazardous materials and are subject to specific shipping and storage regulations. The supply chain is highly dependent on the uninterrupted flow of these consumables, as a shortage can bring an end-user's production line to a halt. The ongoing need for replacement inks and parts creates a continuous revenue stream for manufacturers and their distribution partners. The market is also heavily dependent on a network of distributors and service technicians who provide installation, maintenance, and repair services to end-users on a local level, a critical link in the value chain that ensures uptime and customer satisfaction.
- Government Regulations
Government regulations are a fundamental growth driver in the inkjet coders market, as they establish a legal framework for product identification and traceability. Compliance is a non-negotiable requirement for manufacturers operating in regulated industries. The demand for inkjet coders is directly influenced by the nature and enforcement of these rules.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | General Food Law Regulation (EC) No 178/2002 | This regulation establishes a comprehensive traceability framework for food and feed products. It mandates the ability to trace products through all stages of production, processing, and distribution. This creates a direct demand for inkjet coders to print lot numbers, batch codes, and other variable data on a wide range of packaging, from primary consumer packs to secondary shipping cartons, as a means to achieve compliance. |
| United States | FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) & Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) | The DSCSA mandates an interoperable, electronic system to identify and trace certain prescription drugs as they are distributed in the U.S. The FSMA also has traceability rules for food. Both acts compel pharmaceutical and food manufacturers to implement coding solutions. This creates a powerful demand for high-resolution inkjet coders that can print 2D barcodes and other serialization data with high accuracy and permanence, as required for item-level traceability. |
| China | Food Safety Law of the People's Republic of China | This law emphasizes a stringent product tracing system and requires clear labeling of food products with production dates, batch numbers, and other identifying information. It also mandates the use of QR codes for tracing in some provinces. This regulatory push is a primary driver of demand for inkjet coders, as Chinese manufacturers, particularly those exporting globally, must align their coding capabilities with these national and international standards. |
Inkjet Coders Market Segment Analysis:
- By Product Type: High Resolution Inkjet Coders
The need for high-resolution inkjet coders is a direct consequence of the evolving requirements of both regulatory bodies and brand owners. Traditional continuous inkjet (CIJ) systems are ideal for printing simple codes at high speeds, but they often lack the precision to produce complex graphics, logos, and high-density 2D barcodes, such as GS1 DataMatrix codes. High-resolution inkjet coders, particularly those using Thermal Inkjet (TIJ) technology, address this gap. Their demand is driven by the imperative for pharmaceutical and food companies to implement item-level serialization for traceability. These systems can print crisp, scannable codes on small packaging surfaces with a high degree of legibility, which is crucial for preventing counterfeiting and enabling efficient product recalls. Furthermore, brand owners increasingly use high-resolution codes for marketing purposes, such as linking consumers to product information or loyalty programs via a QR code. This dual demand for regulatory compliance and enhanced consumer engagement is a powerful catalyst for the growth of this segment.
- By End-User Industry: Food & Beverage
The food and beverage industry represents the largest and most consistent market for inkjet coders. This sector’s growth is driven by a non-negotiable set of requirements centered on food safety, regulatory compliance, and brand protection. The need to print essential information like expiration dates, "best before" dates, and batch codes on a vast array of packaging—from cartons and bottles to flexible pouches—is a continuous operational necessity. Regulations in jurisdictions worldwide, such as the EU's General Food Law, compel manufacturers to implement robust traceability systems to protect public health and facilitate recalls. Inkjet coders, especially CIJ systems, are the workhorse technology for this industry due to their versatility in printing on diverse substrates at high line speeds, even in challenging environments with moisture or dust. The sheer volume and variety of products in the food and beverage sector ensure a persistent and high-volume demand for inkjet coding equipment and the associated consumables.
Inkjet Coders Market Geographical Analysis:
US Market Analysis
The US market for inkjet coders is mature and highly sophisticated. The market is driven by a confluence of factors, including the country's extensive manufacturing base, particularly in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and automotive sectors, and a strong regulatory environment. The Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) is a particularly potent driver, as it mandates serialization and traceability for prescription drugs, creating a powerful and ongoing demand for high-resolution and laser coding equipment. The US also has a high degree of automation in its manufacturing and logistics sectors, which necessitates high-speed, reliable coding solutions. The market is defined by a preference for systems that offer both high performance and a low total cost of ownership, including solutions with low solvent consumption and minimal maintenance requirements.
Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil's market for inkjet coders is in a growth phase, spurred by the country's developing industrial base and increasing focus on compliance with international trade and safety standards. The food and beverage sector, a major pillar of the Brazilian economy, is a key growth driver. Manufacturers are modernizing their production lines to improve efficiency and meet export requirements, which often include stringent traceability mandates. The automotive and pharmaceutical industries also contribute to demand as they expand their local production capabilities. While the market can be price-sensitive, there is a growing recognition of the value of reliable, well-supported coding equipment. International players are active in the market through local offices and distributor networks, providing a range of CIJ and TIJ solutions to meet the varying needs of the industrial base.
Germany Market Analysis
Germany is a global hub for high-tech manufacturing and is characterized by a mature and highly arduous market for coding and marking systems. The inkjet coders market is driven by the country's emphasis on precision engineering, efficiency, and compliance with the most stringent European regulations. German manufacturers, particularly in the automotive and pharmaceutical industries, require coding solutions that are not only fast but also seamlessly integrate with complex Industry 4.0 production environments. This creates a strong demand for networked and data-enabled inkjet coders with advanced diagnostic capabilities. The market also shows a preference for solutions that align with sustainability goals, such as printers with lower energy consumption and inks with reduced environmental impact.
Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The market for inkjet coders in Saudi Arabia is rapidly expanding, propelled by the government’s Vision 2030 initiative, which aims to diversify the economy and build a robust manufacturing sector. The market is concentrated in the burgeoning food and beverage, petrochemical, and construction industries. As new industrial cities and manufacturing plants are established, they require modern, reliable coding solutions to meet both domestic and international standards. The market shows a strong demand for continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers due to their ability to operate in the harsh, high-temperature environment of the region. International vendors are well-positioned in this market, often operating through local partners who provide sales, service, and technical support to the growing customer base.
Japan Market Analysis
Japan's market for inkjet coders is characterized by a strong emphasis on technological sophistication and a high degree of integration within factory automation. The market is dominated by its world-class manufacturing sectors, particularly in automotive, electronics, and consumer packaged goods. The market requires coding solutions that offer extreme precision, speed, and reliability to keep up with highly automated and efficient production lines. There is a strong preference for compact systems that can be easily integrated into existing machinery with a small footprint. Japanese companies are also at the forefront of adopting advanced coding technologies, such as those that can print on curved or irregularly shaped surfaces with flawless consistency. The necessity is a reflection of the country's continuous pursuit of manufacturing excellence and its role as a key exporter of high-quality goods.
Inkjet Coders Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The competitive landscape of the global inkjet coders market is led by a few major multinational corporations that offer a comprehensive range of coding and marking solutions. These companies compete based on product innovation, global service networks, and the ability to provide integrated solutions for complex manufacturing environments.
- Domino Printing Sciences Plc: Domino is a key player with a long history in the coding and marking sector. Its strategic positioning is to provide high-performance, reliable, and low-maintenance solutions across a broad range of industries. The company's core product, the Ax-Series of continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers, is a market standard known for its speed and reliability on high-speed production lines. Domino also focuses on developing specialized inks for various applications, such as for food-grade products or high-contrast printing on dark surfaces. The company’s emphasis on a comprehensive service and support network enhances its value proposition, ensuring maximum uptime for its customers.
- Videojet Technologies Inc.: A subsidiary of Veralto Corporation, Videojet is a major competitor with a global footprint. The company's strategic approach is to offer a diverse portfolio of coding solutions, including CIJ, TIJ, and laser systems, to meet virtually any customer need. Videojet's focus on innovation is evident in its advanced software and connectivity options, which allow for seamless integration with enterprise systems and remote monitoring of printer performance. The company’s product lineup, such as the Videojet 1880 series of CIJ printers, is designed to provide enhanced uptime and operational efficiency through features like predictive diagnostics and self-maintenance capabilities.
- Markem-Imaje S.A.: Markem-Imaje, a subsidiary of Dover Corporation, is a prominent global provider of coding and marking solutions. The company’s strategic positioning is built on a foundation of providing versatile and robust solutions for challenging production environments. Markem-Imaje's product portfolio includes the 9000 Series of CIJ printers, which are widely used for their reliability and ability to operate in dusty or humid conditions. The company differentiates itself through its focus on developing advanced software solutions for product serialization and data management, helping customers meet stringent regulatory requirements and improve supply chain traceability.
Inkjet Coders Market Recent Developments:
- September 2025: Domino Printing Sciences introduced the compact Domino N410 digital LED inkjet label press to its product line. This new press is a cost-effective solution designed to make digital label printing more accessible to a wider range of converters. It provides fast access to the flexibility and efficiency of digital printing with a small footprint. The N410 offers consistent 5-color, 600dpi resolution printing at high speeds, and features energy-efficient UV LED curing technology. The launch is a significant step for Domino in expanding its digital printing portfolio and targeting a new segment of the market that may have been deterred by the high initial investment of larger digital presses.
- June 2025: Domino Printing Sciences expanded its portfolio for the life sciences industry by launching the K300 piezo inkjet printer and the Dx-Series of CO2 laser coders. These products are designed to meet stringent regulatory requirements for variable data printing and item-level serialization, particularly for 2D codes on blister foils, flexible films, and vials.
Inkjet Coders Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.499 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 6.124 billion |
| Growth Rate | 6.36% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Product Type, End User Industry, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Global Inkjet Coders Market Segmentation:
- By Product Type
- Continuous Inkjet Coders
- Laser Inkjet Coders
- Thermal Inkjet Coders
- High Resolution Inkjet Coders
- By End User Industry
- Food & Beverage
- Automotive
- Electrical Components & Electronics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America