Report Overview
Gellan Gum Market Report, Highlights
Gellan Gum Market Size:
The gellan gum market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.27%, reaching a market size of US$287.203 million in 2030 from US$211.948 million in 2025.
Gellan gum functions as a microbial polysaccharide, derived from controlled fermentation of sugars by Sphingomonas elodea, forming a linear tetrasaccharide repeat of glucose, rhamnose, and glucuronic acid. This structure underpins its dual forms: high-acyl, which yields soft, elastic gels, and low-acyl, producing firm, brittle ones upon cation interaction. Market dynamics hinge on its role as a multifunctional hydrocolloid gelling, stabilizing, and suspending agent amid rising consumer preferences for clean-label, vegan-compatible ingredients. Producers leverage non-GMO fermentation to meet halal, kosher, and organic standards, aligning with global shifts toward sustainable sourcing. Yet, dependencies on cation-sensitive gelation introduce formulation constraints, particularly in low-mineral environments.
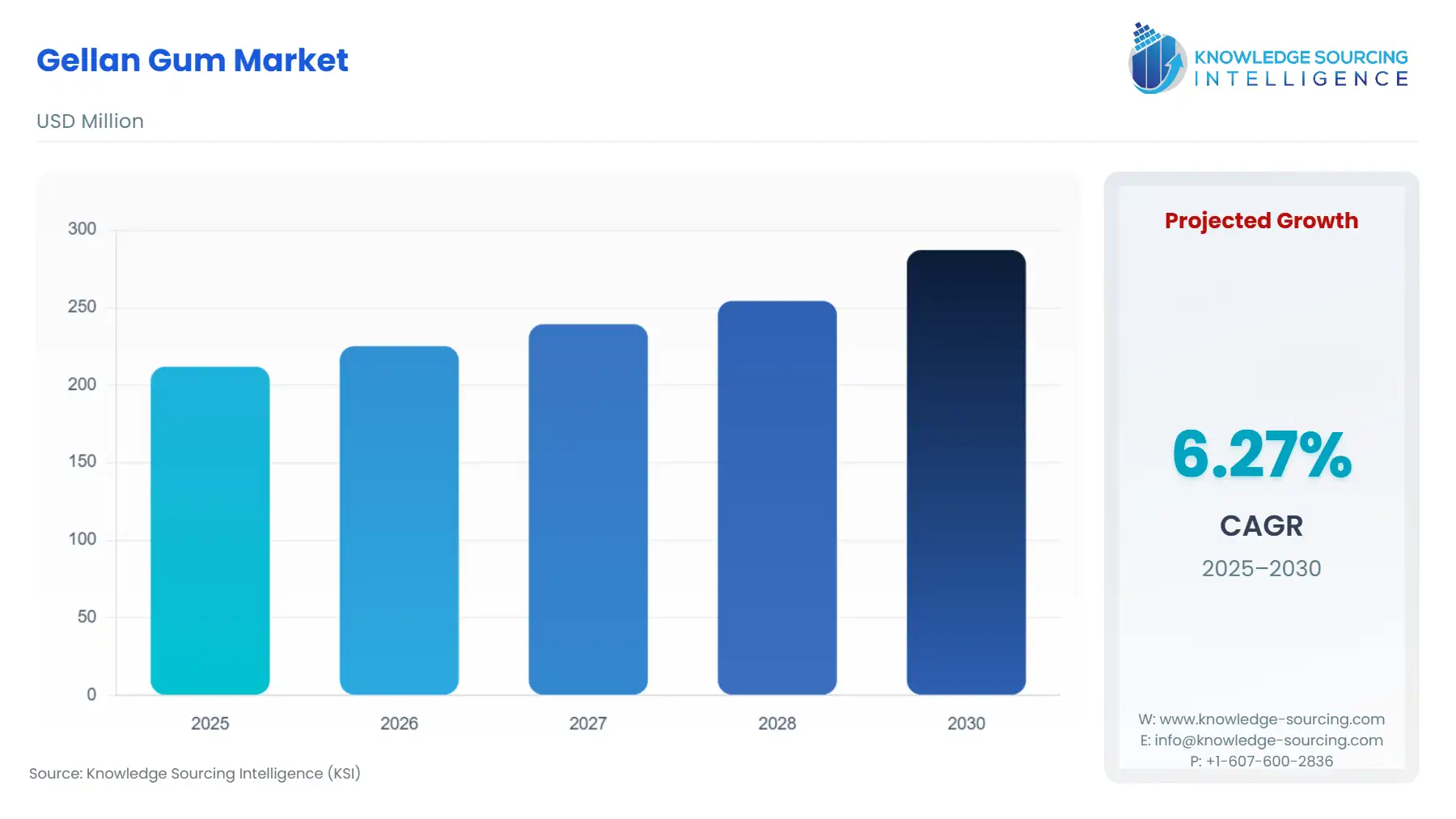
Gellan Gum Market Analysis:
- Growth Drivers
Regulatory clearances catalyze demand by unlocking new formulation avenues. Governing authorities such as the US Food and Drug Administration’s affirmation of gellan gum under 21 CFR 172.665 as a direct food additive permits its use in suspending particulates in beverages such as distilled water at levels directly boosting volumes in ready-to-drink categories. This endorsement ensures processors can incorporate it without reformulation risks, as seen in its application for fluid gels that prevent sedimentation in fruit pulps. Similarly, EFSA's re-evaluation concluded no numerical ADI is necessary, given exposure below body weight daily poses no safety concerns, thereby encouraging European manufacturers to expand into dairy analogs where gellan gum's elastic gels mimic casein structures at 0.01-0.05% concentrations. These approvals eliminate barriers, compelling formulators to select gellan over less stable options, resulting in heightened procurement for stabilizing acidic environments like lemonades.
Microbial fermentation processes propel demand through scalability and purity. Derived from Sphingomonas elodea on glucose or lactose substrates, production yields consistent acyl variants like high-acyl for soft textures in Asian water desserts, low-acyl for brittle gels in confectionery fillings. This method's efficiency, requiring minimal inputs and achieving high purity post-precipitation, supports low-cost scaling. Formulators favor this for its non-animal origin, aligning with vegan trends in plant-based milks and gellan gum suspends proteins without viscosity buildup thereby extending shelf life and reducing waste. Consequently, demand surges in high-throughput beverage lines, where process reliability cuts downtime and enables precise texture control via cation tuning.
Functional versatility in low concentrations drives adoption across diverse matrices. Gellan gum's ability to form low-concentrate fluid gels suspends cocoa or minerals in smoothies, preventing phase separation without mouthfeel interference unlike xanthan, which imparts lingering thickness. In bakery fillings, it retains moisture thereby averting syneresis during freezing, a constraint for starch alone. This efficacy amplifies demand in cost-sensitive sectors; for instance, combining with locust bean gum yields hybrid textures for reduced starch use, enhancing flavor release in most of reformulated products. Regulatory-backed thermal stability further incentivizes gellan gum’s use in retorted soups, where alternatives degrade, ensuring consistent demand from processors seeking operational resilience.
Clean-label and sustainability imperatives further accelerate uptake. As a fermentation-derived, non-GMO hydrocolloid, gellan gum satisfies organic certifications. Owing to its high-performance benefits, gellan gum finds applicability in non-dairy yogurts where it stabilizes emulsions at neutral pH, thereby meeting growth in plant alternatives by enabling nutrient fortification without clumping. As gellan replaces gelatin in confections, preserving melt-in-mouth properties coupled with growing organic culture, the prevalence of usage is expected to show progression. According to the USDA’s “EU Organic Market Begins To Recover” issued in February 2025, organic market in major EU economies namely Germany and France is expected to show steady growth.
Gellan gum's bacterial origin avoids dairy or soy traces, critical for consumers with restrictions, allowing seamless integration into almond milks where it hydrates proteins at cold temperatures. This expands addressable markets, as formulators prioritize it for halal/kosher compliance in Middle Eastern exports. In pharmaceuticals, though secondary, its film-forming in tablets boosts controlled release, indirectly supporting food-grade supply chains through shared fermentation tech.
- Challenges and Opportunities
Cation sensitivity poses formulation hurdles, reducing efficacy in demineralized waters common in purified beverages. Low-acyl gellan gum variants require 750 ppm isopropyl alcohol for gelation, leading to inconsistent textures in low-ion recipes and prompting rejection rates in trials. This headwind curbs demand in ready-to-drink teas, where reformulations add complexity and costs. Likewise, even though the organic culture is growing, however the frequency of expansion is minimal in regions owing to the delay in proper regulatory establishments. According to the “Special Report 19/2024” the uptake of organic farming practices would need to be doubled to achieve the designated target of reaching 25% green deal target set under the “2023-207 CAP”.
Opportunities arise from continuation of non-conventional gellan gum approvals which is poised to unlock premium segments. EU's postponement of gellan inclusion in organic processed food creates a window for compliant variants, potentially lifting demand in certified dairy alternatives to meet EGTOP criteria. Processors can capitalize by blending with pectins for hybrid gels, enhancing suspension in most of more formulations. Likewise, plant-based surges offer expansion avenues as gellan gum's compatibility with pea proteins stabilizes texture of new processed foods & beverages, thereby countering separation in high-pH mixes. This directly elevates volumes, as vegan beverage growth is witnessing a steady growth and relies on its minimal viscosity for clean mouthfeels, outpacing carrageenan in heat stability.
- Raw Material and Pricing Analysis
Gellan gum production hinges on glucose as the primary carbon source, sourced from corn starch hydrolysis, which constitutes most of input costs. Fermentation by Sphingomonas elodea converts glucose into the exopolysaccharide via UDP-sugar pathways. Glucose pricing, tied to corn futures, fluctuated by the environmental factors is pressuring margins. According to the USDA’s agricultural prices report, in August 2025, the corn received price index was US$3.96 per bushel which marked a significant decline of 33% from last month but showed a 12% growth in comparison to August 2024 price index.
Nitrogen sources, including yeast extract and ammonium salts, comprise a considerable share of formulation, influencing biomass and gel purity. Yeast extract's amino acids catalyze enzyme activity for tetrasaccharide assembly, yet its supply chain strains further elevate expenses. Downstream recovery also drives costs through alcohol precipitation and filtration, hence Isopropyl alcohol used in formulation yield most of the composition but incurs with EU solvent residue limits under food additive regulation capping at 750 mg/kg. Drying and milling add energy burdens, where vacuum ovens minimize degradation but hike electricity use
- Supply Chain Analysis
Global gellan gum supply chains center on fermentation facilities in China which over the years has invested in expanding it scale of operations, and now accounts for nearly 70% of the global fermentation capacity. Hence facilities situated in major provinces namely Zhejiang and Shandong host most of capacity, leveraging glucose from domestic corn. Logistical complexities arise from temperature controls gels degrade which is necessitating refrigerated containers usage which further inflate freight on Asia-Europe routes. Likewise, Recent U.S. reciprocal tariffs under Section 301 has also impacted the inflow volume in the United States with more focus being emphasized on domestic production.
- Government Regulations & Programs
|
Jurisdiction |
Key Regulation / Agency |
Market Impact Analysis |
|
United States |
21 CFR 172.665 / FDA |
Permits use as direct additive up to GMP levels, spurring demand in beverages by enabling low-dose stabilization without residue concerns, though solvent limits constrain non-GMP imports, favoring U.S. fermentation for cost savings in pharma gels. |
|
China |
GB 2760-2014 / CFDA |
Authorizes sales of food additive which is driving domestic production surge to meet global share, yet export tariffs under U.S. reciprocity curb overseas sales, thereby redirecting volumes to Asian fortification markets. |
|
European Union |
Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008, E418 / EFSA |
No ADI required post-2018 re-evaluation due to low toxicity, boosting uptake in dairy via heat-stable approvals, but microbial purity mandates elevate validation costs, limiting small-batch entry and channeling demand to certified suppliers. |
Gellan Gum Market Segment Analysis:
- By Application: Gelling Agent
By application, gelling agent is anticipated to account for a considerable share of the market fuelled by its growing demand in applications such as confectionery where low-acyl forms forge brittle networks that mimic gelatin's snap without animal sourcing. In vegan gummies, cation-triggered gels yield transparent structures with superior flavor diffusion versus agar. This specificity counters syneresis in high-sugar matrices, preserving clarity during retort, which sustains appeal in shelf-stable formats amid candy & confectionary trade growth in major regions globally. According to the data provided by the European Commission, in May 2025, the EU chocolate & confectionary export experienced a 20% growth while dairy products experienced a 7% growth.
Likewise, pharmaceutical extensions amplify this, as gelling matrices encapsulate APIs for sustained release, with swelling rates higher than alginates, enhancing colonic targeting in IBD therapies. Regulatory nods under FDA GRAS expedite approvals is fueling demand in bead formulations where gels withstand gastric acid, reducing dosing frequency and boosting patient adherence. Additionally, opportunities in 3D-printed edibles further propel demand, as shear-thinning gels enable layer adhesion without collapse, supporting personalized nutrition trends.
- By End-User: Food & Beverage
Based on end-user, the food & beverage is projected to account for a considerable market share. In food and beverage, gellan gum's suspension capabilities counter protein aggregation in plant milks, where high-acyl variants form thixotropic networks that yield pourable viscosities under shear, thereby directly meeting vegan demand surges annually. Beverage fortification benefits from its low usage, binding calcium in juices without turbidity, enhancing bioavailability through uniform dispersion. In carbonated drinks, gels mitigate foam instability under CO2 pressure, extending shelf life amid fizzy growth in Asia. Drawbacks like cation sensitivity necessitate precise dosing, yet this precision drives premium positioning, with brands citing cost efficiencies over carrageenan.
Gellan Gum Market Geographical Analysis:
The gellan gum market analyzes growth factor across following regions
- North America: The demand for gellan gum surges as demand for plant-based dairy alternatives grows in major regional economies further fueled by the improving vegan culture. Likewise, the bolstering growth in confectionary consumption followed by ongoing efforts to bolster development of food products with high shelf-life has also paved the way for future market expansion. According to the data provide by the National Confectioners Association, in 2025, the total confectionary sales is projected to reach USD54.2 billion thereby showing a 4.9% growth in sales of non-chocolate candy, and 1.9% growth in gums & mints sales in comparison to the preceding year.
- Europe: The European market is poised for a positive expansion fueled by the improved consumer landscape for organic food products followed by efforts to bolster organic production in major regional nations. According to the “Common Agriculture Policy 2023-2027”, the European Union has established goals to achieve 25% of agriculture area under organic farming.
- Asia Pacific: The region is witnessing a considerable technological growth in food ingredients development with major nations namely China showing constant improvement in their fermentation capacity. Likewise, countries like India is also experiencing a positive growth in food & beverage, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics production fueled by the implementation of polices such as “Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI)” which has provided new growth prospects for usage of gellan gums as raw ingredient.
- South America & MEA: The change in consumer landscape which is attributable to the dynamic market trends followed by regulatory standards for chemical ingredients used in industrial sectors has impacted the market growth in South America region, whereas the growing shift towards nutrient-rich food & products has provided new growth prospects in gellan gum market in MEA.
Gellan Gum Market Competitive Environment and Analysis:
The landscape features concentrated players leveraging fermentation scale for differentiation.
- Tate & Lyle positions as innovation leader, integrating CP Kelco acquisition for pectin-gellan blends that enhance meat analogs' juiciness. Key products like KELCOGEL® HA-B suspend particulates in neutral pH plant-based beverages thereby ensuring texture smoothness and stability.
- Cinogel Biotech prioritizes affordability, producing high-acyl and low-acyl gellan gum under ISO/KOSHER offering better flavor release than agar. Their strategy centers on bulk supply to emerging markets, evidenced by stable pricing.
Gellan Gum Market Developments:
- July 2025: Jungbunzlauer Suisse AG launched its new low-acyl gellan gum product “TayaGel LA” at the “IFT FIRST 2025” which showcased the company’s continued investment in development of sustainable ingredients.
- November 2024: Tate & Lyle announced the completion of CP Kelco acquisition which is one of the leading producers of specialty gums including gellan gum. Hence, the acquisition played an integral in expanding Tate & Lyle’s capacity of providing nature-based ingredients gums and ingredients for food & beverages.
Gellan Gum Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Report Metric | Details |
| Gellan Gum Market Size in 2025 | US$211.948 million |
| Gellan Gum Market Size in 2030 | US$287.203 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.27% |
| Study Period | 2020 to 2030 |
| Historical Data | 2020 to 2023 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025 – 2030 |
| Forecast Unit (Value) | USD Million |
| Segmentation |
|
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| List of Major Companies in Gellan Gum Market |
|
| Customization Scope | Free report customization with purchase |
Gellan Gum market Segmentation:
- By Type
- Low-Acyl Gellan Gum
- High-Acyl Gellan Gum
- By Application
- Thickening Agent
- Gelling Agent
- Stabilizer
- Texturizer
- Others
- By End-User
- Food & Beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Others
- By Geography
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- South America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- Israel
- Others
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Indonesia
- Others
- North America