Report Overview
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Highlights
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Size:
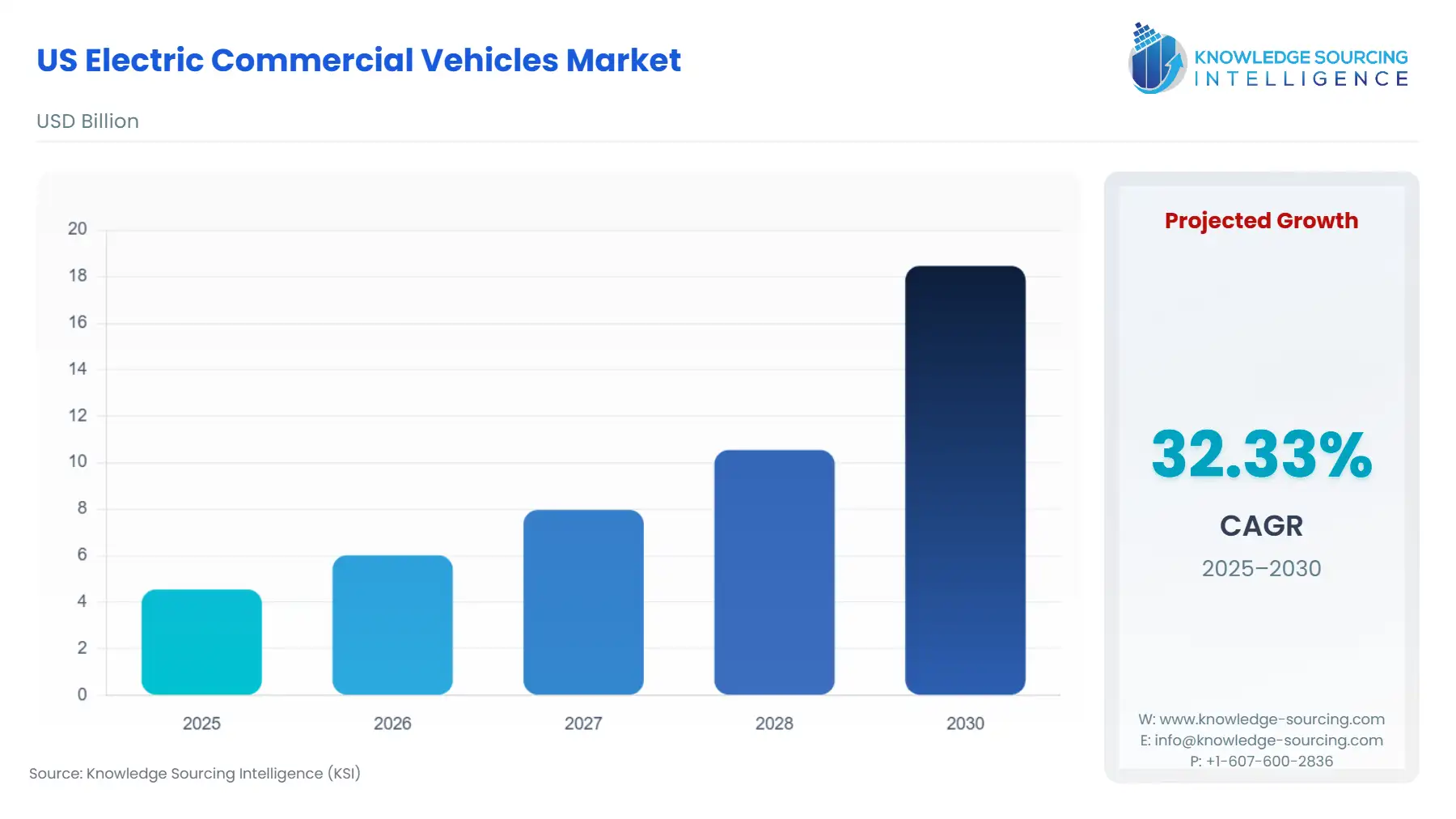
The US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market is projected to surge at a CAGR of 32.33%, rising to USD 18.466 billion in 2030 from USD 4.55 billion in 2025.
The United States electric commercial vehicles (eCV) market is undergoing a rapid transition, shifting from a nascent technology demonstration phase to initial high-volume fleet deployment. This structural change is underpinned by a confluence of stringent emissions regulations and significant federal financial incentives designed to accelerate fleet turnover. The market's current dynamic reflects a strong preference for electric models in applications with predictable routes and centralized depot charging, primarily within the logistics and public transportation sectors. Commercial viability hinges on fleet total cost of ownership (TCO) parity with conventional diesel vehicles, a threshold increasingly challenged by battery cost declines and substantial government subsidies.
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Federal and state policies serve as the primary catalyst, directly stimulating procurement demand. The Commercial Clean Vehicle Tax Credit provides fleets with an economic incentive of up to $40,000 per vehicle, immediately lowering the capital expenditure hurdle for electrification. This subsidy acts as a critical growth factor, allowing fleet operators to realize TCO advantages sooner than solely relying on operational savings. Concurrently, corporate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) mandates among large-scale logistics providers and retailers create non-financial demand, compelling the replacement of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles with zero-emission alternatives to meet public-facing sustainability targets. This requirement is particularly acute for light- and medium-duty vehicles operating in urban centers.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary challenge constraining expansion is the existing charging and refuelling infrastructure deficit. While the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocates billions toward charging networks, the current deployment rate, particularly for high-power megawatt-charging systems required by heavy-duty Class 8 trucks, lags behind vehicle availability. This creates a range-anxiety constraint for potential long-haul fleet buyers. The corresponding opportunity lies in vertical integration and partnership for charging deployment. Companies that offer an integrated ecosystem—vehicle, charging hardware, and energy management software—can capture demand by de-risking the transition for fleet customers, turning infrastructure deficiency into a competitive advantage.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Electric commercial vehicles are physical products, with the lithium-ion battery pack representing a significant portion of the final vehicle cost and the most complex component of the supply chain. Pricing dynamics for key raw materials—lithium, cobalt, and nickel—directly influence the final price point of the eCV. Declining battery pack costs, projected to fall from approximately $122/kWh in 2023 to around $67/kWh by 2032 under a mid-price scenario, directly accelerate the timeline for purchase price parity with diesel trucks. This price convergence acts as a powerful, non-subsidized growth driver, making electric fleets financially superior across the TCO lifecycle. Furthermore, the IRA's domestic content requirements are accelerating investments in US and Free Trade Agreement partner countries' mining and refining capacity for these critical minerals, aiming to secure the supply chain against geopolitical instability.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The eCV supply chain is globally distributed but is undergoing significant regionalization, mandated by US policy. Key production hubs for battery cells and modules remain centered in Asia-Pacific, creating a substantial dependency on international logistics for battery components. However, the IRA's focus on North American assembly and battery component sourcing is catalyzing the construction of gigafactories within the US. This regional shift, while mitigating international logistical complexities and import tariffs, introduces new domestic dependencies on mineral processing and refining capacity. Logistical complexity is heightened by the sheer weight and specialized handling required for battery packs, necessitating a distinct cold chain logistics for battery material transport and a new infrastructure for end-of-life battery recycling.
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Government Regulations:
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Federal (US) |
Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 (e.g., Commercial Clean Vehicle Tax Credit) |
Creates a strong, immediate pull-effect on demand by providing a direct subsidy up to $40,000 for eligible commercial EVs, prioritizing vehicles with North American assembly. |
|
Federal (US) |
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) / Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards for Heavy-Duty Vehicles (Phase 3) |
Increases the regulatory burden and associated operating cost for new ICE commercial vehicles, structurally pushing fleets toward zero-emission alternatives to maintain compliance and avoid penalties, thereby boosting EV demand. |
|
California (and adopting states) |
Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) Rule |
Mandates that a certain percentage of new commercial truck sales in the state must be zero-emission vehicles, creating a non-discretionary, scheduled demand for eCVs among manufacturers and fleet operators. |
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Logistics and Transportation
The Logistics and Transportation segment is the primary engine of near-term eCV demand, driven by the operational profile that maximizes electric powertrain advantages. Last-mile and regional delivery routes, characterized by high utilization, short daily distances (typically less than 200 miles), and return-to-depot operations, perfectly suit current battery energy density and charging capabilities. The high stop-start nature of this application maximizes the benefit of regenerative braking, which reduces wear on conventional friction brakes and recaptures energy, lowering maintenance and operational costs compared to diesel. This compelling TCO case, coupled with intense public and corporate pressure to decarbonize urban delivery, directly accelerates fleet renewal demand for electric vans and light-duty trucks. Furthermore, the ability to centralize charging at a single depot simplifies infrastructure deployment and energy management, significantly lowering the complexity barrier for major logistics providers.
- By Vehicle Type: Heavy-Duty Trucks
The heavy-duty truck segment (Class 8) represents the largest potential long-term demand shift, though it faces the steepest technical and infrastructural headwinds. The necessity for electric Class 8 tractors is currently focused on drayage and regional haul applications with a maximum operational radius of 200-300 miles, leveraging models like the Freightliner eCascadia and Tesla Semi. This requirement is primarily influenced by state-level regulations, particularly the ACT rule in California, and port-level emissions targets. The driver for this segment is the potential for massive fuel and maintenance savings over the vehicle's million-mile lifespan, counteracting the high initial purchase price. For example, the cost advantage of electricity per mile over diesel, coupled with reduced moving parts in the electric powertrain, promises superior long-term financial returns, which creates verifiable demand among major national fleet owners focused on long-term capital asset optimization.
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Competitive Analysis:
The US eCV market competition is marked by a dynamic entry of established legacy OEMs and disruptive technology startups. The competitive landscape is defined by the race to achieve TCO parity, scale manufacturing, and build out proprietary charging and service networks.
- Daimler Truck North America (DTNA): As a market leader in conventional commercial vehicles, DTNA leverages its extensive dealer and service network for a strong strategic advantage. Its key products, the Freightliner eCascadia (Class 8 heavy-duty tractor) and the Freightliner eM2 (Class 6/7 medium-duty truck), represent a strategy of electrifying existing, proven platforms. DTNA’s official newsroom details that the eM2 entered series production at its Portland, Oregon, plant in October 2023, focusing on a range of up to 180 miles for Class 6 and 250 miles for Class 7, positioning it strongly for regional distribution and urban delivery fleets. The company’s integrated approach includes Detroit ePowertrain and Detroit eConsulting for charging infrastructure planning, reducing customer transition risk.
- Tesla, Inc.: Tesla’s positioning is purely disruptive, focusing on maximizing efficiency and performance with the Tesla Semi (Class 8). Its strategy is centered on a radical design and proprietary technology, including a 1,000-volt powertrain and the development of the high-speed Megacharger network. The company's goal of volume production for the 500-mile range Semi is projected to be in 2026. Tesla’s ability to achieve an energy consumption of less than 2kWh per mile, as advertised, represents a significant operational cost advantage that generates strong forward demand among efficiency-focused fleet operators like PepsiCo, which took initial deliveries.
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Developments:
- October 2023: Daimler Truck North America (DTNA) starts Freightliner eM2 Series Production. DTNA officially commenced series production of the all-electric Freightliner eM2 at its Portland, Oregon, facility. This medium-duty truck targets regional and urban delivery applications. The first production units were allocated to major fleet customers, including Penske Truck Leasing and Ryder System, Inc.
- December 2022: Tesla Begins Initial Customer Deliveries of the Semi. Tesla commenced initial customer deliveries of its Class 8 electric truck, the Tesla Semi, to PepsiCo at its facility in Nevada. The vehicle features an advertised 500-mile range and utilizes a 1,000V architecture.
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 4.55 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 18.466 billion |
| Growth Rate | 32.33% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Vehicle Type, Propulsion, Power Output, Application |
| Companies |
|
US Electric Commercial Vehicles Market Segmentation:
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
-
- Buses and Coaches
- Trucks
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Vans
- BY PROPULSION TYPE
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEV)
- BY POWER OUTPUT
- Up to 150 kW
- 150-250 kW
- Above 250 kW
- BY APPLICATION
- Logistics and Transportation
- Public Transportation
- Construction (Excavators, Loaders, Others)
- Mining
- Agriculture (Tractors, Harvesters, Others)
- Others