Report Overview
Advanced Battery Market - Highlights
Advanced Battery Market Size:
The Advanced Battery Market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.18%, reaching USD 158.565 billion in 2030 from USD 85.396 billion in 2025.
The advanced battery market is at the nexus of several transformational shifts in global energy and mobility. The imperative to decarbonize transportation and modernize electrical grids has created an unprecedented demand for sophisticated energy storage solutions. This requirement is not merely for increased capacity but for batteries that offer higher energy density, faster charging times, enhanced safety, and a longer lifecycle. The market's evolution is a direct response to these technical and operational demands, moving beyond conventional battery types to embrace a new generation of technologies.
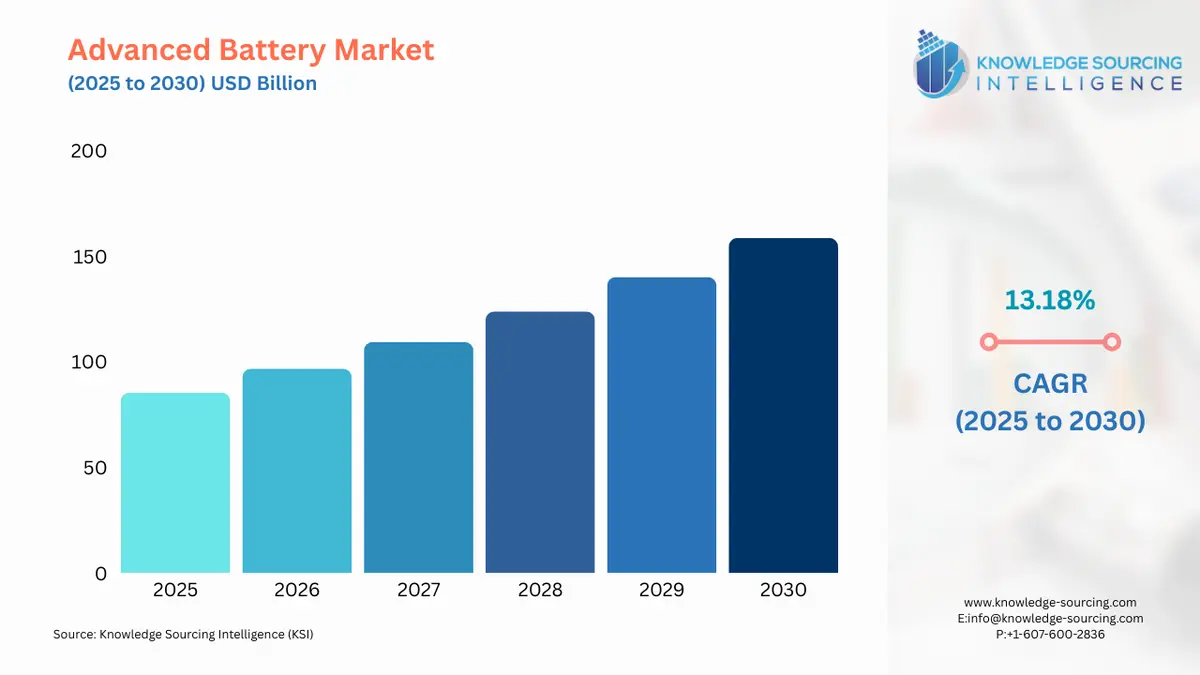
Advanced Battery Market Analysis
Growth Drivers
The advanced battery market's growth is fundamentally driven by a confluence of technological, economic, and regulatory factors that create a direct and sustained increase in demand. The most significant driver is the rapid global adoption of electric vehicles. Governments worldwide are implementing ambitious targets and regulations to phase out internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. For example, the European Union's Green Deal and various national policies championing zero-emission vehicles are directly catalyzing the demand for high-performance, long-range batteries. This shift requires batteries with superior energy density, faster charging capabilities, and improved longevity, thereby pushing the market to innovate and scale production of technologies like high-nickel lithium-ion and, eventually, solid-state batteries.
The market is also significantly propelled by the integration of renewable energy sources into electrical grids. The intermittent nature of solar and wind power necessitates large-scale, reliable energy storage systems to ensure grid stability and a continuous power supply. This has led to a surge in demand for utility-scale stationary energy storage solutions. These systems, often comprising thousands of advanced battery modules, are critical for balancing the grid and are directly mandated by utility companies and regulatory bodies as a prerequisite for new renewable energy projects. Consequently, this creates a new, massive demand segment for the advanced battery market, particularly for technologies like flow batteries and large-format lithium-ion systems designed for long-duration storage.
Challenges and Opportunities
The advanced battery market faces significant challenges, primarily related to its supply chain and raw material dependency. The volatility in the pricing and supply of critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel poses a direct headwind to demand by increasing production costs and, consequently, the final price of battery packs. The concentration of mineral mining and refining, particularly for cobalt and graphite, in a small number of countries creates a geopolitical risk and potential supply bottlenecks. These constraints can slow down the deployment of electric vehicles and energy storage projects, thereby curbing demand.
However, these challenges also present distinct opportunities. The demand for greater supply chain resilience and cost reduction has spurred innovation in alternative battery chemistries. The development and commercialization of cobalt-free batteries, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP), directly responds to the high cost and ethical concerns associated with cobalt mining. Similarly, the emergence of sodium-ion batteries presents a significant opportunity. As a non-lithium technology, it offers a pathway to a more geographically diverse and less expensive supply chain, potentially opening up new low-cost applications and a more stable demand environment. Furthermore, the imperative to mitigate raw material risks has created an opportunity for the development of robust battery recycling and "second-life" applications, which could establish a circular economy, reduce reliance on virgin materials, and create a new revenue stream.
Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
The advanced battery market, particularly for lithium-ion batteries, is inextricably linked to the supply and pricing of key raw materials. The primary components are lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese, and graphite. The price of lithium, a foundational material, is subject to significant volatility influenced by mining output, refining capacity, and global demand from the EV and electronics sectors. Similarly, cobalt, a material historically critical for high-energy-density cathodes, has seen price fluctuations due to its concentrated supply chain, with a substantial portion of the world's reserves located in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Nickel pricing is also a major factor, especially for nickel-rich cathodes that offer higher energy density, as its price is tied to broader industrial demand and market speculation. The price dynamics of these raw materials directly impact the final cost of a battery cell, influencing the affordability of end-user products and, by extension, market growth.
Supply Chain Analysis
The global advanced battery supply chain is a multi-tiered, complex network characterized by a high degree of geographical concentration. It begins with the extraction of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and graphite, primarily from a few countries, including Australia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and China. These raw materials are then transported to specialized refining and processing facilities, most of which are located in China. This refining bottleneck represents a critical point of vulnerability. From there, processed materials are used to manufacture key battery components, including cathodes, anodes, and separators. The final assembly of battery cells and packs is also heavily concentrated in Asia-Pacific, particularly in China, South Korea, and Japan. This centralized structure creates significant logistical complexities and dependencies, making the supply chain susceptible to geopolitical tensions, trade policies, and unexpected disruptions. The lack of a diversified global supply chain poses a risk to consistent production and can impact the responsiveness of the market to sudden changes in demand.
Government Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies are playing an increasingly active role in shaping the advanced battery market. Regulations and policy frameworks are designed to accelerate the transition to sustainable energy and electric mobility while also addressing environmental and supply chain concerns. These regulations directly influence market growth by creating incentives, setting standards, and mandating collection and recycling efforts.
| Jurisdiction | Key Regulation / Agency | Market Impact Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | EU Battery Regulation (2023) | This comprehensive regulation establishes strict rules for battery collection, recycling, and material recovery. It mandates the use of a "digital battery passport" to provide information on material content and carbon footprint, thereby increasing transparency and driving demand for sustainably sourced materials and recycling infrastructure. It directly creates a market for second-life batteries and mandates a circular economy approach, which changes the total cost of ownership and demand for new vs. recycled materials. |
| United States | Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 | The IRA provides significant tax credits and incentives for electric vehicles and battery manufacturing, specifically mandating that a percentage of battery components be manufactured or assembled in North America and that critical minerals be sourced from the U.S. or its free-trade partners. This policy is a direct catalyst for shifting investment and demand for battery production capacity from Asia to North America, fundamentally altering the global supply chain landscape. |
| China | "Made in China 2025" and EV Subsidy Policies | These policies, while evolving, have historically provided substantial subsidies for EV purchases and prioritized domestic battery production. This has created a massive domestic market for both EVs and batteries, solidifying China's position as a global leader in both demand and manufacturing. The policies have accelerated the scale and efficiency of Chinese battery production, enabling them to meet both domestic and international demand. |
Advanced Battery Market Segmentation Analysis:
- By Application: Automotive
The automotive segment stands as the preeminent demand driver for advanced batteries. This is directly attributable to the global pivot towards electrification, catalyzed by both government mandates and evolving consumer preferences. The demand within this segment is not homogeneous; it is highly differentiated by vehicle type. Passenger EVs, for instance, require batteries with high energy density to enable longer driving ranges and faster charging to alleviate "range anxiety." This has led to a sustained, high-volume demand for high-performance lithium-ion chemistries, such as those with high-nickel content (e.g., NMC 811). Furthermore, the commercial vehicle sector, including electric buses and trucks, is creating a distinct demand for batteries that prioritize durability, long cycle life, and safety under high-power charging and discharging cycles. This specialized demand profile is driving the development of robust, large-format battery packs and management systems. The requirement is not just for the battery itself but for an integrated system that can withstand the rigors of commercial use, thereby shaping the technological trajectory of the entire market.
- By Technology: Solid-State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are a transformative technology within the advanced battery landscape, poised to create a new wave of demand by addressing the inherent limitations of conventional liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries. The core demand driver for solid-state technology is its promise of a paradigm shift in performance, primarily in two key areas: safety and energy density. By replacing the flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid one, these batteries mitigate the risk of thermal runaway and fire, which is a significant selling point for manufacturers and consumers, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors. Furthermore, the solid-state design allows for the use of a lithium metal anode, which can theoretically increase energy density by a substantial margin compared to traditional graphite anodes. This higher energy density directly translates into lighter battery packs and longer driving ranges for EVs, thereby creating a strong pull from the automotive industry. As this technology matures, its commercial viability will directly influence future demand, as it offers a superior value proposition in terms of performance and safety, potentially cannibalizing demand from existing lithium-ion chemistries in high-end applications.
Advanced Battery Market Geographical Outlook:
- US Market Analysis
The U.S. advanced battery market is experiencing a significant surge in demand, largely fueled by federal and state-level policy interventions. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) is the single most influential policy, creating a powerful incentive for both the domestic production of EVs and the establishment of a localized battery supply chain. This has directly led to a flurry of announcements for new battery manufacturing plants (gigafactories) across the country. Consumer tax credits for EV purchases also drive demand, which is contingent on the vehicle's battery and its components meeting domestic content requirements. This creates a powerful demand signal for batteries that are manufactured within North America. Furthermore, a growing number of utility-scale energy storage projects, mandated to support the grid's integration of renewable energy, is also a major demand catalyst. - Brazil Market Analysis
Brazil's advanced battery market is emerging, with demand primarily driven by the country's unique energy and resource landscape. While EV adoption is still nascent compared to other regions, there is a growing demand for batteries in grid-scale energy storage, particularly to complement its extensive hydropower infrastructure and nascent solar and wind projects. The country is also a key player in the global lithium supply chain, with significant reserves. This resource abundance positions Brazil to become a more vertically integrated player in the future, potentially reducing its reliance on imports and fostering a domestic battery manufacturing ecosystem. The growth is currently limited by economic factors and a lack of widespread charging infrastructure, but is poised for growth as government policies and private investments in electrification gain momentum. - Germany Market Analysis
Germany is a pivotal market for advanced batteries in Europe, propelled by its powerful automotive industry and strong commitment to renewable energy. The need for advanced batteries is driven by the country's ambitious climate targets and the phasing out of ICE vehicles. German automakers are aggressively electrifying their fleets, which has created a massive and sustained demand for high-quality, high-performance batteries. Furthermore, government incentives for both EV purchases and the installation of residential and commercial energy storage systems are directly fueling demand. The country's strong industrial and research base is also a catalyst, attracting investment in next-generation battery technologies and recycling capabilities. - Saudi Arabia Market Analysis
The advanced battery market in Saudi Arabia is in its early stages but is poised for significant growth, driven by the Kingdom's "Vision 2030" economic diversification plan. The primary growth catalyst is the country's push to become a global leader in green hydrogen production and to increase the share of renewable energy in its power mix. This necessitates large-scale battery storage solutions to manage the intermittency of solar power, which the country is abundant in. Furthermore, the establishment of a domestic automotive industry, including the recent launch of a new EV brand, is expected to create a direct demand for battery manufacturing and assembly. While the market is currently small, strategic national projects and the shift away from oil-based energy are creating a long-term demand signal. - Japan Market Analysis
Japan is a mature and highly innovative market for advanced batteries, with demand historically concentrated in the consumer electronics and automotive sectors. The country has been a pioneer in lithium-ion battery technology and remains a key player in research and development. The growth is driven by a focus on high-performance batteries for hybrid and electric vehicles, as well as by the use of advanced batteries in residential and commercial energy storage systems to enhance grid resilience. Japan's aging population and focus on robotics and automation also create a niche but significant demand for specialized, long-life, and safe batteries. The market is characterized by a strong emphasis on technological excellence and a robust intellectual property landscape.
Advanced Battery Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape of the advanced battery market is dominated by a few major players, primarily from Asia-Pacific, who have established a significant lead in manufacturing scale and technological expertise. This environment is characterized by intense competition, continuous innovation, and strategic partnerships aimed at securing raw material supply and expanding production capacity.
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL)
CATL, based in China, has solidified its position as a global leader in advanced battery manufacturing, particularly for the electric vehicle segment. The company's strategic positioning is built on a massive production scale and a diverse product portfolio that includes lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) battery chemistries. CATL's official publications highlight its focus on technological innovation, including its "Cell-to-Pack" (CTP) technology, which improves energy density and simplifies battery pack design by directly integrating cells into the pack without a separate module. The company's success is a direct result of its ability to scale production rapidly to meet the burgeoning demand from the automotive sector, both domestically and internationally. - Panasonic Corporation
Panasonic is a key player in the advanced battery market, with a long history of supplying batteries to the automotive and consumer electronics sectors. The company's strategic focus is on delivering high-quality, high-performance batteries, with a notable long-standing partnership with Tesla. Panasonic's official newsroom details its commitment to developing next-generation battery technologies, including its cylindrical "4680" battery cell, designed to offer higher energy density and improved cost-efficiency. The company's competitive advantage lies in its technological expertise, stringent quality control, and its deep-rooted relationships with major automakers, which ensure a consistent and high-volume demand stream for its products. - Samsung SDI Co., Ltd.
Samsung SDI has established a strong presence in the market by focusing on batteries for electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and small-sized batteries for consumer electronics. The company's strategic approach involves a combination of large-scale manufacturing and a commitment to R&D for next-generation technologies. Samsung SDI's official press releases have detailed its development of solid-state batteries, signaling a strategic move to secure a leading position in future markets. The company's strong brand reputation and vertical integration with the broader Samsung Group give it a robust foundation to compete in a capital-intensive industry.
Advanced Battery Market Recent Developments:
- August 2024: Lyten, a company focused on lithium-sulfur batteries, entered into a binding agreement to acquire Northvolt's remaining assets in Sweden and Germany. The acquisition includes multiple gigafactories and a major R&D center, valued at around $5 billion. This strategic move aims to accelerate the commercialization of Lyten's lithium-sulfur battery technology by leveraging Northvolt's existing production capacity and infrastructure. The deal is expected to significantly bolster Lyten's ability to meet growing demand for its batteries in various sectors, including energy storage and electric vehicles.
- May 2024: Ion Storage Systems, a US-based startup, initiated the production of its innovative solid-state batteries. These new high-energy-density batteries are designed to be safer and more scalable than traditional lithium-ion batteries, as they do not require compression to function. The company's technology has received backing from the U.S. Department of Energy, and this move to production marks a significant step toward commercializing next-generation battery technology for various applications, including consumer electronics and electric vehicles.
Advanced Battery Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Advanced Battery Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.357 billion |
| Advanced Battery Market Size in 2030 | USD 2.859 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 16.07% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Billion |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Advanced Battery Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Advanced Battery Market Segmentation:
- By Technology
- Lithium-ion Batteries
- Lead-acid Batteries
- Solid-state Batteries
- Nickel-metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
- Flow Batteries
- Sodium-ion Batteries
- Others
- By Application
- Automotive (Electric Vehicles, Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles)
- Energy Storage Systems (Residential, Commercial & Industrial, Utility-scale)
- Consumer Electronics (Smartphones, Laptops, Wearables)
- Industrial (Motive Power, Stationary)
- Medical
- Aerospace & Defense
- Others
- By End-User
- Automotive
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Utility
- Others
- By Region:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- South America
- Middle East & Africa
Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Navigation:
- Advanced Battery Market Size:
- Advanced Battery Market Key Highlights
- Advanced Battery Market Analysis
- Advanced Battery Market Segmentation Analysis:
- Advanced Battery Market Geographical Outlook:
- Advanced Battery Market Competitive Analysis:
- Advanced Battery Market Recent Developments:
- Advanced Battery Market Scope:
- Our Best-Performing Industry Reports:
Page last updated on: September 17, 2025