Report Overview
UV LED Market - Highlights
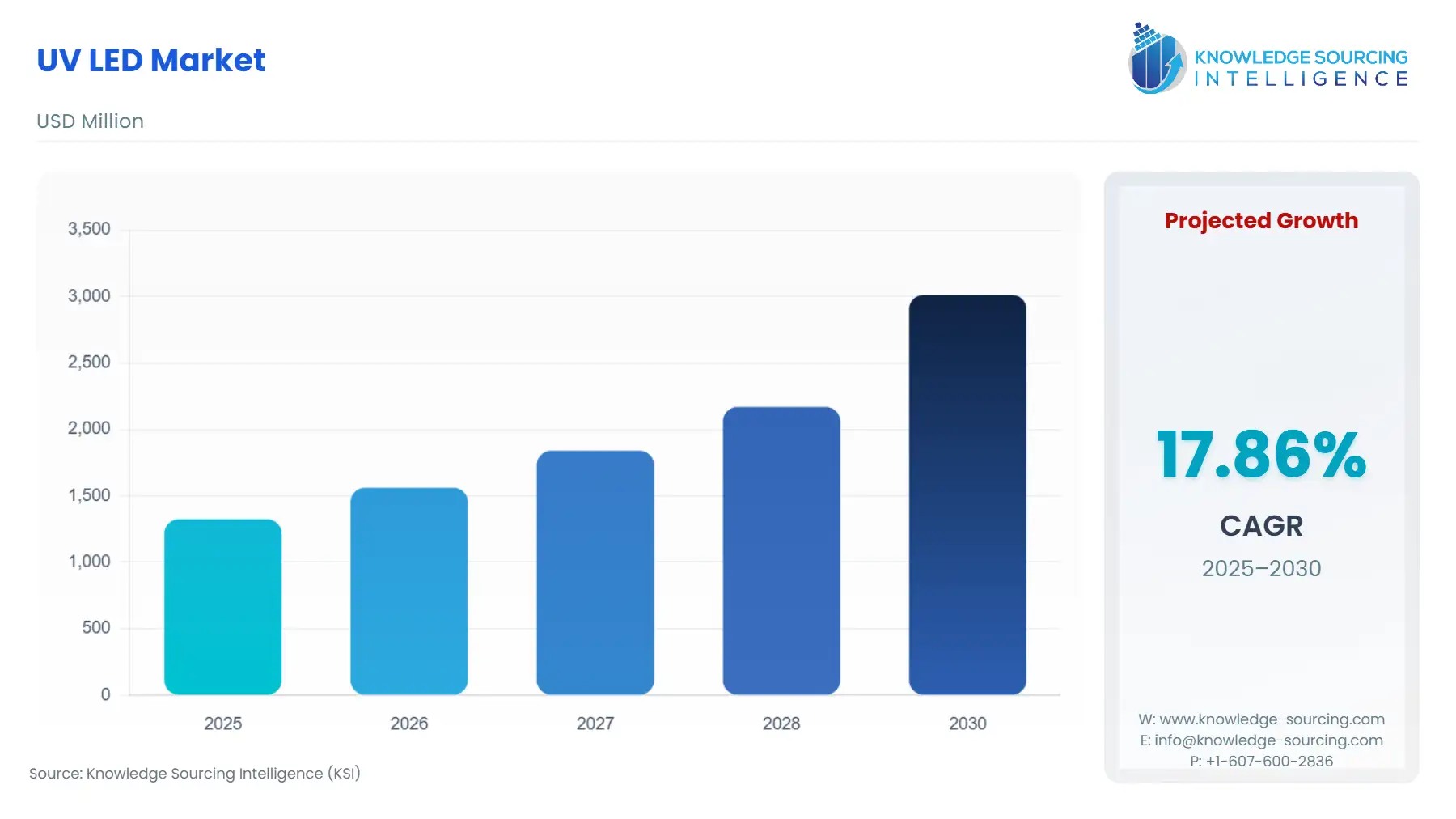
UV LED Market Size:
The UV LED market will grow at a CAGR of 17.86% to be valued at US$3.013 billion in 2030 from US$1.325 billion in 2025.
UV LED Market Introduction:
The ultraviolet (UV) light-emitting diode (LED) market has emerged as a transformative segment within the broader optoelectronics industry, driven by its ability to deliver efficient, eco-friendly, and versatile solutions for a wide range of applications. UV LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit ultraviolet light when an electric current passes through them, offering significant advantages over traditional lighting technologies. These devices have gained prominence in industries such as healthcare, water purification, air disinfection, industrial curing, and agriculture, fueled by growing global demand for sustainable and chemical-free technologies. Unlike conventional lighting, UV LEDs operate within specific wavelength ranges, enabling precise applications that address modern challenges in hygiene, manufacturing, and environmental sustainability.
The UV LED market is propelled by several critical drivers. First, the global push for sustainability has accelerated the adoption of mercury-free technologies. These eliminate the environmental risks associated with mercury, aligning with stringent regulations such as the Minamata Convention on Mercury, which many countries have ratified to phase out mercury-containing products. Second, heightened awareness of hygiene and public health, particularly following global health crises, has increased demand for disinfection and sterilization solutions. These LEDs, especially UV-C LEDs, are highly effective at inactivating pathogens, making them integral to healthcare, water treatment, and air purification systems. Third, advancements in semiconductor technology have improved their efficiency, power output, and lifespan, enabling their integration into compact and portable devices. Finally, the rise of smart technologies and Internet of Things (IoT) applications has facilitated the incorporation of UV LEDs into automated systems, such as HVAC units and consumer appliances, enhancing their market appeal.
Despite its growth potential, the UV LED market faces several restraints. The high manufacturing costs of UV LEDs, particularly those using materials like aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN), remain a significant barrier, limiting adoption in cost-sensitive sectors. Additionally, UV LEDs currently offer lower light output compared to traditional mercury UV lamps, which can restrict their use in high-intensity applications. Safety concerns related to UV exposure also necessitate robust regulations and shielding mechanisms, increasing design complexity. Finally, supply chain constraints, including the availability of high-quality raw materials, can hinder production scalability, particularly amidst geopolitical and economic uncertainties.
UV LEDs vs. Traditional Mercury UV Lamps:
UV LEDs and traditional mercury UV lamps differ fundamentally in design, operation, and environmental impact. Mercury UV lamps, typically low- or medium-pressure vapor lamps, generate UV light through an electric arc in mercury gas, emitting a broad spectrum of wavelengths (200–600 nm). These lamps have been used for decades in disinfection, curing, and water treatment but face significant drawbacks. They contain mercury, a toxic substance that poses environmental and health risks, requiring careful disposal and handling. Mercury lamps also have lower energy efficiency (30–40% for low-pressure lamps, <10% for medium-pressure lamps) and require preheating, delaying full output. Additionally, their bulky design limits integration into compact systems.
In contrast, UV LEDs are solid-state devices that produce UV light through the recombination of electrons and holes in a semiconductor material, typically gallium nitride or AlGaN. They emit a narrow, monochromatic wavelength (e.g., 265 nm or 275 nm for UV-C LEDs), allowing precise targeting for specific applications. UV LEDs are mercury-free, aligning with global sustainability goals, and offer instant-on functionality, eliminating warm-up times. They are compact, durable, and energy-efficient, with lower heat generation and longer lifespans (up to 10,000 hours or more). However, their wall-plug efficiency (3–6% as of recent advancements) remains lower than mercury lamps, though ongoing research is closing this gap.
UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C LEDs:
UV LEDs are categorized into three types based on their wavelength ranges, each suited to specific applications:
UV-A LEDs (315–400 nm): These operate in the near-UV spectrum and are widely used in curing applications, such as drying inks, coatings, and adhesives in printing and manufacturing. They are also employed in forensics, counterfeit detection, and phototherapy. UV-A LEDs are the most mature and cost-effective, dominating the market due to their high efficiency and established production processes.
UV-B LEDs (280–315 nm): These are used in medical phototherapy for treating skin conditions like psoriasis and in agriculture to enhance plant growth by stimulating active compounds. UV-B LEDs are less common than UV-A but are gaining traction due to their targeted biological effects.
UV-C LEDs (200–280 nm): These are the most effective for disinfection and sterilization, as their wavelengths (peaking at 260–280 nm) disrupt the DNA/RNA of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, rendering them inactive. UV-C LEDs are critical in healthcare, water purification, and air disinfection, but they face challenges due to lower efficiency and higher production costs compared to UV-A and UV-B LEDs.
UV LEDs for Disinfection and Sterilization:
UV LEDs, particularly UV-C LEDs, are highly effective for disinfection and sterilization due to their ability to emit germicidal wavelengths that target the genetic material of microorganisms. When UV-C light penetrates the cell walls of bacteria, viruses, or fungi, it is absorbed by DNA or RNA, causing photochemical damage that prevents replication. This chemical-free process is ideal for sensitive environments like hospitals, food processing facilities, and public transportation. For example, UV-C LEDs operating at 265–280 nm can achieve up to 99.9% pathogen inactivation under optimal conditions.
Recent industry developments underscore the growing adoption of UV-C LEDs. In May 2024, Silanna UV introduced a 235 nm Far-UVC LED with a 3mW output, designed for safer disinfection in public spaces due to its reduced penetration into human skin. Similarly, in February 2024, Seal Shield launched the Shyld AI, an autonomous UV-C disinfection system for healthcare facilities, leveraging AI to target high-risk areas. These innovations highlight the shift toward compact, intelligent, and eco-friendly disinfection solutions.
UV LEDs offer several advantages in disinfection: their compact size allows integration into portable devices like sanitizing wands and water purifiers, while their instant-on capability supports intermittent use in point-of-use applications. However, challenges such as limited light intensity and thermal management require ongoing optimization to match the performance of mercury lamps in high-flow systems.
Hence, the UV LED market is poised for significant growth, driven by sustainability, hygiene awareness, and technological advancements. While manufacturing costs and efficiency limitations pose challenges, ongoing innovations are addressing these hurdles. Compared to traditional mercury lamps, the LEDs offer superior environmental and operational benefits, with UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C LEDs catering to diverse applications. Their role in disinfection and sterilization is particularly critical, transforming healthcare, water treatment, and consumer products. As industries prioritize eco-friendly and efficient solutions, UV LEDs are set to redefine the future of ultraviolet technology.
UV LED Market Trends
The demand for UV LEDs in curing applications across the ink, adhesive, and coating industries is significantly contributing to market growth. Rising needs for currency validation, air and water purification, and horticulture lighting are key drivers. Additionally, UV LED use in chip manufacturing and biomedical devices is boosting demand. Technological advancements are enabling UV LEDs to expand into medical, agriculture, security, horticulture, and industrial sectors.
The UV LED market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by advancements in solid-state UV technology and increasing demand for eco-friendly solutions. A key trend is the rise of UV-A LED curing, widely adopted in industrial printing and adhesive curing due to its high efficiency and lifespan (up to 10,000 hours). Unlike mercury-based lamps, UV-A LEDs offer precise wavelength control and mercury-free UV operation, aligning with global regulations like the Minamata Convention.
Another significant trend is the expansion of UV-C disinfection, particularly with germicidal UV LEDs operating at 260–280 nm. These LEDs are transforming healthcare and water purification by inactivating pathogens without chemicals. The emergence of far-UVC LEDs (200–230 nm), such as Silanna UV’s 235 nm LED launched in May 2024, enhances safety for human exposure while maintaining efficacy. Deep UV LEDs are also gaining traction in air purification and surface sterilization, driven by post-pandemic hygiene demands.
Improvements in UV LED efficiency (now 3–6%) and solid-state UV designs are enabling compact, portable devices, such as UV-C sanitizing wands. These trends underscore the shift toward sustainable, high-performance LED solutions across industries.
Some of the major players covered in this report include Lumileds, Honle Group, Nordson Corporation, Nichia Corporation, Mouser Electronics, Seoul Viosys, EPIGAP OSA, AquiSense Technologies, Stanley Electric Co., Ltd., and Arora Technologies Ltd., among others.
UV LED Market Drivers:
Rising Demand for Water Purification, Air Sterilization, and Surface Disinfection
The global emphasis on hygiene and public health has significantly boosted the UV LED market, particularly for UV-C LEDs used in water purification, air sterilization, and surface disinfection. These applications leverage the germicidal properties of UV-C light (260–280 nm) to inactivate pathogens, offering a chemical-free, eco-friendly solution. The demand surged post-pandemic, with industries like healthcare and public transportation adopting UV-C LEDs for surface disinfection and air sterilization in hospitals, offices, and transit systems. For instance, Seal Shield’s Shyld AI, launched in February 2024, uses UV-C LEDs with AI to target high-risk areas in healthcare facilities. Water purification systems are also increasingly integrating such LEDs for their compact size and instant-on functionality, replacing bulky mercury lamps. This trend is driven by consumer demand for sustainable, efficient disinfection solutions, positioning UV LEDs as a cornerstone of modern hygiene practices.
Advancements in UV Curing Inks and 3D Printing Applications
Technological advancements in UV LEDs have revolutionized UV curing inks and 3D printing, driving market growth. UV-A LEDs (315–400 nm) provide precise, energy-efficient curing for inks, coatings, and adhesives in printing and manufacturing. Their rapid curing and low heat output enhance production speed and quality, making them ideal for 3D printing, where UV LEDs cure resin layers with high precision. For example, Fujifilm and IST METZ’s SMARTcure, introduced in 2024, optimizes UV curing inks for graphic arts, reducing energy costs. The mercury-free nature of UV LEDs aligns with environmental regulations, such as the Minamata Convention. Their compact size and long lifespan enable integration into advanced 3D printing systems, supporting industries like automotive and electronics, where UV curing enhances efficiency and sustainability.
Growing Applications in Medical Phototherapy and Counterfeit Detection
The UV LED market is expanding due to innovative applications in medical phototherapy and counterfeit detection. UV-B LEDs (280–315 nm) are used in phototherapy to treat skin conditions like psoriasis by delivering targeted wavelengths that stimulate therapeutic responses. Nichia’s March 2024 launch of UV-B LEDs (308 nm) for medical phototherapy exemplifies this trend. Simultaneously, UV-A LEDs are critical for counterfeit detection, illuminating fluorescent security features in banknotes and documents. Their precision and mercury-free operation make them ideal for security applications in banking and retail. The versatility of UV LEDs, combined with their energy efficiency and durability, supports their adoption in healthcare and security, driven by increasing awareness of their benefits and ongoing advancements in semiconductor technology.
UV LED Market Restraints
High Manufacturing Costs
The UV LED market faces significant challenges due to high manufacturing costs, particularly for UV-C LEDs. These devices require specialized materials like aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN), which are expensive and complex to produce. The intricate fabrication process, including precise doping and high-quality crystal growth, increases production costs, making UV LEDs less competitive in price-sensitive markets compared to mercury lamps. Additionally, thermal management challenges arise due to heat generation in deep UV LEDs, necessitating advanced cooling systems that further elevate costs. These factors limit scalability and adoption in applications like water purification and surface disinfection, where cost-effectiveness is critical. Ongoing research aims to reduce costs through improved semiconductor processes, but high initial investment remains a barrier.
Limited Light Output and Efficiency
Despite advancements, UV LEDs, especially UV-C LEDs, suffer from limited light output and lower external quantum efficiency (3–6%) compared to mercury lamps. This restricts their use in high-intensity applications like large-scale water purification or air sterilization, where mercury lamps still offer superior performance. The lower efficiency stems from material limitations and optical losses in semiconductor structures, requiring higher power inputs to achieve desired germicidal effects. For instance, far-UVC LEDs struggle to deliver sufficient intensity for rapid surface disinfection in large spaces. These limitations hinder market penetration in industrial and healthcare settings, though innovations like Nichia’s UV-C LED (NCSU434C) aim to address this.
UV LED Market Segmentation Analysis
The demand for UV-A LEDs is growing significantly
UV-A LEDs (315–400 nm) dominate the UV LED market due to their maturity, cost-effectiveness, and widespread use in industrial curing, counterfeit detection, and phototherapy. These LEDs offer high efficiency and longevity (up to 10,000 hours), making them ideal for UV curing in printing, coatings, and adhesives. For instance, Fujifilm’s SMARTcure system, launched in May 2024, leverages UV-A LEDs for energy-efficient curing in graphic arts, reducing operational costs. These LEDs are also critical in counterfeit detection, illuminating fluorescent security features in banknotes and documents. Their mercury-free operation aligns with global regulations like the Minamata Convention, driving adoption. Additionally, they support phototherapy for skin treatments, further expanding their market share. Their versatility and established manufacturing processes make UV-A LEDs the leading type, with ongoing advancements enhancing their efficiency and affordability.
By End-User, the Healthcare segment is anticipated to grow considerably
The healthcare sector is the leading end-user of UV LEDs, driven by the demand for disinfection, sterilization, and phototherapy. UV-C LEDs (200–280 nm) are pivotal for germicidal applications, inactivating pathogens in water purification, air sterilization, and surface disinfection in hospitals and clinics. Seal Shield’s Shyld AI, launched in February 2024, integrates UV-C LEDs with AI for autonomous disinfection in healthcare facilities, targeting high-risk areas. UV-B LEDs are used in phototherapy to treat conditions like psoriasis, with Nichia’s 308 nm UV-B LED, introduced in March 2024, showcasing advancements in this area. Their adoption by the healthcare sector is fueled by their compact size, instant-on functionality, and mercury-free operation, addressing hygiene needs post-pandemic and replacing traditional mercury lamps. This segment’s growth is further supported by regulatory shifts and increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to lead the market expansion
The Asia Pacific region, encompassing China, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, and others, leads the UV LED market due to its robust semiconductor manufacturing, technological innovation, and high demand across industries. Japan and South Korea host major players like Nichia Corporation and Seoul Viosys, driving advancements in UV LED technology. For example, Nichia’s UV-C LED (NCSU434C), launched in January 2023, targets disinfection applications, strengthening the region’s market position. China leads in manufacturing and healthcare applications, integrating them into water purification and air sterilization systems to meet stringent hygiene standards. Taiwan contributes through its expertise in semiconductor production, supporting UV-A LED applications in curing and 3D printing. The region’s dominance is further bolstered by government initiatives promoting sustainable technologies and the Minamata Convention compliance, encouraging mercury-free UV solutions. Rapid urbanization and industrial growth in the Asia Pacific continue to drive its adoption.
UV LED Market Key Developments
Kyocera G7A Series Air-cooled UV LED light source: Launched in May 2025, this product is designed for UV curing applications, offering a compact size and high performance for curing inks, adhesives, and resins.
ams OSRAM OSLON UV 3535: Launched in October 2024, this UV-C LED is a high-efficiency product with a long lifespan, suitable for disinfection applications in air, water, and on surfaces. It is designed to be a cost-effective solution for both industrial and consumer-grade uses.
Silanna UV 235nm Quad high-power far-UVC LED: Launched in June 2024, this LED provides a light source for disinfection, water quality sensors, high-performance liquid chromatography, and gas sensors. Its far-UVC wavelength is noted for being effective for air purification and surface disinfection.
UV LEDs Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.325 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2030 | USD 3.013 billion |
| Forecast Unit | Billion |
| Growth Rate | 17.86% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Segmentation | Type, Power Output, End-User, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
UV LEDs Market Segmentation:
The UV LED market is analyzed by type into the following:
UVA
UVB
UVC
UV LEDs Market Segmentation by power output:
Less than 1W
1W-5W
More than 5W
UV LEDs Market Segmentation by end-user:
Manufacturing
Agriculture
Defense
Chemical
Healthcare
Others
UV LEDs Market Segmentation by regions:
Americas (US)
Europe, the Middle East, and Africa (Germany, the Netherlands, and Others)
Asia Pacific (China, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, and Others)