Report Overview
Plant-Based Milk Market - Highlights
Plant-Based Milk Market:
The Plant-based Milk Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.27%, reaching USD 21.808 billion in 2030 from USD 15.354 billion in 2025.
The global plant-based milk market continues its trajectory of growth, driven by a convergence of consumer, health, and ethical trends. Consumers are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional dairy, motivated by a mix of dietary restrictions, such as lactose intolerance and allergies, as well as a heightened awareness of the environmental and ethical considerations associated with animal agriculture. This shift is not confined to dedicated vegan or vegetarian consumers but is expanding rapidly among the broader "flexitarian" population, which is consciously reducing its consumption of animal products. The market's evolution is also shaped by technological advancements in food processing, which have improved the taste, texture, and nutritional profiles of plant-based milks, making them a more viable and appealing substitute for a wider consumer base.
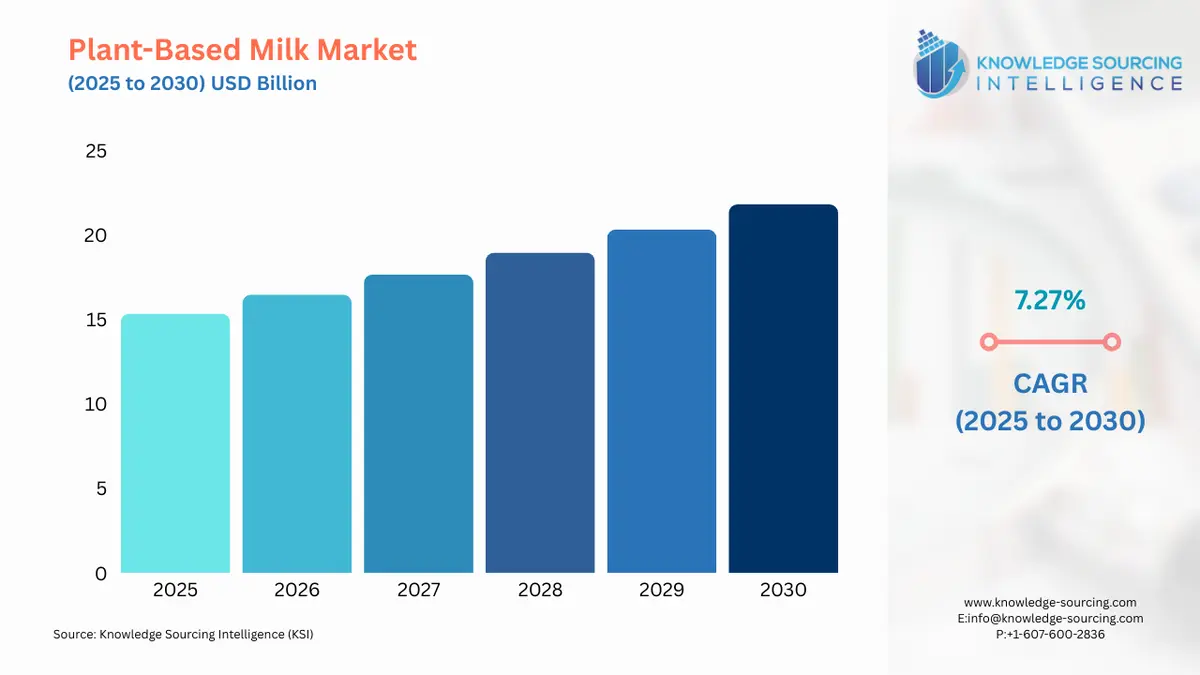
Plant-Based Milk Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers:
The market's expansion is directly linked to several demand-centric drivers. A primary catalyst is the increasing prevalence of lactose intolerance and dairy allergies. According to various public health organizations, a significant portion of the global population is lactose intolerant, and this condition directly creates a demand for lactose-free beverage alternatives. Consumers with this dietary restriction seek products that provide the functional use of traditional milk without causing digestive discomfort. This is the foundational demand driver for the market.
Additionally, a growing number of consumers are adopting flexitarian, vegetarian, or vegan diets. This shift is driven by a combination of personal health goals, environmental concerns, and ethical considerations regarding animal welfare. For these consumers, plant-based milks serve as a direct and often preferred substitute for dairy. The demand impact is seen in the sustained growth of the market, as this demographic actively seeks out a variety of plant-based options to fulfill their daily dietary needs. The perception of plant-based milks as being "healthier" due to lower saturated fat and cholesterol content further propels demand.
Another significant driver is the growing application of plant-based milks in the broader food and beverage industry. Foodservice establishments, from coffee shops to restaurants, are incorporating these alternatives into their menus to cater to a wider customer base. This B2B demand creates a new revenue stream for manufacturers and increases the visibility and accessibility of plant-based products for the average consumer, which in turn stimulates B2C demand.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
The plant-based milk market faces specific challenges that create a demand-side headwind. A notable obstacle is the public's perception of the nutritional profile of plant-based milks compared to traditional dairy. Many consumers rely on dairy for essential nutrients like calcium, Vitamin D, and Vitamin B12. Plant-based milks often lack these nutrients naturally, requiring fortification. This discrepancy can deter potential buyers who are concerned about nutritional equivalence. A secondary challenge is the sensory profile, as some plant-based milks may have a distinct taste or texture that is not comparable to dairy, which can hinder repeat purchases.
These challenges, however, create direct opportunities for innovation and market penetration. The imperative for manufacturers is to close the nutritional and sensory gaps. Fortification with vitamins and minerals presents a clear opportunity to directly address consumer health concerns and increase demand among health-conscious buyers. Furthermore, developing new formulations that improve taste, texture, and mouthfeel can expand the market by attracting a wider audience, including those who are not strictly vegan but are open to dairy alternatives. Blends of different plant bases, such as oat and almond, can be developed to create products with enhanced sensory attributes.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
The production of plant-based milk is a physical process that is highly dependent on the stability of raw material pricing. Key inputs include soybeans, almonds, oats, and coconuts. The pricing of these agricultural commodities is subject to fluctuations based on weather patterns, global supply and demand dynamics, and geopolitical events. For instance, a drought in a major almond-producing region can drive up the cost of raw materials, which in turn increases the final product's price and can suppress consumer demand, particularly among price-sensitive buyers.
Similarly, the pricing of these products is influenced by processing costs, which include grinding, blending, and pasteurization. The supply chain for plant-based milks is more complex than that of conventional dairy, often requiring specialized equipment and logistics for different base ingredients. The final product is typically priced at a premium compared to traditional dairy milk, a factor that remains a significant barrier to wider consumer adoption.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The global supply chain for plant-based milks is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation and regional dependencies. The production process begins with the sourcing of raw materials, which often come from specific geographic hubs. For example, a large portion of the world's almonds are sourced from California, while soybeans are a major crop in the US, Brazil, and Argentina. This concentration of raw material sourcing exposes the supply chain to risks such as crop failures, trade disputes, and logistical bottlenecks.
After sourcing, the raw materials are transported to processing facilities, where they are transformed into liquid milk. These facilities may be located near the source or closer to major consumption markets to reduce transportation costs. The final products are then distributed through a network of retailers, including supermarkets, health food stores, and online channels. The logistical complexities include maintaining temperature controls and managing the shelf life of different products. The supply chain is becoming more globalized, with manufacturers building production facilities in new regions to shorten supply lines and respond more quickly to local demand.
Government Regulations
Government regulations have a profound impact on the plant-based milk market, particularly concerning labeling and marketing. These regulations are designed to ensure consumer clarity and prevent misleading claims. The legal status of terms like "milk" when applied to plant-based products has been a central point of regulatory focus.
- United States: FDA (Food and Drug Administration) - The FDA issued a draft guidance in February 2023 recommending that plant-based milk alternatives using the term "milk" in their name, such as "soy milk" or "almond milk," voluntarily include a nutrient statement on the product label. This statement should compare the product's nutritional profile to that of dairy milk. This guidance promotes transparency, which builds consumer trust and can increase demand by providing clear, fact-based information. It also pushes manufacturers to fortify products to meet or exceed the nutritional content of dairy, creating a demand for more nutrient-rich products.
- European Union: Regulation (EU) No 1308/2013 - The Court of Justice of the European Union has ruled that terms like "milk" and "cheese" are reserved exclusively for animal-based products. Plant-based products cannot use these terms, even with descriptive qualifiers. This regulation creates a significant labeling constraint for manufacturers in the EU. It necessitates the use of alternative terms, which can require consumer education but also encourages a clear distinction between product categories. The regulation shapes market communication and product naming, directly influencing how brands position themselves to consumers.
- China: GB Standards - China's national GB standards for food products, which are updated periodically, set mandatory requirements for domestic and imported goods. These standards often cover labeling, composition, and safety. Strict adherence to these regulations is an entry barrier for international companies but also a mechanism for ensuring product quality. Compliance with these standards is an essential prerequisite for market access, and a clear regulatory framework can foster a predictable environment that stimulates investment and demand.
Plant-Based Milk Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Food and Beverage
The food and beverage segment is the largest application area for plant-based milk, and its growth is due to its versatility and a growing focus on product innovation. This segment’s expansion is driven by the use of plant-based milks as a direct beverage alternative to dairy. This is fueled by the same consumer trends of health, ethics, and sustainability that drive the overall market. However, a significant portion of the demand originates from the B2B sector, where plant-based milks are being adopted as an ingredient in other food products. Coffee shops and bakeries, for instance, have increasingly integrated oat, almond, and soy milks into their offerings. This is a direct response to consumer requests for dairy-free options in coffee, smoothies, and pastries. The demand from this sector has an amplifying effect on the overall market, as it exposes new consumers to the products in a familiar context, prompting them to purchase these products for at-home use. The need for specific plant-based milk types, such as oat milk, is particularly strong in the coffee industry due to its superior frothing and mixing properties, which directly impact the demand for this specific sub-segment. As the food and beverage industry continues to diversify its menus, the demand for plant-based milks as a functional ingredient will continue to be a primary growth driver.
- By End-User: B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
The B2C segment represents the core of the plant-based milk market, with demand driven by individual consumer purchases for household consumption. This segment’s growth is highly influenced by marketing, product variety, and distribution channels. Consumers are not a monolithic group; they have diverse needs and preferences. For instance, consumers with lactose intolerance or a dairy allergy have a non-negotiable need for alternatives, creating a consistent and stable demand base. On the other hand, demand from the flexitarian consumer is more elastic and influenced by factors such as product taste, price, and perceived health benefits. The B2C segment has witnessed a proliferation of new flavors, formulations, and packaging sizes, directly responding to the desire for variety. The strategic positioning of products, such as "barista blends" of oat milk, directly targets consumers who want a high-quality, specialty product for their at-home coffee preparation. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer (D2C) channels has made these products more accessible, removing a key logistical barrier and further stimulating demand. The need for B2C is dynamic and requires continuous innovation in product development and consumer engagement to sustain growth.
Plant-Based Milk Market Regional Analysis
- United States: The US market for plant-based milk is mature and highly developed, driven by a combination of high consumer awareness and a robust retail infrastructure. The primary demand drivers are health-related, including the widespread prevalence of lactose intolerance and a growing focus on preventative wellness. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with lower saturated fat and no cholesterol. The market has moved beyond early adopters, with products now widely available in mainstream supermarkets, not just health food stores. This expanded distribution has made plant-based milks a convenient and accessible option for the average consumer. The competitive environment is dynamic, with both large dairy corporations and specialized plant-based brands vying for market share through product innovation. The demand for specific plant bases, particularly oat and almond, has surged in recent years due to their sensory appeal and versatile applications in coffee and cooking.
- Brazil: Brazil represents a significant growth market in South America, with demand for plant-based milk driven by rising health awareness and a growing middle class. The country has a high rate of lactose intolerance, which serves as a fundamental demand driver. Additionally, a rising urbanization rate and exposure to global dietary trends, often through social media, are influencing consumer choices. The market is still developing compared to North America and Europe, but it shows strong potential. Soy milk is a traditional and well-established segment, but newer alternatives like oat and almond milk are gaining popularity, particularly in major urban centers like São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. The market is also seeing a push towards "clean label" products, where consumers prioritize transparency and minimal processing.
- Germany: Germany is a leading market for plant-based milk in Europe, characterized by a strong consumer base of vegetarians and vegans and a general societal emphasis on sustainability. A deep-seated environmental consciousness drives this growth. Consumers are highly aware of the environmental footprint of traditional dairy production and are actively seeking alternatives with a lower impact. This has created a robust demand for oat and soy milk, which are perceived as more sustainable options. The German market is also driven by consumer desire for high-quality, locally sourced products. While regulatory hurdles exist concerning labeling, German consumers have demonstrated a willingness to pay a premium for plant-based products that align with their ethical and environmental values.
- China: The plant-based milk market in China is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and a shift towards healthier lifestyles. While traditional soy milk has been a staple for centuries, demand for newer alternatives like oat and almond milk is surging, particularly among younger, urban consumers. This growth is not just about a lifestyle choice; it is also driven by a rising awareness of health issues such as obesity and diabetes. Consumers are actively seeking products with functional health benefits, such as high protein or fiber content. The market is fragmented, with both domestic and international brands competing. Another key growth factor is the foodservice sector, where plant-based milks are increasingly used in beverages, especially coffee and bubble tea, which introduces the product to a broad consumer base.
- Nigeria: The Nigerian market for plant-based milk is in its nascent stage but presents significant long-term potential. The market expansion is driven by a combination of factors, including high rates of lactose intolerance, a large and growing population, and increasing health consciousness among the urban middle class. The market is currently small but is expanding as both local and international brands begin to introduce products. The primary challenge is the premium pricing of these products compared to traditional dairy and the need for a robust cold chain infrastructure. Market growth is currently concentrated in major cities, where consumers have greater access to modern retail channels and a stronger interest in global food trends. The market is largely untapped and represents a greenfield opportunity for companies willing to invest in local production and distribution.
Plant-Based Milk Market Competitive Landscape
The plant-based milk market is highly competitive, featuring a mix of multinational food and beverage conglomerates and specialized plant-based companies. The competitive landscape is defined by product innovation, strategic partnerships, and a focus on building brand equity.
- Danone S.A.: Danone, a global leader in the food and beverage industry, holds a significant position in the plant-based market through its Alpro and Silk brands. The company's strategy is to leverage its extensive distribution network and marketing capabilities to make plant-based products accessible to a mass market. Danone's approach is to provide a wide range of products, including multiple bases like soy, almond, oat, and coconut. The company's official publications highlight its commitment to providing "health-centric" and "sustainable" product options. For example, the company’s investor and press materials often discuss its efforts to advance its plant-based portfolio to meet consumer demand for alternatives. Danone's scale allows it to invest heavily in research and development to improve the taste and nutritional profile of its products.
- Oatly Group AB: Oatly is a Swedish company that has emerged as a major player, particularly in the oat milk segment. Oatly's strategy is centered on strong brand identity and a focus on sustainability. The company's products are marketed as a lifestyle choice, appealing to consumers who prioritize environmental and ethical considerations. Oatly's official newsroom details its "Barista Edition" oat milk, which is specifically formulated for use in coffee and has been a major driver of demand in the B2B foodservice sector. The company's success is a direct result of its ability to create a product that not only functions as a dairy alternative but also performs exceptionally well in a key application, thereby creating a new demand segment.
Plant-Based Milk Market Developments
- April 2025: Müller UK & Ireland, a major dairy producer, acquired the kefir brand Biotiful. While Biotiful is primarily known for its fermented dairy products, the acquisition is part of Müller's strategic effort to expand its portfolio into the growing functional health food and drink market, which includes plant-based and dairy-alternative products. This move signals a trend of traditional dairy companies buying into the plant-based and health-focused sectors to diversify their offerings and adapt to changing consumer preferences.
- January 2024: Oatly Group AB announced the launch of two new oat milk varieties in North America, Oatly Unsweetened and Oatly Super Basic. This launch marked the company's first major innovation to its core beverage portfolio in five years and was designed to cater to a broader range of consumer lifestyles and dietary preferences.
Plant-Based Milk Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Plant-Based Milk Market Size in 2025 | USD 15.354 billion |
| Plant-Based Milk Market Size in 2030 | USD 21.808 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.27% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Plant-Based Milk Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Plant-Based Milk Market Segmentation:
- By Source
- Almond
- Soy
- Oat
- Coconut
- Rice
- Others (Cashew, Hemp, Pea, etc.)
- By Application
- Food and Beverage
- Personal Care
- Others
- By Packaging
- Aseptic Cartons
- PET/HDPE Bottles
- Others
- By Distribution Channel
- Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Online Channels
- Others
- By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Navigation:
- Plant-Based Milk Market:
- Plant-Based Milk Market Key Highlights:
- Plant-Based Milk Market Analysis
- Government Regulations
- Plant-Based Milk Market Segment Analysis:
- Plant-Based Milk Market Regional Analysis
- Plant-Based Milk Market Competitive Landscape
- Plant-Based Milk Market Developments
- Plant-Based Milk Market Scope:
- Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Page last updated on: September 18, 2025