Report Overview
Medical Laser System Market Highlights
Medical Laser System Market Size:
The Medical Laser System Market is expected to increase from USD 6.144 billion in 2025 to USD 9.030 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 8.01%.
The medical laser system market is undergoing a period of profound technical and structural evolution, propelled by the convergence of miniaturization technology and patient-centric care models. These advanced systems, integral to precision medicine, facilitate procedures across diverse specialties, moving beyond historically dominant applications like ophthalmology into high-growth areas such as minimally invasive surgery, dermatology, and dentistry. The market's current trajectory is fundamentally shaped by external economic pressure to reduce healthcare costs and a concurrent internal push for enhanced clinical outcomes, situating laser technology as a strategic imperative for modern healthcare providers seeking efficiency and efficacy.
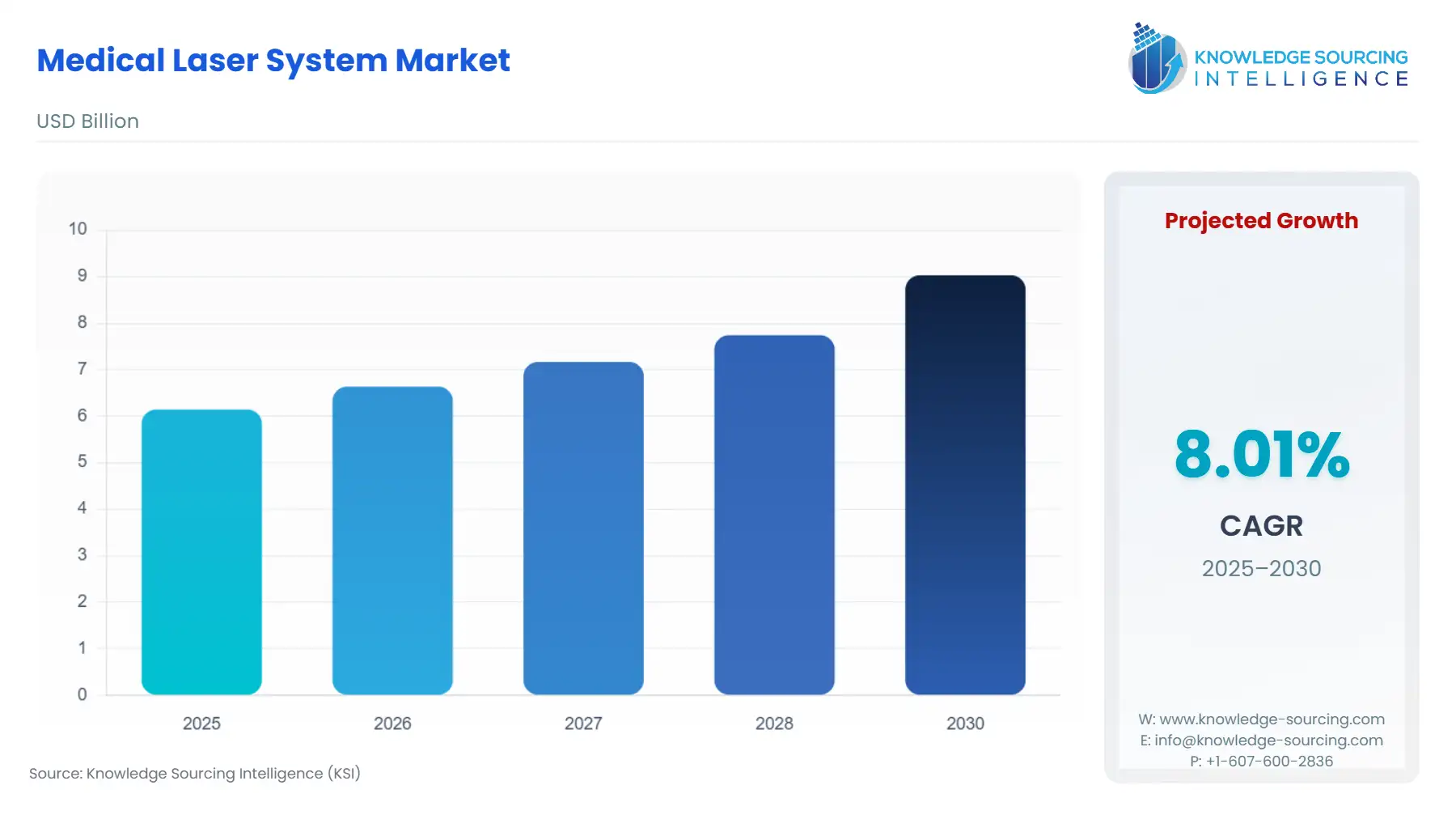
The medical laser system market is undergoing a period of profound technical and structural evolution, propelled by the convergence of miniaturization technology and patient-centric care models. These advanced systems, integral to precision medicine, facilitate procedures across diverse specialties, moving beyond historically dominant applications like ophthalmology into high-growth areas such as minimally invasive surgery, dermatology, and dentistry. The market's current trajectory is fundamentally shaped by external economic pressure to reduce healthcare costs and a concurrent internal push for enhanced clinical outcomes, situating laser technology as a strategic imperative for modern healthcare providers seeking efficiency and efficacy.
Medical Laser System Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The sustained growth of the Medical Laser System Market is directly tied to advancements in clinical utility that enhance operational efficiency and patient outcomes, thereby increasing demand for specialized laser platforms.
The expansion of the Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC) model across jurisdictions like the United States creates direct demand for new capital equipment. As the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continues to move procedures off the Inpatient Only (IPO) list, the increasing volume of laser-dependent surgeries such as extracapsular cataract removal, which accounted for approximately 19% of FFS Medicare ASC volume in 2023 compels ASCs to invest in new ophthalmic and surgical laser systems to meet patient volume.
Global demographic shifts toward an aging population act as a macro-level catalyst for demand, particularly within ophthalmology. The prevalence of age-related eye conditions, including cataracts and glaucoma, escalates significantly with age. This trend generates a non-cyclical, continuous need for YAG and excimer lasers used in cataract and refractive surgeries. The escalating patient volume strains existing capacity, driving demand for faster, more precise laser platforms.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The market faces significant headwinds from the high capital cost of advanced systems and the subsequent training imperative. Laser systems, especially those using femtosecond or picosecond pulse technologies, represent substantial capital expenditures, which can constrain adoption, particularly among smaller clinics or healthcare systems in emerging economies. The complexity of operating and maintaining these sophisticated machines also increases the total cost of ownership (TCO) and necessitates specialized physician and technician training, placing a constraint on the velocity of demand adoption.
Concurrently, a major opportunity exists in the proliferation of diode laser applications in non-traditional settings, specifically in dentistry. Diode lasers offer clinical advantages over conventional methods, including minimal to no required anesthesia, optimal coagulation for less bleeding, and reduced post-operative pain. Furthermore, their relatively low cost and compact size make them highly accessible to individual dental and cosmetic clinics. This compelling value proposition drives a high-volume demand opportunity in a largely untapped market segment, shifting procedure protocols away from traditional drills and scalpels.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Medical laser systems are physical products, necessitating a stable and predictable supply chain for critical optical and electronic components. The pricing and supply stability of solid-state laser crystals such as Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (Nd:YAG) and KTP (Potassium Titanyl Phosphate) are paramount. The fabrication of these high-purity, optically precise crystals is concentrated in specialized facilities, primarily located in Asia, creating single-source or concentrated sourcing risk. Price volatility for essential doping materials, such as rare earth elements, and disruptions in the fabrication process can directly impact the cost of goods sold (COGS) for system manufacturers. This inherent concentration risk necessitates strategic, long-term procurement agreements and drives a strategic push toward component standardization across product lines to mitigate material cost inflation and supply disruption.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for medical laser systems is inherently complex, characterized by a tiered structure. Tier 1 suppliers focus on core laser engines (solid-state, gas, or diode modules), which rely on Tier 2 suppliers for high-purity raw materials (crystals, gas mixtures, and semiconductor wafers). Key production hubs for the most critical components, particularly sophisticated laser crystals and high-power diode assemblies, are predominantly situated in China and the US. The logistical complexities involve stringent quality control for cleanroom assembly and dependency on reliable, high-speed international freight for finished systems. Dependencies are particularly acute for custom optics and beam delivery mechanisms, which are often single-sourced due to intellectual property constraints and specialized manufacturing requirements. This global dependency renders the entire supply chain vulnerable to geopolitical trade policies and unforeseen logistical shocks.
Medical Laser System Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
European Union |
Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) (Regulation (EU) 2017/745) |
Constraints Demand by increasing compliance costs and time-to-market. The MDR classifies surgical lasers as Class IIb devices, demanding stricter clinical evidence, enhanced post-market surveillance, and comprehensive quality management systems. This has resulted in some manufacturers withdrawing legacy products due to the prohibitive cost of re-certification, limiting available supply. |
|
United States |
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 510(k) Premarket Notification |
Directly Catalyzes Demand for proven, 'substantially equivalent' devices. While the process ensures safety, the 510(k) pathway facilitates market entry for novel laser systems that demonstrate equivalence to a predicate device, accelerating commercialization. Manufacturers focus R&D on iterative improvements over existing cleared devices to expedite market access and capture demand quickly. |
|
Asia-Pacific (China) |
National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) |
Constraints and Re-routes Demand through mandatory, often lengthy, local testing and clinical data requirements. The NMPA process can delay product launches, compelling global manufacturers to either delay entry or partner with local firms, segmenting the market and pushing initial regional demand toward locally approved devices. |
Medical Laser System Market Segment Analysis
- By Application: Ophthalmology
The Ophthalmology segment remains a cornerstone of the medical laser market, with demand fundamentally driven by the rising incidence of age-related vision disorders. The utility of lasers in this segment is non-discretionary for essential procedures like cataract removal, refractive surgery (LASIK/PRK), and the treatment of secondary cataracts (YAG capsulotomy). The introduction and adoption of femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery (FLACS) directly increased demand for these specific, high-precision laser platforms as ophthalmologists sought to improve surgical predictability and reduce the energy required during phacoemulsification. The aging patient demographic, as noted by the World Health Organization's report on vision, projects a surge in global eye care demand, ensuring a robust, long-term demand curve for advanced excimer, Nd:YAG, and femtosecond laser systems.
- By End-User: Hospitals & Surgical Centers
Hospitals and Surgical Centers drive the highest volume demand for complex, multi-functional, and high-power laser systems, especially in the surgical and cardiovascular segments. Demand here is characterized by the need for devices capable of a wide range of procedures, from laparoscopic surgery and lithotripsy (urology) to angioplasty (cardiovascular). The purchasing decisions are less price-sensitive than in smaller clinics, focusing instead on system reliability, service contracts, and compatibility with existing surgical theaters. The concentration of high-risk, Class III procedures in these settings, such as those requiring Ho:YAG (Holmium) or Nd:YAG (Neodymium) lasers, solidifies their position as the primary end-users for the highest-tier laser equipment, with demand intrinsically linked to annual surgical procedure volumes.
Medical Laser System Market Geographical Analysis
- US Market Analysis (North America)
The US market exhibits a robust, highly competitive environment where demand is catalyzed by favorable reimbursement policies (particularly from Medicare/Medicaid) and a strong push toward decentralized care in Ambulatory Surgical Centers. High disposable incomes support demand for elective, aesthetic laser procedures, while the mature healthcare infrastructure facilitates the rapid adoption of expensive, cutting-edge technology like picosecond and femtosecond lasers. Regulatory clarity through the FDA's 510(k) process streamlines product introduction, keeping the demand pipeline fluid.
- Brazil Market Analysis (South America)
Demand in Brazil is increasingly bifurcated. High-end cosmetic and aesthetic applications, particularly in major urban centers, mimic the demand patterns of developed markets. Conversely, the public healthcare system faces significant capital budget constraints, limiting the penetration of advanced surgical laser systems. Local demand is price-elastic, favoring mid-range, versatile systems. Regulatory processes, which can be complex, often lead to delayed access to the newest global technologies, suppressing demand for the most recent launches.
- Germany Market Analysis (Europe)
The German market is characterized by a strong emphasis on clinical evidence and quality, driving demand for technologically superior and highly certified systems. The presence of universal healthcare mandates rigorous cost-benefit analyses, meaning adoption is contingent on demonstrated clinical efficacy and long-term TCO benefits. Compliance with the EU MDR is a non-negotiable factor, favoring large, established manufacturers who can manage the regulatory burden, which constrains the entry of smaller, innovative firms and shapes local demand toward established brands.
- UAE Market Analysis (Middle East & Africa)
The UAE market acts as a major hub for luxury medical tourism, creating concentrated, high-volume demand for premium aesthetic laser systems. Government initiatives to develop world-class medical cities further bolster demand for advanced surgical and ophthalmic laser technology, driven by an appetite for the latest generation of minimally invasive devices. High per-capita healthcare spending and minimal price sensitivity make this a crucial launch market for manufacturers introducing top-tier, high-cost platforms.
- China Market Analysis (Asia-Pacific)
China represents a massive, rapidly expanding market where demand is fueled by the expansion of its middle class, which increases the affordability of elective cosmetic procedures, and massive government investment in modernizing hospital infrastructure. Local demand is highly responsive to domestic manufacturing capabilities, which compete effectively on price for mid- to low-end laser systems. However, demand for the highest-end, complex surgical lasers remains dependent on imports due to their advanced technological requirements, with NMPA approvals acting as the primary bottleneck controlling demand flow.
Medical Laser System Market Competitive Environment and Analysis
The Medical Laser System Market features a highly competitive landscape dominated by a few multinational corporations that maintain market share through diverse product portfolios, intellectual property, and extensive global service networks. Competition is primarily based on technological differentiation, clinical efficacy data, and the ability to navigate complex global regulatory regimes. The intense capital requirements and the need for dedicated service infrastructure serve as formidable barriers to entry for new competitors.
- Boston Scientific Corporation maintains a powerful position, particularly in the urology and gastroenterology laser segments. The company's strategic positioning is built on its deep integration within the surgical and interventional procedure value chain. A key product is the Moses Technology Holmium Laser System, which is specifically engineered to improve the efficiency and efficacy of lithotripsy and other endoscopic procedures. Their focus on high-power laser fibers and platforms ensures a sustained demand stream from hospitals and ASCs performing stone management and soft tissue surgery.
- Alcon Inc. dominates the core Ophthalmology segment, leveraging a comprehensive portfolio of cataract, vitreoretinal, and refractive surgery technologies. Alcon's strategic positioning relies on its long-standing relationships with ophthalmic clinics and its ability to bundle equipment, consumables, and IOLs. The company's WAVELIGHT EX500 Excimer Laser and its various femtosecond laser platforms, such as the LenSx Laser, are foundational to their strategy, capturing demand for both essential and elective vision correction procedures.
- Cynosure Lutronics (Hologic, Inc.) focuses predominantly on the aesthetic and dermatological laser segment. The company’s strategic objective is market leadership in elective, non-invasive procedures. Their portfolio, which includes the PicoSure Pro picosecond laser for tattoo removal and skin revitalization, and the Elite iQ platform for hair removal, directly addresses the growing consumer demand for fast, effective cosmetic treatments in dermatology and cosmetics clinics globally.
Medical Laser System Market Developments
- August 2025: Alcon announced an agreement to acquire STAAR Surgical. This acquisition, which includes the EVO Visian ICL family of lenses, represents a strategic capacity addition for Alcon in the refractive eye surgery market. The move is designed to integrate a premium implantable lens technology into Alcon’s existing ophthalmic portfolio, strengthening its competitive position against other vision correction modalities, including laser systems.
- July 2025: Boston Scientific Corporation received FDA approval for expanded labeling of its FARAPULSE Pulsed Field Ablation System. While primarily an ablation system, this regulatory clearance for use in the pulmonary vein and posterior wall ablation in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation enhances Boston Scientific's capacity to offer advanced, minimally invasive cardiac solutions. This expansion drives new capacity utilization for their electrophysiology division, leveraging their existing hospital equipment supply chain.
- March 2025: Alcon completed the acquisition of a majority interest in Aurion Biotech, Inc. The acquisition is a direct strategic investment in innovative cell therapy for corneal endothelial disease, signaling Alcon's intent to broaden its product offerings beyond traditional laser and lens technologies into regenerative medicine. This capacity addition diversifies Alcon's future revenue streams in the high-value corneal segment of the ophthalmology market.
Medical Laser System Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 6.144 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 9.030 billion |
| Growth Rate | 8.01% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Type, Application, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Medical Laser System Market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Solid laser systems
- Gas laser systems
- Diode laser systems
- Dye laser systems
- Others
- By Application
- Dermatology
- Dentistry
- Ophthalmology
- Surgical
- Urology & Gynecology
- Cardiovascular
- Others
- By End-User
- Hospitals & Surgical Centers
- Dermatology & Cosmetics Clinics
- Ophthalmic Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East & Africa
- Asia Pacific