Report Overview
Global Electronic Toll Collection Highlights
Electronic Toll Collection Market Size:
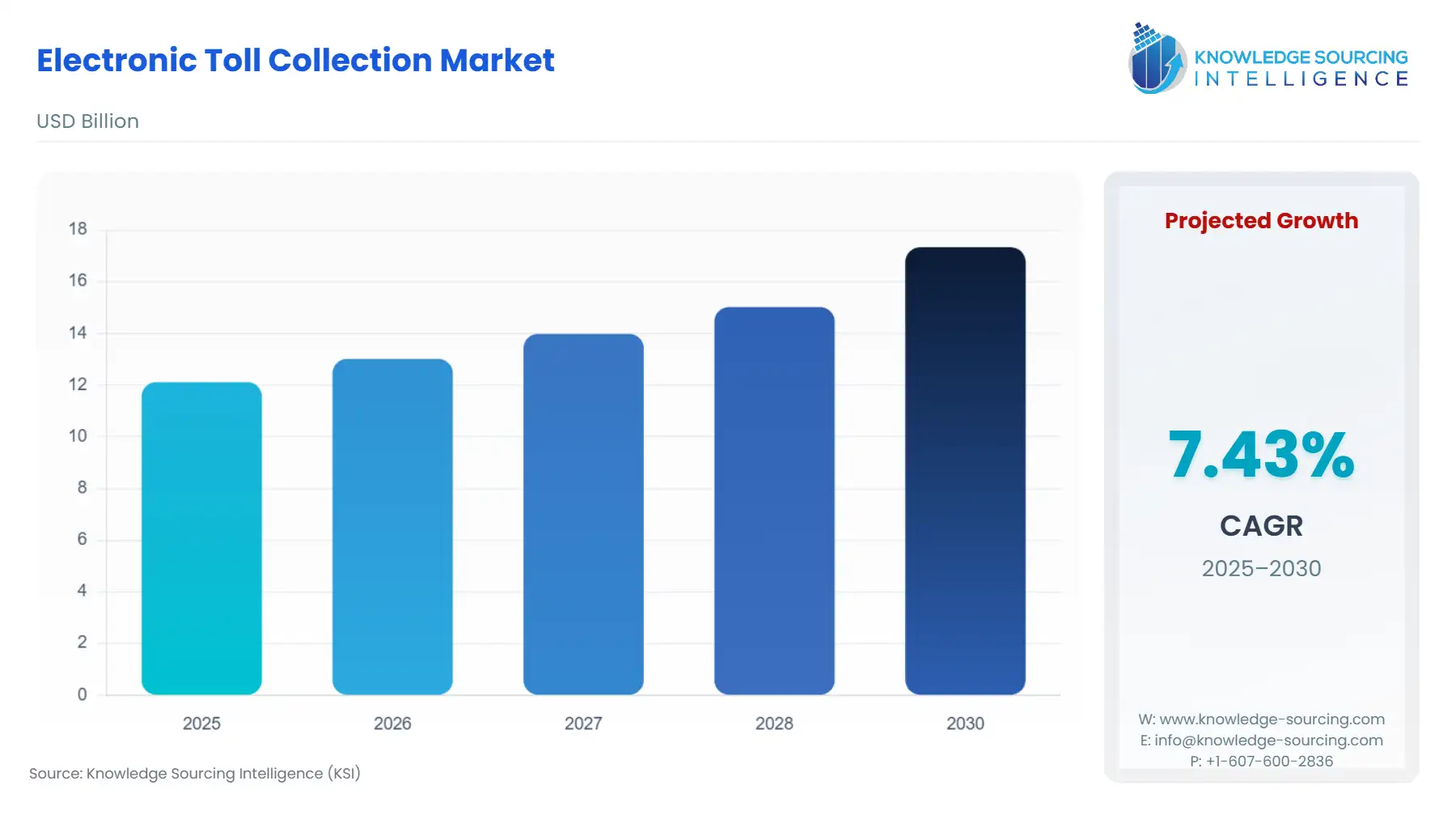
The Global Electronic Toll Collection Market is expected to grow from USD 12.117 billion in 2025 to USD 17.337 billion in 2030, at a CAGR of 7.43%.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Introduction:
The Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) market is experiencing robust growth as global transportation systems evolve to meet the demands of urbanization, environmental sustainability, and technological advancement. ETC systems, which automate toll payments on highways, bridges, and urban corridors, have become integral to modern intelligent transportation systems (ITS). These systems leverage advanced toll road technology—such as Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), Dedicated Short-Range Communication (DSRC), Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), and Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR)—to enable seamless, cashless transactions, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance road safety. By allowing vehicles to pass toll points without stopping, ETC systems improve traffic flow, minimize emissions from idling vehicles, and streamline revenue collection for road infrastructure maintenance.
The global ETC market is driven by the urgent need to address escalating traffic congestion, particularly in urban areas with high vehicle densities. As cities grow, traditional manual toll booths, which require vehicles to stop for cash or card payments, exacerbate delays, increase fuel consumption, and contribute to air pollution. ETC systems mitigate these issues by enabling high-speed toll collection, with technologies like RFID transponders and GNSS allowing vehicles to pass at speeds up to 290 km/h while maintaining accurate billing. For instance, India’s FASTag system, mandated by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), has achieved over 98% adoption across 1,200 toll plazas, processing millions of transactions daily and reducing wait times significantly. Similarly, Germany’s Toll Collect system, a GNSS-based solution for commercial vehicles, exemplifies how toll collection systems can scale to national networks, enhancing efficiency and equity in road usage charges. These advancements align with ITS goals of optimizing traffic management and supporting smart city initiatives.
Another key driver is the global push for environmental sustainability. ETC systems reduce vehicle idling at toll plazas, cutting greenhouse gas emissions and aligning with climate goals. In Europe, countries like France and Germany integrate ETC into congestion pricing and low-emission zones to curb urban pollution. For example, the European Commission’s support for unified tolling systems across member states, such as the Serbia-Montenegro agreement, promotes seamless cross-border travel while reducing environmental impact. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) has reduced fuel tax revenues, prompting governments to adopt ETC for mileage-based user fees (MBUF). The U.S. is exploring MBUF to replace declining fuel taxes, with pilot programs underway to assess GNSS-based tolling for fair road usage charges.
Technological innovation further propels the ETC market. The integration of toll road technology with ITS enables real-time traffic monitoring and data analytics, providing insights into congestion patterns and facilitating proactive management. Companies like Thales and TransCore are pioneering solutions such as Thales’ PITZ® system, deployed in Guatemala’s Palin-Escuintla corridor in 2021, which processes over 120 vehicles per minute and supports multiple payment methods, including mobile apps. Similarly, Taiwan’s Far Eastern Electronic Toll Collection Co. (FETC) exported its AI-based ETC system to Thailand’s M9 expressway, increasing traffic flow by 1.8 times. These developments highlight the market’s shift toward interoperable, cloud-based, and AI-enhanced solutions that improve scalability and user convenience.
Despite its growth, the ETC market faces significant restraints. High initial investment costs for infrastructure—such as RFID readers, cameras, and back-office systems—pose a barrier, particularly for developing countries. For instance, deploying ETC systems requires sophisticated hardware and software, with ongoing maintenance adding to operational expenses. This financial burden often necessitates public-private partnerships (PPPs) to distribute costs. Another restraint is the lack of interoperability and standardization across regions. Variations in technologies like RFID, DSRC, and GNSS create challenges for cross-border travel and system integration, as seen in regions with fragmented tolling standards. Privacy concerns also hinder adoption, as drivers worry about data collection from transponders and ANPR systems, potentially perceiving them as invasive.
Governments and private companies implement and finance ETC systems through a combination of public funding, private investment, and innovative financing models. Governments typically lead ETC deployment by setting regulatory frameworks and investing in infrastructure. For example, India’s NHAI mandated FASTag to streamline toll collection, funding initial setups through budgetary allocations and toll revenues. In Europe, Germany’s Toll Collect system is a joint venture between public and private entities, with companies like Deutsche Telekom contributing technological expertise. PPPs are increasingly common, enabling governments to share financial risks with private firms. In Brazil, road concessionaires like CCR Group finance ETC systems through toll revenues, while governments provide land and regulatory support. Private companies, such as Kapsch TrafficCom and Cubic Corporation, develop and maintain toll collection systems, often securing contracts through competitive bidding. For instance, TransCore’s contract with the Thousand Islands Bridge Authority modernized cross-border tolling between the U.S. and Canada, funded by bridge revenues and government grants.
Financing also leverages subscription-based models and data monetization. Companies like Axxès, which joined the Avanci Aftermarket program, offer interoperable tolling solutions across Europe, generating revenue through service fees and licensing. Additionally, ETC systems integrate with mobile payment platforms, as seen in Cubic’s Umo Handheld Reader, which supports tap-to-pay and 5G connectivity, enhancing user convenience and operator revenue. Governments incentivize adoption through subsidies and concessional schemes, such as India’s “One Vehicle, One FASTag” initiative, which streamlined compliance and reduced toll evasion.
In conclusion, the global ETC market is poised for sustained growth, driven by urbanization, environmental priorities, and technological advancements. While challenges like high costs and interoperability issues persist, strategic collaborations between governments and private companies ensure the continued expansion of ETC systems. By leveraging ITS and innovative financing, the market is transforming transportation infrastructure, making it more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Trends:
The ETC market is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the need for efficient, seamless transportation systems. RFID tolling remains a cornerstone, with systems like India’s FASTag achieving over 98% adoption across 1,200 toll plazas, enabling quick vehicle identification via transponders for congestion-free tolling. Meanwhile, DSRC ETC, leveraging short-range communication, supports high-speed tolling, as seen in Japan’s ETC 2.0, which processes transactions at speeds up to 290 km/h. GNSS tolling is gaining traction for its scalability, exemplified by Germany’s Toll Collect system, which uses satellite-based tracking for flexible, distance-based charges without physical toll booths.
Emerging technologies like ANPR and Video Tolling enhance AET, allowing seamless transactions in MLFF environments. For instance, Thales’ PITZ® system in Guatemala integrates ANPR for real-time license plate reading, processing over 120 vehicles per minute. AI for ETC and Machine Learning in tolling are transforming operations by optimizing traffic flow and detecting evasion, as seen in Taiwan’s FETC AI-based system, exported to Thailand’s M9 expressway, boosting throughput by 1.8 times. Mobile-based toll payment systems, like Cubic’s Umo Handheld Reader, support tap-to-pay and 5G connectivity, enhancing user convenience. These trends underscore the shift toward interoperable, data-driven ETC solutions, improving efficiency and sustainability in global transportation networks.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Dynamics:
Market Drivers:
- Urbanization and Traffic Congestion Reduction through All-Electronic Tolling
Rapid urbanization is a key driver for the ETC market, as cities face increasing traffic congestion that demands efficient toll collection systems. All-electronic tolling eliminates manual toll booths, enabling seamless vehicle flow and reducing delays. Technologies like RFID tolling and ANPR allow vehicles to pass toll points without stopping, minimizing congestion and emissions. For example, India’s FASTag system, deployed across national highways, streamlines tolling for millions of vehicles, enhancing traffic throughput. AET supports ITS by integrating real-time traffic data, helping urban planners optimize road networks. As urban populations grow, the need for scalable, high-speed tolling solutions drives investment in ETC, with governments prioritizing infrastructure upgrades to improve mobility and sustainability in densely populated regions. - Environmental Sustainability with GNSS Tolling
The push for environmental sustainability significantly fuels the ETC market, as GNSS tolling and other toll road technologies reduce vehicle idling, cutting greenhouse gas emissions. By enabling MLFF, ETC systems eliminate the need for vehicles to stop at toll plazas, lowering fuel consumption and air pollution. Germany’s Toll Collect system, a GNSS-based solution, charges commercial vehicles based on distance traveled, promoting equitable road usage while reducing environmental impact. This aligns with global climate goals, such as Europe’s low-emission zones, where ETC supports congestion pricing to deter high-pollution vehicles. Additionally, the decline in fuel tax revenues due to electric vehicle adoption drives governments to adopt GNSS tolling for mileage-based user fees, ensuring sustainable funding for road maintenance while supporting eco-friendly transportation policies. - Technological Advancements in AI for ETC and Mobile-Based Toll Payment
Advancements in AI for ETC and mobile-based toll payment are transforming the ETC market by enhancing operational efficiency and user experience. AI and Machine Learning in tolling optimize traffic flow and detect toll evasion, as seen in Taiwan’s FETC system, which uses AI to improve throughput on Thailand’s M9 expressway. Mobile-based toll payment systems, like Cubic’s Umo Handheld Reader, integrate 5G and tap-to-pay functionality, offering drivers convenient, cashless options. These innovations align with ITS, enabling real-time data analytics for traffic management. Companies like Thales leverage Video Tolling and ANPR to process high volumes of transactions, as demonstrated in Guatemala’s Palin-Escuintla corridor. These technological leaps drive market growth by meeting the demand for scalable, user-friendly toll collection systems that support smart city initiatives and seamless mobility.
Market Restraints:
- High Infrastructure Costs for DSRC ETC and Video Tolling
The high cost of deploying DSRC ETC and Video Tolling infrastructure poses a significant restraint for the ETC market. Implementing toll collection systems requires substantial investment in hardware like RFID readers, cameras, and back-office systems, as well as ongoing maintenance. For instance, DSRC ETC systems, used in Japan’s ETC 2.0, demand sophisticated roadside units and vehicle transponders, increasing upfront costs. Video Tolling, reliant on high-resolution cameras and ANPR, adds complexity due to the need for robust data processing and storage. These costs are particularly challenging for developing countries or regions with limited budgets, often requiring public-private partnerships to offset expenses. The financial burden limits widespread adoption, slowing market expansion despite the benefits of reduced congestion and improved efficiency. - Interoperability Challenges in Multi-Lane Free Flow Systems
The lack of standardization and interoperability in MLFF systems restricts the ETC market’s growth. Variations in technologies like RFID tolling, DSRC ETC, and GNSS tolling across regions create compatibility issues, particularly for cross-border travel. For example, Europe’s fragmented tolling standards complicate seamless toll collection, requiring drivers to use multiple transponders or accounts. This lack of uniformity increases operational complexity for toll operators and frustrates users, hindering adoption. Efforts like the European Commission’s push for unified tolling, as seen in the Serbia-Montenegro agreement of August 2023, aim to address this, but progress is slow. Additionally, privacy concerns over data collected by ANPR and GNSS tolling systems further complicate standardization efforts, as varying regulations on data protection create barriers to implementing cohesive MLFF solutions.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Segmentation Analysis:
- By Component: Automatic Vehicle Identification
Automatic Vehicle Identification (AVI) is the cornerstone of the ETC market, enabling seamless and accurate vehicle detection for toll transactions without requiring vehicles to stop. AVI systems primarily use technologies like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and ANPR to identify vehicles via transponders or license plates, ensuring efficient toll collection in MLFF environments. For instance, India’s FASTag system, leveraging RFID-based AVI, is deployed across over 1,200 toll plazas, streamlining tolling for millions of vehicles daily and reducing congestion. Similarly, Thales’ PITZ® system in Guatemala integrates ANPR for real-time license plate reading, processing over 120 vehicles per minute. AVI supports ITS by providing data for traffic management and enforcement, enhancing road safety and operational efficiency. Its dominance stems from its reliability and adaptability, making it critical for modern toll collection systems in urban and highway settings. - By Technology: Radio Frequency Identification
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is the leading technology in the ETC market due to its cost-effectiveness, reliability, and widespread adoption. RFID tolling uses transponders attached to vehicles that communicate with roadside readers, enabling high-speed, contactless toll collection. Systems like Japan’s ETC 2.0 utilize RFID to process transactions at speeds up to 290 km/h, minimizing delays and supporting AET. RFID’s low-cost infrastructure and ease of integration make it ideal for large-scale deployments, as seen in India’s FASTag, which has achieved near-universal adoption on national highways. The technology’s ability to operate in MLFF setups ensures scalability, accommodating high traffic volumes without physical toll booths. Additionally, RFID supports interoperability, allowing regional systems to integrate with broader ITS networks, enhancing user convenience and operational efficiency across diverse geographies.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Geographical Outlook:
- By Geography: Asia Pacific
The Asia Pacific region dominates the ETC market, driven by rapid urbanization, massive infrastructure investments, and government-led digital tolling initiatives. Countries like India, China, and Thailand are at the forefront, with India’s FASTag system exemplifying large-scale RFID tolling adoption across national highways. China’s extensive highway network integrates Global Positioning System (GPS) and ANPR for efficient toll collection, supporting its vast urban populations. Thailand’s M9 expressway, upgraded with Taiwan’s FETC AI-based ETC system, showcases the region’s embrace of advanced toll road technology, boosting traffic throughput significantly. The Asia Pacific market benefits from high vehicle ownership rates and smart city initiatives, aligning with ITS to optimize traffic flow and reduce emissions. Government policies, such as India’s mandate for cashless tolling, further accelerate ETC deployment, positioning the region as a leader in innovative tolling solutions.
List of major companies:
- Conduent Incorporated
- Cubic Corporation
- EFKON GmbH
- Kapsch TrafficCom AG
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Key Developments:
- In January 2025, TransCore, a prominent provider of electronic tolling solutions, introduced its Infinity tolling technology. This launch is a significant product development aimed at modernizing tolling systems, with its initial deployment for the transportation networks in West Virginia, U.S. This new technology is designed to improve the efficiency and reliability of tolling operations, potentially incorporating advanced features to handle complex traffic and payment scenarios.
- In September 2024, in a strategic move to expand its global tolling services, Neology acquired P Square Solutions. This acquisition created a new business division, Neology PSquare, which significantly enhances Neology's capabilities and market presence. The integration of P Square Solutions' expertise is expected to improve Neology's offerings in the tolling and mobility sector, allowing it to provide more comprehensive and integrated solutions to its clients worldwide.
Electronic Toll Collection Market Scope:
| Report Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Total Market Size in 2026 | USD 12.117 billion |
| Total Market Size in 2031 | USD 17.337 billion |
| Growth Rate | 7.43% |
| Study Period | 2021 to 2031 |
| Historical Data | 2021 to 2024 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026 – 2031 |
| Segmentation | Component, Technology, Geography |
| Geographical Segmentation | North America, South America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, Asia Pacific |
| Companies |
|
Electronic Toll Collection Market Segmentation:
The global electronic toll collection market has been segmented by component, technology, and geography.
- By Component
- Automatic Vehicle Identification
- Automatic Vehicle Classification
- Video Enforcement System
- By Technology
- Dedicated Short Range Communication
- Global Positioning System
- Global System for Mobile Communication
- Digital Tachography
- Radio Frequency Identification
- By Geography
- North America
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
- Asia Pacific