Report Overview
Global Thin-Film PV Module Highlights
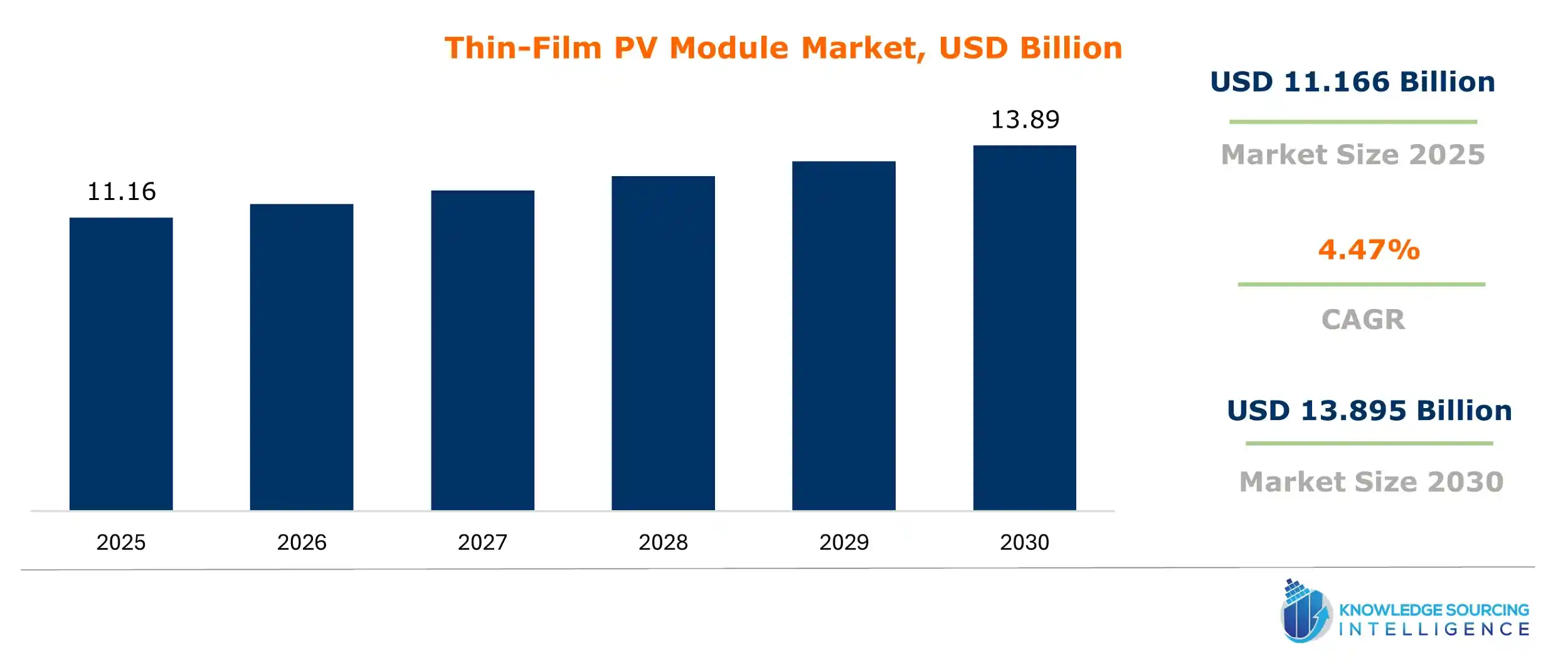
Thin-Film PV Module Market Size:
The global thin-film PV module market is valued at US$11.166 billion in 2025 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.47% over the forecast period to US$13.895 billion in 2030.
Thin-film solar modules are made from thin-film solar cells. Thin-film solar cells (TFSCs) are second-generation solar cells made from multiple thin-film layers of photovoltaic (PV) materials. These solar cells have a fragile layer of thickness, measured in nanometers, compared to conventional P-N junction solar cells. As such, thin-film PV modules are more flexible and lightweight and are used in developing integrated photovoltaics.
Thin-film technology has been relatively economical despite being less efficient than conventional c-Si (crystalline silicon) technology. However, this technology has significantly improved due to constant research and development. As a result of R&D, the efficiency of CdTe and CIGS PV cells is now over 21%, which has outperformed multi-crystalline silicon that dominates the solar PV module industry.
The installation process of thin-film solar panels or modules is much easier and takes less effort than conventional silicon panels or modules. This is because thin-film solar panels are flexible and lightweight and can be applied in areas where conventional solar panels cannot be installed. Moreover, thin-film modules are made from thin-film solar cells, which contain a significantly lesser quantity of silicon, resulting in fewer emissions during their production than standard solar modules. These modules need a larger area to be installed, such as commercial/institutional buildings, streets, forest areas, and large open/rooftop spaces. For example, thin-film modules can be used in street lights and traffic. These modules can also be installed on the rooftops of buses to power small appliances such as fans and Wi-Fi modems.
Thin-Film PV Module Market Growth Drivers:
The rising focus on the renewable energy sector, especially solar, is significantly driving the demand for thin-film modules, thereby fuelling market growth. Countries worldwide have set targets to increase the share of renewable energy sources in total electricity generation because of growing concerns regarding environmental sustainability, reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and the rising cost of electricity. For instance, Spain also aims at 120 GW of installed renewable energy, primarily wind and solar, capacity by 2030 under the country’s national integrated energy and climate plan (NECP 2021-30). Canada, with one of the world's cleanest electricity systems, also aims to increase the share of zero-emitting renewable sources to 90% by 2030 from around 80% in 2016. In India, the government aims to install 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, out of which solar includes 100 GW. All these targets and goals to increase the overall share of renewable energy sources in total electricity generation are substantially driving the demand for thin-film modules worldwide.
Another strong driver of the thin-film photovoltaic module market is the imposition of tariffs on c-Si solar panels by the United States. These tariffs imposed on importing crystalline silicon-based solar panels to protect domestic manufacturing have increased the cost of importing these panels, thus burdening developers and project managers with financial pressure. Due to this, manufacturers and developers are increasingly looking towards alternative technologies to help them bypass the additional costs. Thin-film PV modules have also become viable for balancing price and functionality. Thin-film modules have lower manufacturing costs and can operate with high efficiency in various environmental conditions, making them a viable alternative for projects requiring cost-effective solar energy solutions that do not compromise the output.
In addition, flexibility and lightweight design make thin-film PV modules especially advantageous for wider applications. Their versatility in being applied on curved surfaces or irregular shapes, such as rooftops or building facades, has further increased the demand in niche and special markets. Besides this, the continued improvement in efficiency through R&D has enabled thin-film modules to catch up with c-Si panels and make them even more competitive. These characteristics, coupled with the economic push created by tariffs, have fueled the surge in the adoption of thin-film PV modules, positioning them as a key player in the global solar energy landscape. This trend is rising due to the ability of thin-film technology to meet the challenge of costs and innovation in energy in an evolving market.
The rising investments in R&D to improve the efficiency and the performance of thin-film solar modules are opening significant opportunities in their broader adoption in the solar PV market. It has been known for so long that cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), and amorphous silicon (a-Si) have the promise of high performance at reduced cost. However, challenges in efficiency and durability have not allowed them to compete with crystalline silicon solar panels. Increased funding and attention from governments, research institutions, and private sector players have led to breakthroughs in materials science, manufacturing techniques, and energy conversion efficiency, driving the competitiveness of thin-film technologies. These improvements make thin-film modules attractive to large-scale utility applications and niche areas such as building-integrated photovoltaics and portable solar devices.
In addition, the increasing emphasis on greenness and environmentalism further fuels the growth of thin-film solar modules. Thin-film technology utilizes far less material and energy input in its manufacturing processes compared to crystalline silicon modules. Investments in R&D improve not only the energy efficiency of these modules but also help resolve issues like recycling and lifecycle management, thus further making them more attractive in a world increasingly moving towards green technologies. This makes thin-film solar modules' improved capabilities, cost, and environmental benefits poised to capture an increasingly large share of the global solar PV market in the next few years. This increasing market presence shows there is much potential in renewing energy sources through consistent efforts in R&D.
Thin-Film PV Module Market Key Developments:
- In April 2022, First Solar Inc. signed a master supply agreement (MSA) with Silicon Ranch, one of the nation's leading independent power producers, to deliver 4 gigawatts (GW) DC of innovative, responsibly-produced thin-film photovoltaic (PV) solar modules. Since 2015, the collaboration between these industry experts has expanded significantly across the United States, with more than 30 projects totaling more than 1 GW.
- In April 2022, EPFL researchers in Neuchâtel created a tandem solar cell with a validated efficiency of 29.2 percent, as noted by EPFL. Combining a perovskite solar cell with a textured silicon solar cell enabled this breakthrough.
List of Top Thin-Film PV Module Companies:
- Solar Frontier Kabushiki Kaisha
- United Solar Ovonic LLC
- Soltecture Solartechnik GmbH
- TS Solartech Sdn Bhd
- NanoPV Solar Inc
Thin-Film PV Module Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Thin-Film PV Module Market Size in 2025 | US$11.166 billion |
| Thin-Film PV Module Market Size in 2030 | US$13.895 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.47% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in Thin-Film PV Module Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
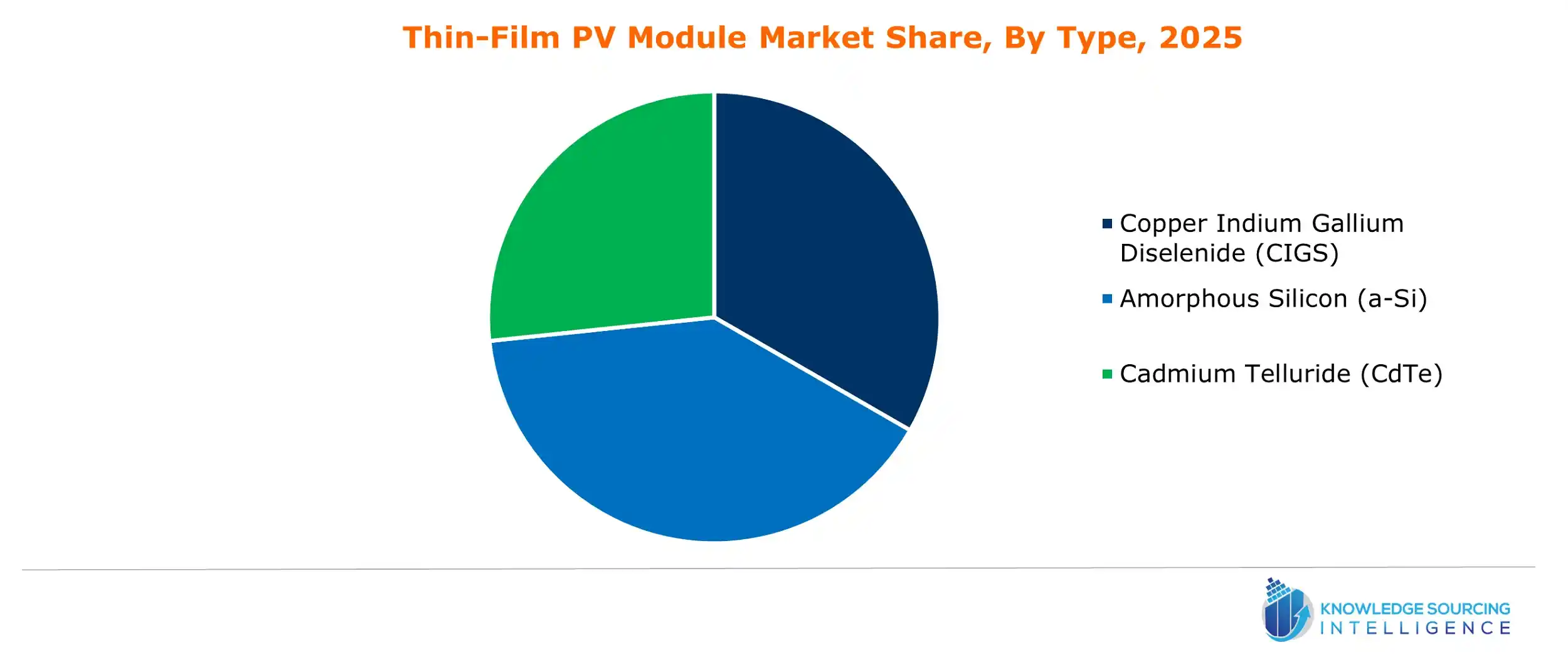
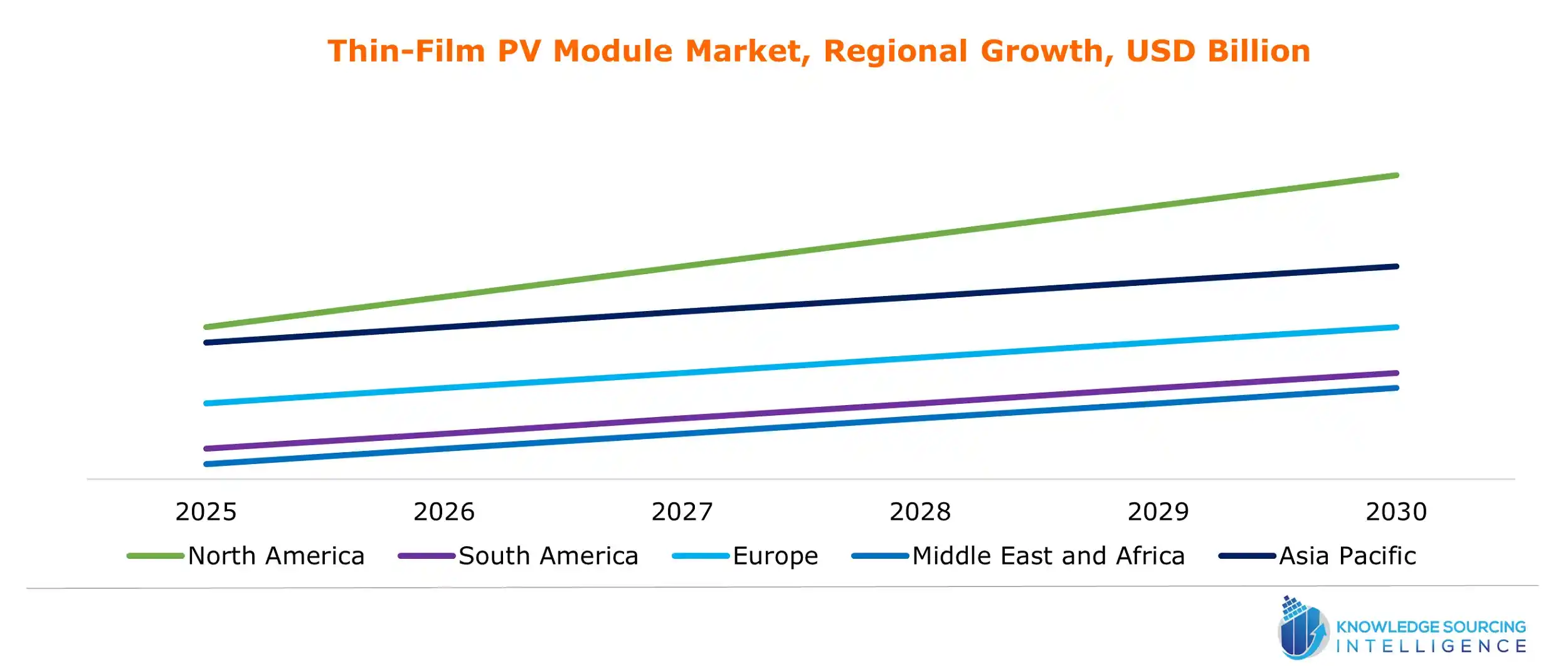
Thin-Film PV Module Market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Copper Indium Gallium Diselenide (CIGS)
- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si)
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe)
- By Application
- Building Integrated PV
- Rooftop applications
- Utility-scale applications
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Spain`
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- UAE
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Thailand
- Taiwan
- Others
- North America
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
- Power And Control Cable Market
- Electrically Conductive Adhesives Market
- Electromechanical Relay Market