Report Overview
South Korea Electric Vehicle Highlights
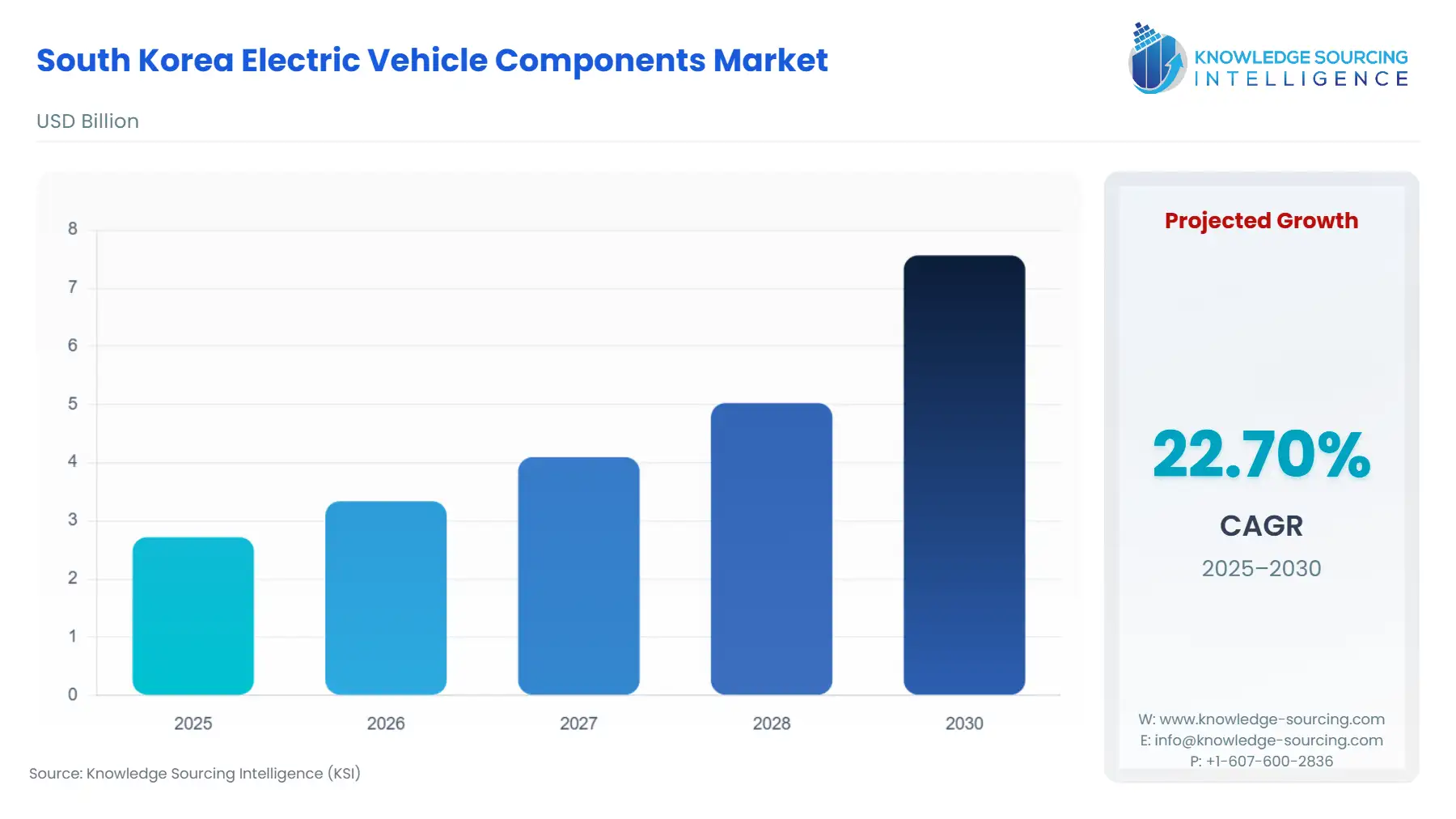
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Size:
The South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 22.70%, achieving USD 7.566 billion in 2030 from USD 2.72 billion in 2025.
The South Korean Electric Vehicle Components market functions as a critical global nexus, uniquely positioned by its concentration of world-class battery producers and a government-led push for e-mobility adoption. This robust domestic ecosystem is fundamentally tied to the national industrial strategy, which aims to transition the traditional automotive parts sector into a future-vehicle manufacturing powerhouse. The market's current trajectory is not merely a reflection of global EV trends but is a direct consequence of concerted domestic policy actions, establishing a powerful demand-pull environment for high-value components, including advanced battery cells, power electronics, and thermal management systems. The strategic focus remains on scaling production capacity while navigating complex global raw material dependencies, which constitute the principal headwind to sustained, rapid growth.
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Government incentives and regulatory targets serve as the primary catalyst propelling demand for EV components. The "2030 National Determined Contribution (NDC) Upgrade Plan" targets 4.5 million Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) on the road by 2030. This mandate directly increases the required output of essential components—battery packs, electric motors, and inverters—to meet domestic production quotas. Furthermore, the expansion of the domestic charging network, supported by significant government fiscal outlays, reduces consumer range anxiety, thereby increasing BEV adoption and, in turn, escalating the demand for components like on-board chargers and high-efficiency power electronics.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The key challenge for the domestic component market is the acute supply chain concentration for critical raw materials. South Korean producers rely heavily on imports for a high percentage of key minerals, creating a structural vulnerability to price volatility and geopolitical instability. This constraint limits the ability of component manufacturers to rapidly scale production and mitigate rising input costs, potentially depressing final EV component demand by increasing the cost of the end-product. The primary opportunity lies in the aggressive vertical integration and geographic diversification strategies being pursued by domestic battery giants, including securing stakes in overseas mining and refining operations and establishing dedicated component production hubs in Free Trade Agreement (FTA) partner countries. This strategic repositioning enhances supply chain resilience and creates direct, secure demand channels for domestically-produced high-value components destined for global assembly lines.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The EV component market, being dominated by physical products, is intrinsically linked to the supply and pricing dynamics of key battery materials. South Korea has a near-total net import reliance for all critical minerals, relying on foreign sources for the majority of its precursor cathode materials, synthetic graphite, and lithium hydroxide. This dependence subjects the domestic component supply chain to volatile global commodity prices. The pricing mechanism for battery components is thus highly sensitive to these upstream material costs. To counter this, manufacturers are pushing the technological envelope by increasing the nickel content in Lithium-Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) cathodes for higher energy density and simultaneously exploring the development of cost-effective LFP battery chemistries, which utilize less expensive materials, to stabilize component pricing and unlock demand in lower-cost vehicle segments.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The South Korean component supply chain is highly complex, centered on three dominant domestic battery cell manufacturers—LG Energy Solution, SK On, and Samsung SDI—which anchor the entire ecosystem. These companies are key nodes in the global supply chain, serving not only domestic Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) like Hyundai Motor Group but also major foreign automakers in Europe and North America. Logistical complexity arises from the necessity to import the majority of refined critical minerals, which are then processed into active cathode and anode materials domestically before final assembly into battery cells. The global production strategy involves substantial capacity expansion in overseas markets, particularly the United States, driven by geopolitical trade acts. This necessitates a dual supply chain: one for domestic and Asian markets, and an increasingly localized, FTA-compliant supply chain for the North American market.
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
South Korea |
Ministry of Environment (MOE) Purchase Subsidies |
Directly stimulates consumer demand for BEVs and FCEVs by reducing the initial purchase cost, creating an imperative for OEMs to increase vehicle production, thereby escalating the need for all components. |
|
South Korea |
Clean Air Conservation Act (Article 58 on Low-Emission Motor Vehicles) |
Establishes the legal framework for annual supply targets for zero-emissions vehicles, mandating the shift from Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicle production toward electric, which guarantees a long-term, structural demand floor for EV components. |
|
South Korea |
Future Vehicle Industry Development Strategy |
Supports the transformation of conventional vehicle parts companies into future vehicle component suppliers, driving R&D investment and increasing the domestic supply of sophisticated components like power electronics and thermal management systems. |
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component Type: Battery Pack
The Battery Pack segment is the nucleus of the South Korea EV component market, as it accounts for the single largest portion of an EV's cost and directly determines vehicle performance metrics such as range and charging speed. The sustained domestic and global ramp-up of BEV production by Hyundai Motor Group and foreign OEMs, who rely on the "K-trio" for supply, drives this segment’s growth. A critical factor impacting requirement is the technological push for higher energy density to extend driving range, which necessitates consistent demand for high-nickel cathode materials. Concurrently, the strategic pivot toward prismatic battery form factors by domestic manufacturers is creating a new demand channel within the component ecosystem, driven by the form factor's advantages in cost-effectiveness and cell-to-pack integration favoured by key European automakers. The need for greater thermal stability in high-energy-density packs also drives a collateral requirement for advanced thermal management components within the battery system itself.
- By End-User: OEMs
The Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) segment is the foundational consumer of components, driven intrinsically by their domestic and export production volumes. The shift by major South Korean OEMs, such as Hyundai Motor Group and Kia Corporation, toward dedicated electric vehicle platforms—like the Electric-Global Modular Platform (E-GMP)—directly alters and solidifies component demand. This move generates a massive, consolidated demand for standardized, high-performance components, including integrated drive units (IDUs) encompassing the electric motor, gearbox, and inverter. Moreover, the OEMs' global expansion strategies, particularly their need to meet regional content requirements under trade agreements like the US Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), translates into specific, non-negotiable demand for locally sourced or FTA-compliant components, compelling domestic component suppliers to localize or diversify their global manufacturing footprint to retain OEM contracts.
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Competitive Analysis:
The South Korean EV components market is characterized by a high degree of concentration and vertical integration, with competition focused on battery cell technology leadership and global manufacturing capacity. The competitive environment is defined by three world-leading, domestically-based battery manufacturers, with rivalry centered on cost efficiency, energy density, and supply chain security.
- LG Energy Solution Ltd.
LG Energy Solution maintains a robust strategic position by offering the broadest product portfolio, including pouch, cylindrical, and the newly emphasized prismatic battery form factors. The company’s strategy involves aggressive capacity expansion, particularly through joint ventures in North America, to ensure compliance with trade act requirements, securing future long-term contracts with major global OEMs like General Motors and Tesla. Their continued investment in high-nickel cathode technology and recent engagement with LFP development positions them to address both premium and mass-market segments.
- SK On Co. Ltd.
SK On’s strategy is deeply integrated with its primary customer, Hyundai Motor Group, supplying batteries for key EV models. The company differentiates itself with high-performance pouch-type batteries and a strong focus on high-speed charging capability. Their strategic positioning involves substantial investment in US manufacturing facilities, aligning production capacity with the accelerated EV roadmaps of key domestic and foreign automakers to secure a future market share based on compliant, localized supply.
- Samsung SDI Co. Ltd.
Samsung SDI focuses on premium and high-performance segments, with a strong emphasis on prismatic and cylindrical cells. The company's key strategic positioning lies in a technology-first approach, prioritizing R&D spending to develop next-generation battery technologies, including solid-state concepts. Its supply is concentrated on key European automakers and premium US brands, where performance and safety are prioritized over cost-volume in the initial stages.
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Developments:
- September 2025: Samsung SDI showcased its new SBB 1.7 (high-nickel NCA) and the SBB 2.0, which features its first-ever adoption of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) cells in the prismatic form factor for Energy Storage Systems (ESS). The LFP cell is a significant component strategy change, aimed at overcoming the traditional low energy density of LFP cells while maximizing cost and safety advantages. The technology is dual-use for both ESS and potential EV applications in the cost-effective segment, and the prismatic battery form factor is a core component technology. This highlights the push by major South Korean battery firms to diversify battery chemistry beyond high-nickel chemistries to capture the mass-market segment.
- August 2025: Hyundai Motor Group and Kia Motors officially formed a "Battery Safety Task Force" with South Korea's three major battery makers (LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI, and SK On) to collectively improve EV battery safety standards. This collaboration, which began work a year prior, involves sharing patent rights and jointly developing new safety technologies focusing on five areas, including fire prevention technologies and design quality. While not a single product launch, it represents a massive, multi-company strategic alignment on a critical component (the battery pack and cells) that will drive the design and technology of future South Korean-made EV components.
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 2.72 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 7.566 billion |
| Growth Rate | 22.70% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Vehicle Type, Technology, End User |
| Companies |
|
South Korea Electric Vehicle Components Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT TYPE
- Battery Pack
- Electric Motor
- Power Electronics
- Inverter
- Converter (DC-DC)
- On-Board Charger
- Thermal Management System
- Body & Chassis
- Other Components
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY END-USER
- OEMS
- Aftermarket