Report Overview
Virtual Machine Market - Highlights
Virtual Machine Market Size:
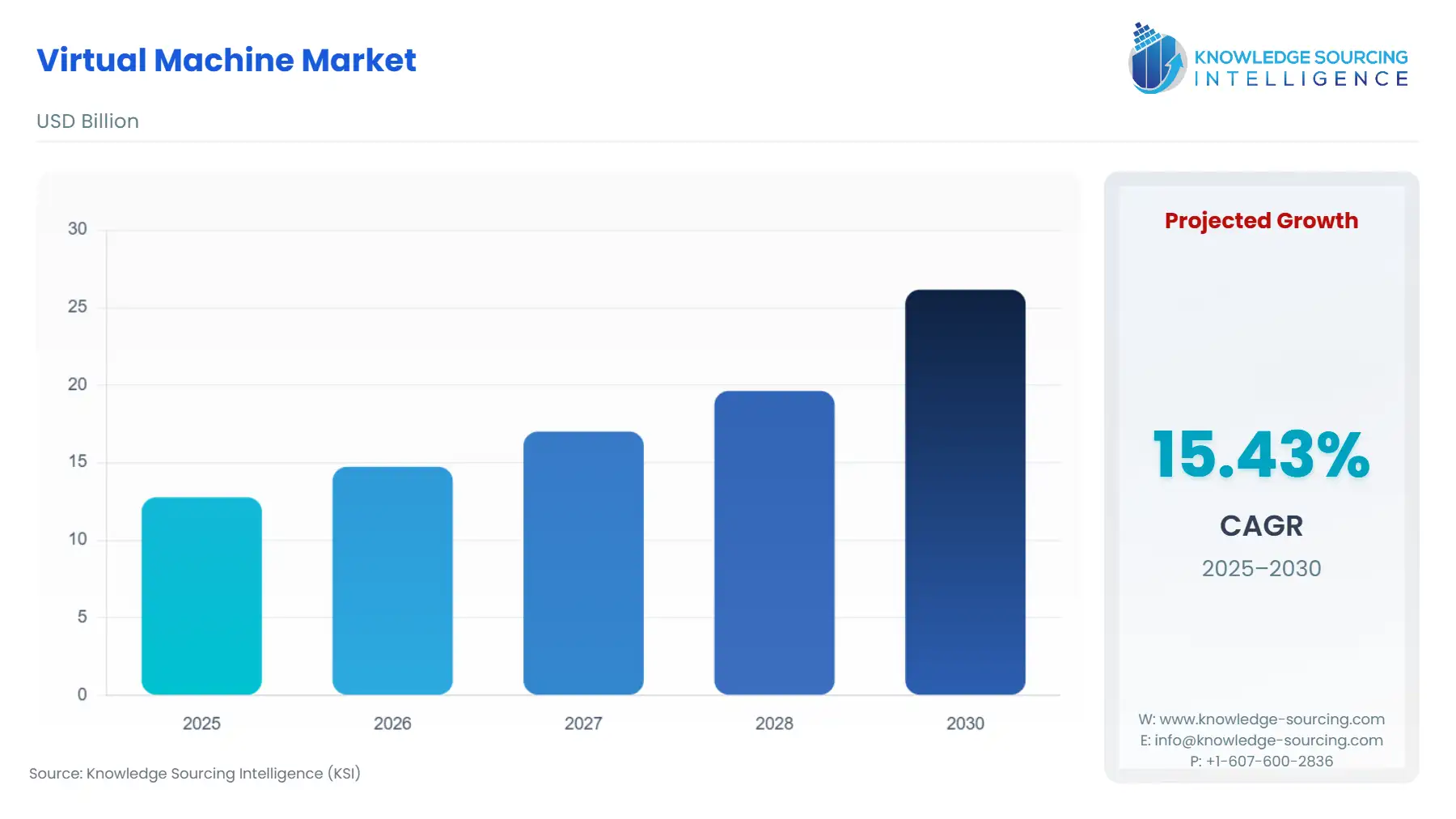
Virtual Machine Market is projected to grow at a 14.97% CAGR, increasing from USD 12.765 billion in 2025 to USD 29.476 billion in 2031.
Virtual Machine Market Key Highlights:
Virtual Machine Market Trends:
The concept of virtual machines (VMs) includes software programs that emulate a physical computer system within a host machine. Each VM functions independently, possessing its operating system and resources, allowing users to seamlessly switch between different environments without the need for dedicated hardware. VMs are not confined to a single physical machine; multiple VMs can coexist on a single host, sharing its resources such as CPU cycles, network bandwidth, and memory.
The adoption of VMs has accelerated over the past two decades, driven by the increasing demand for efficient and cost-effective computing solutions. Server virtualization, a prominent application of VMs, has become a cornerstone of modern data centers, enabling organizations to consolidate multiple physical servers into a single host machine. This consolidation not only optimizes resource utilization but also reduces data center footprint and associated energy costs.
In the realm of computing, the global virtual machine (VM) market has emerged as a dynamic force, driven by the innovative concept of emulating physical computer systems through software. This technology enables the creation of isolated environments, allowing multiple operating systems or applications to run simultaneously on a single physical machine. As a result, VMs have become indispensable tools for optimizing resource utilization, enhancing cost-effectiveness, and fostering flexibility in computing landscapes. Public cloud services have embraced the power of VMs, leveraging them to deliver virtual application resources to multiple users concurrently. This approach has revolutionized cloud computing, enabling providers to offer cost-effective and scalable computing solutions that adapt seamlessly to fluctuating demands.
Traditionally, VMs have been instrumental in server virtualization, empowering IT teams to consolidate computing resources and streamline operations. By partitioning a single physical server into multiple virtual machines, organizations can maximize hardware utilization, reduce costs, and simplify management tasks. Furthermore, VMs have proven invaluable in executing tasks that pose potential risks to the host environment. For instance, VMs can be employed to safely access virus-infected data or test new operating systems without compromising the integrity of the underlying system. This isolation capability ensures that any potential hazards are contained within the virtual environment, safeguarding the host system from harm.
Virtual Machine Market Growth Drivers:
Cost efficiency: Virtual machines enable the consolidation of multiple virtualized workloads onto a single physical server, leading to cost savings in terms of hardware, energy, and maintenance. This cost efficiency is a significant driver for the adoption of virtual machines, especially in data centers and cloud environments.
Flexibility and scalability: Virtual machines provide the flexibility to create, deploy, and move workloads across different physical servers quickly and easily. This agility allows organizations to scale their IT infrastructure up or down based on demand, leading to improved resource utilization and operational efficiency.
Disaster recovery and business continuity: Virtualization technology, including virtual machines, plays a critical role in disaster recovery and business continuity strategies. By encapsulating an entire workload into a VM, organizations can replicate and move workloads to a different location in the event of a disaster, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss.
Resource isolation and security: Virtual machines offer strong isolation between workloads, allowing for enhanced security and compliance. Each VM operates independently, and any changes or issues within one VM do not affect others, providing a layer of protection against security threats and malware.
Testing and development: Virtual machines are widely used for software development, testing, and quality assurance. Developers can create and run multiple VM instances with different configurations, operating systems, and software versions, enabling efficient testing and development processes without the need for physical hardware.
Virtual Machine Market Key Players:
Products offered by key companies:
Amazon WorkSpaces can be used to provide remote workers with secure access to corporate resources, such as applications, data, and email. It can be used to enable BYOD (bring your device) initiatives by allowing employees to use their own devices to access their workspaces. It can help to reduce IT support costs by providing a self-service portal for employees to manage their workspaces.
VMware workstation player is a desktop hypervisor application that delivers local virtualization features and is available for free for personal use. It allows you to run a single virtual machine on a Windows or Linux PC.
Virtual Machine Market Segmentation Analysis:
Prominent growth in the BFSI segment within the virtual machine market:
The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector has become a major catalyst for the virtual machine market's expansion. This sector is embracing virtualization technologies wholeheartedly due to the numerous advantages they provide, including cost savings, enhanced security, scalability, and improved disaster recovery capabilities. The BFSI sector's growing preference for cloud-based virtualization solutions has further solidified its position as a key driver of virtual machine market growth. The adoption of virtualization in the BFSI sector is fueled by the need for cost-effective IT solutions that enhance resource utilization, flexibility, and scalability, aligning seamlessly with the sector's evolving technology needs and changing business requirements.
The adoption of virtualization in the BFSI segment is primarily driven by the need for cost-effective IT solutions that enhance resource utilization, flexibility, and scalability, aligning with the sector's evolving technology needs and changing business requirements. Virtualization has become an indispensable tool for BFSI organizations, enabling them to optimize their IT infrastructure, enhance security, and achieve greater operational efficiency.
Virtual Machine Market Geographical Outlook:
The North American region is expected to hold a significant share of the virtual machine market:
North America is poised to maintain a commanding position in the virtual machine (VM) market, driven by a multitude of factors. One cornerstone of the region's dominance is the strong presence of leading VM and cloud computing service providers. These industry giants, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and VMware, have played a pivotal role in shaping the market's growth and stability. Their innovative solutions and extensive customer reach have made VMs an integral part of IT operations across North America. Furthermore, the region has a robust IT infrastructure, which serves as the bedrock for VM adoption. The region's widespread availability of high-speed internet, advanced data centers, and skilled IT professionals has created an environment conducive to the deployment and effective utilization of VM technologies.
The increasing adoption of virtualization technologies across diverse industries, including BFSI, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, is another key factor driving the demand for VMs in North America. Businesses in these sectors are recognizing the numerous benefits of virtualization, including enhanced resource utilization, improved scalability, and reduced IT costs. The growing emphasis on cost efficiency, flexibility, and security in IT operations has further propelled the adoption of virtualization solutions in North America. VMs offer a cost-effective way to consolidate multiple workloads onto a single physical server, maximizing resource utilization and reducing hardware expenses. Additionally, VMs provide the flexibility to rapidly provision and deploy new IT environments, catering to the dynamic needs of modern businesses.
Moreover, the region's well-established regulatory framework and standards for data security and privacy have contributed to the widespread implementation of virtualization technologies, particularly in sensitive sectors such as BFSI. VMs offer enhanced security capabilities, allowing businesses to isolate and protect sensitive data while maintaining the flexibility and scalability of a virtualized environment.
List of Top Virtual Machine Companies:
Amazon.com Inc.
Citrix Systems Inc.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise LP
Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
IBM Corporation
Virtual Machine Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Companies |
|
Report Metric | Details |
Virtual Machine Market Size in 2025 | USD 12.765 billion |
Virtual Machine Market Size in 2030 | USD 26.159 billion |
Growth Rate | CAGR of 15.43% |
Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
Base Year | 2024 |
Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
Segmentation |
|
Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
List of Major Companies in the Virtual Machine Market |
|
Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Virtual Machine Market Segmentation
By Type
System Virtual Machine
Process Virtual Machine
By Deployment
Cloud
On-Premise
By Enterprise Size
Small & Medium Enterprise
Large Enterprise
By End-User
BFSI
IT & Telecommunication
Media & Entertainment
Retail
Healthcare
Others
By Geography
North America
United States
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
Germany
France
United Kingdom
Spain
Others
Middle East and Africa
Saudi Arabia
UAE
Others
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Indonesia
Thailand
Others