Report Overview
Global Synthetic Vinegar Market Highlights
Synthetic Vinegar Market Size:
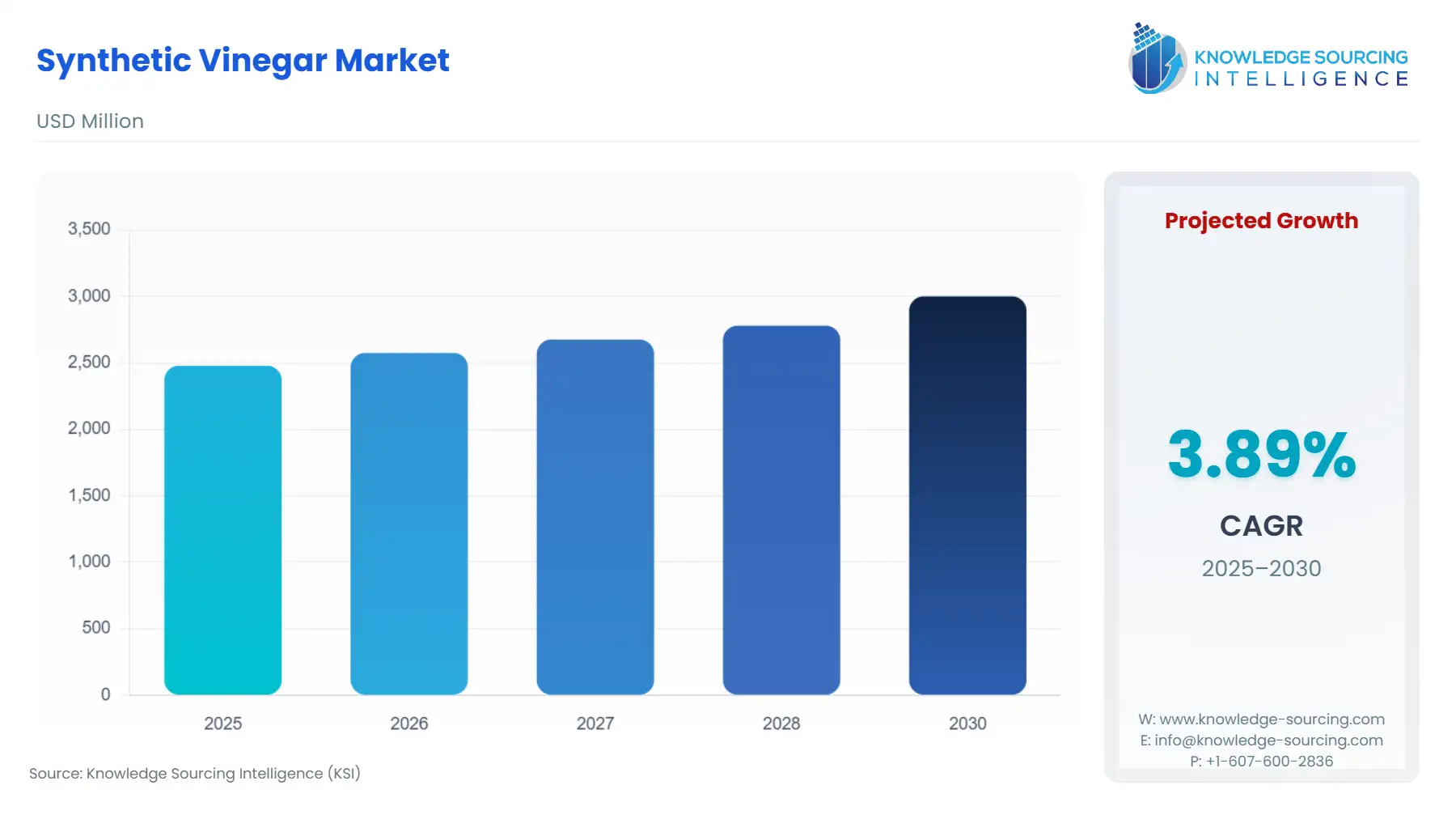
The global synthetic vinegar market is anticipated to increase at a CAGR of 3.89% during the forecasted period and account for US$2,479.949 million in 2025, increasing to US$3,001.822 million in 2030.
The synthetic vinegar market, a critical segment of the broader acetic acid market, is experiencing robust growth driven by its cost-effectiveness and versatile applications in food processing, industrial cleaning, and agriculture. Synthetic vinegar, primarily composed of diluted acetic acid derived from petrochemical sources or fermented alcohol, serves as a cost-efficient alternative to naturally fermented vinegar. Unlike traditional vinegar produced through double fermentation of agricultural materials, synthetic vinegar offers consistent acidity and extended shelf life, making it a preferred choice for industrial vinegar applications, food preservatives, and cleaning vinegar. Its widespread use spans food and beverage, household cleaning, and non-food sectors like organic pesticides, aligning with global trends toward affordable and sustainable solutions.
Synthetic vinegar is produced through chemical synthesis, typically by oxidizing ethanol to acetaldehyde and then to acetic acid, which is diluted to achieve standardized acidity levels, often 5-10% for food-grade applications. It is widely used as white vinegar in culinary applications like pickling, sauces, and dressings, and as cleaning vinegar due to its antimicrobial properties. The acetic acid market underpins this growth, with synthetic vinegar offering a lower-cost alternative to fermented vinegars derived from apples, grapes, or grains. Its neutral flavor and consistent quality make it ideal for large-scale food preservative applications in processed foods, such as condiments and canned goods, and for industrial vinegar uses in cleaning and chemical manufacturing. Recent industry developments highlight the market’s momentum. These innovations reflect the market’s focus on scalability, cost efficiency, and sustainability, positioning synthetic vinegar as a staple in both industrial and consumer applications. Several factors propel the market’s growth:
Cost Efficiency in Food Processing: Synthetic vinegar’s lower production costs drive its adoption as a food preservative in sauces, pickles, and condiments, especially in Asia-Pacific markets like China and India.
Growth in Cleaning Applications: The demand for eco-friendly cleaning vinegar fuels market expansion, with white vinegar used as a natural disinfectant in households and commercial settings.
Industrial Applications: Industrial vinegar supports non-food uses like organic pesticides and chemical synthesis, driven by sustainability trends.
Global Food Industry Expansion: Rising demand for processed foods increases the need for diluted acetic acid as a reliable food preservative.
Despite growth, the market faces challenges:
Regulatory Restrictions: In regions like Europe, regulations (e.g., EU Regulation No 583/2012) restrict labeling synthetic vinegar as “vinegar” in retail, limiting consumer market penetration.
Consumer Preference for Natural Products: Health-conscious consumers favor fermented vinegars for perceived health benefits, challenging synthetic vinegars in retail settings.
How Does Synthetic Vinegar Compare to Natural Vinegar?
Synthetic vinegar and natural vinegar differ significantly in production, composition, and application, impacting their suitability for various uses. Synthetic vinegar, primarily diluted acetic acid, is produced through chemical synthesis, often starting with ethanol oxidation to acetaldehyde, followed by bacterial fermentation or direct synthesis from petrochemical sources. This process yields a product with consistent acidity (typically 5-10%) and a neutral flavor, lacking the bioactive compounds like polyphenols found in natural vinegars. For example, white vinegar, a common form of synthetic vinegar, is widely used as a food preservative due to its uniform quality and cost-effectiveness, with production costs 40-60% lower than fermented vinegars. Its extended shelf life (often over 24 months unopened) and predictable performance make it ideal for industrial vinegar applications, such as large-scale food processing and cleaning vinegar for disinfecting surfaces. Natural vinegar, produced through double fermentation of agricultural materials like apples, grapes, or grains, contains trace compounds like vitamins (B1, riboflavin) and minerals, contributing to perceived health benefits. For instance, apple cider vinegar is marketed for digestion and weight management, driving its popularity in North America and Europe. However, natural vinegar’s production is slower, more resource-intensive, and subject to flavor variations, making it less suitable for standardized food preservative applications. Its shorter shelf life (6-12 months unopened for some varieties) and higher cost limit its use in industrial vinegar contexts compared to synthetic vinegar. In the food and beverage industry, synthetic vinegar dominates due to its affordability and consistency, critical for products like pickles and sauces. In contrast, natural vinegars are preferred in premium culinary applications, such as gourmet dressings, where flavor complexity is valued. For cleaning vinegar, synthetic vinegar’s high acidity and low cost make it a go-to choice, while natural vinegars are less common due to cost and residue concerns. Safety-wise, both are generally safe, but some regions, like the Philippines, restrict diluted acetic acid sales as vinegar due to potential health risks if improperly formulated. Overall, synthetic vinegar excels in cost-driven, high-volume applications, while natural vinegar appeals to health-conscious and premium markets.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Overview & Scope:
Synthetic vinegar is a type of vinegar that is prepared chemically, initially with ethanol oxidation to convert to acetaldehyde, which then changes to acetic acid by bacterial fermentation. The product formed after this process can be diluted to the desired concentration for diverse applications. It is used as an alternative to naturally produced fermented vinegar. They are increasingly used in diverse sectors, especially food processing, as they are cost-effective, provide longer shelf life, and are available in simpler quality than naturally produced vinegar. Synthetic vinegar is gaining traction in the food industry for applications in sauces, condiments, and pickled products. Its consistent acidity and lower production costs make it ideal for large-scale food manufacturing. Food producers are increasingly using synthetic acetic acid-based vinegar as a cost-effective preservative to extend shelf life while maintaining safety. Synthetic vinegar is seeing rising demand in non-food industries, such as agriculture, where it serves as an organic pesticide, reducing reliance on synthetic chemical fertilizers amid growing environmental concerns. Additionally, it is used in industrial cleaning products as a biodegradable, cost-effective alternative, broadening the market's growth potential. The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets for synthetic vinegar, fueled by urbanization and industrialization in countries like South Africa and the UAE. The region's growing population, coupled with increasing demand for affordable food preservatives, industrial cleaning agents, and agricultural applications, is driving market growth. Some of the major players covered in this report include Mohan Meakin Group, HIC-ABF Special Foods Pvt Ltd, Morton Foods Limited, Pou Chong Foods Pvt. Ltd., and Al-Amin Foods, among others.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Trends:
Integration of Multi-Modal Natural Language Processing
The synthetic vinegar market is experiencing robust growth, driven by its cost-effective preservative properties and consistent quality in diverse applications. Synthetic vinegar, produced through the chemical synthesis of acetic acid, offers a reliable, low-cost alternative to natural vinegar, particularly in the B2B vinegar market. Its uniform acidity and extended shelf life make it ideal for industrial applications of vinegar, such as food preservation in sauces, pickles, and processed foods. The industrial applications of vinegar also extend to cleaning solutions and organic pesticides, enhancing sustainability. The B2B vinegar market thrives in regions like Asia-Pacific, where rapid industrialization drives demand for consistent quality products. Innovations in chemical synthesis of acetic acid further bolster efficiency and eco-friendly production, solidifying synthetic vinegar’s market dominance.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Growth Drivers vs. Challenges:
Drivers:
Expansion of the Food Processing Industry: The synthetic vinegar market is significantly driven by the growing food processing industry, where synthetic vinegar serves as a cost-effective preservative in condiments and sauces and the pickle industry. Its consistent acidity and affordability make it ideal for large-scale production of processed foods like ketchup, mayonnaise, and pickled vegetables. Synthetic vinegar ensures consistent quality, critical for standardized food products, and its low cost supports scalability in the B2B vinegar market. The global rise in processed food consumption, particularly in emerging economies, fuels this driver, as manufacturers rely on diluted acetic acid to extend shelf life and enhance flavor profiles in a variety of culinary applications.
Further, The demand for eco-friendly industrial cleaning solutions is a key driver for the synthetic vinegar market, with white vinegar widely used as a natural disinfectant in commercial and household settings. Its antimicrobial properties and low cost make it a preferred alternative to chemical cleaners, aligning with sustainability trends. Synthetic vinegar’s versatility in cleaning applications, from surface disinfection to descaling, drives its adoption in industries like hospitality and manufacturing. The B2B vinegar market benefits from this trend, as businesses prioritize cost-effective, green alternatives, particularly in North America and Europe, where environmental regulations encourage the use of cleaning vinegar over harsher chemicals. Additionally, the synthetic vinegar market is bolstered by its expanding role in agricultural pesticides and other non-food applications. Synthetic vinegar, derived from the chemical synthesis of acetic acid, is used as an organic herbicide and soil conditioner, offering a sustainable alternative to synthetic pesticides. This driver is fueled by the global shift toward eco-friendly farming practices, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America, where agricultural pesticides based on diluted acetic acid are gaining traction. Industrial vinegar is used in chemical manufacturing and textile processing, further driving market growth as industries seek cost-effective, versatile solutions to meet regulatory and environmental demands.
Challenges:
Regulatory Restrictions on Labeling and Use: The synthetic vinegar market faces challenges from stringent regulations, particularly in regions like Europe, where labeling synthetic vinegar as “vinegar” for retail sale is restricted under EU Regulation No 583/2012. This limits market penetration in consumer-facing segments like condiments and sauces, as synthetic vinegar must be clearly distinguished from naturally fermented vinegars. In some countries, such as the Philippines, regulations restrict diluted acetic acid sales as food-grade vinegar due to potential health concerns if improperly formulated, impacting the B2B vinegar market. These regulatory hurdles increase compliance costs and complicate marketing, restraining growth in regions with strict food and labeling standards.
Consumer Preference for Natural and Fermented Vinegars: A significant restraint for the synthetic vinegar market is the growing consumer preference for natural, fermented vinegars, driven by perceived health benefits and flavor complexity. Natural vinegars, such as apple cider vinegar, are marketed for wellness properties, like aiding digestion, which synthetic vinegar lacks due to its absence of bioactive compounds. This trend challenges synthetic vinegar in retail markets for condiments and sauces and the pickle industry, particularly in North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers favor organic and artisanal products. The preference for natural alternatives limits synthetic vinegar’s market share in consumer-facing applications, despite its consistent quality and cost advantages, pushing manufacturers to focus on industrial applications of vinegar to maintain competitiveness.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Segmentation Analysis:
The need for Acetic Acid-Based Synthetic Vinegar is increasing significantly
Acetic acid-based synthetic vinegar leads the synthetic vinegar market due to its widespread use and cost-effective production through the chemical synthesis of acetic acid. This type, often referred to as white vinegar, is produced by oxidizing ethanol or synthesizing acetaldehyde into acetic acid, diluted to achieve consistent acidity levels (typically 5-10%). Its consistent quality makes it ideal for food processing, including condiments and sauces, and the pickle industry, as well as industrial cleaning solutions. Its affordability and versatility drive its dominance, particularly in the B2B vinegar market, where scalability and uniformity are critical.
By Application, the Food and Beverages sector is expected to grow considerably
The food and beverages segment dominates the synthetic vinegar market, driven by its role as a cost-effective preservative in vinegar in food processing. Acetic acid-based synthetic vinegar is extensively used in condiments and sauces, the pickle industry, and other processed foods like canned goods, due to its reliable acidity and extended shelf life. For instance, Celanese Corporation expanded acetic acid production in China, targeting food and beverage applications to meet demand for cost-effective preservatives. The segment’s growth is fueled by rising global consumption of processed foods, particularly in the Asia-Pacific, where synthetic vinegar ensures consistent quality in large-scale production.
By Distribution Channel, the Business-to-Business (B2B) segment is growing notably
The business-to-business (B2B) channel is the leading distribution segment in the synthetic vinegar market, driven by high demand from food manufacturers, cleaning product suppliers, and agricultural sectors. B2B vinegar market transactions involve bulk supply of acetic acid-based synthetic vinegar for industrial applications of vinegar, including food processing and industrial cleaning solutions. The B2B channel’s dominance stems from the need for cost-effective, high-volume synthetic vinegar to meet industrial demands, particularly in emerging markets.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Key Developments:
In April 2024, Celanese Corporation expanded its acetic acid production capacity in China, focusing on synthetic vinegar for cost-effective preservative applications in the B2B vinegar market. The expansion targets growing demand for industrial applications of vinegar in processed foods, reinforcing consistent quality for large-scale food manufacturers in the Asia-Pacific.
Synthetic Vinegar Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2025 | 2,479.949 million |
| Total Market Size in 2030 | 3,001.822 million |
| Forecast Unit | Million |
| Growth Rate | 3.89% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Segmentation | Type, Application, Distribution Channel, Region |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Synthetic Vinegar Market Segmentation:
By Type
Acetic Acid-Based Synthetic Vinegar
Diluted Glacial Acetic Acid
Blended Synthetic Vinegar
By Application
Food and Beverages
Cleaning Product
Others
By Distribution Channel
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
By Region
North America
USA
Canada
Mexico
South America
Brazil
Argentina
Others
Europe
United Kingdom
Germany
France
Italy
Spain
Others
Middle East & Africa
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Others
Asia Pacific
China
India
Japan
South Korea
Taiwan
Thailand
Others