Report Overview
Agricultural Enzymes Market Size, Highlights
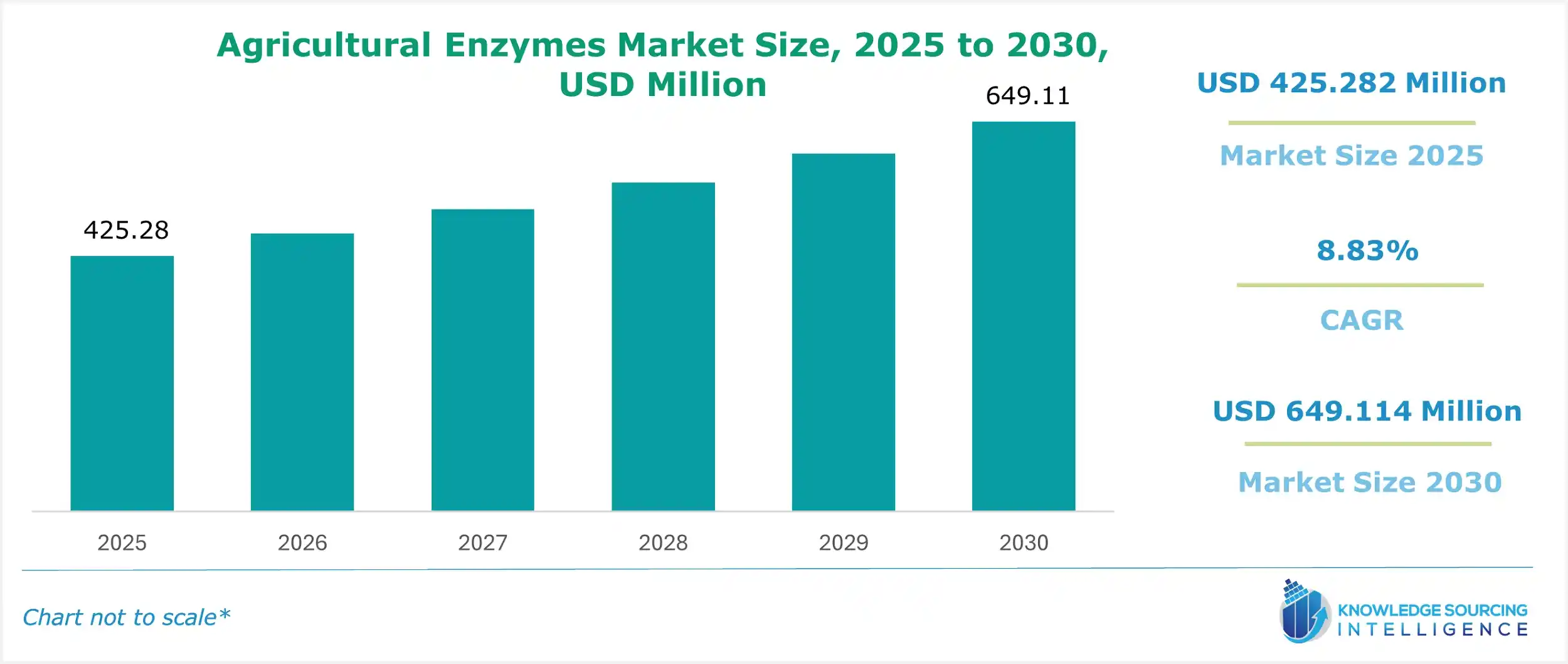
Agricultural Enzymes Market Size:
The agricultural enzymes market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.83% from USD 425.282 million in 2025 to USD 649.114 million in 2030.
The agricultural enzymes market is a dynamic and evolving segment of the global agricultural industry, centered on utilizing specialized biological catalysts—enzymes—to enhance various farming processes. Naturally occurring proteins known as enzymes play a vital role in speeding up biochemical reactions in plants, soil, and livestock feed. They offer sustainable and efficient alternatives to conventional synthetic agrochemicals. As the global agricultural sector seeks to increase food production while reducing environmental impact, enzymes have become essential for enhancing crop yields, improving soil health, and boosting livestock productivity. Their adoption reflects a broader shift towards sustainable farming practices, driven by the need to address challenges such as nutrient depletion, pest resistance, environmental degradation, and the increasing demand for organic produce.
Enzymes are specific proteins that catalyze chemical reactions without being consumed. In agriculture, they optimize processes that directly impact crop growth, soil fertility, and animal nutrition. Their primary applications include soil management, crop protection, and feed efficiency enhancement. In soil management, enzymes such as cellulases, amylases, and ureases are vital in breaking down complex organic matter, such as plant residues and compost, into simpler compounds that release essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This process enhances soil fertility, improves water retention, and promotes microbial activity, creating a healthier environment for plant growth. For instance, urease enzymes facilitate the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide, making nitrogen more accessible to plants. Similarly, cellulases degrade cellulose in plant matter, aiding in nutrient cycling and soil structure improvement.
In crop protection, enzymes like proteases and chitinases provide a natural method for managing pests and diseases. Proteases degrade proteins in pest cuticles or pathogen cell walls, weakening their structural integrity and reducing their impact on crops. Chitinases break down chitin in fungal cell walls and insect exoskeletons, providing an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, aligning with the growing demand for organic and residue-free produce. These enzyme-based solutions reduce the environmental footprint of farming by minimizing the use of synthetic chemicals, which can accumulate in soil and water systems, causing long-term ecological harm.
In livestock production, enzymes such as phytases, amylases, and proteases are incorporated into animal feed to enhance nutrient bioavailability. For example, phytases decompose phytic acid in grains, liberating bound phosphorus and other minerals that would otherwise be indigestible to monogastric animals such as poultry and swine. This improves feed efficiency, reduces the need for supplemental minerals, and lowers phosphorus excretion, which can contribute to environmental pollution in water bodies. By enhancing nutrient absorption, enzymes lower feed costs for livestock farmers while promoting animal health and growth.
Several major factors drive the agricultural enzymes market. First, the global population, anticipated to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, is raising the demand for food production, necessitating innovative solutions to boost agricultural productivity. Enzymes enable farmers to achieve higher yields without expanding arable land, which is increasingly scarce. Second, the growing consumer preference for organic and sustainably produced food is driving demand for enzyme-based solutions, as they are considered safer and more environmentally friendly than chemical alternatives. Third, advancements in biotechnology, particularly in microbial fermentation and genetic engineering, have enabled the development of highly efficient and cost-effective enzyme formulations tailored to specific crops, climates, and soil types. These innovations have expanded the accessibility of enzymes, even in regions with limited resources. Regulatory pressures to reduce chemical fertilizers and pesticides are prompting farmers to adopt enzyme-based alternatives, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations like the European Union.
Despite its potential, the agricultural enzymes market has several restraints. The high cost of enzyme production, driven by complex manufacturing processes like microbial fermentation, can limit adoption, particularly among smallholder farmers in developing regions. Moreover, limited awareness and technical knowledge about enzyme applications create obstacles, as many farmers may not have access to training or extension services. Regulatory variations across countries may complicate market expansion, as enzyme products must meet diverse safety and efficacy standards. Furthermore, the efficacy of enzymes can be influenced by environmental factors such as soil pH, temperature, and moisture, requiring careful application to achieve optimal results. These challenges are being addressed through ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving enzyme stability and reducing production costs.
The future of the agricultural enzymes market is promising, with ongoing innovations poised to overcome current limitations. Advances in genetic engineering are making it possible to create enzymes that have enhanced specificity and are more resilient to environmental stressors. Furthermore, improvements in microbial fermentation technologies are lowering production costs, making enzymes more accessible to farmers worldwide. The integration of enzymes with precision agriculture technologies, such as sensor-based soil monitoring, is also enhancing their effectiveness by enabling targeted applications. As the global agricultural sector prioritizes sustainability and efficiency, the agricultural enzymes market is expected to play a pivotal role in supporting food security while mitigating environmental impact.
Agricultural Enzymes Market Drivers:
- Increasing demand for food worldwide
The global population is projected to reach approximately 9.7 billion by 2050, significantly increasing the demand for food production. This demographic pressure, shrinking arable land due to urbanization, soil degradation, and climate change, necessitates innovative solutions to maximize agricultural output. Agricultural enzymes solve this challenge by enhancing crop yields and improving resource efficiency. For instance, enzymes like cellulases and ureases improve soil fertility by breaking down organic matter, releasing essential nutrients that boost plant growth. This enables farmers to increase their productivity without expanding cultivated land, which is crucial in areas where land is limited. Furthermore, enzymes found in livestock feed, like phytases, improve nutrient absorption, allowing farmers to produce more meat, milk, and eggs while using fewer resources. Enzymes can enhance crop and livestock production, making them essential in addressing global food security challenges.
- Rising Preference for Sustainable and Organic Farming Practices
Consumer awareness of environmental and health concerns has driven a surge in demand for organic and sustainably produced food. Enzymes offer a natural, eco-friendly alternative to synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, aligning with this trend. For example, enzymes like chitinases and proteases provide biological pest control by targeting pest and pathogen structures, reducing the need for chemical pesticides that can leave harmful residues in food and the environment. Similarly, enzyme-based soil conditioners enhance nutrient availability without the environmental drawbacks of chemical fertilizers, such as groundwater contamination or soil acidification. The organic farming sector, which is growing rapidly in regions like North America and Europe, relies heavily on such biological solutions to meet certification standards. Furthermore, enzymes contribute to sustainable practices by improving soil health and reducing waste in livestock production, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and farmers alike.
- Advancements in Biotechnological Research
Recent breakthroughs in biotechnology, especially in microbial fermentation and genetic engineering, have transformed the agricultural enzymes market. These advancements have led to the creation of highly specific, efficient, and cost-effective enzyme formulations that cater to various agricultural needs. For instance, genetic engineering enables scientists to modify microorganisms to produce enzymes that have improved stability and activity under different environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or varying soil pH levels. Microbial fermentation techniques have also scaled up enzyme production, reducing costs and making these products more accessible to farmers worldwide. Biotechnology has enabled the development of enzyme blends tailored for specific crops, such as cereals, legumes, or fruits, and suited for regions with distinct climatic or soil conditions. These innovations improve the efficacy of enzymes and expand their applicability, driving adoption across both large-scale and smallholder farming operations.
- Regulatory Pressures to Decrease Chemical Inputs
Stringent regulations in many regions, particularly in the European Union, North America, and parts of Asia, are encouraging farmers to minimize the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides due to their environmental and health impacts. For example, chemical runoff from fertilizers can cause eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems, while pesticide residues pose risks to both biodiversity and human health. Enzymes offer an environmentally friendly alternative, as they are biodegradable and have minimal ecological impacts. Regulatory bodies in these regions often incentivize or mandate the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices, creating a favorable environment for enzyme-based products. For example, the European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy emphasizes reducing chemical pesticide use by 50% by 2030, encouraging the adoption of biological solutions like enzymes. This regulatory push is driving investment in enzyme research and development, further fueling market growth.
- Need for Cost-Effective Livestock Production
Livestock farming is a resource-intensive industry, where feed costs represent a significant part of operational expenses. Enzymes like phytases, amylases, and proteases enhance feed efficiency by breaking down complex nutrients, enabling animals to extract more energy and nutrients from their diet. This reduces the need for costly feed supplements and lowers overall production costs. Furthermore, enzymes such as phytases help to decrease the phosphorus excretion in livestock waste, reducing environmental pollution and aligning with regulations designed to minimize agricultural runoff. As the global demand for animal protein rises, especially in developing economies, the use of enzymes in livestock feed is increasingly seen as a vital strategy for optimizing costs and ensuring environmental compliance.
Agricultural Enzymes Market Restraints:
- High Production Costs
The production of agricultural enzymes involves complex and resource-intensive processes, such as microbial fermentation and purification, significantly increasing costs. These processes require specialized equipment, controlled environments, and high-quality raw materials, making enzyme production more expensive than traditional chemical fertilizers and pesticides. For small farmers, especially in developing regions, the cost of enzyme-based products can be too high, making them difficult to access. Although advancements in biotechnology, like optimized fermentation techniques, are slowly lowering these costs, the initial investments needed for research, development, and large-scale production continue to pose a significant barrier. Furthermore, the requirement for specific storage and transportation conditions, such as temperature control to ensure enzyme stability, adds to the overall expenses, making these products less affordable for farmers in resource-limited areas.
- Limited Awareness and Technical Knowledge Among Farmers
Another significant market restraint is the lack of awareness and technical expertise among farmers, particularly in developing countries and rural areas. Many small-scale farmers are unfamiliar with the benefits and applications of enzymes, often relying on traditional farming practices or chemical inputs due to their familiarity and perceived reliability. The effective use of enzymes requires understanding specific application methods, such as optimal timing, dosage, and soil conditions, which demand training and extension services. Access to educational resources is often limited in regions with underdeveloped agricultural infrastructure. Without sufficient knowledge transfer, farmers may be reluctant to adopt enzyme-based solutions, which could slow market penetration and growth.
- Varying Regulatory Frameworks Across Regions
The agricultural enzymes market is subject to diverse regulatory standards across countries, creating challenges for manufacturers and distributors. Enzymes used in agriculture must meet stringent safety, efficacy, and environmental standards, which vary significantly by region. For example, the European Union has rigorous approval processes for biological products, requiring extensive testing to ensure they pose no risk to human health or the environment. In contrast, the regulatory frameworks in some developing countries are often less clearly defined, which can lead to delays in product approvals and inconsistent enforcement. These variations complicate market entry, increase compliance costs, and create uncertainty for companies looking to expand globally. Streamlining approval processes or harmonizing regulations could help alleviate these challenges, but such changes tend to occur slowly.
- Environmental Sensitivity of Enzymes
The efficacy of agricultural enzymes is highly dependent on environmental conditions, such as soil pH, temperature, moisture levels, and microbial activity, which can limit their performance. For instance, enzymes like ureases or cellulases may lose activity in extreme temperatures or highly acidic or alkaline soils, reducing their effectiveness. Farmers must be attentive when applying enzymes due to their sensitivity to environmental conditions. This monitoring can be particularly difficult in areas with unpredictable weather or limited access to precision agriculture tools. Moreover, enzymes typically require more frequent applications compared to chemical alternatives, as their effectiveness tends to decrease over time in specific environments. This environmental dependency complicates their use and may deter farmers who prefer more stable, predictable chemical inputs.
Agricultural Enzymes Market Segmentation Analysis:
- The carbohydrate segment is growing significantly
Carbohydrases, including amylases, cellulases, and xylanases, are the leading enzyme types due to their versatility in soil fertility, crop growth, and livestock feed applications. These enzymes break down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, enhancing nutrient availability. In soil management, cellulases decompose plant residues, releasing carbon and nitrogen, improving soil structure, and promoting microbial activity. In livestock feed, xylanases enhance nutrient digestibility in grains, reducing feed costs and waste. Their eco-friendly nature and alignment with sustainable farming practices, combined with biotechnological advancements, make carbohydrates the dominant enzyme type.
- The rising consumption of cereals is expanding its market growth
Cereals, such as wheat, rice, corn, and barley, dominate the crop type segment due to their global economic importance as staple crops. Enzymes like cellulases and ureases enhance soil fertility for cereal production by releasing essential nutrients, while proteases and chitinases provide biological pest control, supporting residue-free grains. The high nutrient demands of cereals and their use in food, feed, and biofuels drive enzyme demand. Extensive cultivation in major agricultural regions further solidifies cereals as the leading crop type.
- The North American market is growing considerably
North America, led by the United States and Canada, is the dominant geographic segment due to its advanced agricultural infrastructure and regulatory support for sustainable practices. Enzymes play a crucial role in enhancing soil fertility and managing organic pest control for crops such as corn and soybeans. In Canada, enzymes are utilized to promote soil health, especially in challenging climates. The country's advancements in biotechnology, along with strong extension services, encourage the adoption of enzymes, further solidifying North America’s leadership in this market.
List of Top Agricultural Enzymes Companies:
- Novozymes A/S
- BASF SE
- Corteva Inc.
- Syngenta AG
- Elemental Enzymes Inc.
Agricultural Enzymes Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Agricultural Enzymes Market Size in 2025 | USD 425.282 million |
| Agricultural Enzymes Market Size in 2030 | USD 649.114 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 8.83% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in the Agricultural Enzymes Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Agricultural Enzymes Market Segmentation:
By Type
- Phosphatases
- Ureases
- Dehydrogenases
- Proteases
- Others
By Sources
- Microbial-based
- Plant-based
- Animal-based
By Formulation
- Liquid
- Solid
By Crop Type
- Cereals & Grains
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Oilseeds & Pulses
- Turf & Ornamentals
By Region
- North America
- USA
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Others
- Europe
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- Others
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Others