Report Overview
Synthetic Rubber Market - Highlights
Synthetic Rubber Market:
The Synthetic Rubber Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.37%, reaching USD 42.802 billion in 2030 from USD 34.562 billion in 2025.
The synthetic rubber market operates as a foundational component within the global manufacturing sector. Its dynamics are inextricably linked to macro-economic trends and specific industrial requirements. The market's size and trajectory are primarily dictated by the performance of its key end-user industries, including automotive, construction, and industrial manufacturing. Unlike natural rubber, synthetic rubber's molecular structure can be engineered to possess specific properties, such as enhanced abrasion resistance, thermal stability, or chemical inertness. This versatility makes it an indispensable material for a wide array of high-performance applications. The market's evolution is currently characterized by a critical balance between maintaining cost competitiveness in a volatile raw material environment and investing in innovative, sustainable solutions to meet evolving regulatory and consumer demands.
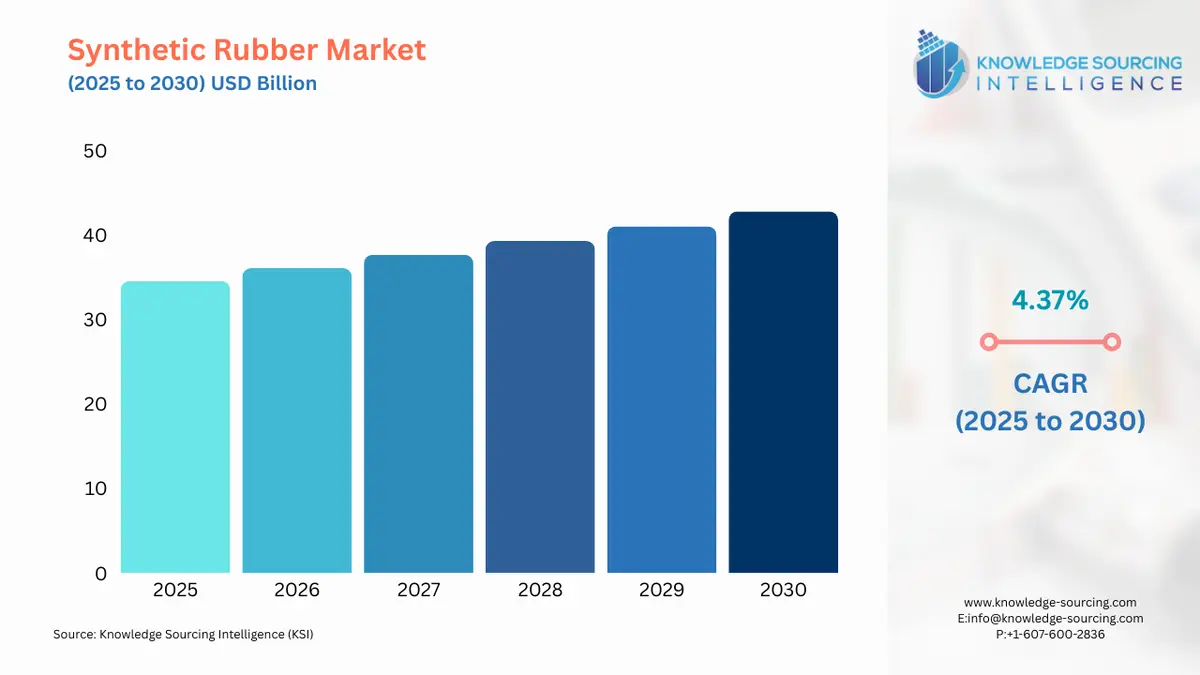
Synthetic Rubber Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers:
The automotive industry's continued expansion is a principal catalyst for the synthetic rubber market. This growth is not just from the overall volume of new vehicle production but from specific technological shifts within the sector. The rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) creates a distinct demand for specialized synthetic rubber. EVs, which are heavier than internal combustion engine vehicles due to their battery packs, require tires with lower rolling resistance and higher durability. These performance characteristics are achieved through the precise formulation of synthetic rubbers like Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Polybutadiene Rubber (BR), which directly enhances demand for these specific types. Additionally, non-tire automotive applications, such as seals, gaskets, and hoses, also rely heavily on synthetic rubber for its superior resistance to heat, oils, and other automotive fluids. The expansion of these applications, driven by increasingly complex engine and chassis designs, directly drives demand for high-performance elastomers.
Industrialization and urbanization, particularly in emerging economies, constitute another critical demand driver. As countries build new infrastructure and expand their manufacturing capabilities, the demand for construction materials, industrial goods, and consumer products grows. Synthetic rubber is a key component in a wide range of industrial applications, including conveyor belts, hoses, and industrial mats, due to its durability and resistance to harsh operating conditions. The footwear industry also represents a significant and consistent consumer, using synthetic rubber for shoe soles and other components that require durability and slip resistance. The rising living standards and increased consumer spending in countries across the Asia-Pacific region, for example, directly correlate with an increased demand for products like footwear and consumer goods, which in turn fuels the market for synthetic rubber.
- Challenges and Opportunities:
The primary challenge facing the synthetic rubber market is the price volatility of its primary raw materials. Synthetic rubber is a petroleum-derived product, with monomers like butadiene and styrene originating from crude oil refining and natural gas processing. Fluctuations in global crude oil prices, driven by geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, or shifts in demand, directly impact the cost of production. This instability makes it difficult for manufacturers to forecast and manage costs, which can compress profit margins and lead to price fluctuations for end-users. This reliance on a non-renewable resource also presents a long-term sustainability challenge.
This challenge, however, creates a significant opportunity. The imperative for sustainability has compelled manufacturers to explore and invest in bio-based and recycled alternatives. Companies are developing synthetic rubber from renewable feedstocks, such as bio-based butadiene, which reduces their dependence on petrochemicals. Furthermore, advancements in recycling technologies, particularly for end-of-life tires, offer a circular economy solution by converting discarded rubber into valuable raw materials. The development and commercialization of these sustainable materials present an opportunity for companies to gain a competitive advantage by appealing to environmentally-conscious consumers and meeting increasingly stringent regulatory requirements.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis:
The synthetic rubber market's pricing is fundamentally tied to the costs of its primary chemical building blocks. The most common types, such as SBR and BR, are produced from butadiene, a C4 fraction from naphtha cracking. The price of butadiene, and by extension, the final price of the synthetic rubber product, is therefore highly sensitive to the dynamics of the crude oil market. When crude oil prices rise, the cost of naphtha and its derivatives increases, directly elevating the cost of butadiene and synthetic rubber. Conversely, a decline in crude oil prices can lower production costs but also introduce price uncertainty for manufacturers and buyers.
This relationship creates a complex pricing environment where manufacturers must carefully manage their inventories and hedging strategies to mitigate risk. The supply chain for these raw materials is also susceptible to logistical bottlenecks and production halts. A production issue at a single naphtha cracker or butadiene extraction facility can have a ripple effect throughout the entire synthetic rubber supply chain, leading to price spikes and supply constraints. As a result, companies in the synthetic rubber sector often seek to secure long-term contracts with their feedstock suppliers to ensure a more stable and predictable supply of raw materials.
- Supply Chain Analysis:
The global synthetic rubber supply chain is a complex, multi-tiered network. At its core are the major petrochemical producers that manufacture the base monomers. These are then supplied to synthetic rubber manufacturers, who polymerize the monomers into various grades of solid or liquid rubber. These products are subsequently sold to downstream industries, with the automotive and tire industries representing the largest end-users. The supply chain is highly concentrated in specific geographical hubs. The Asia-Pacific region, especially China, is a dominant production center due to its extensive petrochemical infrastructure and large-scale manufacturing capabilities. Other key production hubs include Western Europe and North America, which cater to their respective domestic automotive and industrial markets. Logistical complexities, particularly involving the transportation of bulk chemicals and finished rubber products across continents, are a persistent factor. Dependencies on single-source suppliers or specific trade routes create vulnerabilities that can be exposed by economic shifts, trade disputes, or geopolitical events. For instance, disruptions in shipping lanes or a new set of tariffs can directly impact the cost and availability of materials, affecting the final price of a product.
Synthetic Rubber Market Government Regulations
Government regulations play a decisive role in shaping the synthetic rubber market by influencing production processes, material composition, and end-of-life product management. Environmental protection agencies worldwide are increasingly imposing stricter standards on industrial emissions and waste disposal, which compels manufacturers to invest in cleaner technologies and more sustainable production methods. Regulations aimed at improving vehicle fuel efficiency and tire safety, for instance, drive the development of high-performance "green tires" that require specific types of synthetic rubber. These regulations do not merely increase production costs; they fundamentally alter demand by making certain product attributes a regulatory imperative.
- United States: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Green Chemistry Program - This program provides funding and recognition for the development of sustainable synthetic rubber technologies. The initiative directly incentivizes the production of bio-based and eco-friendly elastomers, stimulating R&D and creating a new demand segment for "green" synthetic rubber products.
- European Union: Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) - REACH legislation requires synthetic rubber manufacturers to register and provide data on the safety of chemicals used in their products. This regulation drives demand for materials with a lower environmental and health impact and can create significant barriers to entry for non-compliant products, compelling market players to reformulate and re-evaluate their supply chains.
- India: The Rubber Board (under the Rubber Act of 1947) - The Rubber Board regulates the production and marketing of synthetic rubber, requiring manufacturers to obtain a license. This regulatory framework creates a structured market, ensuring compliance with established standards and providing a degree of market stability, which in turn influences investment decisions and production capacity.
Synthetic Rubber Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Tire and Non-Tire Automotive
The tire industry stands as the largest consumer of synthetic rubber, representing a foundational pillar of demand. The primary driver is the sheer scale of global vehicle production and the subsequent replacement tire market. Within the tire segment, demand is highly specific to the type of rubber. Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) and polybutadiene rubber (BR) are the dominant types used. SBR is prized for its excellent abrasion resistance and strong grip, making it essential for the treads of passenger car tires. BR, on the other hand, is a critical component for its high resilience and low heat buildup, which improves tire durability and reduces rolling resistance. The ongoing push for fuel efficiency, driven by government mandates and consumer preferences, creates a specific demand for "green tires." These tires are designed with compounds that minimize rolling resistance, a property that is engineered through the precise blending of SBR and BR. The increasing penetration of electric vehicles (EVs) is a new and powerful demand catalyst. EVs, being heavier and producing instant torque, require tires that can handle greater loads and resist accelerated wear. This necessitates the use of more robust and specialized synthetic rubber compounds, directly increasing the demand for high-performance grades.
The non-tire automotive segment also provides a robust and diverse source of demand. This application area includes a multitude of components like seals, gaskets, hoses, belts, and mounts. Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) is a key material in this segment due to its exceptional resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. The increased complexity of modern engine systems, which operate at higher temperatures and pressures, directly elevates the demand for NBR and other oil-resistant elastomers. The sealing components in an automobile, from engine gaskets to O-rings in fuel systems, are critical for vehicle performance and safety. As a result, automakers mandate strict quality and performance standards for these rubber parts, which reinforces demand for high-grade synthetic rubber. The growth of this segment is not just tied to vehicle production numbers but also to the evolution of vehicle design and the increasing use of electronics and advanced fluid systems, all of which require reliable, durable rubber components.
- By End-User: Industrial Equipment
The industrial equipment end-user segment is a significant and stable market for synthetic rubber. This sector’s growth is driven by the need for durable, reliable, and application-specific components in a wide range of machinery and manufacturing processes. Synthetic rubber is used in the production of conveyor belts, hoses, rollers, gaskets, and seals for industrial machinery. The properties of synthetic rubber, such as its resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, are essential for these applications to withstand harsh operating environments and ensure equipment longevity. For instance, conveyor belts used in mining or manufacturing facilities must endure constant friction and heavy loads, a performance requirement met by specific formulations of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Polybutadiene Rubber (BR). The demand for these components is directly linked to the health of the global manufacturing sector, which is influenced by industrial output, infrastructure development projects, and capital expenditure on new machinery. The rising adoption of automation in manufacturing processes further drives demand for high-precision synthetic rubber parts that can operate reliably in complex robotic and automated systems.
Synthetic Rubber Market Regional Analysis
- United States: The United States represents a mature but technologically advanced market for synthetic rubber, with demand primarily driven by the automotive, construction, and consumer goods sectors. The country's automotive industry, including both traditional and electric vehicle manufacturing, is a major consumer, particularly for high-performance elastomers used in tires and under-the-hood components. The US market is characterized by a strong emphasis on product quality, safety, and environmental standards, with regulations from agencies like the EPA directly influencing product development. The ongoing transition to EVs creates a new demand stream for specialized tire compounds. The construction sector also provides a steady source of demand for synthetic rubber used in sealants, adhesives, and roofing materials. The US market is also a significant hub for specialty synthetic rubbers used in medical devices and industrial equipment, reflecting the country's advanced manufacturing capabilities and stringent regulatory environment.
- Brazil: The synthetic rubber market in Brazil is closely tied to the country's economic cycles and its automotive and footwear industries. As the largest economy in South America, Brazil's industrial output and infrastructure projects are key demand catalysts. The automotive sector, which includes both vehicle manufacturing and a large replacement tire market, is the principal end-user for synthetic rubber. However, the Brazilian market can be susceptible to economic fluctuations and political instability, which can directly impact consumer spending on durable goods and investment in new industrial projects. The footwear industry is another major consumer of synthetic rubber, leveraging its durability and versatility for a wide range of products. Brazil's unique position as a significant producer of natural rubber also creates a competitive dynamic, where the price relationship between natural and synthetic rubber directly influences demand.
- Germany: Germany serves as a key market for synthetic rubber in Europe, driven by its robust and technologically advanced automotive and machinery sectors. The German automotive industry is a global leader, with a strong focus on high-performance vehicles and precision engineering. This concentration on high-value products creates a significant demand for specialized synthetic rubber grades that offer superior performance characteristics, such as enhanced durability and resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures. The country's strong commitment to sustainability, as evidenced by its national and EU-level regulations, also pushes the market toward the adoption of bio-based and recycled synthetic rubbers. The machinery and industrial equipment sectors in Germany also provide a stable source of demand, requiring high-quality elastomers for seals, gaskets, and other critical components in manufacturing and engineering applications.
- South Africa: South Africa's synthetic rubber market is a representative of the broader Middle East & Africa (MEA) region, with demand primarily influenced by its automotive, mining, and construction industries. The automotive sector, which includes a mix of local manufacturing and a significant import market, is a key consumer of synthetic rubber, particularly for tire production and replacement. The mining industry, which is a cornerstone of the South African economy, generates demand for heavy-duty synthetic rubber components like conveyor belts and hoses that can withstand abrasive and corrosive environments. The construction sector also contributes to demand through its use of sealants and adhesives. However, the market is subject to economic and political challenges that can affect investment and industrial output. The demand for synthetic rubber in South Africa is therefore tied to the performance of these core industries and the country's ability to maintain a stable economic environment for industrial growth.
- China: China is the single largest producer and consumer in the global synthetic rubber market. The country's market growth is driven by its massive and rapidly growing manufacturing base, particularly in the automotive, footwear, and construction sectors. The sheer volume of vehicle production and the extensive road network create an immense demand for synthetic rubber for both original equipment and replacement tires. China's status as a global manufacturing hub also means there is a high demand for synthetic rubber in the production of industrial goods and consumer products for both domestic consumption and export. The government's industrial policies and infrastructure initiatives, such as the Belt and Road Initiative, provide a powerful, demand-side catalyst. However, the Chinese market is also characterized by intense competition and a significant focus on cost, which puts pressure on manufacturers to optimize their production processes. The government's push for "green" manufacturing and stricter environmental regulations is also reshaping the market, driving a shift toward more sustainable production methods and products.
Synthetic Rubber Market Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the synthetic rubber market is highly concentrated, with a few multinational corporations holding a significant share. These companies compete on several fronts, including product innovation, production capacity, global reach, and strategic partnerships. Success in this market requires not only the ability to produce large volumes of standard grades but also the technical expertise to develop and commercialize specialized elastomers for high-performance applications. Companies are constantly engaged in R&D to improve product attributes like durability, chemical resistance, and sustainability, which allows them to capture new demand in evolving end-user industries.
- LANXESS AG: LANXESS is a specialty chemicals company with a strong position in the synthetic rubber market. The company's strategy focuses on delivering high-performance materials for demanding applications. Its portfolio includes a wide range of synthetic rubbers, such as Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) and Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR), which are used in automotive seals, hoses, and gaskets where resistance to oils and heat is paramount. LANXESS's approach is to provide application-specific solutions, positioning itself as a technical partner rather than a commodity supplier. The company's strategic acquisitions and ongoing investments in R&D are aimed at expanding its product offerings and reinforcing its market leadership in specialty elastomers.
- Zeon Corporation: Zeon Corporation is a leading manufacturer of specialty synthetic rubbers and high-performance elastomers. The company's competitive advantage lies in its focus on niche applications that require superior performance. Zeon is a major global producer of Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), which is used in automotive, industrial, and medical applications. The company’s portfolio also includes Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR), which provides enhanced resistance to heat and chemicals, making it suitable for seals and gaskets in more extreme environments. Zeon's strategy is centered on technological innovation and a commitment to developing specialized materials that meet the stringent requirements of high-value end-user industries, allowing it to command a premium in the market.
- Sinopec Corporation: Sinopec is a dominant player in the global petrochemical and synthetic rubber markets, leveraging its scale and integrated supply chain. As one of the world's largest oil and gas companies, Sinopec has a distinct advantage in raw material sourcing, which provides it with a high degree of cost competitiveness. The company produces a vast portfolio of synthetic rubbers, including Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) and Polybutadiene Rubber (BR), catering primarily to the massive domestic Chinese market for tires and industrial goods. Sinopec’s strategic positioning is rooted in its ability to produce synthetic rubber at a massive scale and its strong presence in the rapidly expanding Asia-Pacific region. The company's focus is on meeting the high-volume demand of its core markets, while also investing in technology to enhance its product portfolio.
Synthetic Rubber Market Recent Developments
- May 2025: Goodyear Tire & Rubber Company announced a definitive agreement to sell the majority of its Goodyear Chemical business to Gemspring Capital Management. The transaction, valued at approximately $650 million, includes Goodyear's synthetic rubber production facilities in Texas and a research office in Ohio. Goodyear stated that the sale is part of its strategic plan to optimize its portfolio and create shareholder value. The deal also includes a long-term supply agreement, ensuring continued access to the products.
- March 2024: ARLANXEO, a leading producer of performance elastomers, showcased a portfolio of sustainable and innovative synthetic rubber solutions at the India Rubber Expo 2024. This included an expansion of its Keltan® Eco portfolio, which now features bio-circular products alongside its existing bio-based grades. The new offerings are designed to meet the rising demand for environmentally friendly materials in the automotive and construction sectors, contributing to more sustainable mobility and urbanization.
Synthetic Rubber Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Synthetic Rubber Market Size in 2025 | USD 34.562 billion |
| Synthetic Rubber Market Size in 2030 | USD 42.802 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.37% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Synthetic Rubber Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Synthetic Rubber Market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
- Polybutadiene Rubber (BR)
- Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR)
- Butyl Rubber (IIR)
- Styrenic Block Copolymers (SBC)
- Others
- By Application
- Tire
- Non-Tire Automotive
- Industrial Goods
- Footwear
- Consumer Goods
- Others
- By End-User
- Automotive
- Construction
- Footwear
- Industrial
- Consumer Goods
- Medical
- Adhesives and Sealants
- Other
- By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Navigation:
- Synthetic Rubber Market:
- Synthetic Rubber Market Key Highlights:
- Synthetic Rubber Market Analysis
- Synthetic Rubber Market Government Regulations
- Synthetic Rubber Market Segment Analysis:
- Synthetic Rubber Market Regional Analysis
- Synthetic Rubber Market Competitive Landscape
- Synthetic Rubber Market Recent Developments
- Synthetic Rubber Market Scope:
- Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Page last updated on: September 18, 2025