Report Overview
Regenerative Medicine Market Size, Highlights
Regenerative Medicine Market Size:
The Regenerative Medicine Market is expected to grow from USD 25.458 billion in 2025 to USD 60.997 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 19.10%.
The regenerative medicine market is a highly specialized and evolving sector of the biomedical industry, centered on the development of therapies that repair, replace, or regenerate damaged or diseased cells, tissues, and organs. Unlike traditional pharmaceuticals that manage symptoms, regenerative medicine seeks to address the root cause of a condition by harnessing the body's innate healing mechanisms or by introducing new, therapeutic cells, genes, or biomaterials. The market's foundation is built on decades of foundational research in stem cell biology, tissue engineering, and gene therapy. This research has now translated into a pipeline of clinical-stage products and a growing number of commercialized therapies. The field holds immense promise for treating a wide array of conditions, from chronic degenerative diseases like osteoarthritis and heart failure to acute injuries and genetic disorders, where conventional treatments offer limited efficacy or are associated with significant morbidity.
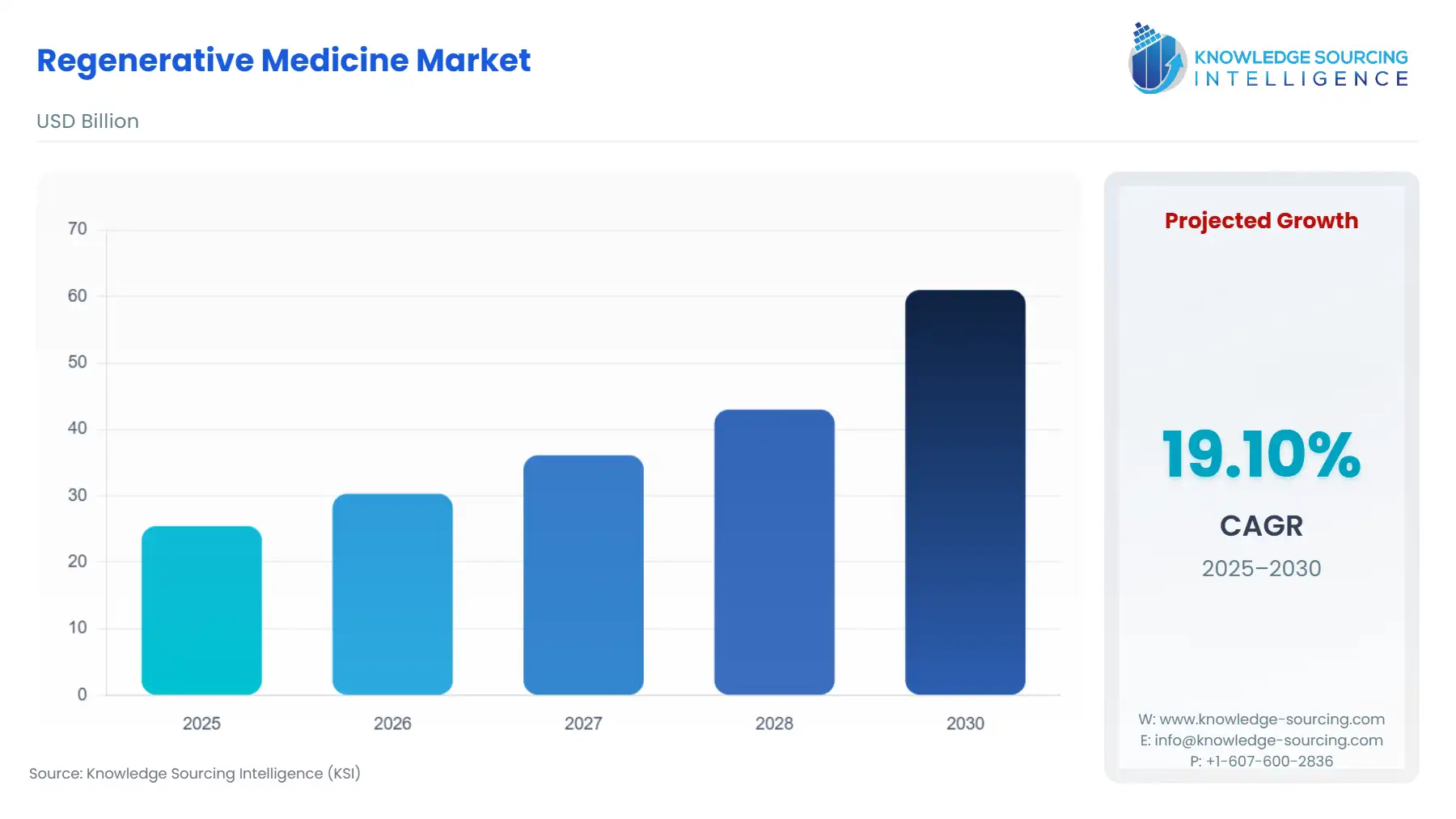
Regenerative Medicine Market Analysis:
Growth Drivers
- The market of regenerative medicine therapies is directly propelled by the increasing global incidence of chronic and degenerative diseases. As populations age, conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, orthopedic injuries, and neurodegenerative disorders become more prevalent. Conventional treatments, including surgical interventions and symptom-based pharmaceuticals, often fail to provide a curative solution and are associated with a significant financial and healthcare burden. The inherent limitations of these traditional approaches, coupled with the global shortage of donor organs for transplantation, create a powerful demand for alternative, curative therapies. Regenerative medicine, by offering the potential for long-term tissue repair and functional restoration, emerges as a compelling alternative that can address this unmet medical need. This paradigm shift from managing symptoms to repairing the body drives a direct and growing demand for products that can restore lost function.
- Another critical catalyst is the substantial public and private funding and investment flowing into the sector. Government agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), provide significant grants and funding to academic institutions and biotech companies. CIRM, for example, was established with a significant investment from California taxpayers, and it has since played a crucial role in funding stem cell research and translating it into clinical-stage therapies. This financial support directly fuels the research and development pipeline, moving therapies from the laboratory to clinical trials and, ultimately, to commercialization. This government-led de-risking of early-stage research directly encourages private investment, which is essential for the expensive and lengthy clinical development process. This ecosystem of public and private funding creates a fertile ground for innovation and ensures a continuous supply of new regenerative medicine products, thereby stimulating future demand.
Challenges and Opportunities
- The regenerative medicine market faces significant headwinds, primarily related to high treatment costs and complex manufacturing processes. Many advanced therapies, particularly autologous cell therapies where a patient's own cells are harvested, processed, and reinjected, are exceptionally expensive and difficult to scale. The "vein-to-vein" process involves complex logistics, specialized cleanroom facilities, and a high degree of personalization, making it a financial and logistical challenge for healthcare systems. This high cost directly constrains demand by limiting patient access and creating reimbursement hurdles with public and private insurers.
- This challenge, however, presents a pivotal opportunity for innovation. The industry is actively pursuing the development of allogeneic therapies—where cells are sourced from a healthy donor and can be used to treat multiple patients—and "off-the-shelf" products. These solutions offer a path to greater scalability, reduced manufacturing complexity, and lower per-treatment costs. The development of therapies like allogeneic CAR-T cells or pre-engineered tissue products could transform the market by making regenerative medicine accessible to a much broader patient population. The opportunity is also significant in the area of supply chain and manufacturing innovation. The shift towards decentralized, automated manufacturing platforms is a key area of focus, as it can reduce the logistical burden and costs associated with patient-specific therapies. Companies that can effectively address the cost and scalability challenges will be uniquely positioned to capture significant market share and accelerate the adoption of these transformative therapies.
Supply Chain Analysis
The regenerative medicine supply chain is a distinct and complex logistical network, differing significantly from that of traditional pharmaceuticals. It is not a linear process of chemical synthesis and packaging; rather, it is a living supply chain. The process begins with the sourcing of biological materials, which can range from a patient’s own cells (autologous) to cells from a healthy donor (allogeneic) or even animal tissue. These materials are then transported to a specialized manufacturing facility, where they are processed under strict Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) conditions. The logistical complexities are immense, particularly for autologous therapies, as the chain must be "vein-to-vein," meaning it tracks a patient’s cells from their body back to their body, with no room for error or contamination.
Key production hubs are typically located in regions with a strong biotech and academic research presence, such as the Boston-Cambridge area, parts of California, and key European cities like London and Basel. Logistical dependencies include specialized cryogenic shipping containers, real-time monitoring of temperature and chain of custody, and a robust network of clinics and hospitals capable of handling and administering these sensitive therapies. This high degree of complexity and the cold-chain requirements make the supply chain a significant barrier to entry and a critical competitive differentiator. Any disruption to the supply of key reagents or to the specialized logistics network can severely impact a company's ability to deliver its therapies.
Government Regulations
The regulatory environment is a primary determinant of market growth for regenerative medicine products. Agencies like the FDA and the EMA serve as both gatekeepers and facilitators, and their policies directly influence the pace of product development and commercialization. The establishment of clear and predictable regulatory pathways has been a significant catalyst for the market's growth.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation | The FDA regulates regenerative medicine products as drugs, biologics, or medical devices. The RMAT designation, established under the 21st Century Cures Act, is a critical demand driver. It provides an expedited pathway for promising regenerative therapies, offering benefits like early and frequent communication with the FDA and eligibility for priority review and accelerated approval. This designation significantly reduces the time and cost of clinical development, thereby increasing the willingness of companies to invest in these therapies and accelerating their availability to the market. This framework has directly catalyzed the demand for R&D and subsequent commercialization. |
| European Union | European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) Regulation | The ATMP regulation, which defines and provides a specific regulatory framework for cell and gene therapy, and tissue-engineered products, has been crucial for legitimizing and standardizing the market. The EMA's Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT) provides scientific and regulatory expertise, which helps to streamline the approval process. While the fragmented nature of healthcare and reimbursement across EU member states can be a challenge, the clear regulatory pathway established by the EMA creates a predictable environment for companies, encouraging them to pursue commercialization in the European market and, therefore, increasing demand for approved therapies. |
| Japan | Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and the Act on the Safety of Regenerative Medicine | Japan has positioned itself as a global leader in regenerative medicine by implementing a unique, fast-track approval process. The Act allows for conditional, time-limited approval of regenerative medicine products based on early clinical trial data, as long as the therapy shows a high likelihood of efficacy and safety. This policy significantly reduces the time to market and provides a powerful incentive for companies to commercialize their products in Japan first. This regulatory environment has directly and rapidly increased demand for clinical research and commercialization within the country, creating a highly competitive and innovative market. |
Regenerative Medicine Market Segment Analysis:
By Technology: Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy represents a foundational pillar of the regenerative medicine market, driven by its versatility and potential to treat a wide range of diseases. Stem cells, with their ability to differentiate into specialized cell types and self-renew, are a potent therapeutic tool. The necessity for these therapies is directly linked to their ability to treat conditions where conventional medicine has failed, particularly in oncology and hematology. For example, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been a standard of care for decades for certain cancers and blood disorders. The development and FDA approval of products like Omisirge (omidubicel-onlv) for patients with hematologic malignancies demonstrates the continued maturation of this segment. The market for these therapies is further propelled by ongoing research into new applications, such as using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for orthopedic conditions or cardiac regeneration. The market is witnessing a shift from allogeneic umbilical cord blood therapies toward more sophisticated, engineered products that offer enhanced engraftment and reduced immunogenicity. The necessity is therefore not just for stem cells, but for stem cell products that offer superior therapeutic outcomes and a clear clinical benefit, validated through rigorous clinical trials.
By End-User: Hospitals and Clinics
Hospitals and clinics are the primary end-users of regenerative medicine products, acting as the nexus for patient treatment, clinical trials, and commercial adoption. This segment’s growth is a direct function of several factors, including regulatory approvals, reimbursement policies, and the complexity of administering these therapies. As more regenerative medicine products receive regulatory clearance from agencies like the FDA and EMA, hospitals and clinics are compelled to integrate these therapies into their treatment protocols to offer patients cutting-edge care. The market is also shaped by the need for specialized infrastructure and trained personnel. Hospitals that invest in dedicated cell therapy units and have the logistical capabilities to handle complex cold-chain logistics are in a strong position to become leaders in this field. Reimbursement is a critical demand driver; as public and private payers establish clear pathways for covering the high costs of these treatments, hospitals can more readily adopt and offer them. This segment's expansion is therefore closely tied to the market's overall maturation, as validated products, clear regulatory guidance, and favorable reimbursement policies become more common.
Regenerative Medicine Market Geographical Analysis:
US Market Analysis
The US market is the largest and most dynamic for regenerative medicine, driven by a robust R&D ecosystem, significant public and private investment, and a clear regulatory framework from the FDA. The market is fueled by a high incidence of chronic diseases and a healthcare system that generally rewards innovation. The FDA's RMAT designation has been a critical catalyst, accelerating the development and commercialization of new therapies. The market is concentrated in major academic medical centers and specialized clinics that are equipped to handle complex cell and gene therapy procedures. The US market's competitive landscape is defined by its ability to attract and retain capital for clinical trials and its well-established network of specialized research and manufacturing facilities. The primary local factors impacting demand include the evolving landscape of private insurance reimbursement and the presence of regional initiatives like CIRM in California.
Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil's regenerative medicine market is emerging, driven by a large population and a growing need for advanced healthcare solutions. The market is primarily focused on applications in orthopedics, wound healing, and certain stem cell-based therapies. It is currently concentrated in private hospitals and clinics that serve a patient population with the ability to pay for non-reimbursed treatments. Local demand is a function of academic research, which is strong in certain areas, and the regulatory environment, which is developing its own frameworks. A key challenge and opportunity is the fragmented nature of the healthcare system and the need for clear regulatory guidance to formalize the market and attract further investment from global players. As the public and private healthcare systems evolve, the demand for approved and scalable regenerative therapies is expected to grow.
Germany Market Analysis
Germany is a major European hub for regenerative medicine, with a sophisticated research infrastructure and a strong industrial base. The need for these therapies is driven by a well-established healthcare system and a strong academic and biotech sector. The EMA's ATMP regulation provides a clear pathway for approval, and Germany's robust public health insurance system is a key determinant of market access. The German market is a leader in tissue engineering and gene therapy applications, with a focus on high-quality, scientifically validated treatments. Local demand factors include a high level of patient awareness and a collaborative ecosystem between academic institutions, biotech companies, and hospitals. Germany's market is characterized by a strong emphasis on clinical evidence and a willingness to invest in innovative, high-value therapies.
Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The regenerative medicine market in Saudi Arabia is in its infancy but is poised for significant growth, driven by the government's Vision 2030 initiative to diversify the economy and build a world-class healthcare sector. The necessity for regenerative therapies is currently focused on private health facilities catering to a high-net-worth population and on government-funded research projects. The market is primarily driven by the need to address chronic diseases and a desire to adopt the latest medical technologies to position the country as a regional healthcare leader. The regulatory environment is evolving, with an increasing emphasis on adopting international standards. The local demand for regenerative therapies is expected to grow as the government invests in research infrastructure and as regulatory clarity improves, attracting more international companies and clinical trials to the region.
Japan Market Analysis
Japan's regenerative medicine market is a global leader, distinguished by its unique and highly supportive regulatory framework. The country's need for these therapies is unparalleled due to the government’s proactive policy of fast-track approvals under the Act on the Safety of Regenerative Medicine. This has created a direct and powerful demand for clinical-stage and commercially approved products. Japanese companies and academic institutions are at the forefront of research, particularly in iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell) technologies. The market is characterized by a strong demand for therapies that address an aging population, including musculoskeletal and cardiovascular conditions. Local factors such as the government’s strategic commitment to regenerative medicine, a strong patient advocacy community, and a well-funded research ecosystem make Japan an attractive market for both domestic and international players.
Regenerative Medicine Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The regenerative medicine market is characterized by intense competition and a diverse set of players, from specialized biotech startups to large, established pharmaceutical companies. Competition is based on a company's ability to navigate the complex regulatory environment, secure intellectual property, and develop a scalable and commercially viable manufacturing process.
- Regenexx: Regenexx operates in the regenerative medicine space, specifically focusing on interventional orthopedics. The company's strategic positioning is to provide non-surgical, cell-based procedures for musculoskeletal conditions. It leverages a network of licensed physicians who use proprietary, research-based methods and patented protocols for preparing and applying autologous cell injectates. Regenexx's competitive strength lies in its extensive patient outcome registry and its focus on publishing its research in peer-reviewed journals, which provides a data-driven approach in a market with many unproven treatments. This strategy directly drives demand by building trust and demonstrating clinical efficacy within its specific niche.
- Orgenesis Inc.: Orgenesis is a global biotech company that is strategically positioned to address the challenges of manufacturing and accessibility of cell and gene therapies. The company is developing a decentralized, automated platform to produce cell and gene therapies at the point of care, which aims to reduce logistical complexities and costs. This focus on decentralized manufacturing is a key competitive differentiator, as it directly addresses a major market constraint. Orgenesis’s recent acquisition of assets from Neurocords LLC, which is focused on spinal cord injury therapies, strengthens its portfolio and expands its pipeline in a high-need area, showcasing its strategy of building a robust portfolio through targeted acquisitions and a focus on scalable manufacturing.
- Vericel Corporation: Vericel is a leader in advanced therapies for sports medicine and severe burn care. The company’s strategic positioning is built on two FDA-approved products: MACI for orthopedic applications and Epicel for burn care. MACI (autologous cultured chondrocytes on a porcine collagen membrane) is used to repair symptomatic, full-thickness cartilage defects of the knee. Epicel (cultured epidermal autografts) is used to treat patients with deep dermal or full-thickness burns. Vericel's competitive strength lies in its validated commercial products and its focus on a clear market need. The demand for Vericel’s products is directly driven by physician and patient adoption following regulatory approval and the establishment of reimbursement pathways. Its commercial success demonstrates the viability of regenerative medicine products in addressing specific, high-need applications.
Regenerative Medicine Market Recent Developments:
November 2025: University of Chicago School of Medicine, in collaboration with Terumo BCT, achieved the first-ever automated end-to-end manufacturing of T cell receptor (TCR) T cell therapy by completing activation, transduction, and expansion in a single Quantum Flex™ bioreactor, advancing scalable production for autologous therapies targeting solid tumors and other challenging diseases.
November 2025: Regenerative Medical Technologies Group (RMTG) subsidiary CELLGENIC launched the Peptide Pen product line at the ISSCA Global Summit in Cancún, featuring pre-loaded devices with peptide formulations for recovery, immune support, metabolic optimization, and wellness, exclusively distributed to licensed physicians across 30+ countries to enhance regenerative and longevity therapies.
October 2025: Lab-grown embryo-like structures produce blood stem cells: Scientists at the University of Cambridge generated self-organizing embryo-like structures from human stem cells that mimic early developmental stages and produce blood stem cells capable of differentiating into multiple blood lineages, a breakthrough with potential applications in regenerative therapies.
June 2025: CRISPR editing in blood stem cells shows senescence risk: Researchers at SR-Tiget (Milan) found that CRISPR/Cas9 editing of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can trigger inflammatory and senescence-like responses, potentially undermining long-term regenerative capacity. They demonstrated that transient p53 inhibition and anti-inflammatory treatment (Anakinra) can mitigate these effects.
April 2025: FDA approves Zevaskyn (prademagene zamikeracel): The U.S. FDA granted approval for Zevaskyn, a cell-based gene therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), making it the first such therapy for this severe genetic skin disorder.
List of Top Regenerative Medicine Companies:
- Amgen Inc.
- Biogen Inc.
- CRISPR Therapeutics AG
- Editas Medicine, Inc.
- Fate Therapeutics, Inc.
Regenerative Medicine Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 25.458 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 60.997 billion |
| Growth Rate | 19.10% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Technology, Application, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Regenerative Medicine Market Segmentation:
- By Technology
- Stem cell Therapy
- Gene Therapy
- Tissue Engineering
- Others
- By Application
- Cardiovascular
- Oncology
- Dermatology
- Orthopedics and Musculoskeletal
- Wound Healing
- Ophthalmology
- Others
- By End-User
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Government
- Academic Research Institutes
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Spain
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Others
- North America