5G NTN Evolution: Advancements and Breakthroughs in Connectivity

NTN enables connectivity in areas that were formerly inaccessible by terrestrial networks, regardless of whether it be over terrain, or deserts, among others. It accomplishes this by using satellites as well as non-terrestrial vehicles. The capacity to operate in disaster zones and drive potential technologies such as UAMs. Furthermore, by tackling coverage issues and advanced applications that ground-based architecture alone cannot solve, satellites may complement 5G and increase the economic impact of 5G networks.
Source: 3GPP
In the above table, three-type of satellite-based NTN platforms are mentioned. Numerous Internet of Things (IoT) applications that can be supported by LEO and GEO utilize NTN technology, especially in distant and difficult-to-reach places. For instance, to democratize the availability of the Internet of Things, Sateliot, the first firm to run an LEO nanosatellite constellation using the 5G-IoT standard, debuted Sateliot_0 "The GroundBreaker" in April 2023.
Additionally, ZTE has collaborated with China Mobile to perform the pilot test using the GEO satellite, taking into account the market demands for space IoT and the significance of NB-IoT NTN applications. To send air-interface messages, an L-band satellite, and terrestrial gateway station are situated between NTN endpoints and base stations.
Source: 3GPP, Rohde & Schwarz
Major corporations are working together to optimize GEO and NGSO multi-orbit systems to deliver seamless, global availability for D2D application scenarios across significant verticals, namely consumer mobile device, automobile, and Internet of Things (IoT) connections. In February 2023, for instance, to provide the most advanced space-based D2D technologies for international voice, text, and data accessibility, Omnispace, and Ligado Networks declared an MOU that will merge their respective licensed mobile satellite network range. The partnership paves the way for the establishment of multi-band, multi-orbit satellite services that will allow common mobile communication for over five billion mobile subscribers in regions where terrestrial mobile service is currently insufficient. These satellite offerings will utilize huge portions of satellite bandwidth in the L- and S-Bands.
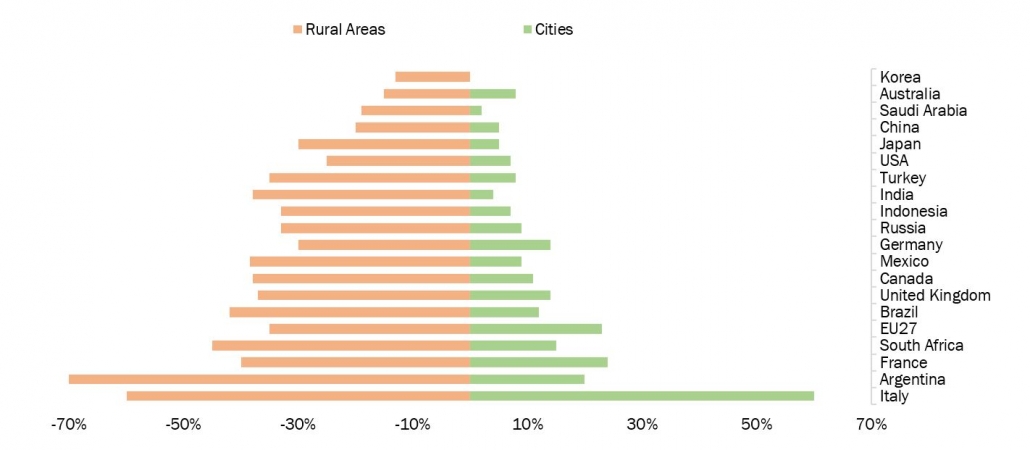 Source: OECD
Consequently, the use of satellite-based connectivity could be crucial in utilizing existing communication networks to provide 5G capabilities in the coming years and narrow the digital gap. For instance, Coverage Above and Beyond, a ground-breaking new proposal to offer cell phone service anywhere, was unveiled by T-Mobile and SpaceX in August 2022. T-Mobile intends to offer nearly full coverage in the majority of locations in the United States, including many of the remotest regions that were previously inaccessible by conventional cell signals. It aims to accomplish this by utilizing Starlink, SpaceX's LEO satellites, and T-Mobile's sector-leading wireless network.
Source: OECD
Consequently, the use of satellite-based connectivity could be crucial in utilizing existing communication networks to provide 5G capabilities in the coming years and narrow the digital gap. For instance, Coverage Above and Beyond, a ground-breaking new proposal to offer cell phone service anywhere, was unveiled by T-Mobile and SpaceX in August 2022. T-Mobile intends to offer nearly full coverage in the majority of locations in the United States, including many of the remotest regions that were previously inaccessible by conventional cell signals. It aims to accomplish this by utilizing Starlink, SpaceX's LEO satellites, and T-Mobile's sector-leading wireless network.
Source: 5G Americas
- Current Types Of Satellite-Based NTN Systems
Satellite-Based NTN Platform Types
|
Platforms |
Altitude Range (in Km) |
Typical Beam Footprint Size (in Km) |
|
LEO |
300 - 1,500 | 100 - 1,000 |
|
MEO |
7,000 - 25,000 |
100 - 1,000 |
| GEO | 35,786 |
200 - 3,500 |
- 5G NTN Spectrum
5G NTN Spectrum (FR1 and FR2)
| Band | Uplink | Downlink | Duplex | |
| First 3GPP NTN FR1 bands for L-Band and S-Band (IoT) | n255 | 1626.5 – 1660.5 MHz | 1525.0 – 1559.0 MHz | FDD |
| n256 | 1980.0 – 2010.0 MHz | 2170.0 – 2200.0 MHz | FDD | |
| Existing 3GPP FR2-1 Bands | n257 | 26.50 – 29.50 GHz | 26.50 – 29.50 GHz | TDD |
| n258 | 24.25 – 27.50 GHz | 24.25 – 27.50 GHz | TDD | |
| n259 | 39.50 – 43.50 GHz | 39.50 – 43.50 GHz | TDD | |
| n260 | 37.00 – 40.00 GHz | 37.00 – 40.00 GHz | TDD | |
| n261 | 27.50 – 28.35 GHz | 27.50 – 28.35 GHz | TDD | |
| n262 | 47.20 – 48.20 GHz | 47.20 – 48.20 GHz | TDD | |
| Proposed 3GPP NTN FR2-0/FR2-1 bands * for K-Band and KA-Band (VSAT) | n510 | 17.70 – 20.20 GHz | 27.50 – 28.35 GHz | FDD |
| n511 | 17.70 – 20.20 GHz | 28.35 – 30.00 GHz | FDD | |
| n512 | 17.70 – 20.20 GHz | 27.50 – 30.00 GHz | FDD |
- Vast 5G NTN Use Cases
- Satellite-Based Connectivity
Digital Divide As Measured By Fixed Broadband Download Speeds (Q4,2020)
 Source: OECD
Consequently, the use of satellite-based connectivity could be crucial in utilizing existing communication networks to provide 5G capabilities in the coming years and narrow the digital gap. For instance, Coverage Above and Beyond, a ground-breaking new proposal to offer cell phone service anywhere, was unveiled by T-Mobile and SpaceX in August 2022. T-Mobile intends to offer nearly full coverage in the majority of locations in the United States, including many of the remotest regions that were previously inaccessible by conventional cell signals. It aims to accomplish this by utilizing Starlink, SpaceX's LEO satellites, and T-Mobile's sector-leading wireless network.
Source: OECD
Consequently, the use of satellite-based connectivity could be crucial in utilizing existing communication networks to provide 5G capabilities in the coming years and narrow the digital gap. For instance, Coverage Above and Beyond, a ground-breaking new proposal to offer cell phone service anywhere, was unveiled by T-Mobile and SpaceX in August 2022. T-Mobile intends to offer nearly full coverage in the majority of locations in the United States, including many of the remotest regions that were previously inaccessible by conventional cell signals. It aims to accomplish this by utilizing Starlink, SpaceX's LEO satellites, and T-Mobile's sector-leading wireless network.
- Leading Players
- Space X - In 2022, the international satellite-to-cellular network initiative "Coverage and Above and Beyond," a joint venture between SpaceX and T-Mobile, was launched. The firms presented strategies for extending 5G coverage using second-generation Starlink satellites to eliminate mobile dead zones, such as in remote locations in the middle of the ocean. The two businesses announced recently that they will start piloting 5G connectivity in the latter half of 2023.
Major Broadband and Satellite Providers, 2023
|
Operator |
Satellite system (deployed) | Spectrum | Operational | Services |
|
Space X (Starlink) |
12,000+ (3,580) | Ku-band | Yes | Broadband |
| Kuiper | 3236 (0) | Ka band | Estimated 2024 |
Broadband |
|
Echostar |
10 GEO (10) | Ku, Ka, S bands | Yes | Broadband |
| HughesNet | 3 GEO (2) | Ka band | Yes |
Broadband |
| Inmarsat | 14 GEO (14) | TBD | TBD |
Broadband to IoT |
- Kuiper Systems LLC - Amazon's Project Kuiper aims to provide global internet access to users using a fleet of LEO satellites. In 2024, Amazon is anticipated to launch its first batch of satellites, and later that year, it is expected to start offering service to its first clients. It is yet unknown where Project Kuiper will launch its internet service and how much it will cost consumers.
- EchoStar Corporation - In February 2023, satellite provider EchoStar stated it would begin constructing a constellation of 28 LEO satellites around the world alongside supplier Astro Digital. These satellites will broadcast signals using the business's S-band spectrum ownership. For IoT applications, the system will at first support the LoRa protocol, but EchoStar claimed that this move is a component of a long-term plan to create "a worldwide non-terrestrial 5G network."
- Inmarsat - To deliver ultra-reliable, two-way satellite connectivity for smartphones, IoT devices, cars, and other sectors, MediaTek and Inmarsat strengthened their alliance as of April 2023. The two major players in the industry are working to make it possible for mobile carriers, smartphone makers, and additional device manufacturers to deliver satellite offerings, such as two-way text messaging, disaster communications, device monitoring, and surveillance, amongst other features. The MediaTek/Inmarsat partnership offers the industry a very practical strategy by utilizing tried-and-tested 5G NTN guidelines, current chipsets, and the most dependable universal satellite infrastructure, enabling a speedy rollout of new NTN services.
- 5G Network Security Market: https://www.knowledge-sourcing.com/report/5g-network-security-market
- 5G Network And Service Assurance Market: https://www.knowledge-sourcing.com/report/5g-network-and-service-assurance-market
- Global 5G Device Market: https://www.knowledge-sourcing.com/report/global-5g-device-market
Get in Touch
Interested in this topic? Contact our analysts for more details.
Latest Thought Articles

Top OSAT Companies Driving Semiconductor Assembly and Test Services Worldwide
Recently
EV Charging Stations Market Outlook: Smart Charging, Fast Charging, and Regional Expansion
Recently
Future of Corporate Wellness: Global Trends and Regional Outlook
Recently
Regional Breakdown of the Mechanical Keyboard Market: Who Leads and Why?
Recently