Report Overview
Global Plastics Market - Highlights
Global Plastics Market Size:
The Global Plastics Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.23%, reaching USD 727.864 billion in 2030 from USD 620.767 billion in 2025.
The global plastics market is a foundational component of the modern industrial economy, providing essential materials for a vast range of applications from packaging to medical devices. The market's trajectory is characterized by a complex interplay of traditional demand drivers and emergent pressures related to sustainability and resource management. Historically, the market's expansion has been propelled by the material's inherent properties, including its versatility, low cost, and durability, which have made it indispensable for a variety of consumer and industrial goods. However, the industry now navigates a challenging environment marked by heightened public and regulatory scrutiny over plastic waste and its environmental footprint.
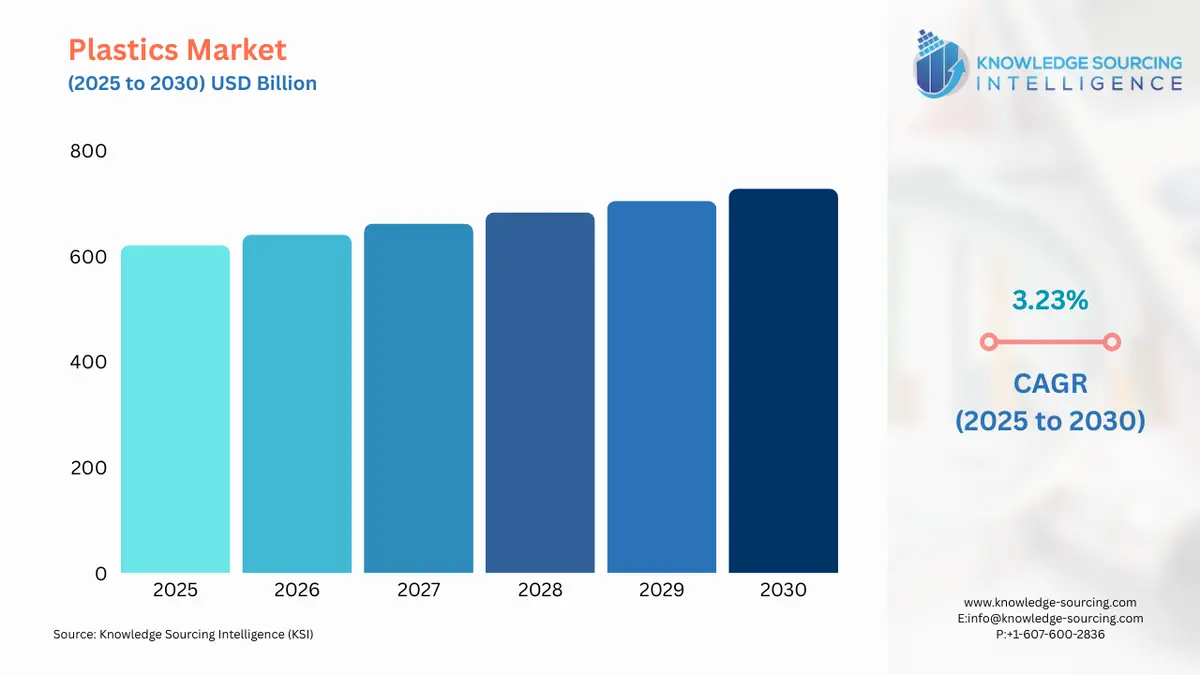
Global Plastics Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary growth drivers of the global plastics market are rooted in the material's functional benefits across multiple end-user industries. The packaging sector, as the largest consumer, drives consistent demand due to its need for cost-effective and lightweight materials that offer superior barrier protection for food, beverages, and other goods. For example, the use of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in bottling and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) in milk jugs and detergent containers is an established practice that directly links consumer product consumption to plastic demand. Similarly, the building and construction industry utilizes plastics for their durability, insulation properties, and corrosion resistance, with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) being a key material in pipes, window frames, and flooring. The construction of new residential and commercial buildings directly translates into sustained demand for these plastic products.
Technological advancements within the automotive and transportation sectors also serve as a powerful catalyst for plastics demand. As original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) seek to reduce vehicle weight to meet fuel efficiency standards and extend the range of electric vehicles, they are increasingly replacing traditional materials like metal with engineered plastics. This substitution directly increases the demand for high-performance plastics and composites in components such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior panels. This shift is an imperative for the industry, as it provides a solution to both regulatory pressures and consumer preferences for more efficient vehicles. The healthcare sector is another significant demand driver. The medical and healthcare industry relies on single-use plastics for hygiene and sterility, with applications ranging from sterile packaging and syringes to medical tubing and surgical instruments. The continuous growth in global healthcare infrastructure and the persistent need for sterile medical supplies directly contribute to the market's expansion.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The global plastics market faces significant headwinds, primarily from public and regulatory pressure to mitigate plastic waste. The most pressing challenge is the perception of plastics as a linear, single-use material that contributes to environmental pollution. This challenge manifests in direct policy actions, such as bans on single-use plastics, which can decrease demand for certain types of virgin polymers. For instance, regulations targeting plastic bags and straws reduce their market, compelling producers and end-users to find alternative materials or circular solutions.
Conversely, these challenges are simultaneously creating new opportunities. The imperative to address plastic waste has catalyzed a massive shift towards the circular economy. This dynamic has created a burgeoning market for recycled plastics, including mechanically and chemically recycled polymers. Companies that can scale their recycling operations and offer high-quality recycled content are uniquely positioned to capture new market share. The opportunity lies in the development of advanced recycling technologies that can process previously non-recyclable plastic waste, enabling its reintroduction into the value chain and reducing reliance on fossil-based feedstocks. Furthermore, there is an opportunity to innovate in the development of bioplastics and other sustainable alternatives that meet performance requirements while having a lower environmental footprint. This creates a new segment for growth and allows companies to diversify their product portfolios and align with evolving consumer and regulatory preferences.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The global plastics market is a downstream consumer of crude oil and natural gas, with the price and availability of these fossil-based feedstocks having a direct impact on the cost of virgin polymers. Ethylene and propylene, derived from naphtha and other hydrocarbon fractions, are the fundamental building blocks for a majority of commodity plastics, including polyethylene and polypropylene. Fluctuations in crude oil prices, therefore, directly influence the cost of plastic production. An increase in the price of oil translates into higher production costs for plastics, which can compress profit margins for manufacturers and, in turn, affect the final price for end-users. Conversely, periods of low oil prices can make virgin plastics more economically competitive compared to recycled materials, which may face their own collection and processing cost challenges. This pricing dynamic is a constant consideration for manufacturers, as they must balance the cost of raw materials with market requirements and pricing power. The supply chain for these raw materials is complex, involving multiple stages of extraction, refining, and polymerization, which are subject to geopolitical and economic factors.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global plastics supply chain is a complex network of production, logistics, and distribution. At its core, it is a feedstock-to-end-product model, beginning with the extraction of crude oil and natural gas. These raw materials are then processed in refineries and petrochemical plants to produce monomers such as ethylene, propylene, and benzene. These monomers are subsequently polymerized into resins and pellets, which are the primary products of the upstream plastics industry. Major production hubs are concentrated in regions with abundant feedstock and well-established petrochemical infrastructure, such as North America, the Middle East, and Asia-Pacific.
From these hubs, the plastic resins are distributed to a global network of plastic converters and manufacturers. Logistical complexities include international trade barriers, shipping costs, and the need for specialized storage to prevent degradation of the materials. Dependencies exist throughout the chain; for instance, a disruption in a single major cracker facility can create ripple effects on the global supply of ethylene, impacting the production of a wide range of polyethylene products. The supply chain is increasingly facing the challenge of integrating a reverse logistics system for recycling, requiring the establishment of new collection, sorting, and processing infrastructure to handle post-consumer plastic waste.
- Government Regulations
Government regulations are a primary force shaping the global plastics market, directly influencing demand and production methods. The focus of these regulations has shifted from general waste management to specific mandates on material composition, recycling targets, and the prohibition of certain products. These policies create direct market impacts by penalizing the use of specific plastic types, thereby reducing the need for those materials, and by creating new demand for recycled content.
Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis
- European Union: The European Green Deal, Circular Economy Action Plan, and Single-Use Plastics Directive. These comprehensive policies mandate minimum recycled content in new products, restrict the use of single-use plastics (e.g., straws, cutlery), and set ambitious recycling targets. This directly curtails demand for virgin polymers in specific applications while simultaneously creating a new, regulated market for recycled plastics, compelling manufacturers to invest in circular solutions.
- United States: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) National Strategy to Prevent Plastic Pollution. The EPA strategy, while not a single, comprehensive law, outlines a framework for national action. Its focus on circularity, infrastructure development for recycling, and source reduction influences state-level policy and drives voluntary corporate commitments. The strategy encourages demand for recycled materials and incentivizes investments in advanced recycling technologies.
- China: "Solid Waste Law" and new recycled plastics standards. China's policies have evolved from banning the import of plastic waste to establishing its own robust domestic recycling infrastructure. The government has implemented new national standards for recycled plastics (GB/T 45090-2024), which provide a framework for testing, labeling, and quality control. This action directly creates a domestic market for high-quality recycled materials and standardizes the recycling process, thereby increasing the confidence of end-users in adopting recycled content.
Plastics Market Segment Analysis
- By Application: Packaging
The packaging segment stands as the cornerstone of plastics consumption globally, primarily due to the functional superiority of plastic materials for containment, protection, and preservation. Plastic packaging demand is directly driven by the expansion of the food and beverage industry, the growth of e-commerce, and the need for lightweight, durable containers that can reduce transportation costs and food waste. PET is a dominant material in this segment, valued for its clarity, strength, and barrier properties, which make it ideal for bottling water and carbonated drinks. HDPE and LDPE are extensively used for flexible and rigid packaging, including food wraps, bags, and bottles, because of their excellent moisture barrier and malleability. The need for these materials is directly linked to global population growth and rising disposable incomes, which increase the consumption of consumer packaged goods. While environmental pressures are a significant headwind, the industry has responded with innovations like lightweighting and the development of monomaterial packaging designs that are easier to recycle, thereby sustaining and evolving demand within this critical application. The shift toward sustainable packaging solutions has also introduced new demand for recycled and bio-based plastics, reshaping the competitive dynamics within this segment.
- By End-User Industry: Automotive
The automotive industry's demand for plastics is a function of a clear economic and performance imperative: weight reduction. Every kilogram of weight removed from a vehicle improves fuel efficiency and, in the case of electric vehicles, extends battery range. This direct correlation makes plastics an indispensable material for modern vehicle manufacturing. The need for materials like polypropylene (PP) and acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) is driven by their high strength-to-weight ratio, which allows them to be used in a wide array of non-structural components. Applications range from interior dashboards, door panels, and consoles to exterior components like bumpers, grilles, and fenders. The increasing complexity of vehicle electronics also drives demand for plastics with specific electrical and thermal properties. The industry's shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is a particularly strong growth catalyst. EVs require a greater number of plastic components for battery packs, charging ports, and thermal management systems, thereby changing the demand profile from traditional combustion engines to new, high-performance polymers. This necessity is further supported by the industry's commitment to using recycled plastics in non-critical components to meet corporate sustainability goals and consumer preferences.
Plastics Market Geographical Analysis:
- US Market Analysis
The US plastics market is characterized by a mature industrial base and a high-demand consumer economy. The market is primarily driven by the packaging, automotive, and building & construction sectors. The automotive industry in the US, for instance, is a consistent consumer of plastics for lightweighting initiatives aimed at improving fuel efficiency. The domestic supply chain for key feedstocks, particularly from abundant shale gas resources, provides a competitive advantage for US-based plastics manufacturers. While a federal-level comprehensive plastics regulation has been absent, state-level and municipal regulations on single-use plastics and recycling are becoming increasingly prevalent. These localized policies directly impact demand, often creating a fragmented market where companies must adapt their strategies to different regulatory landscapes. The US market is also a hub for innovation, with significant investments in advanced recycling technologies and bioplastics development, which is creating a new segment of demand.
- Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil's plastics market is the largest in Latin America, with demand primarily fueled by the country's extensive packaging, consumer goods, and agricultural sectors. The growth of the middle class and an expanding consumer base have driven the robust growth of plastic packaging for food and beverages. The agricultural sector, a cornerstone of the Brazilian economy, uses plastics for irrigation pipes, films, and protective covers, all of which contribute to sustained demand. The country's plastics industry is highly integrated with its petrochemical sector, with companies like Braskem being major regional producers. The Brazilian government's policies and economic stability, particularly fluctuations in currency and commodity prices, have a direct impact on the domestic market's health. While recycling infrastructure exists, it remains underdeveloped compared to more mature economies, creating a significant opportunity for future investment and growth in the circular economy segment.
- Germany Market Analysis
Germany’s plastics market is a leader in Europe, distinguished by its focus on high-performance engineering plastics and a strong commitment to circular economy principles. The country’s market expansion is heavily driven by its globally dominant automotive industry and its robust manufacturing sector. German companies use advanced plastics for applications requiring precision and high performance, such as in medical devices, electrical components, and specialized industrial equipment. The country is a frontrunner in recycling and waste management policies, with a highly developed "Duales System" that mandates and facilitates the collection and recycling of packaging waste. These regulations create direct demand for recycled plastics and place a premium on easily recyclable materials, thereby incentivizing eco-design. The German market is shifting towards high-value, sustainable solutions rather than volume-based commodity plastics.
- Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The plastics market in Saudi Arabia is a critical component of its economic diversification strategy, with the country being a major global producer of petrochemicals. This growth is driven by local consumption but also heavily oriented toward exports. The plastics industry in Saudi Arabia benefits from access to low-cost raw materials, primarily ethane derived from natural gas. This feedstock advantage makes Saudi Arabian producers highly competitive on the global stage, allowing them to serve markets across Asia, Europe, and Africa. The government's Vision 2030 program aims to expand the non-oil industrial base, which includes significant investments in plastics conversion and manufacturing. This initiative directly fuels demand for a variety of plastic resins, from commodity polymers for packaging to more specialized materials for construction and other industrial applications. The market's future growth is tied to the expansion of domestic manufacturing capabilities and the ability to leverage its feedstock advantage to meet global demand.
- Japan Market Analysis
Japan's plastics market is mature, highly specialized, and focused on innovation and high-quality materials. The country’s necessity for plastics is concentrated in the automotive, electrical & electronics, and medical & healthcare sectors. Japanese companies are at the forefront of developing advanced polymers for applications like lightweight components for high-speed trains, precision parts for consumer electronics, and sterile medical equipment. The growth is not driven by sheer volume but by the need for superior material properties, such as thermal resistance, conductivity, and durability. The Japanese government has implemented policies to promote recycling and reduce plastic waste, which has increased the demand for recycled plastics and bioplastics. The market's future is tied to the country's ability to maintain its technological edge and to develop circular solutions that address its environmental commitments while continuing to supply high-performance materials to its core industries.
Plastics Market Competitive Analysis:
The global plastics market is dominated by a few large, vertically integrated chemical and energy companies that produce the foundational polymers. These companies compete on scale, access to low-cost feedstock, and technological innovation. The competitive landscape is shaped by strategic capacity expansions, mergers, and acquisitions aimed at consolidating market position and diversifying product portfolios.
- LyondellBasell: A major global producer of polyolefins and a pioneer in polyolefin technologies. The company's strategic positioning is centered on its wide-ranging portfolio of products, including polypropylene, polyethylene, and advanced polymers. A core element of its strategy is the development of circular solutions, such as its Circulen product portfolio, which includes polymers from mechanically and chemically recycled sources. The company's focus on innovation is demonstrated by its collaborations and investments in advanced recycling.
- SABIC: A global leader in diversified chemicals, with a strong presence in the plastics market. SABIC's competitive advantage stems from its direct access to low-cost feedstocks in Saudi Arabia and its extensive global manufacturing footprint. The company is actively pursuing a sustainability strategy, with its TRUCIRCLE portfolio offering a range of recycled and certified renewable polymers. SABIC's strategic alliances and investments in chemical recycling are designed to secure its position in the emerging circular economy.
- Braskem: A leading producer of thermoplastic resins in the Americas and a pioneer in bio-based plastics. Braskem's strategy is differentiated by its focus on sustainable solutions, particularly through its "I'm green" brand, which produces bio-based polyethylene from sugarcane. The company's competitive edge in Latin America is bolstered by its strong regional market presence and its commitment to circularity initiatives. Braskem is strategically investing in mechanical and advanced recycling to expand its portfolio of recycled content and meet growing demand for sustainable materials.
Plastics Market Developments:
- July 2025: LyondellBasell's joint venture, GXLYB, received a No Objection Letter from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its recycled polypropylene (PP) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resins, which can be used in food-contact applications. This development directly impacts demand by expanding the potential uses for recycled content into a high-value, regulated market segment.
- July 2025: Braskem completed its first commercial sale of circular polyethylene (PE) in South America, a product derived from certified post-consumer recycled resin. This event demonstrates the company's commitment to scaling its circular economy initiatives and establishes a new demand pathway for recycled materials in a key regional market.
- September 2024: Braskem announced the official opening of its Renewable Innovation Center in Lexington, Massachusetts. The center is dedicated to developing new technologies for renewable chemicals and sustainable materials, reinforcing the company's strategic focus on diversifying its product offerings and meeting future demand for environmentally friendly plastics.
Plastics Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Plastics Market Size in 2025 | USD 620.767 billion |
| Plastics Market Size in 2030 | USD 727.864 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 3.23% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Plastics Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Global Plastics Market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Others
- By Application
- Packaging
- Building & Construction
- Automotive & Transportation
- Consumer Goods
- Electrical & Electronics
- Medical & Healthcare
- Others
- By End-User Industry
- Packaging
- Construction
- Automotive
- Consumer Goods
- Electrical & Electronics
- Medical Devices
- Textiles
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Navigation:
- Global Plastics Market Size:
- Global Plastics Market Key Highlights:
- Global Plastics Market Analysis
- Plastics Market Segment Analysis
- Plastics Market Geographical Analysis:
- Plastics Market Competitive Analysis:
- Plastics Market Developments:
- Plastics Market Scope:
- Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Page last updated on: September 22, 2025