Report Overview
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Highlights
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Size:
The Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market is forecast to advance at a CAGR of 24.11%, attaining USD 3.322 billion in 2030 from USD 1.128 billion in 2025.
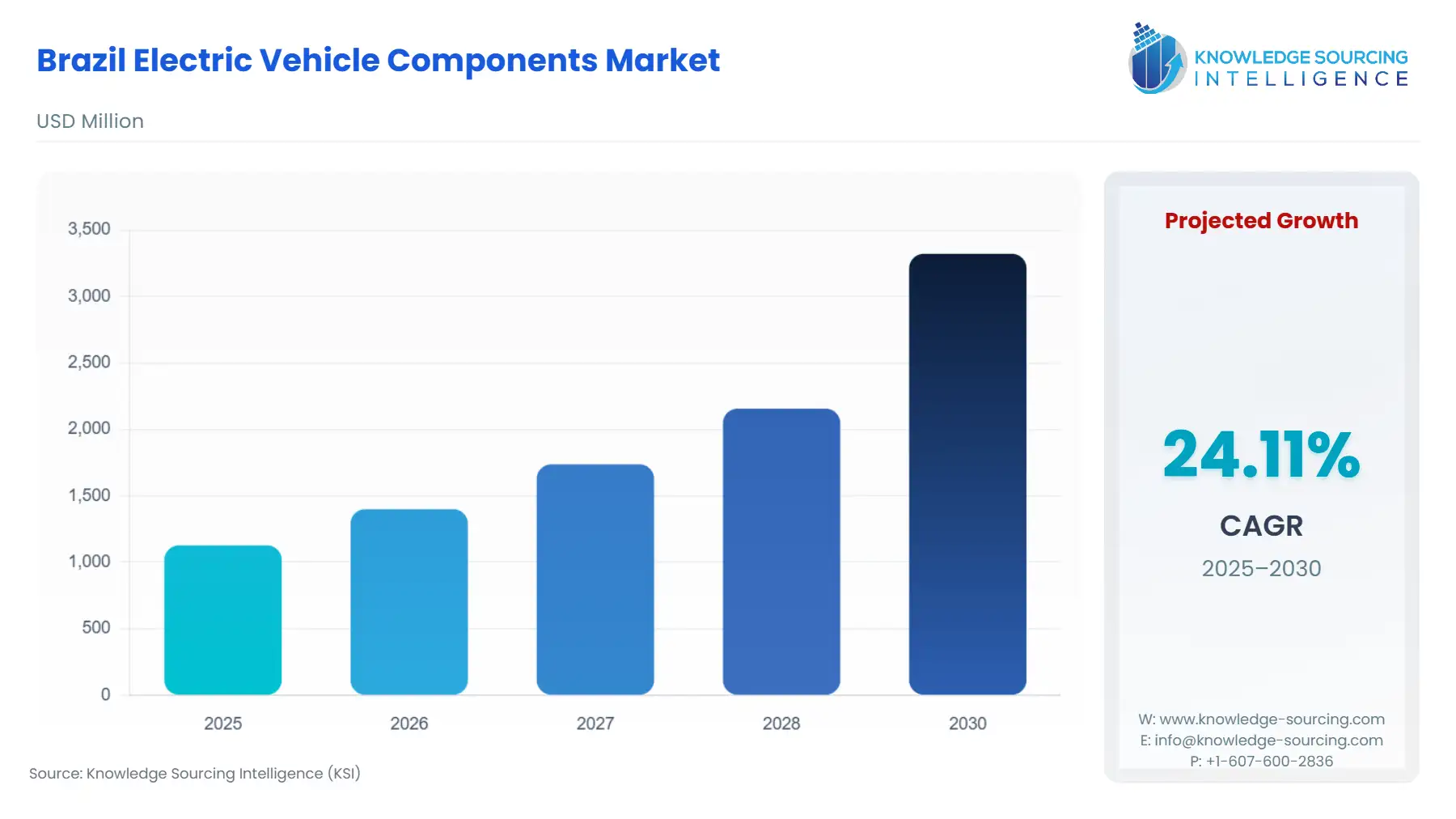
The Brazilian Electric Vehicle Components Market is undergoing a rapid transition, catalyzed by a confluence of accelerating consumer demand and decisive government industrial policy. Historically reliant on imports for sophisticated EV components, the market's trajectory is now fundamentally shifting toward domestic production. The substantial 90% year-over-year surge in EV sales in 2024 established a compelling demand signal for automakers. This organic market momentum is reinforced by regulatory mechanisms, such as the MOVER program, which explicitly links fiscal incentives to the local development and manufacturing of sustainable mobility solutions. This strategic alignment between escalating consumer uptake and policy-driven localization creates a mandatory, immediate business imperative for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and their suppliers to establish a robust, in-country supply chain for components like battery packs, electric motors, and power electronics.
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Analysis
- Growth Drivers
The primary factor propelling market growth is the exponential increase in overall EV adoption, which directly increases the underlying demand for components. With total EV sales reaching 177,360 units in 2024, a significant escalation from 93,930 units in 2023, OEMs require a proportionally larger volume of battery cells, electric motors, and inverters. Furthermore, the expansion of the charging infrastructure, evidenced by over 12,000 charging stations as of late 2024, mitigates range anxiety and accelerates the adoption of Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) and Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs). This shift to plug-in models, which constituted 71% of total EV sales in 2024, drives a specific, heightened necessity for high-capacity battery packs and sophisticated on-board charging systems.
- Challenges and Opportunities
The primary constraint facing the market is the existing reliance on imported components, resulting in a large trade deficit for automotive parts. This dependency exposes local assemblers to global supply chain volatility and currency risk, challenging cost competitiveness. The accelerated tariff hike on SKD and CKD vehicle imports, effective January 2027, presents an immediate opportunity. This policy transition is a powerful lever, forcing global OEMs to pivot rapidly from assembly operations toward deep localization. The opportunity lies in domestic players, including established local automotive suppliers and new entrants, capturing the significant investment capital, already exceeding $26 billion in announced OEM investments, earmarked for local component production capacity, particularly for battery processing and electric motor manufacturing.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
As a physical product market, the Brazilian EV components sector is fundamentally influenced by the supply chain of critical raw materials, specifically lithium. Brazil holds significant lithium resources, notably in Minas Gerais, positioning it to develop a localized supply chain for lithium processing and battery production. The need for high-purity lithium, essential for battery cathodes, is increasing with the surge in EV sales. Price volatility remains a key challenge for financial planning, with lithium carbonate prices fluctuating significantly throughout 2023. Establishing local processing and refinement capacity, as companies are beginning to do, is critical for mitigating pricing risk and stabilizing the input costs for local battery pack manufacturers, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of the final component.
- Supply Chain Analysis
The global supply chain for EV components is highly complex, marked by a dependency on production hubs in Asia, particularly for battery cells and power electronics. For the Brazilian market, this translates into a high import content in domestically assembled vehicles. Local logistical complexities, including varied infrastructure quality and high internal transport costs, further complicate the final cost of components. The supply chain is fragmented, with local players primarily focusing on lower-value components or assembly, while high-value, intellectual property-intensive components like inverters and advanced thermal management systems are largely imported. Strengthening local supply chains, especially in the state of São Paulo, a hub for automotive manufacturing, is necessary to reduce lead times and improve responsiveness to the domestic market's increasing component demand.
Government Regulations:
The regulatory framework is a key determinant of component demand in Brazil, shifting from primarily regulating final vehicle emissions to directly incentivizing component localization.
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
Brazil (Federal) |
Green Mobility and Innovation Program (MOVER), Law ? 14.902, enacted June 2024 |
Provides R&D-linked tax credits and IPI (Industrialized Products Tax) bonuses for sustainable mobility, directly increasing demand for locally-developed, high-efficiency components like Electric Motors and Power Electronics. |
|
Brazil (Federal) |
Import Tariff Hike (Gecex-Camex) |
Accelerated increase of import duties on CKD/SKD EVs to 35% by January 2027. Mandates Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to drastically accelerate local component sourcing and manufacturing investment to maintain cost-competitiveness. |
|
Brazil (National) |
ANEEL (National Electric Energy Agency) Normative Resolution 819/2019 |
Regulates the procedures and conditions for EV recharging activities, including commercial exploration, thereby reducing infrastructure uncertainty and indirectly boosting demand for all EV types and their components. |
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Segment Analysis:
- By Component Type: Battery Pack
The battery pack segment is the core value driver, directly proportional to the explosive growth in plug-in vehicle sales (BEVs and PHEVs), which accounted for 71% of all EV sales in 2024. This segment's growth is driven by the mandate for range extension and higher energy density, particularly for the expanding passenger car and light commercial vehicle segments. OEMs are focused on localized battery pack assembly, which creates immediate, scaled demand for locally sourced thermal management systems and Battery Management Systems (BMS). The high upfront cost of this component makes localization an imperative for achieving price parity with combustion-engine vehicles. Investment in lithium-ion battery production capacity is projected to increase by 40% due to rising demand, positioning Brazil as a key regional supplier and securing local requirements for lithium processing capabilities.
- By End-User: OEMs
The OEM segment is the largest end-user, driven by high volume, stringent quality standards, and long-term contract predictability. The surge in demand from OEMs is fundamentally driven by their compliance requirements under the MOVER program. Announced investments exceeding $26 billion by major global automakers are specifically conditional on establishing local manufacturing footprints to qualify for tax incentives. This governmental push is translating into firm demand for local, tier-one suppliers capable of providing complete, tested component sub-systems (e.g., integrated e-axles, power electronic modules) at scale. The competition among OEMs, including new Chinese entrants, to meet the record EV sales volume is further pressuring the establishment of high-capacity, localized component supply chains to ensure production stability and cost management.
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Competitive Analysis:
The competitive landscape is characterized by the strategic entry of global Tier 1 suppliers and EV-focused manufacturers, creating tension with established, traditional automotive suppliers. Competition is increasingly focused on the localization of high-value components.
- BYD
BYD has committed a significant BRL 5.5 billion (US$1 billion) investment to establish a major industrial complex in Camaçari, Bahia. Their strategic positioning is to vertically integrate, encompassing not just final vehicle assembly but also bus/truck chassis production and lithium processing. This approach directly addresses Brazil's supply chain dependency, as it creates an entirely localized demand stream for their own components, including Blade Batteries and electric motors, aiming for high domestic content to minimize exposure to import tariffs and secure a cost advantage. The company started production in Brazil in July 2025.
- Stellantis
Stellantis announced a $5.9 billion investment in South America in March 2024, their largest ever in the region, with a core focus on the Betim, Brazil, site. Their strategy centers on Bio-Hybrid technologies, a blend of Brazil's dominant flex-fuel technology with electrification, including Bio-Hybrid electrified dual-clutch transmissions and BEV platforms. This positioning leverages Brazil’s existing ethanol infrastructure while moving into electrification, creating a specific, immediate demand for hybrid-specific components and new transmission systems that differ from purely BEV architectures.
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Developments:
- July 2025: BYD Begins Production in Brazil. BYD officially began production at its industrial complex in Camaçari, Bahia. The facility, which has a designated capacity of 150,000 battery-powered and plug-in hybrid vehicles per year, marks a significant capacity addition for localized EV production and a foundational step for its vertical component supply chain in the country.
- June 2024: MOVER Program Enactment. Brazil enacted the Green Mobility and Innovation Program (MOVER) into law. This program replaces Rota 2030, establishing stricter environmental standards, mandating lifecycle carbon footprinting, and providing over $4.8 billion in R&D-linked tax credits through 2028, directly stimulating component innovation and localization.
- March 2024: Stellantis Announces $5.9 Billion Investment. Stellantis announced a BRL 30 billion ($5.9 billion) investment plan for South America through 2030, which includes the introduction of Bio-Hybrid electrified powertrains and battery electric vehicle production at its Betim, Brazil, manufacturing site.
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 1.128 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 3.322 billion |
| Growth Rate | 24.11% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component Type, Vehicle Type, Technology, End User |
| Companies |
|
Brazil Electric Vehicle Components Market Segmentation:
- BY COMPONENT TYPE
- Battery Pack
- Electric Motor
- Power Electronics
- Inverter
- Converter (DC-DC)
- On-Board Charger
- Thermal Management System
- Body & Chassis
- Other Components
- BY VEHICLE TYPE
- Passenger Cars
- Commercial Vehicles
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers
- BY TECHNOLOGY
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- BY END-USER
- OEMS
- Aftermarket